Abstract
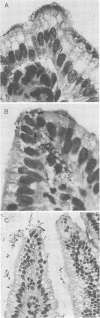
Bacterial attachment-effacement (att-eff) is emerging as an important virulence characteristic common to both enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC). The contribution of the plasmid-encoded EPEC adherence factor to the production of mucosal lesions and diarrhea was investigated in gnotobiotic piglets. Bacterial att-aff in the intestinal mucosa of piglets infected with plasmid-cured EPEC strain E2348/69 (O127) was indistinguishable from that in piglets infected with the parent strain, but the distribution of lesions was different; it occurred in the small intestines of 6 of 7 piglets infected with the parent strain compared with only 2 of 11 (P = 0.006) infected with the plasmid-cured strain. Plasmid-encoded factors in EPEC and EHEC strains did not appear to contribute to bacterial competition with normal gut microflora. Of 13 strains belonging to five EPEC serogroups, O55, O142, O26, O119, and O111, 3 fulfilled the criteria for EHEC (2 O26 and 1 O111). There were three distinct patterns of bacterial association with the intestinal mucosa of infected piglets. (i) EHEC strains caused bacterial att-eff associated with extensive destruction of surface and glandular epithelia in the large intestines with little or no inflammatory response. (ii) Some EPEC strains caused severe diarrhea which correlated with the extent of bacterial att-eff in the proximal small intestine, disruption of the epithelial cell membrane, and inflammation. It is suggested that, with respect to virulent strains, this degree of involvement determines the clinical outcome. Mildly pathogenic strains (O127 and O119), in which bacterial att-eff was restricted to the distal halves of the small and large intestines, caused little or no diarrhea. In such strains, nonimmune host factors (smaller, poorly feeding, and lethargic piglets) tended to play a determining role with regard to the degree of involvement of the small intestine and hence the clinical outcome. (iii) One strain (O55) caused illness and mucosal damage which could not be accounted for by the sparse bacterial att-eff observed in the gut. Instead, bacteria penetrated into and proliferated in the lamina propria, undermining the villous tips in the small intestine. Bacterial att-eff was the most important virulence factor in most of the strains examined, but plasmid-mediated factors facilitated bacterial adhesion in the small intestine, which may explain the reduced pathogenicity of the plasmid-cured variant of strain E2348/69 for human volunteers.
Full text
PDF
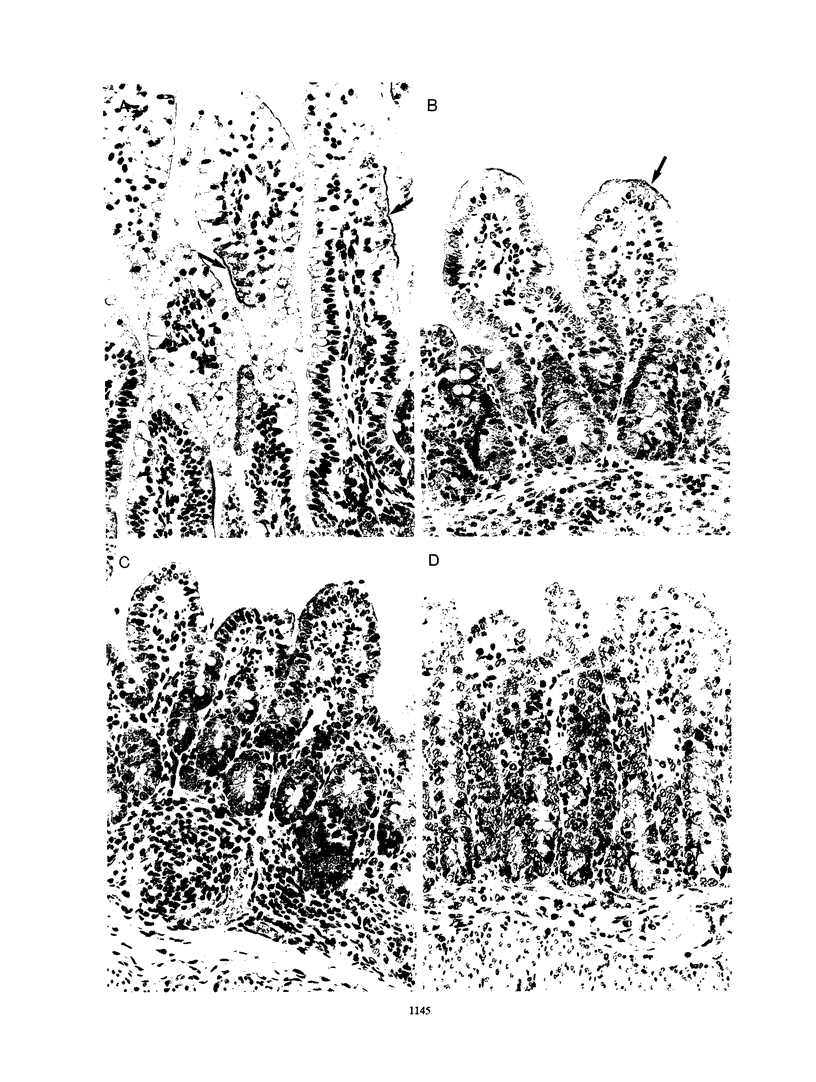


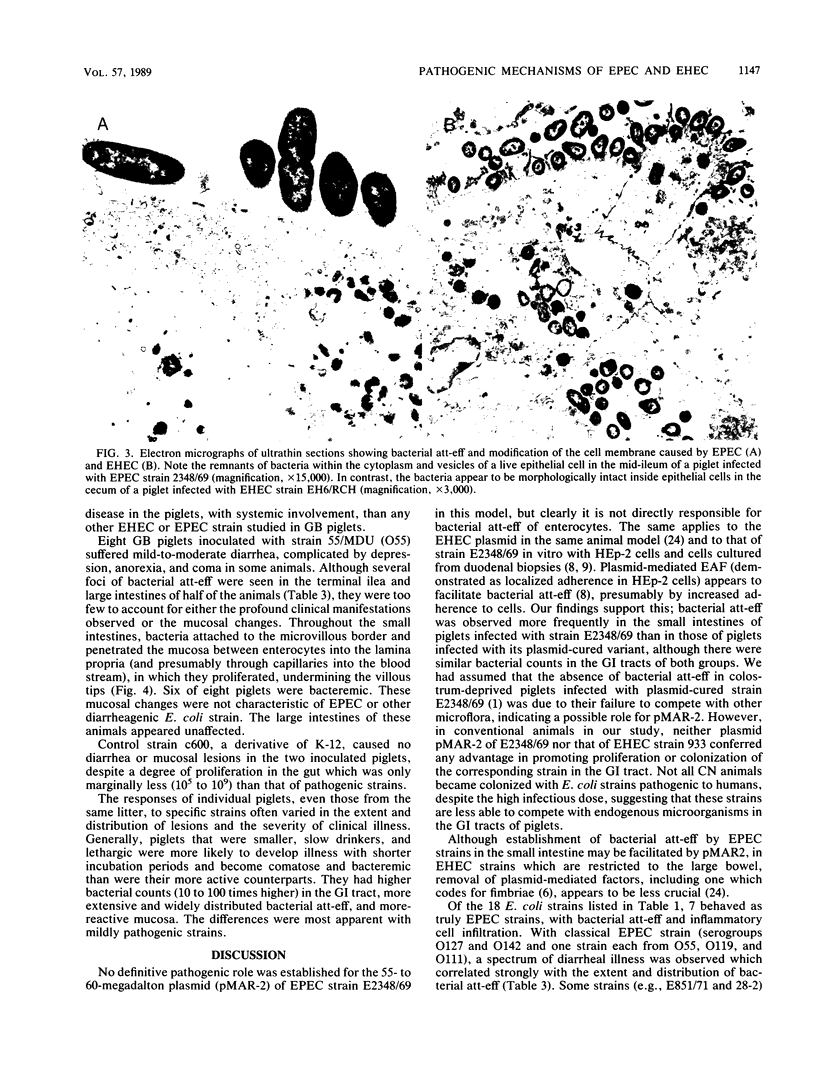
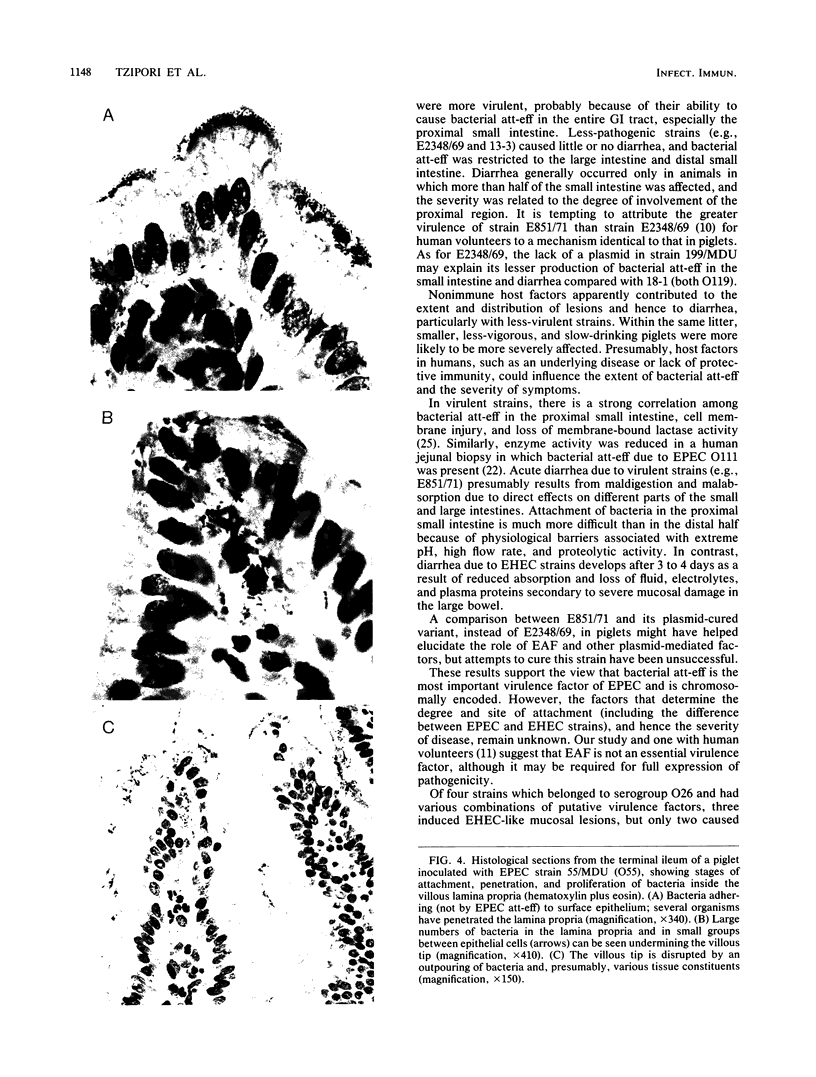


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Duimstra J. R. Infection of gnotobiotic pigs with an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain associated with an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):953–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.953-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Heesemann J., Laufs R., O'Brien A. D., Tacket C. O., Levine M. M. A plasmid of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 is required for expression of a new fimbrial antigen and for adhesion to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.455-461.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Pai C. H., Jadusingh I. H., Macinnis M. L., Shaffer E. A., Hershfield N. B. The histopathology of rectosigmoid biopsies from adults with bloody diarrhea due to verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;88(1):78–82. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., McNeish A. S. Role of plasmid-encoded adherence factors in adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.78-85.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makin T. J., Tzipori S. Inexpensive techniques for the production and maintenance of gnotobiotic piglets, calves and lambs. Aust Vet J. 1980 Aug;56(8):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1980.tb09558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for a developmentally regulated glycolipid receptor for shigella toxin involved in the fluid secretory response of rabbit small intestine. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1023–1031. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Maher K. O., Mackie P., Kaper J. B. Characterization of plasmids encoding the adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2370–2377. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2370-2377.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R. J., Partin J. C., Saalfield K., McAdams A. J. An ultrastructural study of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in human infants. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1983 Jun;4(4):291–304. doi: 10.3109/01913128309140582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley T. E., Jones E. W., Corley L. D. Attachment and penetration of Escherichia coli into intestinal epithelium of the ileum in newborn pigs. Am J Pathol. 1969 Sep;56(3):371–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. J., Hart A., Batt R. M., McDougall C., McLean L. Ultrastructural and biochemical changes in human jejunal mucosa associated with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (0111) infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Jan;5(1):70–73. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198601000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Chandler D., Smith M. The clinical manifestation and pathogenesis of enteritis associated with rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections in domestic animals. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1983;7(3-4):193–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth I. K., Chapman C., Birden R., Brittingham J., Jackson C., Hogg J. The pathogenesis of hemorrhagic colitis caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):712–716. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth K. I., Smithers J., Jackson C. Studies in gnotobiotic piglets on non-O157:H7 Escherichia coli serotypes isolated from patients with hemorrhagic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):590–597. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]