Abstract
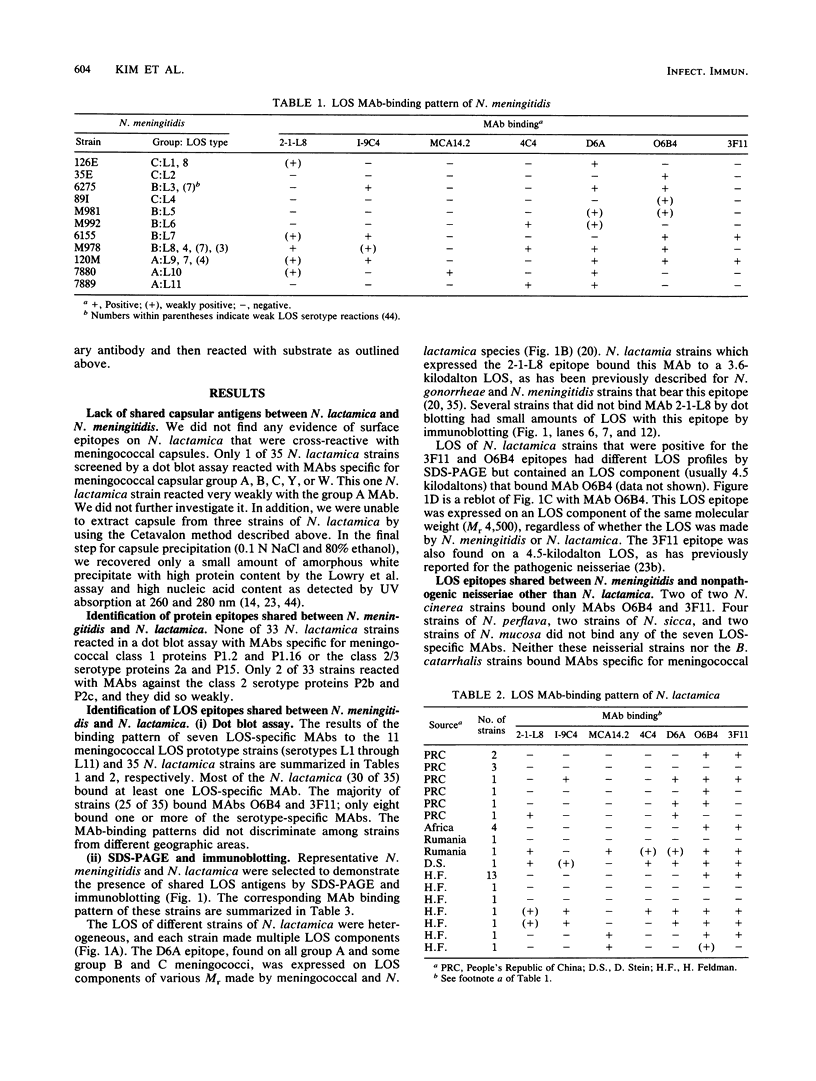
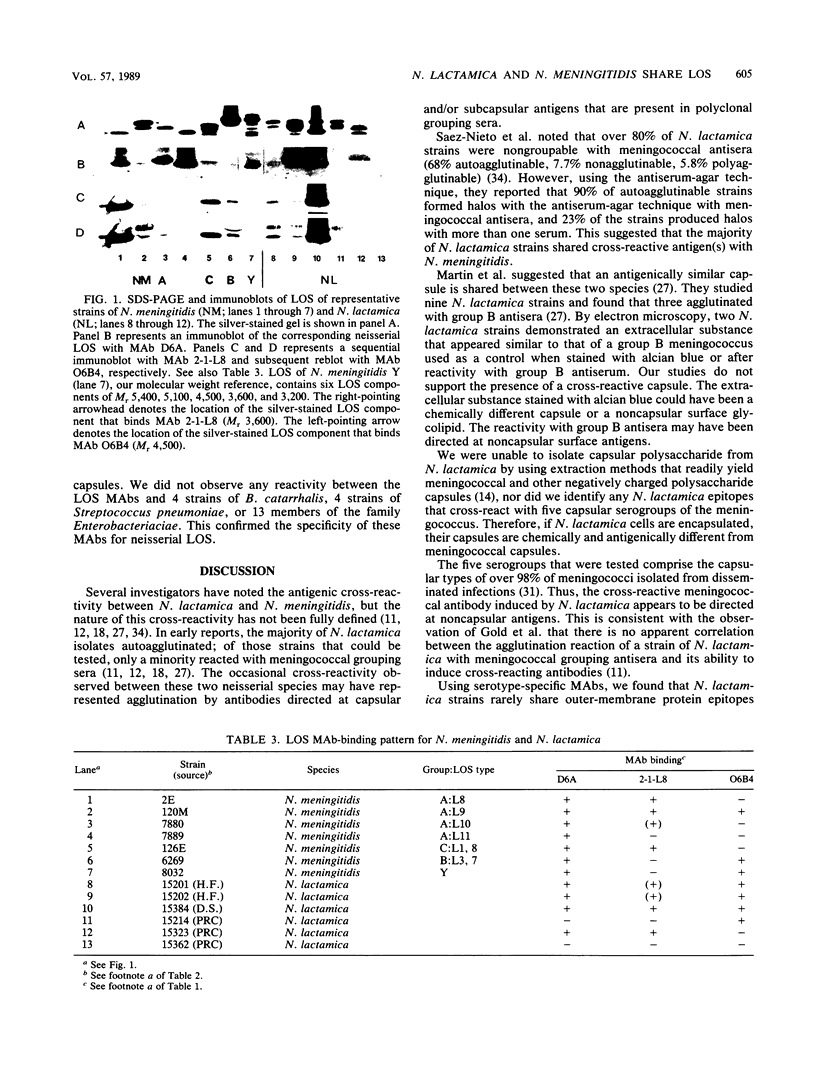
Neisseria lactamica, a common human pharyngeal commensal, contributes to acquired immunity to Neisseria meningitidis. To define the surface antigens shared between these two species, we used monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to study 35 N. lactamica strains isolated in various parts of the world for cross-reactivity with meningococcal capsules, outer membrane proteins, and lipooligosaccharides (LOS). No N. lactamica strain reacted significantly with MAbs specific for capsular group A, B, C, Y, or W, and we were unable to extract capsular polysaccharide from them. Only 2 of 33 strains reacted weakly with MAbs against class 2 serotype proteins P2b and P2c. None reacted with MAbs specific for meningococcal class 1 protein P1.2 or P1.16 or class 2/3 serotype protein P2a or P15. Most N. lactamica strains (30 of 35) bound one or more of seven LOS-specific MAbs. Two LOS epitopes, defined by MAbs O6B4 and 3F11, that are commonly found on pathogenic Neisseria species were found on 25 of 35 N. lactamica. Analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting showed that the LOS of N. lactamica are composed of multiple components that are physically and antigenically similar to the LOS of pathogenic Neisseria species. Among four other commensal neisserial species, only Neisseria cinerea shared LOS epitopes defined by MAbs O6B4 and 3F11. Previous studies have shown that pharyngeal colonization with N. lactamica induces bactericidal antibodies against the meningococcus. We postulate that shared N. lactamica and meningococcal LOS epitopes may play an important role in the development of natural immunity to the meningococcus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoun L., Lavitola A., Aubert G., Prère M. F., Cremieux A. C., Martin P. M. Human antibody response to the 70-Kd common neisserial antigen in patients and carriers of meningococci or non-pathogenic Neisseria. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Mar-Apr;139(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER U., PAEPCKE E. [Studies on asaccharolytic Neisseria in the human nasopharynx]. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1962;148:269–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Black W. J., Cannon J. G. Neisserial antigen H.8 is immunogenic in patients with disseminated gonococcal and meningococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):650–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Mitchell E. B., Jr Difficulties in differentiating Neisseria cinerea from Neisseria gonorrhoeae in rapid systems used for identifying pathogenic Neisseria species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):731–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.731-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Stewart P. W. Monoclonal antibody that recognizes an outer membrane antigen common to the pathogenic Neisseria species but not to most nonpathogenic Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.994-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun P. K., Sensabaugh G. F., Vedros N. A. Genetic relationships among Neisseria species assessed by comparative enzyme electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):3105–3115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-3105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zollinger W. D., Poolman J. T. Serotype antigens of Neisseria meningitidis and a proposed scheme for designation of serotypes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):504–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Goldschneider I., Lepow M. L., Draper T. F., Randolph M. Carriage of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica in infants and children. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):112–121. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Brandt B. L., Broud D. D., Goroff D. K., Baker C. J. Immune response of infants and children to disseminated infections with Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):71–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Wiggins G. L., Weaver R. E., Schubert J. H. Current status of lactose-fermenting Neisseria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):444–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Mandrell R. E., Hu Z., Westerink M. A., Poolman J. T., Griffiss J. M. Electromorphic characterization and description of conserved epitopes of the lipooligosaccharides of group A Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2631-2638.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by hemagglutination inhibition. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):471–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.471-475.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R., Schneider H., Apicella M., Zollinger W., Rice P. A., Griffiss J. M. Antigenic and physical diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Lavitola A., Aoun L., Ancelle R., Cremieux A. C., Riou J. Y. A common neisserial antigen evidenced by immunization of mice with live Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):229–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.229-233.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. V., Laviotola A., Ohayon H., Riou J. Y. Presence of a capsule in Neisseria lactamica, antigenically similar to the capsule of N. meningitidis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):279–285. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietzner T. A., Barnes R. C., JeanLouis Y. A., Shafer W. M., Morse S. A. Distribution of an antigenically related iron-regulated protein among the Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.60-68.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H. Meningococcal disease: still with us. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):71–91. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., MacGregor R. R., Beaty H. N. Bactericidal antibody after colonization with Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):56–62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of gonococcal antigens responsible for induction of bactericidal antibody in disseminated infection. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI108867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez-Nieto J. A., Dominguez J. R., Monton J. L., Cristobal P., Fenoll A., Vazquez J., Casal J., Taracena B. Carriage of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica in a school population during an epidemic period in Spain. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Jun;94(3):279–288. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Jarvis G. A. Elaboration of a 3.6-kilodalton lipooligosaccharide, antibody against which is absent from human sera, is associated with serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):672–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.672-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Williams G. D., Pier G. B. Immunological basis of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):13–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Wilson C. Variability of the lytic susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sera. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E. Immunotype epitopes of Neisseria meningitidis lipooligosaccharide types 1 through 8. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1652–1656. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1652-1656.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Altieri P., Berman S. Complex of meningococcal group B polysaccharide and type 2 outer membrane protein immunogenic in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):836–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI109383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Type-specific antigens of group A Neisseria meningitidis: lipopolysaccharide and heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):451–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.451-458.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



