Abstract
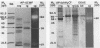
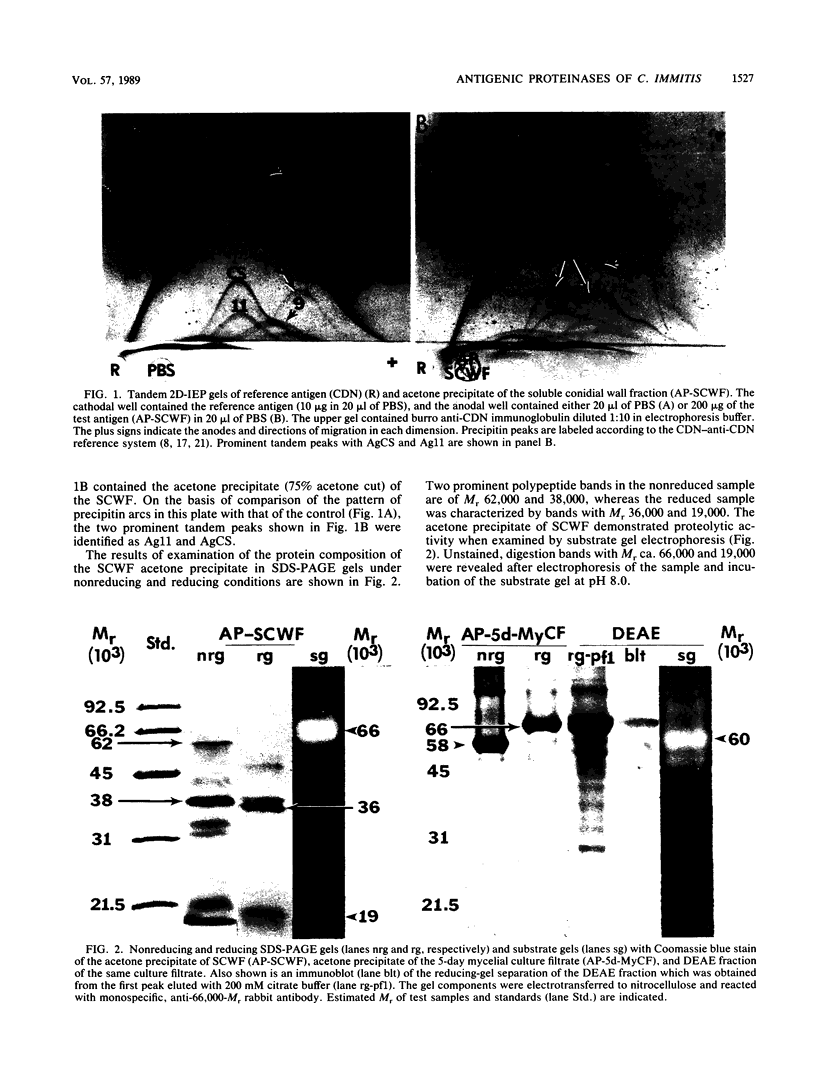
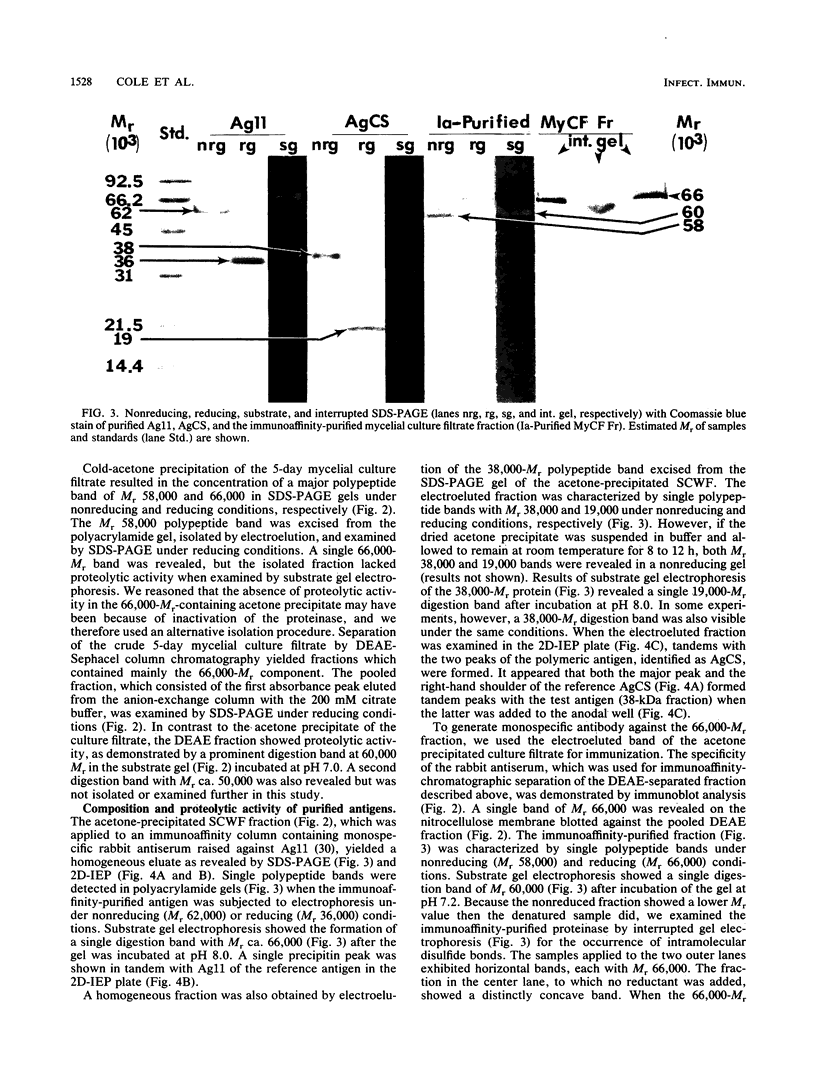
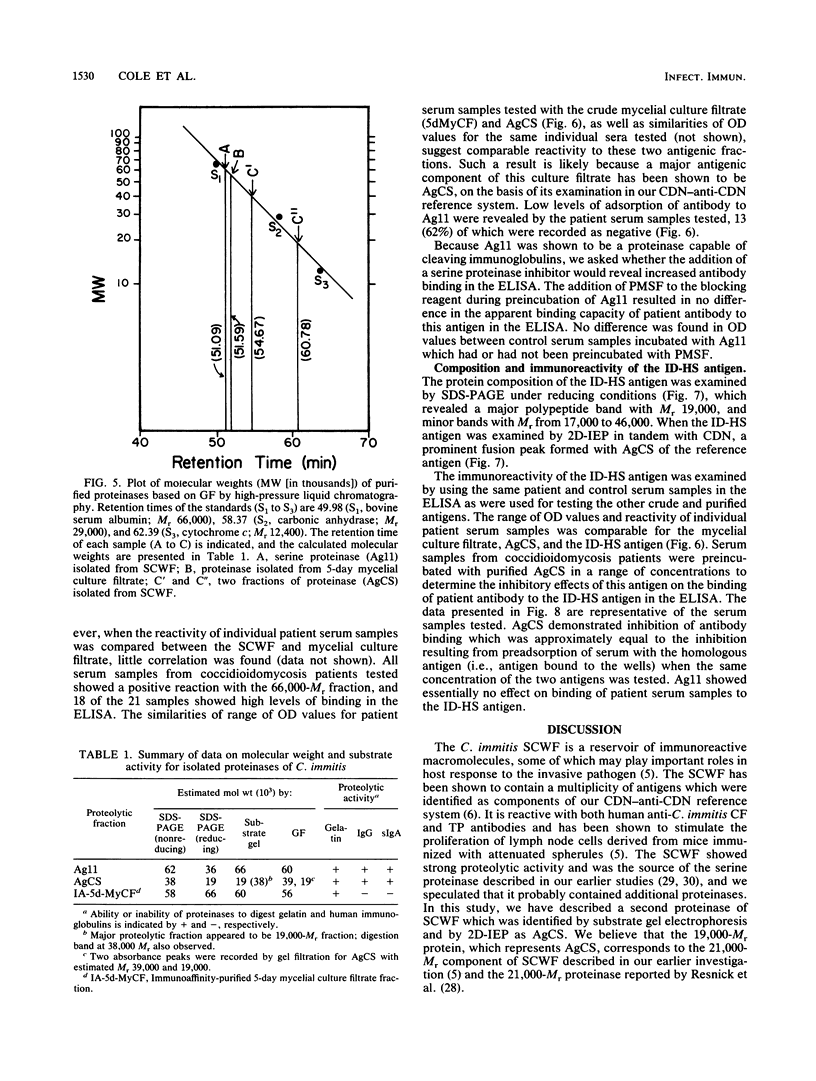
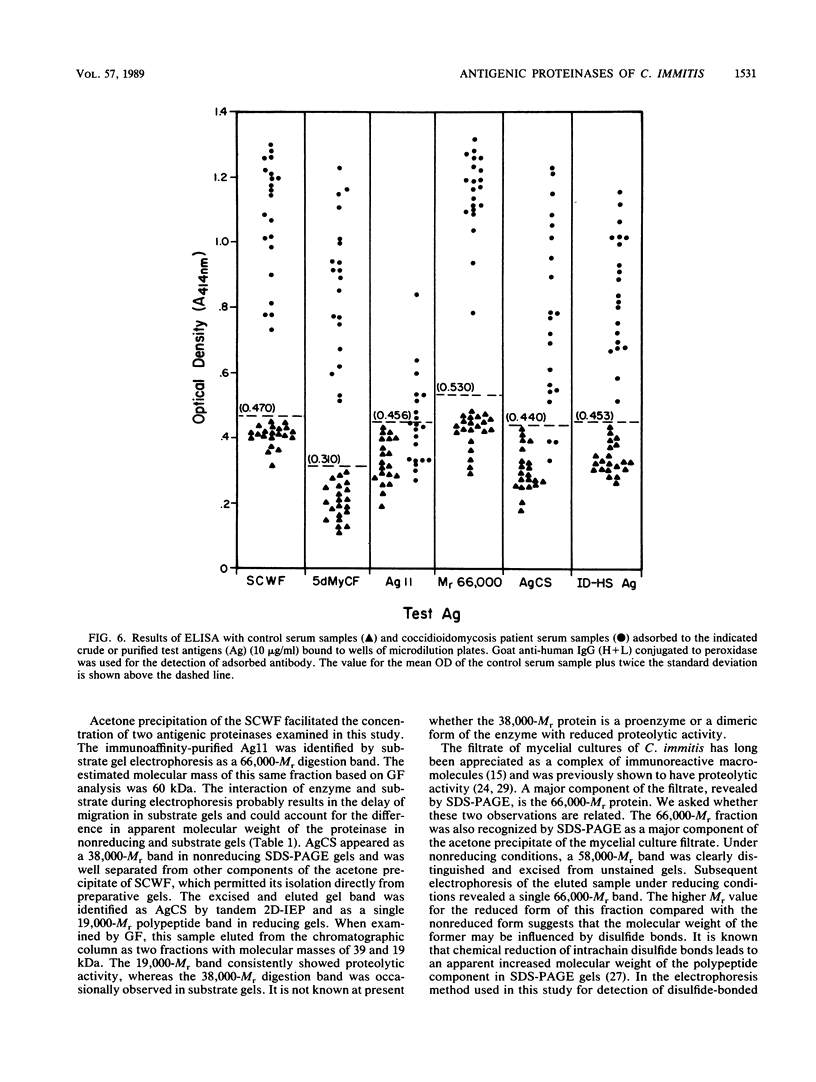
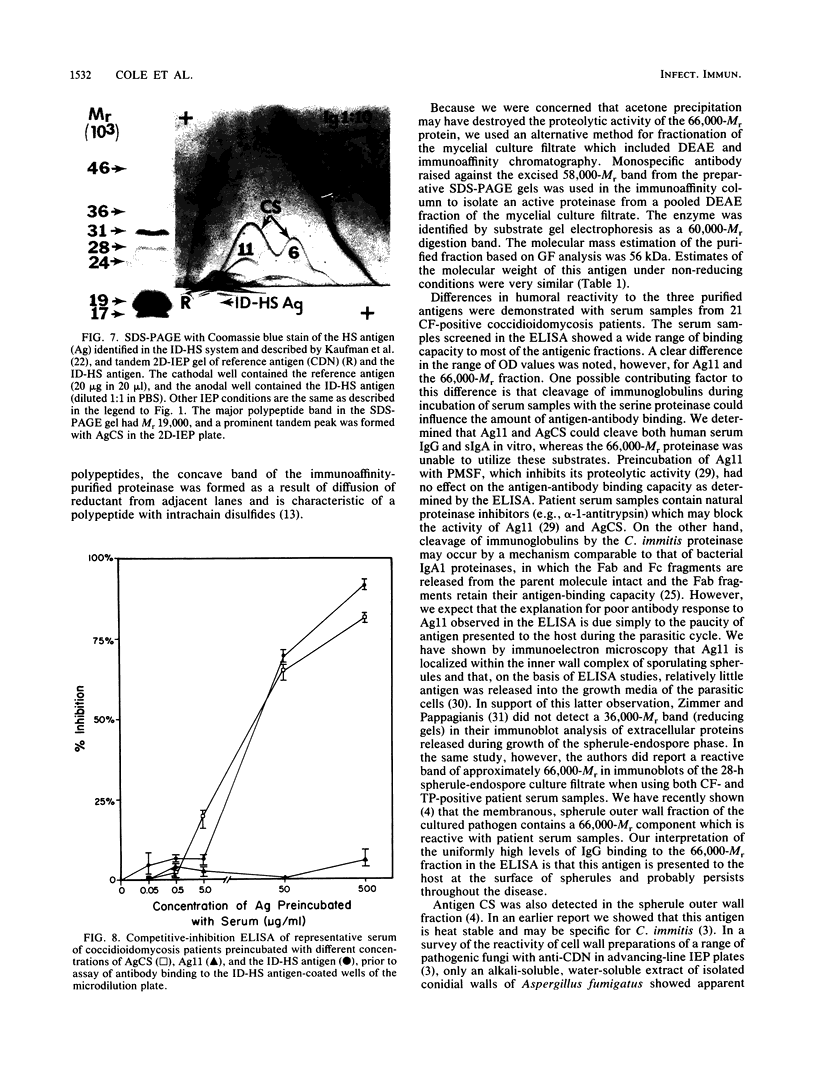
Three antigens with proteolytic activity have been isolated from crude, water-soluble fractions of the saprobic phase of the fungal pathogen Coccidioides immitis. Two proteinases, identified in our immunoelectrophoresis reference system as Ag11 and AgCS, were isolated from the soluble conidial wall fraction (SCWF). Ag11 was previously shown to be a serine proteinase and was characterized in this study as a 60-kilodalton (kDa) fraction by gel filtration (GF). The purified proteinase demonstrated little or no reactivity with 21 serum samples from coccidioidomycosis patients in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; this may be due to limited presentation of this antigen to the host during the course of coccidioidomycosis. AgCS was separated by GF chromatography into two fractions identified by molecular masses of 39 and 19 kDa. Most proteolytic activity was shown by substrate gel electrophoresis to be associated with the lower-molecular-mass fraction. AgCS was reactive with 18 of the 21 serum samples and shown to be the major component of a heat-stable antigen previously reported to be immunospecific for C. immitis. The third antigen with proteolytic activity was isolated from the 5-day mycelial culture filtrate and identified by GF as a 56-kDa fraction. Uniformly high levels of immunoreactivity between 18 of the 21 patient sera and the 56-kDa antigen were demonstrated. Antigens with proteolytic activity may play important roles in fungus-host interactions as well as morphogenesis of the pathogen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brass C., Levine H. B., Stevens D. A. Stimulation and suppression of cell-mediated immunity by endosporulation antigens of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):431–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.431-436.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. L., Osir E. O., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Law J. H. Humoral antibody responses to specific antigens of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Franco M., Zhu S., Yuan L., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Immunoreactivity of a surface wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2695–2701. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2695-2701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Sun S. H. An immunoreactive, water-soluble conidial wall fraction of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):657–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.657-667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Franco M., Bukownik E., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Isolation and morphology of an immunoreactive outer wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2686-2694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Antigenic identity of biologically active antigens in coccidioidin and spherulin. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2590–2596. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2590-2596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Isolation of a coccidioidin component that reacts with immunoglobulin M precipitin antibody. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.449-453.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Huppert M. Coccidioidomycosis: factors affecting the host-parasite interaction. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):372–390. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Adler J. P., Rice E. H., Sun S. H. Common antigens among systemic disease fungi analyzed by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.479-485.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Spratt N. S., Vukovich K. R., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Antigenic analysis of coccidioidin and spherulin determined by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.541-551.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. G., Huppert M., Pappagianis D. Comparison and diagnostic value of the coccidioidin heat-stable (HS and tube precipitin) antigens in immunodiffusion. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.515-518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. G. Specific and rapid identification of medically important fungi by exoantigen detection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:209–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupan D. M., Nziramasanga P. Collagenolytic activity of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):360–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.360-361.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Barber B. H., Faulkes R. A., Crumpton M. J. Albumin associated with purified pig lymphocyte plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):49–57. doi: 10.1042/bj1920049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick S., Pappagianis D., McKerrow J. H. Proteinase production by the parasitic cycle of the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T., Sun S. H. Possible role of a proteinase in endosporulation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1551–1559. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1551-1559.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunoblot analyses of spherule-endospore-phase extracellular protein and mycelial-phase antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.64-70.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]