Abstract
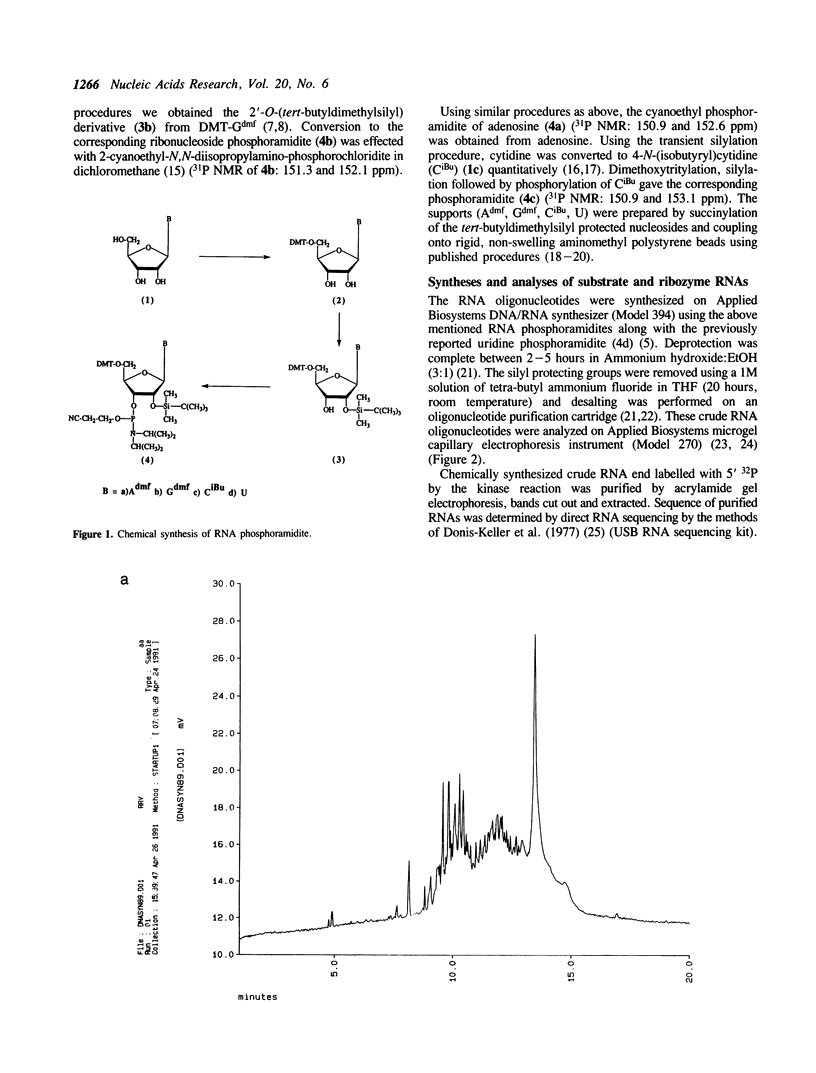
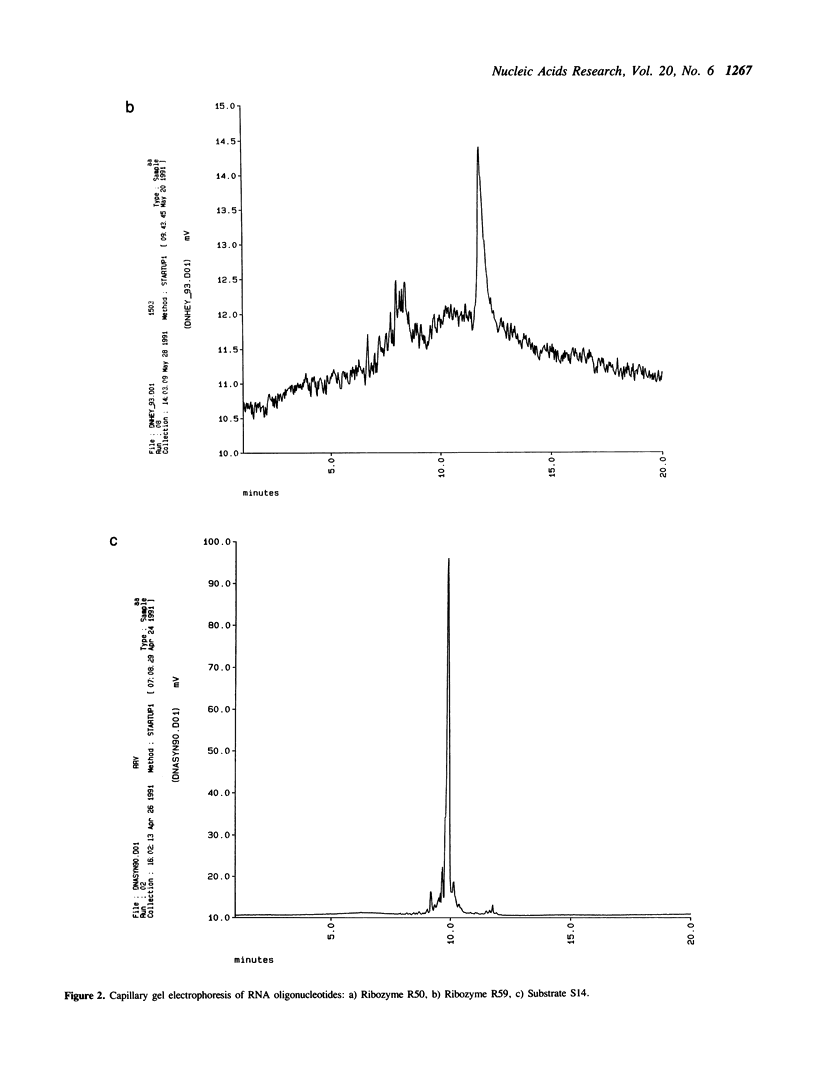
The exocyclic amine protecting groups in oligonucleotide synthesis which require 8-16 hours at 55 degrees C for deprotection in ammonia have been replaced with more labile base protecting groups (dimethylformamidine for adenine and guanine and isobutyryl for cytosine). Using these fast oligonucleotide deprotecting groups which require 2-3 hours at 55 degrees C for complete deprotection, a new set of cyanoethyl phosphoramidite ribonucleoside monomers and supports has been developed. Ribozymes and substrate RNAs which were synthesized with these phosphoramidites were assayed and were found to have full catalytic (biological) activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen A. S., Najarian D. R., Paulus A., Guttman A., Smith J. A., Karger B. L. Rapid separation and purification of oligonucleotides by high-performance capillary gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9660–9663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R., Hicks M., Cruz P. 'Hairpin' catalytic RNA model: evidence for helices and sequence requirement for substrate RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):299–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R. RNA catalytic properties of the minimum (-)sTRSV sequence. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4929–4933. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser R. J., MacKellar S. L., Vinayak R. S., Sanders J. Z., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E. Specific-primer-directed DNA sequencing using automated fluorescence detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6087–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride L. J., McCollum C., Davidson S., Efcavitch J. W., Andrus A., Lombardi S. J. A new, reliable cartridge for the rapid purification of synthetic DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Apr;6(4):362–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Sarver N. RNA enzymes (ribozymes) as antiviral therapeutic agents. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Jul;8(7):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringe S. A., Francklyn C., Usman N. Chemical synthesis of biologically active oligoribonucleotides using beta-cyanoethyl protected ribonucleoside phosphoramidites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5433–5441. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulhof J. C., Molko D., Teoule R. The final deprotection step in oligonucleotide synthesis is reduced to a mild and rapid ammonia treatment by using labile base-protecting groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):397–416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., McCollum C., Lotys C., Andrus A. New reagents and solid support for automated oligonucleotide synthesis. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1990;(22):63–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T., Ogilvie K. K., Pon R. T. Prevention of chain cleavage in the chemical synthesis of 2'-silylated oligoribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3501–3517. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]