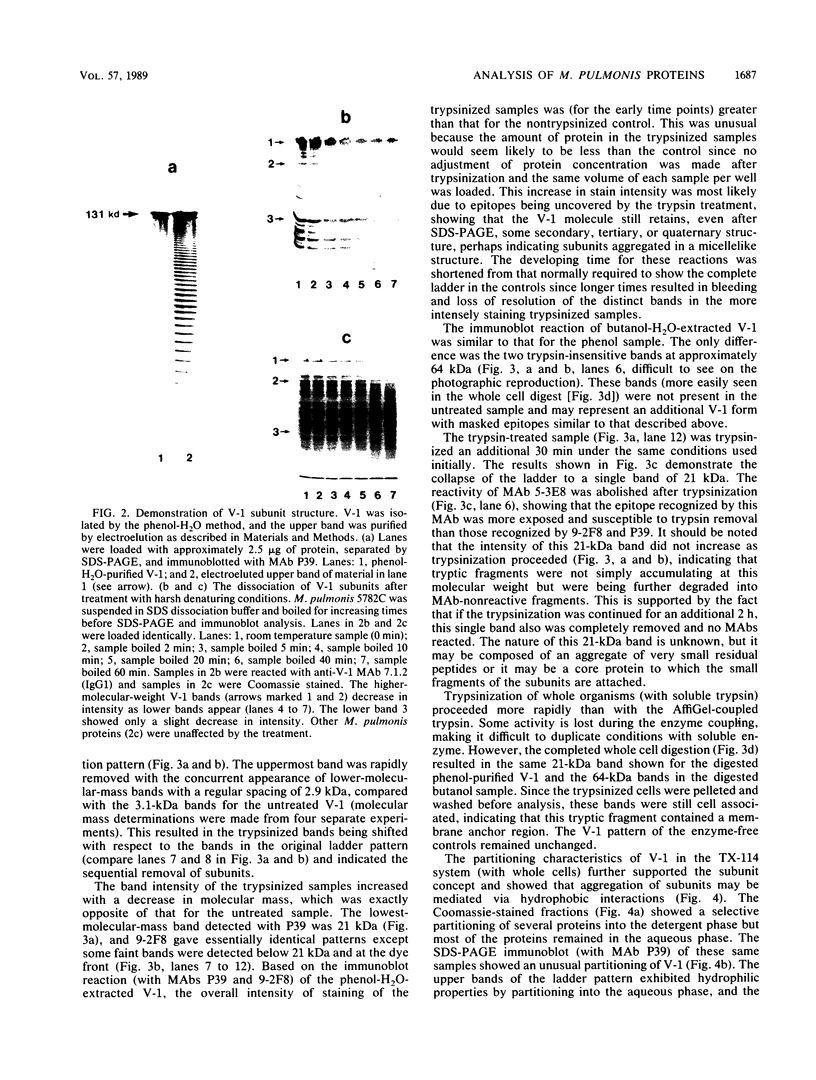
Abstract
It was previously shown that multiple structural variants of the V-1 antigen (variable antigen 1) of Mycoplasma pulmonis could be found within a single strain. This antigen is unusual in that it produces a ladder pattern after sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The present study showed that some variants of V-1 could be extracted into the aqueous phase of a phenol-H2O system. Analysis with anti-V-1 monoclonal antibodies showed that the phenol-H2O-extracted V-1 had a regular spacing of 3.1 kilodaltons (kDa) between bands and trypsinization of this extracted V-1 resulted in the gradual symmetrical collapse (2.9-kDa increments) of the ladder into a single band, suggesting the presence of multiple identical subunits within the V-1 structure. The upper band from the phenol-H2O-extracted V-1 was isolated and analyzed by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoblotting, resulting in the regeneration of the original ladder pattern with 3.1-kDa spacing between bands. When V-1 was boiled for increasing times in the presence of SDS, the staining intensity of the upper band decreased with the concurrent appearance of additional lower-molecular-weight bands. Finally, by using whole cells, it was found that the lower-molecular-weight species of the ladder pattern selectively partitioned into the hydrophobic phase of a Triton X-114 phase partitioning system, and the higher-molecular-weight bands were found in the aqueous phase. These data indicate that the V-1 bands are composed of subunits which may aggregate via hydrophobic interactions and that these aggregates at least partially dissociate when exposed to harsh denaturing conditions, resulting in the characteristic ladder pattern of V-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Weddell G. N., Davitz M. A., Nussenzweig V., Martin D. W., Jr Signal for attachment of a phospholipid membrane anchor in decay accelerating factor. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1280–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.2446389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H. Derrick Edward Award Lecture. The pathogenic potential of mycoplasmas: Mycoplasma pulmonis as a model. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S18–S34. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Watson H. L., Blalock D. K., Horowitz S. A., Duffy L. B. Protein antigens of genital mycoplasmas. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S391–S398. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S., Bloch K. Proteolipid formation in Mycoplasma capricolum. Influence of cholesterol on unsaturated fatty acid acylation of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11814–11818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S. Phospholipids as acyl donors to membrane proteins of Mycoplasma capricolum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10771–10776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybvig K., Alderete J., Watson H. L., Cassell G. H. Adsorption of mycoplasma virus P1 to host cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4373–4375. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4373-4375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. A., Garrett B., Davis J. K., Cassell G. H. Isolation of Mycoplasma pulmonis membranes and identification of surface antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1314–1320. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1314-1320.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Johnston K. H., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Location of variable and conserved epitopes among the multiple serotypes of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):623–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Cassell H. Experimental Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in pathogen-free mice. Models for studying mycoplasmosis of the respiratory tract. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jul;72(1):63–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Identification of cross-reactive antigens between Mycoplasma pulmonis and Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.115-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Wieslander A. Selective acylation of membrane proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethman H. C., Boyer M. J., Wise K. S. Triton X-114 phase fractionation of an integral membrane surface protein mediating monoclonal antibody killing of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1094-1100.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Fernandez R., Tai J. Y., Rothbard J., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal pili. Primary structure and receptor binding domain. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1351–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H., Kaufman B., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. Immunoenzymatic analysis by monoclonal antibodies of bacterial lipopolysaccharides after transfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Lipoglycans from mycoplasmas. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11(2):157–186. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G., So M. Phase and antigenic variation of pili and outer membrane protein II of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):196–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A. G., Barclay A. N., Watts A., Williams A. F. A glycophospholipid tail at the carboxyl terminus of the Thy-1 glycoprotein of neurons and thymocytes. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1003–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.2865810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., McDaniel L. S., Blalock D. K., Fallon M. T., Cassell G. H. Heterogeneity among strains and a high rate of variation within strains of a major surface antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1358–1363. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1358-1363.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewski H., Blanchard A., Nyström S., Wieslander A., Thomas D. Amphiphilic properties of spiralin, the major surface antigen of spiroplasmas. A preliminary report. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):439–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






