Abstract
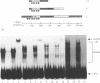
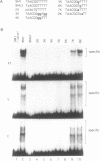
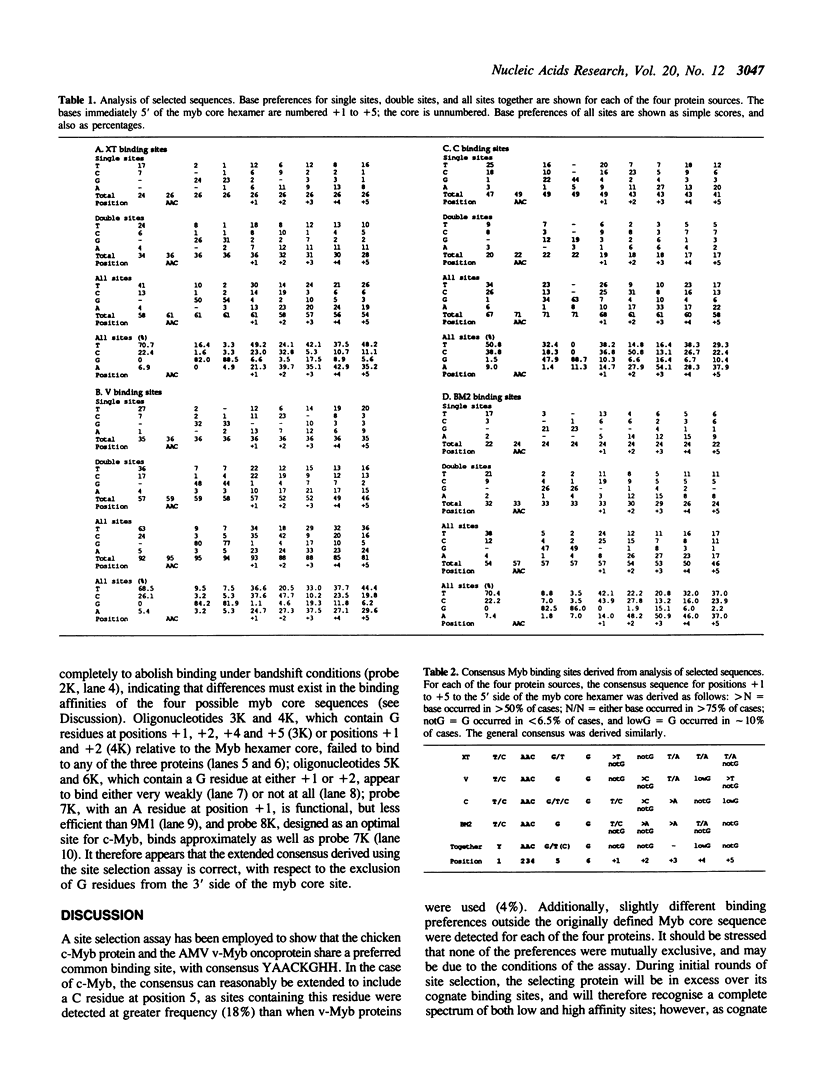
The chicken c-myb gene and the v-myb oncogene transduced by avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) encode DNA binding transcription activators. The DNA binding domain of AMV v-Myb displays a number of amino acid changes relative to c-Myb; v-Myb proteins in which one or more of three crucial residues in the DNA binding domain are mutated to resemble the c-Myb sequence display altered transformation phenotypes. In order to establish whether the spectrum of DNA binding sites which AMV v-Myb can recognise is different from that seen by chicken c-Myb, a site selection protocol was used to derive consensus binding sequences for three variant Myb proteins made in vitro, and also using nuclear extract from the v-myb transformed cell line BM2. The results show that the original consensus binding site defined for v-Myb, YAA-CKG, can be extended to YAACKGHH, and that this new consensus holds for both v-Myb and chicken c-Myb.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for products of avian oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2843–2850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Leutz A., Gibson T., Graf T. DNA-binding domain ancestry. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):134–134. doi: 10.1038/342134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Reakes C. F., Watson R. J. Characterization of the sequence-specific interaction of mouse c-myb protein with DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):161–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Watson R. J. Nucleotide preferences in sequence-specific recognition of DNA by c-myb protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3913–3919. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Golay J., Frampton J., Nakano T., Ness S. A., Graf T. Mutations in v-myb alter the differentiation of myelomonocytic cells transformed by the oncogene. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90424-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. The highly conserved amino-terminal region of the protein encoded by the v-myb oncogene functions as a DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Marknell A., Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specific mim-1 gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler T., Arnold H., Biedenkapp H., Klempnauer K. H. Characterization of the v-myb DNA binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1703–1710. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C. W., Sippel A. E., Vingron M., Klempnauer K. H. Drosophila and vertebrate myb proteins share two conserved regions, one of which functions as a DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3085–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. A sensitive method for the determination of protein-DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6197–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ishii S., Gonda T. J. Increase in specific DNA binding by carboxyl truncation suggests a mechanism for activation of Myb. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1875–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Moscovici G., Bishop J. M. A temperature-sensitive phenotype of avian myeloblastosis virus: determinants that influence the production of viral mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):767–773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.767-773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]