Abstract
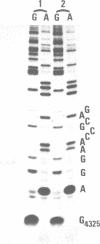
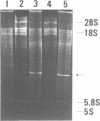
Trichosanthin is a ribosome-inactivating protein from root tubers of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. In this paper, the mechanism of action of trichosanthin on eukaryotic ribosomes was studied. A fragment of about 450 nucleotides was released from 28S ribosomal RNA after treatment of rat liver ribosome with trichosanthin and its isolated ribosomal RNAs were treated with aniline. Analysis of nucleotide sequence of 5' terminus of this fragment revealed that the aniline-sensitive site of the phosphodiester bond was between positions A4324 and G4325 in the 28S rRNA. Adenine was recovered by ion-exchange column chromatography from the 50% ethanol soluble fraction of the reaction mixture in which rat liver ribosomes were treated with trichosanthin. Thin-layer chromatographic analysis indicated that 1 mol of adenine was released from 1 mol of ribosomes. When the ribosomes were incubated with trichosanthin in the presence of inorganic [32P]phosphate, little incorporation of radioactivity into 28S rRNA was observed, indicating that the release of adenine was not mediated by phosphorolysis. These results demonstrate that trichosanthin inactivates the ribosomes by cleaving the N-C glycosidic bond of adenylic acid at 4324 of 28S rRNA in a hydrolytic fashion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casellas P., Dussossoy D., Falasca A. I., Barbieri L., Guillemot J. C., Ferrara P., Bolognesi A., Cenini P., Stirpe F. Trichokirin, a ribosome-inactivating protein from the seeds of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maximowicz. Purification, partial characterization and use for preparation of immunotoxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Endo Y., Wool I. G. The sequence of the nucleotides at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in rat 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12768–12770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Olvera J., Wool I. G. The structure of rat 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7819–7831. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. J., Robertus J. D., LoPresti M., Stone K. L., Williams K. R., Wu P., Hwang K., Piatak M. Primary amino acid sequence of alpha-trichosanthin and molecular models for abrin A-chain and alpha-trichosanthin. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8665–8669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Huber P. W., Wool I. G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassur S. M., Whitlock H. W., Jr UV shadowing--a new and convenient method for the location of ultraviolet-absorbing species in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNINGS J. C., OLSON B. H., ROGA V., JUNEK A. J., SCHUURMANS D. M. ALPHA SARCIN, A NEW ANTITUMOR AGENT. II. FERMENTATION AND ANTITUMOR SPECTRUM. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:322–326. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.322-326.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Joseph M., Bailey M. C. Purification and characterization of trichosanthin. Homology to the ricin A chain and implications as to mechanism of abortifacient activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11628–11633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. S., Hwang K. M., Caldwell S. E., Gaston I., Luk K. C., Wu P., Ng V. L., Crowe S., Daniels J., Marsh J. GLQ223: an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus replication in acutely and chronically infected cells of lymphocyte and mononuclear phagocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON B. H., GOERNER G. L. ALPHA SARCIN, A NEW ANTITUMOR AGENT. I. ISOLATION, PURIFICATION, CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, AND THE IDENTITY OF A NEW AMINO ACID. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:314–321. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.314-321.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S. Ricin and ricinus agglutinin, toxic lectins from castor bean. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:330–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R., Olsnes S., Eiklid K. The cytotoxic activity of Shigella toxin. Evidence for catalytic inactivation of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Bailey S., Miller S. P., Bodley J. W. Modification of ribosomal RNA by ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1349–1357. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L. Ribosome-inactivating proteins up to date. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao S. W., Yan K. T., Yeung H. W. Selective killing of choriocarcinoma cells in vitro by trichosanthin, a plant protein purified from root tubers of the Chinese medicinal herb Trichosanthes kirilowii. Toxicon. 1986;24(8):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., STAEHELIN T., NOLL H. Ribosomal aggregate engaged in protein synthesis: characterization of the ergosome. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:430–435. doi: 10.1038/197430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung H. W., Li W. W., Feng Z., Barbieri L., Stirpe F. Trichosanthin, alpha-momorcharin and beta-momorcharin: identity of abortifacient and ribosome-inactivating proteins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Mar;31(3):265–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]