Abstract
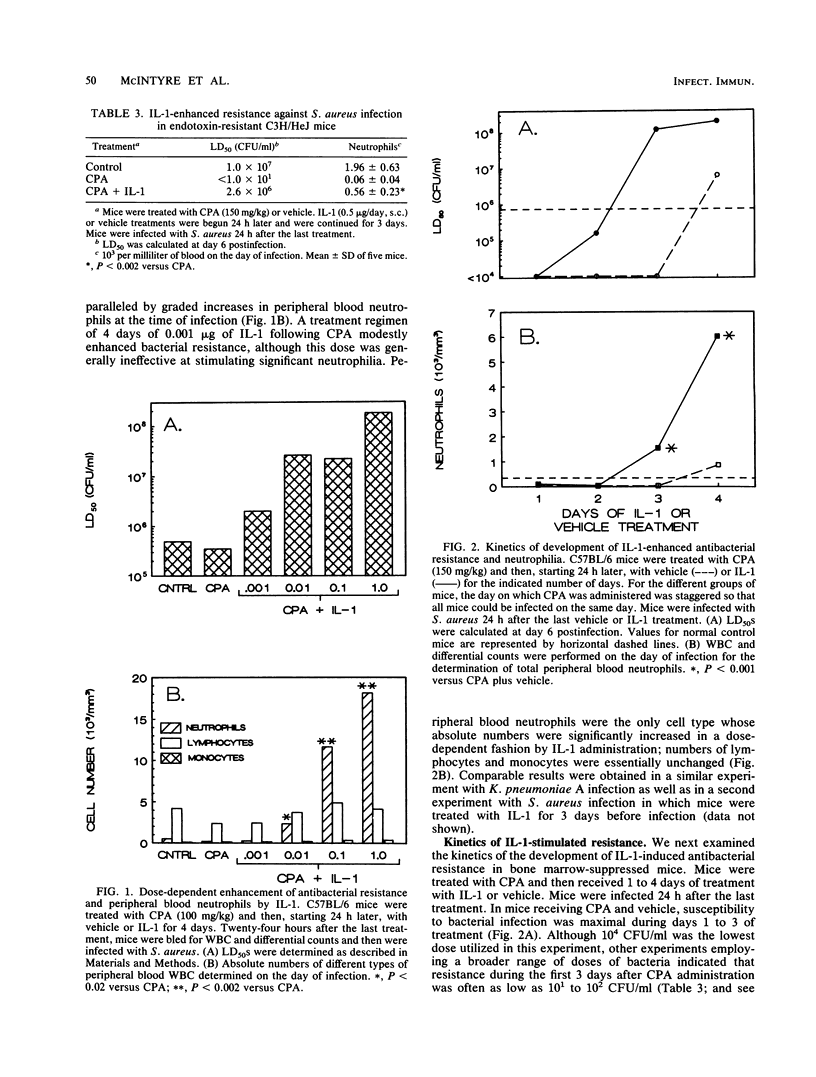
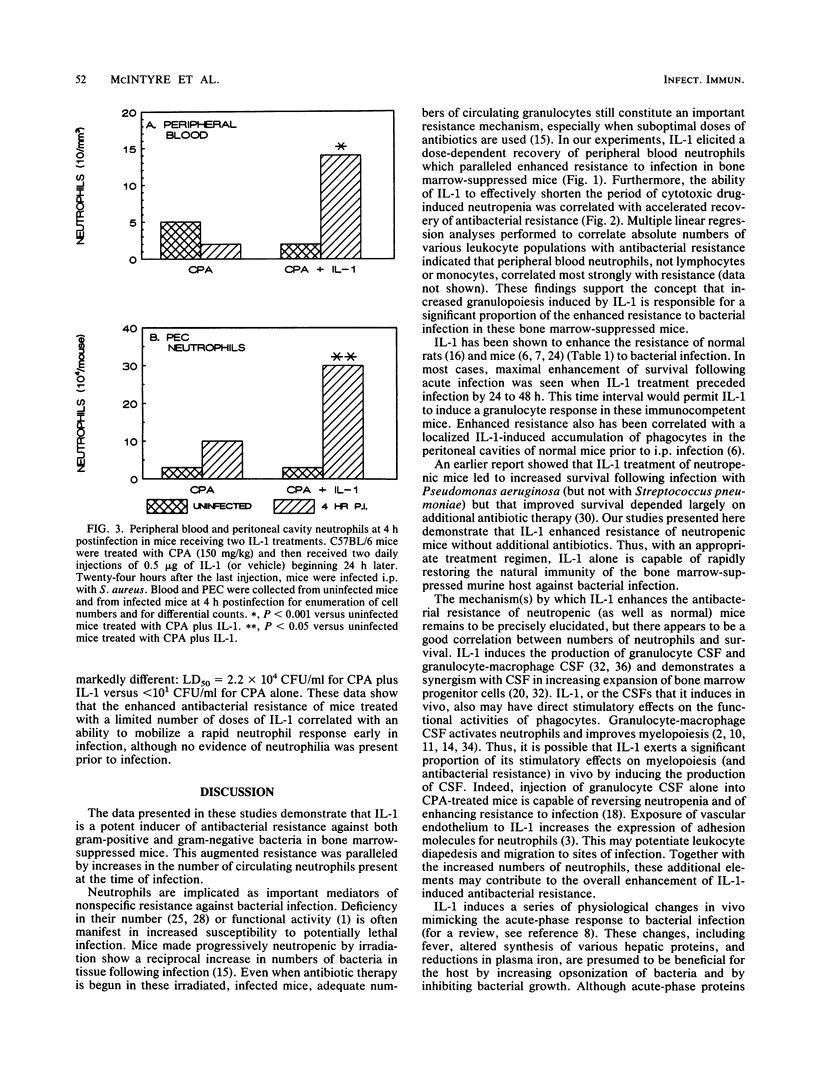
The effect of recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1) on the resistance of normal and bone marrow-suppressed mice against bacterial infection was evaluated. IL-1 induced neutrophilia and enhanced the resistance of normal mice against acute, systemic intraperitoneal infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mice with cyclophosphamide-induced bone marrow suppression were neutropenic and exhibited increased susceptibility to infection. Treatment of neutropenic C57BL/6 and C3H/HeJ mice with IL-1 before infection accelerated recovery of peripheral neutrophil counts and stimulated resistance against infection. Increases in neutrophils and enhancement of resistance induced by IL-1 were both dose and time dependent. Both neutrophilia and augmented resistance to infection were eliminated by a second dose of cyclophosphamide administered during the IL-1 treatments. Bone marrow-suppressed mice treated with IL-1 showed, at 4 h postinfection, greater increases in peripheral blood neutrophils and in numbers of peritoneal exudate neutrophils than suppressed mice treated with vehicle. The data suggest that the IL-1-stimulated recovery of myelopoiesis is an important factor in the enhancement of antibacterial resistance in bone marrow-suppressed, neutropenic mice. These findings indicate that IL-1 may be efficacious in limiting the duration of the neutropenia and of the increased risk for the development of bacterial infection associated with bone marrow suppression.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Schmalsteig F. C., Finegold M. J., Hughes B. J., Rothlein R., Miller L. J., Kohl S., Tosi M. F., Jacobs R. L., Waldrop T. C. The severe and moderate phenotypes of heritable Mac-1, LFA-1 deficiency: their quantitative definition and relation to leukocyte dysfunction and clinical features. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):668–689. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. C., Gasson J. C., Quan S. G., Fleischmann J., Weisbart R., Oette D., Mitsuyasu R. T., Golde D. W. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances neutrophil function in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2763–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Buckley M., Sathe Y. S., Freireich E. J. Quantitative relationships between circulating leukocytes and infection in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Feb;64(2):328–340. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-64-2-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Infections in cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975 Jun;2(2):89–128. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Purified human and recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha induced accumulation of inflammatory peritoneal neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes: possible contributions to antibacterial resistance. Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J., Kurtz R. S. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha on the host response to bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann J., Golde D. W., Weisbart R. H., Gasson J. C. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances phagocytosis of bacteria by human neutrophils. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):708–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gasson J. C. Enhancement of neutrophil function by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor involves recruitment of a less responsive subpopulation. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):652–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladue R., Girard A., Newborg M. Enhanced antibacterial resistance in neutropenic mice treated with human recombinant interleukin-1 beta. Agents Actions. 1988 Jun;24(1-2):130–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01968091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. E., Mitsuyasu R. T., DeLeo M. J., Oette D. H., Golde D. W. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on myelopoiesis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 3;317(10):593–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709033171003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogeterp J. J., Mattie H., Krul A. M., van Furth R. Quantitative effect of granulocytes on antibiotic treatment of experimental staphylococcal infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):930–934. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Pulliam L. A. Stimulation of antimicrobial activity in the rat with leukocytic endogenous mediator. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Mar;17(3):162–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Kilian P. L., Gubler U., Stern A. S., Chizzonite R. Molecular biology of interleukin-1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):631–639. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Matsubara S., Matsuno T., Tamura M., Hattori K., Nomura H., Ono M., Yokota T. Protective effect of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on microbial infection in neutropenic mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2715–2720. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2715-2720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki D. Y., Eisenman J. R., Conlon P. J., Larsen A. D., Tushinski R. J. Interleukin 1 regulates hematopoietic activity, a role previously ascribed to hemopoietin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5267–5271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Warren D. J. Synergy of interleukin 1 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: in vivo stimulation of stem-cell recovery and hematopoietic regeneration following 5-fluorouracil treatment of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7134–7138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Shapiro J., Lin B. F., Douches S., Neta R. Interaction of recombinant IL-1 and recombinant tumor necrosis factor in the induction of mouse acute phase proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2260–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Sztein M. B., Oppenheim J. J., Gillis S., Douches S. D. The in vivo effects of interleukin 1. I. Bone marrow cells are induced to cycle after administration of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Ohashi T., Minami A., Nakamura S. Enhanced resistance of mice to bacterial infection induced by recombinant human interleukin-1a. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1436–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1436-1440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal G. M., McCall E., Stueve T., Bagby G. C., Jr Interleukin 1 stimulates endothelial cells to release multilineage human colony-stimulating activity. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1772–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutschka P. J. Infections and immunodeficiency in bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 May;7(5 Suppl):S22–S29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaschek R., Urbaschek B. Induction of nonspecific resistance and stimulation of granulopoiesis by endotoxins and nontoxic bacterial cell wall components and their passive transfer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;459:97–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb20819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Douches S. D., Kaufman E. N., Neta R. Induction of colony stimulating factor in vivo by recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren D. J., Moore M. A. Synergism among interleukin 1, interleukin 3, and interleukin 5 in the production of eosinophils from primitive hemopoietic stem cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):94–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Largen M., McAdam K. P. Genetic control of endotoxic responses in mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):39–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. M., Levin F. C., Levin J. Effects of cyclophosphamide on murine bone marrow and splenic megakaryocyte-CFC, granulocyte-macrophage-CFC, and peripheral blood cell levels. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):222–228. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Yuschenkoff V. N., Schiffer S., Chang D., McCall E., Dinarello C. A., Brown M. A., Altrock B., Bagby G. C., Jr Vascular endothelial cells and granulopoiesis: interleukin-1 stimulates release of G-CSF and GM-CSF. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. A low dose of recombinant interleukin 1 protects granulocytopenic mice from lethal gram-negative infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1620–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


