Abstract
The presence of a chlamydia-specified antigen associated with the plasma membrane of infected cell lines was demonstrated by indirect immunofluorescence staining with a monoclonal antibody, designated 47A2, specific for the chlamydial genus-specific lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antigen. Staining of HeLa, L-929, and McCoy cells infected with the L2 or F serovar of Chlamydia trachomatis was observed either without fixation or following aldehyde fixation and brief drying. The 47A2-reactive antigen appeared to be present on the plasma membrane, on bleb-like structures on the host cell surface, and on proximal processes of neighboring uninfected cells. Antibodies to chlamydial protein antigens such as the major outer membrane protein produced no surface staining under similar conditions. Membrane vesicles elaborated from infected cells were enriched for the 47A2-reactive antigen. Superinfection of chlamydia-infected cells with vesicular stomatitis virus, an enveloped virus which buds from the plasma membrane, allowed purification of progeny virions that were enriched with chlamydial LPS. These results are consistent with the presence of chlamydial LPS in the plasma membranes of infected host cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bard J., Levitt D. Chlamydia trachomatis (L2 serovar) binds to distinct subpopulations of human peripheral blood leukocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Feb;38(2):150–160. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Newhall W. J., 5th, Terho P., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Jones R. B. Antigenic analysis of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis with murine monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):530–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.530-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brade L., Nano F. E. Chemical and serological investigations on the genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope of Chlamydia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2508–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Nano F. E., Schlecht S., Schramek S., Brade H. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of recombinants from Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella minnesota rough mutants expressing in their lipopolysaccharide a genus-specific chlamydial epitope. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):482–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.482-486.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H., Brade H. Antigenic properties of Chlamydia trachomatis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):569–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.569-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Schramek S., Schade U., Brade H. Chemical, biological, and immunochemical properties of the Chlamydia psittaci lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.568-574.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Hakomori S., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Immunochemical studies on chlamydial group antigen (presence of a 2-keto-3-deoxycarbohydrate as immunodominant group). J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. T-cell-mediated immunopathology in viral infections. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):89–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Wyrick P. B., Davis C. H., Rumpp J. W. Chlamydia psittaci elementary body envelopes: ingestion and inhibition of phagolysosome fusion. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):741–751. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.741-751.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett A. J., Harrison M. J., Manire G. P. A search for the bacterial mucopeptide component, muramic acid, in Chlamydia. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):315–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L., Koba S., Partyka M., Maślanka K., Kryczka W., Szerszén B., Bartosz B. Disturbances of cell-mediated immunity in ornithosis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1984;32(2):177–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Lipid composition of purified vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):59–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.59-70.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Rudbach J. A. Endotoxin-cell-membrane interactions leading to transmembrane signaling. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1981;8:187–218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3917-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nano F. E., Caldwell H. D. Expression of the chlamydial genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope in Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):742–744. doi: 10.1126/science.2581315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Leinonen M., Saikku P., Mäkelä P. H. The genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia: resemblance to the lipopolysaccharide of enteric bacteria. Science. 1983 Jun 17;220(4603):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6344216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Brade H. Chemical characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):573–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.573-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Schachter J. Failure to detect cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1271–1274. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1271-1274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvigstad E., Hirschberg H. Lack of cell-mediated cytotoxicity towards Chlamydia trachomatis infected target cells in humans. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Jun;92(3):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
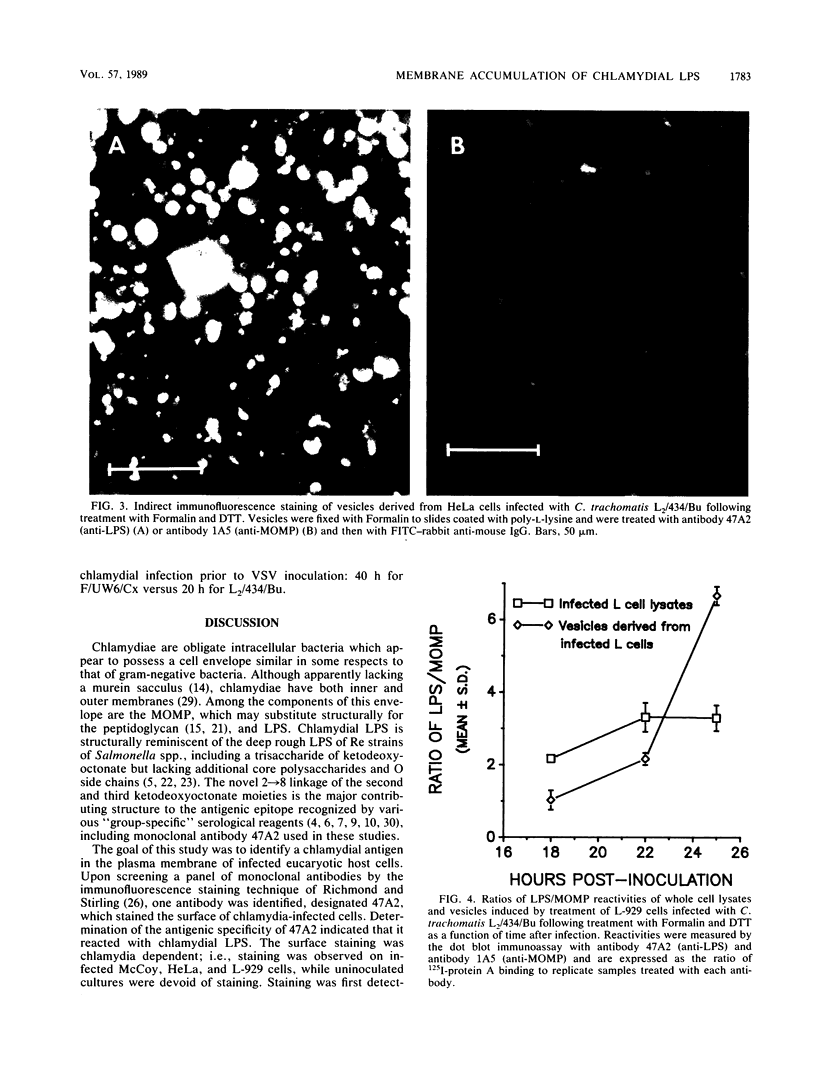
- Richmond S. J., Stirling P. Localization of chlamydial group Antigen in McCoy cell monolayers infected with Chlamydia trachomatis or Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):561–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.561-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Perkins R. G., Zschunke M. A., Hoerl B. J., Maercklein P. B. Plasma membrane vesiculation in 3T3 and SV3T3 cells. I. Morphological and biochemical characterization. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:229–243. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Matsumoto A., Manire G. P., Higashi N. Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the envelopes of mature elementary bodies and developmental reticulate forms of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):355–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.355-360.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornley M. J., Zamze S. E., Byrne M. D., Lusher M., Evans R. T. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to the genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia and their use for antigen detection by reverse passive haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):7–15. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N. G., Hadlow W. J., Moos A. B., Caldwell H. D. Ocular delayed hypersensitivity: a pathogenetic mechanism of chlamydial-conjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7480–7484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Coalson J. J., Grubbs B. Cellular immunity to the mouse pneumonitis agent. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):630–639. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zee Y. C., Hackett A. J., Talens L. Vesicular stomatitis virus maturation sites in six different host cells. J Gen Virol. 1970;7(2):95–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-7-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]