Abstract
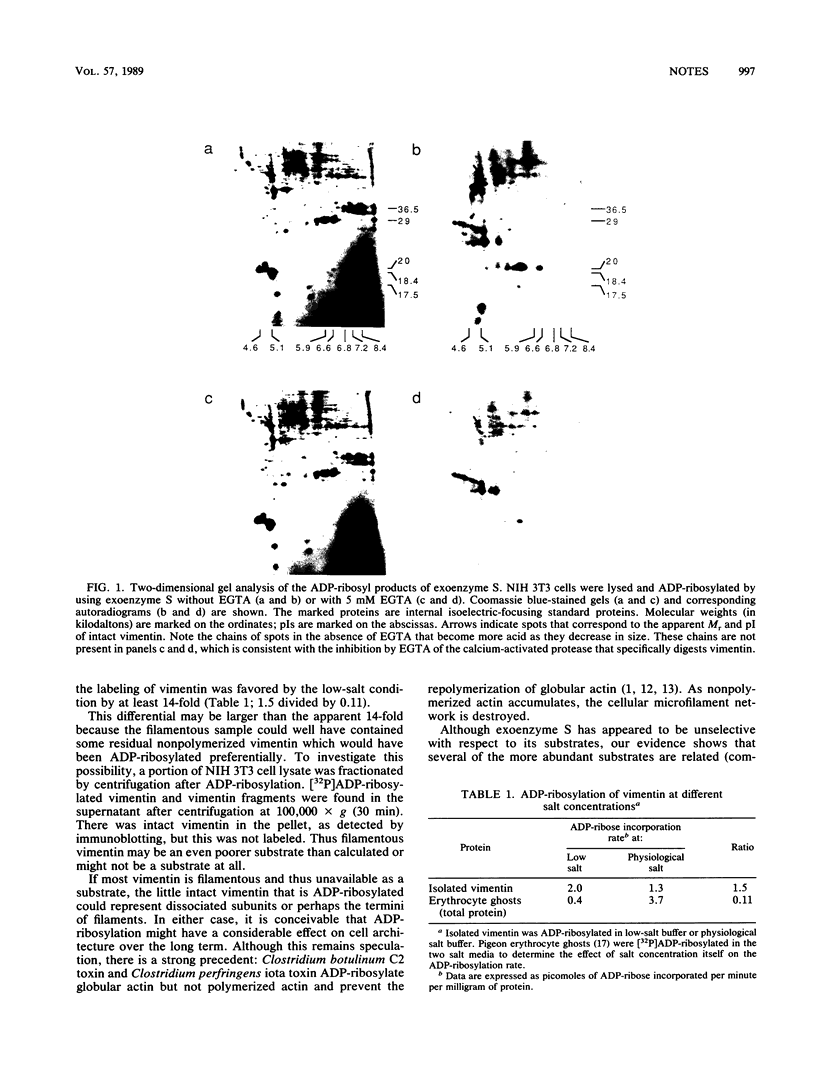
Exoenzyme S, which had been thought to be unselective, catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of only a subset of cellular proteins. The intermediate filament protein vimentin is one of the more abundant substrates. Disassembled vimentin, and proteolytic fragments of vimentin that cannot form filaments, is more readily ADP-ribosylated than is filamentous vimentin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Ankenbauer T., Schering B., Jakobs K. H. ADP-ribosylation of platelet actin by botulinum C2 toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Coburn J. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins by bacterial toxins in the presence of NAD glycohydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 28;954(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J., Bjorn M. J., Maxwell E. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S: an adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase distinct from toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Properties of Ca2+-activated protease specific for the intermediate-sized filament protein vimentin in Ehrlich-ascites-tumour cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Frank D. W., Stenzel P., Lile J. D., Iglewski B. H. Role of exoenzyme S in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):175–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02013593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of exoenzyme S to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:40–48. doi: 10.1159/000410470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. C., McConkey E. H., Guard N. L. Vimentin-derived proteins: differences between normal human fibroblasts and transformed human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schering B., Bärmann M., Chhatwal G. S., Geipel U., Aktories K. ADP-ribosylation of skeletal muscle and non-muscle actin by Clostridium perfringens iota toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):225–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L., Stiles B. G., Zepeda H. H., Wilkins T. D. Molecular basis for the pathological actions of Clostridium perfringens iota toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.118-122.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Vorgias C. E. Involvement of the N-terminal polypeptide of vimentin in the formation of intermediate filaments. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:43–67. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Hwang W. S., Shahrabadi M. S., Que J. U. Alteration of pulmonary structure by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(2):133–141. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Que J. U. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):579–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.579-586.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolkalis M., Gill D. M., Coburn J. Assay and purification of cytosolic factor required for cholera toxin activity. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:246–249. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]