Abstract
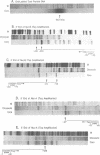
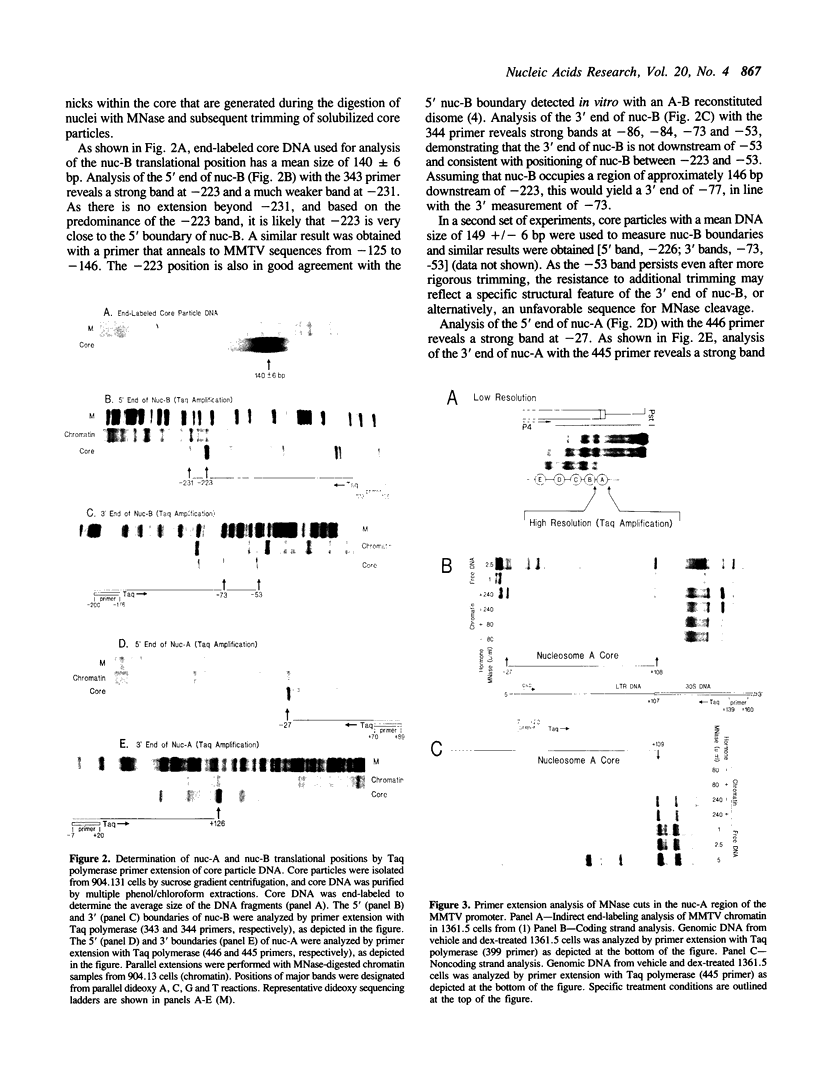
We have previously demonstrated that an array of six nucleosomes are phased on the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) long terminal repeat (1,2). In this study, we devised a new assay to measure the translational positions of specific nucleosomes on the MMTV promoter. Nucleosome core particles were purified and shown to contain A and B nucleosomal DNA by Taq polymerase primer extension with nucleosome-specific primers. The 5' and 3' boundaries of A and B nucleosomes were measured by extending to the end of the core DNA with internal primers. This approach yielded results consistent with major translational positions of -23 to +123 and -221 to -75 for A and B nucleosomes, respectively. The micrococcal nuclease cleavage patterns of A and B nucleosome regions in isolated nuclei are conserved at base-pair resolution in multiple murine cell lines containing either stable MMTV-reporter chimeras or endogenous proviruses. As the refined nucleosome positions place important transcription factor binding sites at the 3' edge of the B nucleosome and in the nucleosome A/B linker, we propose that linker histone depletion and chromatin unfolding may be required to expose these cis-elements during steroid hormone-induced transcription initiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Dong F., van Holde K. E. Use of selectively trypsinized nucleosome core particles to analyze the role of the histone "tails" in the stabilization of the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., John S., Berard D. S., LeFebvre P., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid receptor-dependent disruption of a specific nucleosome on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter is prevented by sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3977–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., John S., Hager G. L. Histone hyperacetylation does not alter the positioning or stability of phased nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3490–3497. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong F., Hansen J. C., van Holde K. E. DNA and protein determinants of nucleosome positioning on sea urchin 5S rRNA gene sequences in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5724–5728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Elgin S. C. Patterns of DNA structural polymorphism and their evolutionary implications. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer B., Linxweiler W., Hörz W. DNA engineering shows that nucleosome phasing on the African green monkey alpha-satellite is the result of multiple additive histone-DNA interactions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Richard-Foy H., Wolford R. G., Berard D. S., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of transcription at an amplified, episomal promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2045–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Specific glucocorticoid receptor binding to DNA reconstituted in a nucleosome. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3073–3079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Barettino D., Truss M., Beato M. Structural features of a regulatory nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;216(4):975–990. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(99)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. Y., Dean A., Simpson R. T. Yeast alpha 2 repressor positions nucleosomes in TRP1/ARS1 chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2247–2260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning in vivo and in vitro. Bioessays. 1986 Apr;4(4):172–176. doi: 10.1002/bies.950040408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60841-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Local protein-DNA interactions may determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmids. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):250–252. doi: 10.1038/315250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Zatchej M. Chromatin folding modulates nucleosome positioning in yeast minichromosomes. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):945–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90240-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Klug A. The bending of DNA in nucleosomes and its wider implications. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):537–561. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]