Abstract
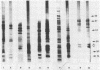
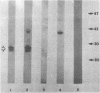
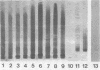
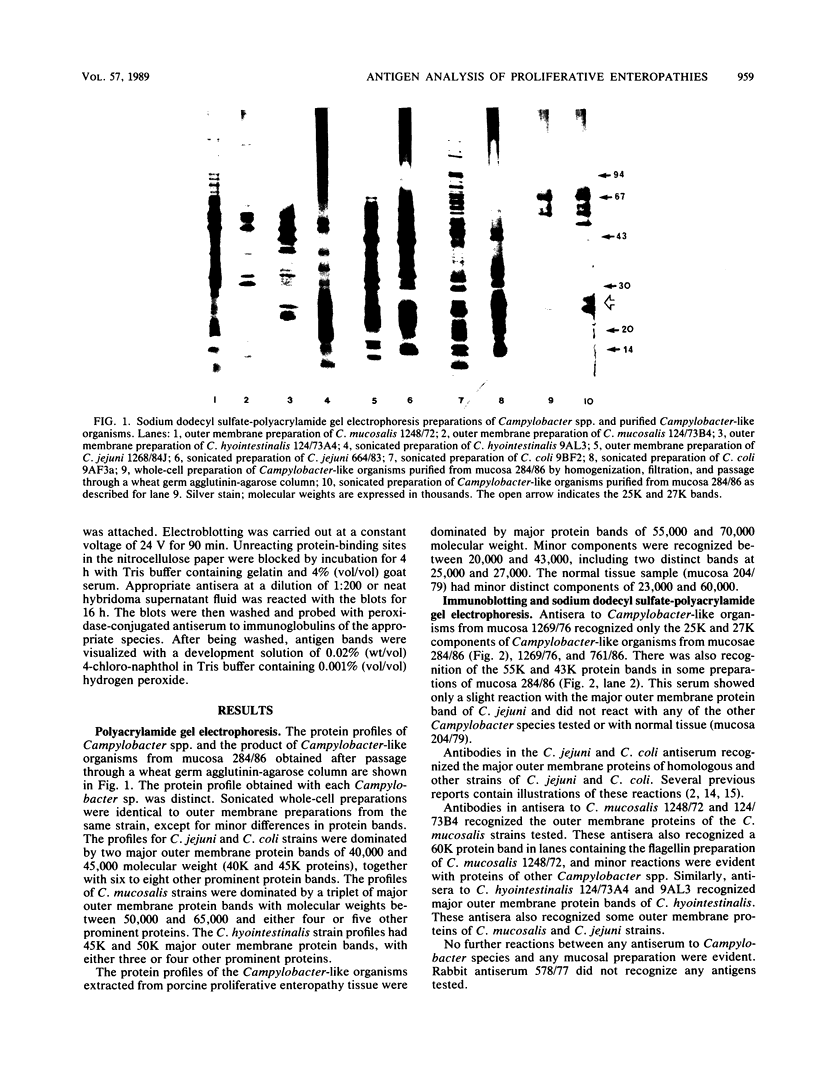
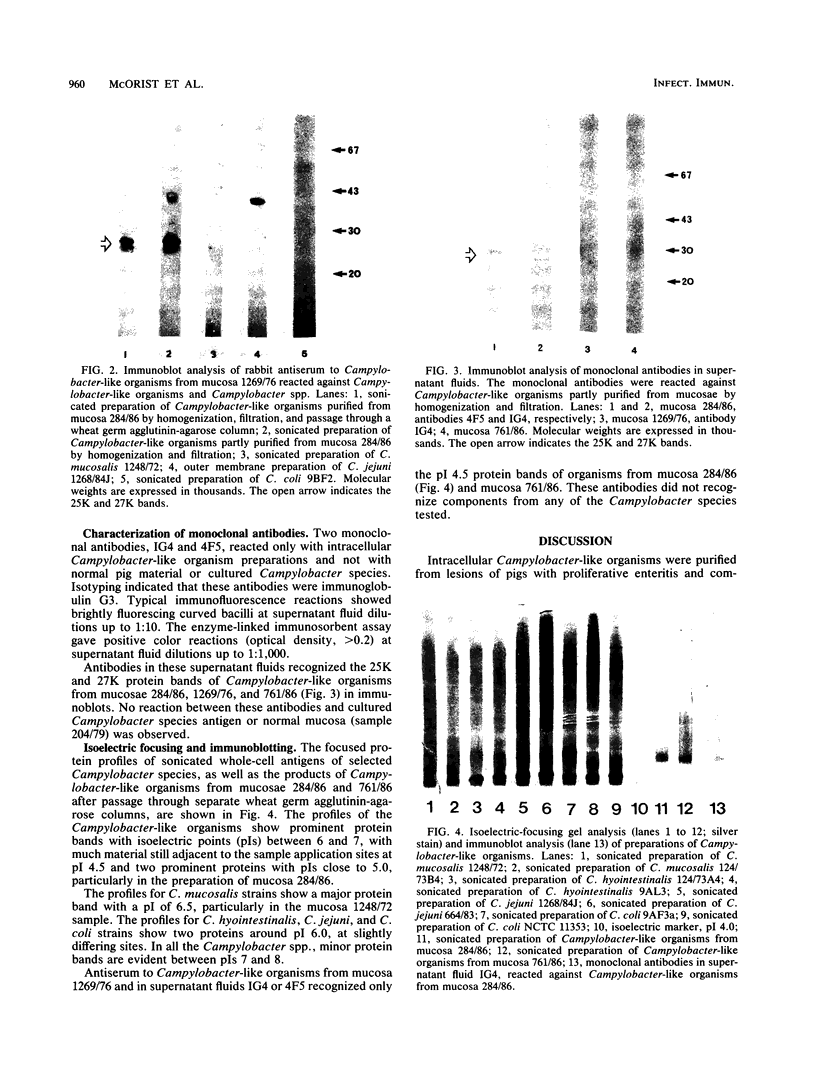
Whole-cell and outer membrane preparations of Campylobacter mucosalis, C. hyointestinalis, C. jejuni, and C. coli isolated from porcine intestines were compared with preparations of intracellular Campylobacter-like organisms extracted directly from the lesions of pigs with proliferative enteropathy. By gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, outer membrane and total protein profiles of C. mucosalis, C. hyointestinalis, C. jejuni, and C. coli were significantly different from each other and from those of the Campylobacter-like organisms. Immunoblotting of these preparations with rabbit antisera or monoclonal antibodies prepared against the intracellular Campylobacter-like organisms showed strong reactions only with a 25,000- to 27,000-molecular-weight component of preparations of the intracellular organisms. Antisera to cultivable Campylobacter species isolates did not react with preparations of intracellular organisms. Isoelectric focusing of sonicated preparations showed protein profile differences and an immune-reactive component in the intracellular organisms with a pI of 4.5. This study suggests that the intracellular Campylobacter-like organism associated with proliferative enteropathy may be a novel bacterium with significant antigenic differences from the Campylobacter species previously associated with the disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boosinger T. R., Thacker H. L., Armstrong C. H. Campylobacter sputorum subsp mucosalis and Campylobacter hyointestinalis infections in the intestine of gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Oct;46(10):2152–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrand L., Pählson C., Gustavsson S., Schwan A. Monoclonal antibodies for rapid identification of Campylobacter pyloridis. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1402–1403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzler M. E., Branstrator M. L. Differential localization of cell surface and secretory components in rat intestinal epithelium by use of lectins. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):329–343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Chang K., Kurtz H. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis (new species) isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative ileitis. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Mar;44(3):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immunochemical techniques. Part B. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):1–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwazaki M., Namioka S., Yabiki T. Gnotobiotic pigs exposed to Vibrio coli. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1971 Fall;11(3):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolk A. H., Ho M. L., Klatser P. R., Eggelte T. A., Kuijper S., de Jonge S., van Leeuwen J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis (BCG) and M. leprae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):511–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C. Intestinal adenomatosis in the pig: a bacteriological study. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Nov;17(3):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., MacIntyre N. Demonstration of a new intracellular antigen in porcine intestinal adenomatosis and hamster proliferative ileitis. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Jun;10(4):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Molecular identification of surface protein antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.675-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Outer membrane characteristics of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):898–906. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.898-906.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapother M. E., Joens L. A., Glock R. D. Experimental reproduction of porcine proliferative enteritis. Vet Rec. 1987 Dec 5;121(23):533–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney E., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C. Behaviour of Campylobacter sputorum subspecies mucosalis in gnotobiotic pigs. Res Vet Sci. 1984 May;36(3):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McOrist S., Boid R., Lawson G. H., McConnell I. Monoclonal antibodies to intracellular campylobacter-like organisms of the porcine proliferative enteropathies. Vet Rec. 1987 Oct 31;121(18):421–422. doi: 10.1136/vr.121.18.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Human antibody response to outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter jejuni during infection. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):739–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.739-743.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the flagella of Campylobacter jejuni: production, characterization and lack of effect on the colonization of infant mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Apr;96(2):131–141. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya T., Kubo M., Watase H. Campylobacter species isolated from swine with lesions of proliferative enteritis. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Apr;47(2):285–294. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L., Rowland A. C., Lawson G. H. Experimental reproduction of porcine intestinal adenomatosis and necrotic enteritis. Vet Rec. 1977 Jan 1;100(1):12–13. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O., Gondrosen B., Kapperud G., Underdal B. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from domestic and wild mammals in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):855–859. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.855-859.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland A. C., Lawson G. H. Intestinal adenomatosis in the pig: immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Nov;17(3):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland A. C. Porcine intestinal adenomatosis: a possible relationship with necrotic enteritis, regional ileitis and proliferative haemorrhagic enteropathy. Vet Rec. 1975 Sep 6;97(10):178–181. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.10.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stills H. F., Jr, Hook R. R., Jr, Sprouse R. F. Utilization of monoclonal antibodies to evaluate the involvement of Campylobacter jejuni in proliferative ileitis in Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetis auratus). Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2240–2246. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2240-2246.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Chai J., Louie T. J., Goudreau C., Lior H., Newell D. G., Pearson A. D., Taylor D. E. Antigenic analysis of Campylobacter flagellar protein and other proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):108–112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.108-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Skelton S. K., Feeley J. C. Interaction of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli with lectins and blood group antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):134–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.134-135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]