Abstract
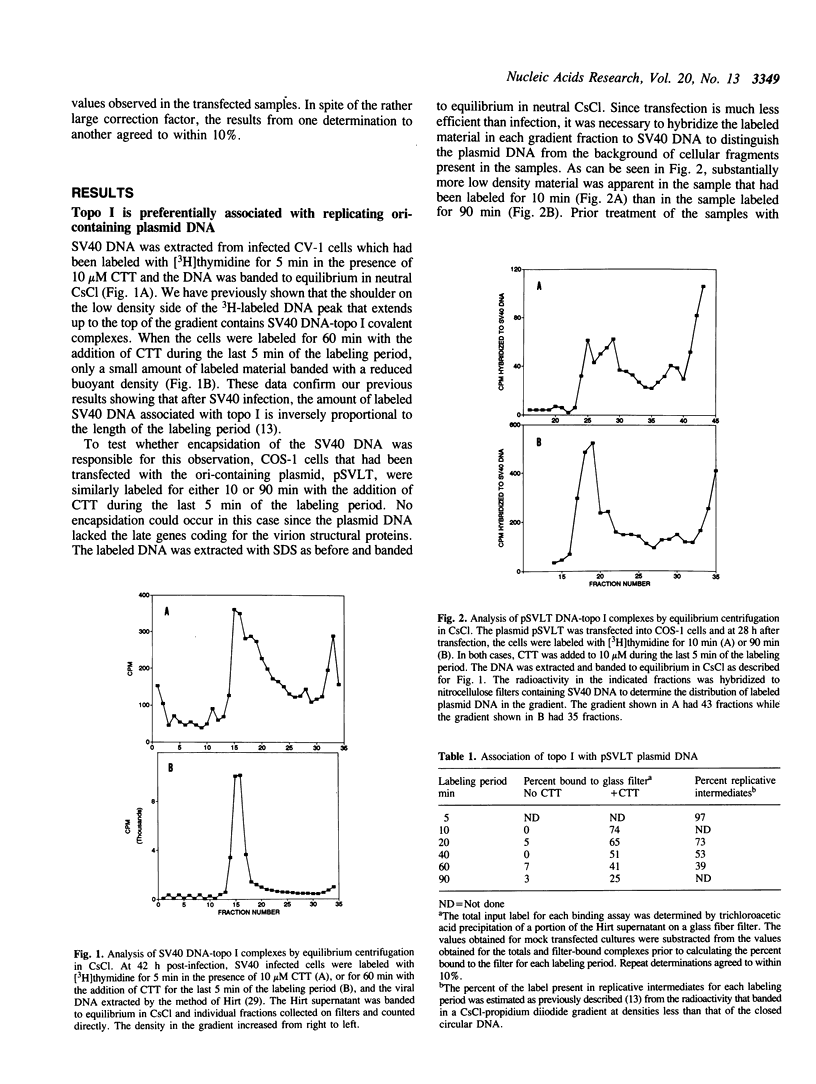
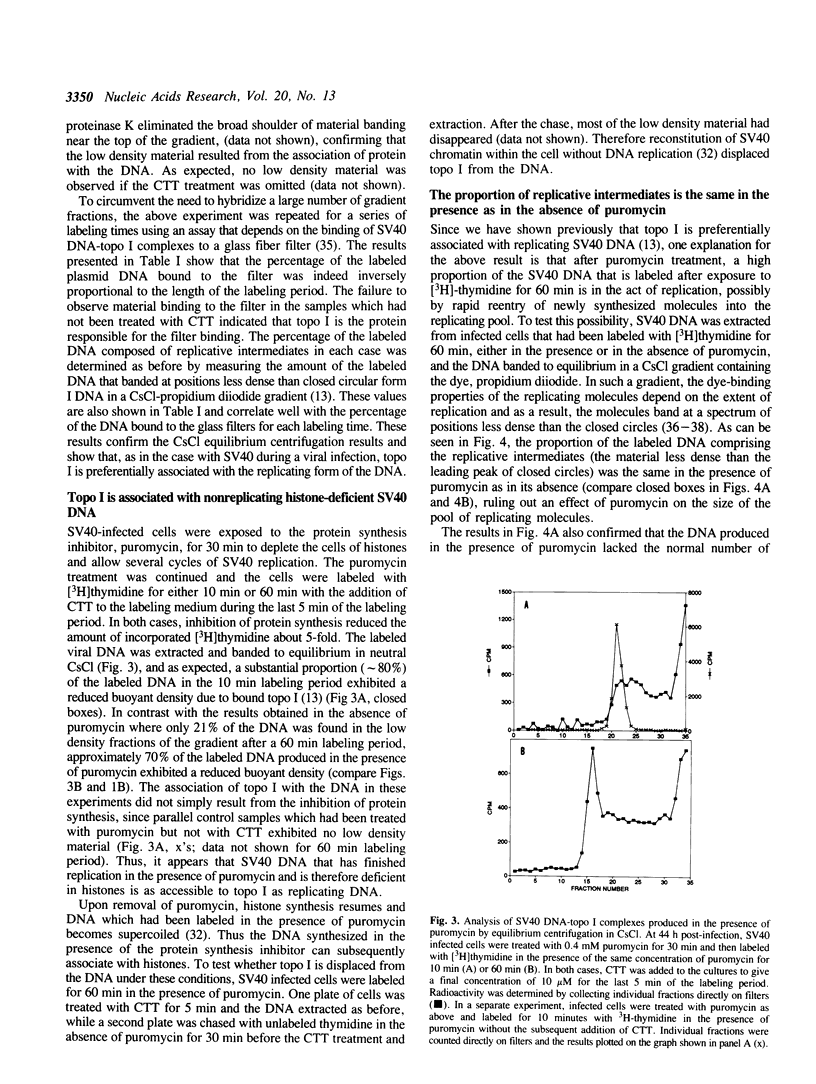
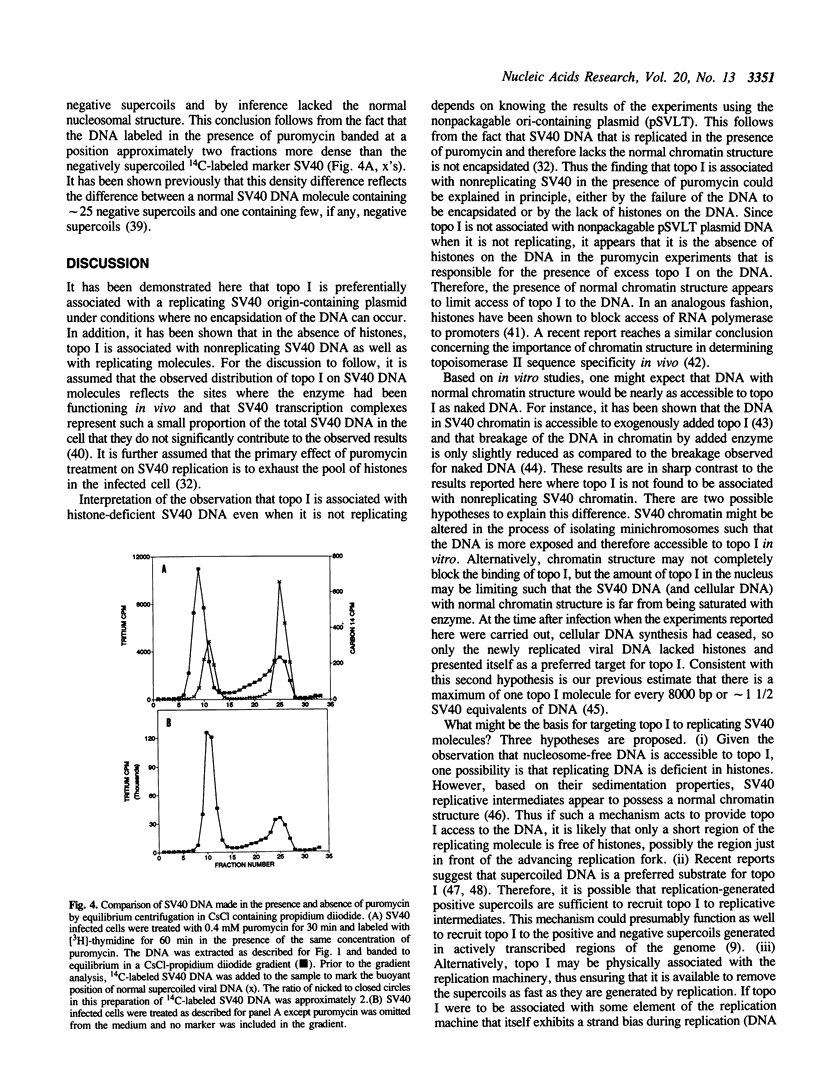
Based on the use of equilibrium centrifugation in CsCl to separate covalent complexes between topoisomerase I and DNA from protein-free DNA, it was concluded previously that the topoisomerase is preferentially associated with replicating SV40 DNA (Champoux, J. J. 1988. J. Virol. 62:3675-3683). One explanation for the failure to find the enzyme associated with nonreplicating viral DNA is that most of the completed DNA is rapidly sequestered for encapsidation and inaccessible to topoisomerase I. This explanation has been ruled out in the present work by the finding that topoisomerase I in COS-1 cells is also preferentially associated with the replicative form of an SV40 origin-containing plasmid that lacks the genes coding for the virion structural proteins and therefore cannot be encapsidated. Thus it appears that some structural feature of the replicating DNA or the replication complex specifically recruits the topoisomerase to the DNA. SV40 DNA which is produced in the presence of the protein synthesis inhibitor, puromycin, is deficient in histones and as a result lacks normal chromatin structure. Topoisomerase I was found to be associated with SV40 DNA under these conditions whether or not it was replicating. This observation is interpreted as an indication that under normal conditions, chromatin structure limits access of topoisomerase I to the nonreplicating viral DNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andoh T., Ishii K., Suzuki Y., Ikegami Y., Kusunoki Y., Takemoto Y., Okada K. Characterization of a mammalian mutant with a camptothecin-resistant DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avemann K., Knippers R., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Camptothecin, a specific inhibitor of type I DNA topoisomerase, induces DNA breakage at replication forks. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3026–3034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., DiNardo S., Voelkel-Meiman K., Sternglanz R. Need for DNA topoisomerase activity as a swivel for DNA replication for transcription of ribosomal RNA. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):414–416. doi: 10.1038/326414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilloni G., Di Martino E., Caserta M., di Mauro E. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I reaction is topology dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7071–7085. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilloni G., Di Martino E., Di Mauro E., Caserta M. Regulation of the function of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I: topological conditions for inactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3080–3084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. DNA is linked to the rat liver DNA nicking-closing enzyme by a phosphodiester bond to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4805–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Evidence for an intermediate with a single-strand break in the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3488–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., McConaughy B. L. Purification and characterization of the DNA untwisting enzyme from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4638–4642. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme: attachment of the enzyme to 3'-terminus of the nicked DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Strand breakage by the DNA untwisting enzyme results in covalent attachment of the enzyme to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Topoisomerase I is preferentially associated with isolated replicating simian virus 40 molecules after treatment of infected cells with camptothecin. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3675–3683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3675-3683.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs D. H., Pearson G. D. Filter-binding assay for covalent DNA-protein complexes: adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V., Sollner-Webb B. Sites of topoisomerase I action on X. laevis ribosomal chromatin: transcriptionally active rDNA has an approximately 200 bp repeating structure. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng W. K., Faucette L., Johnson R. K., Sternglanz R. Evidence that DNA topoisomerase I is necessary for the cytotoxic effects of camptothecin. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Elgin S. C. Localization of specific topoisomerase I interactions within the transcribed region of active heat shock genes by using the inhibitor camptothecin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Pflugfelder G., Wang J. C., Lis J. T. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz S. B., Chang C. K., Grollman A. P. Studies on camptothecin. I. Effects of nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;7(6):632–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Mayer A., Levine A. Replicating SV40 molecules containing closed circular template DNA strands. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;233(37):72–75. doi: 10.1038/newbio233072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen E., Mollerup S., Thomsen B., Bonven B. J., Bolund L., Westergaard O. Sequence-dependent effect of camptothecin on human topoisomerase I DNA cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llopis R., Perrin F., Bellard F., Gariglio P. Quantitation of transcribing native simian virus 40 minichromosomes extracted from CV1 cells late in infection. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):82–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.82-90.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J., Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs can be studied in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. E., Champoux J. J. Mapping in vivo topoisomerase I sites on simian virus 40 DNA: asymmetric distribution of sites on replicating molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):541–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. E., Champoux J. J. The basis for camptothecin enhancement of DNA breakage by eukaryotic topoisomerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8521–8532. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter A., Ruff J. DNA topoisomerase I cleavage sites in DNA and in nucleoprotein complexes. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9741–9748. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman A., Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. Characterization of the replicative intermediates of polyoma virus. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Szopa J., Han F. S., Cheng Y. C., Richter A., Scheer U. Association of DNA topoisomerase I and RNA polymerase I: a possible role for topoisomerase I in ribosomal gene transcription. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):411–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00303034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Kelly T. J., Jr, Thoren M. M., Salzman N. P. Structure of replicating simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid molecules. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):478–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.478-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapka R. M., Powelson M. A., Strayer J. M. Swiveling and decatenation of replicating simian virus 40 genomes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapka R. M. Topoisomerase inhibitors can selectively interfere with different stages of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4221–4227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Milman G. Short-term, high-efficiency expression of transfected DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1641–1643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P. Chromatin structure, not DNA sequence specificity, is the primary determinant of topoisomerase II sites of action in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4973–4984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M., Eason R. Nucleoprotein complexes in simian virus 40-infected cells. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):363–371. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.363-371.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M., Eason R. Supercoiling of SV40 DNA can occur independently of replication. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 10;241(106):46–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio241046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Dean F., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. In vitro replication of duplex circular DNA containing the simian virus 40 DNA origin site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J., Liu L. F. Roles of DNA topoisomerases in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Champoux J. J. Interaction of the DNA untwisting enzyme with the SV40 nucleoprotein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):623–635. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Involvement of DNA topoisomerase I in transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


