Abstract
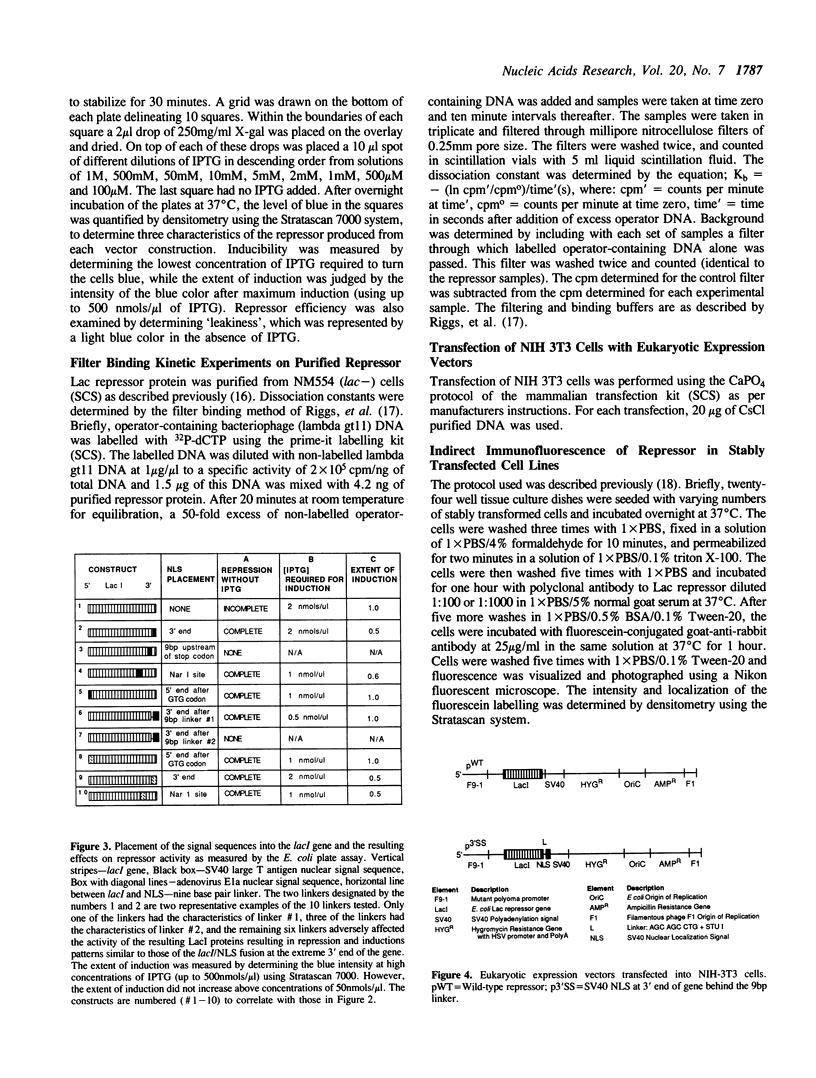
Eukaryotic expression vectors designed to produce E. coli Lac repressor protein targeted to the nucleus of mammalian cells were constructed. These constructions carry the lac repressor gene (lacI) fused at different positions to a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) from either the SV40 large T antigen or the adenovirus E1a. When the NLS's were fused to the lacI gene at the 5' end, the protein produced exhibited tighter repression of beta-galactosidase expression than the unmodified LacI protein. Localization sequences at the extreme 3' end of the gene generally diminished induction by IPTG, while introduction of the SV40 NLS nine base pairs upstream of the 3' end eliminated repressor activity. When either NLS was placed at the 3' end behind a random nine base pair linker, the activity of the LacI protein depended on the sequence of the linker, and in 9 of 10 linkers tested, activity of the protein was adversely affected. The one exception was the fusion protein from p3'ss, which had the NLS at the 3' end of lacI behind the nine base pair linker, AGC AGC CTG (ser-ser-leu). This protein exhibited efficient nuclear accumulation, strong repressor activity and greater sensitivity to IPTG induction. The functional linker from the p3'ss fusion protein extends the leucine zipper heptad repeat located at the C-terminus of the protein. These data support the role of the leucine zipper in tetramer formation and predict that extension of this zipper will further stabilize the protein. This modified lacI gene should be valuable for improved adaptation of the prokaryotic regulatory system to eukaryotic cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti S., Oehler S., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. Dimer-to-tetramer assembly of Lac repressor involves a leucine heptad repeat. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Pfahl M. Repressors. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:1–99. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60478-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Figge J., Hansen U., Wright C., Jeang K. T., Khoury G., Livingston D. M., Roberts T. M. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Functional analysis of the regulatory region of polyoma mutant F9-1 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4789–4809. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakerian A. E., Tesmer V. M., Manly S. P., Brackett J. K., Lynch M. J., Hoh J. T., Matthews K. S. Evidence for leucine zipper motif in lactose repressor protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J. Sequence of the lacI gene. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):765–769. doi: 10.1038/274765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano T. J., Deuschle U., Bujard H., McAllister W. T. Regulation of coliphage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases by the lac repressor-operator system. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada F., Oshima Y., Horiuchi T. Dissociation of the lac repressor into subunits. J Biochem. 1973 Jun;73(6):1299–1302. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Wilson F., Daniels C., Leveton C., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Expression and rescuing of a cloned human tumour necrosis factor gene using an EBV-based shuttle cosmid vector. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):355–361. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Baim S. B., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Conversion of the lac repressor into an allosterically regulated transcriptional activator for mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3343–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. H., Ferguson B. Q., Rosenberg M. Pentapeptide nuclear localization signal in adenovirus E1a. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2451–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J. Multicopy expression vectors carrying the lac repressor gene for regulated high-level expression of genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepper R. I., Levinson D. A., Stanger B. Z., Campos-Torres J., Abbas A. K., Leder P. IL-4 induces allergic-like inflammatory disease and alters T cell development in transgenic mice. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hanahan D., Gluzman Y. Infection of eucaryotic cells by helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses: early region 1 is not obligatory for integration of viral DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyborski D. L., Short J. M. Analysis of inducers of the E.coli lac repressor system in mammalian cells and whole animals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4647–4653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



