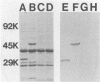
Abstract
The heat-modifiable major outer membrane protein (P1) of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) has been shown to be both exposed on the cell surface and capable of inducing the synthesis of antibodies protective against experimental Hib disease. Chemical mutagenesis of a recombinant plasmid containing the Hib gene encoding P1 resulted in inactivation of P1 expression by this plasmid. The mutated P1 gene was transformed into Hib to obtain an isogenic mutant lacking only the ability to synthesize this surface protein. In addition, the P1 gene was inserted into a plasmid shuttle vector and used to construct a recombinant Hib strain that overexpressed the P1 protein. Lack of P1 expression did not affect the ability of Hib to grow in vitro. Neither the absence nor the overproduction of P1 affected expression of capsular polysaccharide and lipooligosaccharide by Hib. The P1-negative mutant and the P1-overexpressing strain were both as susceptible to the bactericidal activity of pooled normal human serum as was the wild-type parent strain, while the P1-negative mutant was as resistant to the bactericidal activity of normal infant rat serum as was the wild-type parent strain. The P1-negative mutant was no less virulent than was the wild-type parent strain in an animal model system, such that both the numbers of animals infected by this mutant and the mean magnitudes of the resultant bacteremias were essentially identical to those obtained with challenge by the wild-type parent strain. Similarly, overexpression of P1 did not detectably affect the virulence of Hib. These data indicate that this protective protein antigen plays no detectable role in the expression of virulence by Hib, as assessed in an animal model system.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Outer-membrane protein subtypes of Haemophilus influenzae type b and spread of disease in day-care centers. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):210–217. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. N., Said B., Ghosn C. R., Beach J. V., Nunn W. D. Purification and characterization of an outer membrane-bound protein involved in long-chain fatty acid transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1412–1419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochi S. L., Broome C. V. Vaccine prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: past, present and future. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):12–19. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Black W. J., Kawula T. H., Barritt D. S., Dempsey J. A., Kverneland K., Jr, Stephenson A., Schepart B. S., Murphy G. L., Cannon J. G. Recombination among protein II genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae generates new coding sequences and increases structural variability in the protein II family. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. B., Pifer M. L. Plasmid cloning vectors resistant to ampicillin and tetracycline which can replicate in both E. coli and Haemophilus cells. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum R. S., Syriopoulou V. P., Smith A. L., Scheifele D. W., Willard J. E. Loss of plasmid DNA coding for beta-lactamase during experimental infection with Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):548–553. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichenlaub R. Mutants of the mini-F plasmid pML31 thermosensitive in replication. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):559–566. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.559-566.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales F. R., Leachman S., Norgard M. V., Radolf J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Evans C., Hansen E. J. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding the heat-modifiable major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2993–3000. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2993-3000.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Munson R. S., Jr Prospects for prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease by immunization. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):448–461. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Quinn-Dey T., Zlotnick G. W. Biologic activities of antibody to a peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein of Haemophilus influenzae against multiple clinical isolates of H. influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2878–2883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2878-2883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Antibody response of infants to cell surface-exposed outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b after systemic Haemophilus disease. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.82-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Patrick C. C., Hermanstorfer L., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Conservation of epitopes in the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.513-520.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
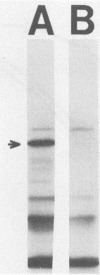
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H. Detection of antibody-accessible proteins on the cell surface of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):950–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.950-953.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Gonzales F. R., Chamberlain N. R., Norgard M. V., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., Pelzel S. E., Gaddy B., Clausell A. Cloning of the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2709–2716. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2709-2716.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott R. M., Meyer E. M., Vogt M. Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.517-524.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Patrick C. C., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide: stability of expression and association with virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1979–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1979-1986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R. Protection of infant rats from Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by antiserum to purified outer membrane protein a. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2612-2618.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Characterization of serologically dominant outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1183-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Grass S. Purification, cloning, and sequence of outer membrane protein P1 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2235–2242. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2235-2242.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nano F. E. Identification of a heat-modifiable protein of Francisella tularensis and molecular cloning of the encoding gene. Microb Pathog. 1988 Aug;5(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Kimura A., Jackson M. A., Hermanstorfer L., Hood A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Antigenic characterization of the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2902–2911. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2902-2911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow J. K., Brown D. C., Boling M. E., Mattingly A., Gordon M. P. Repair of deoxyribonucleic acid in Haemophilus influenzae. I. X-ray sensitivity of ultraviolet-sensitive mutants and their behavior as hosts to ultraviolet-irradiated bacteriophage and transforming deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):546–558. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.546-558.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H., Walter R. B. Effect of glycerol on plasmid transfer in genetically competent Haemophilus influenzae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 May;203(2):296–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00333969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Schneerson R., Kendall-Morris S., Robbins J. B. Differential complement resistance mediates virulence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.95-104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Laprade R., Coulton J. W. Properties of the porin of Haemophilus influenzae type b in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 25;861(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Lyew D. J., Coulton J. W. Transmembrane permeability channels across the outer membrane of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.918-924.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Brenneman G., Lepow M., Lum M., Burkhart K., Chiu C. Y. Haemophilus influenzae type b anticapsular antibody responses to PRP-pertussis and PRP-D vaccines in Alaska native infants. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):719–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogev R., Hansen E. J. Dissociation of virulence and protection from infection by mutant analysis in Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1944–1947. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1944-1947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. Contribution of lipopolysaccharide to pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae: comparative virulence of genetically-related strains in rats. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]