Abstract
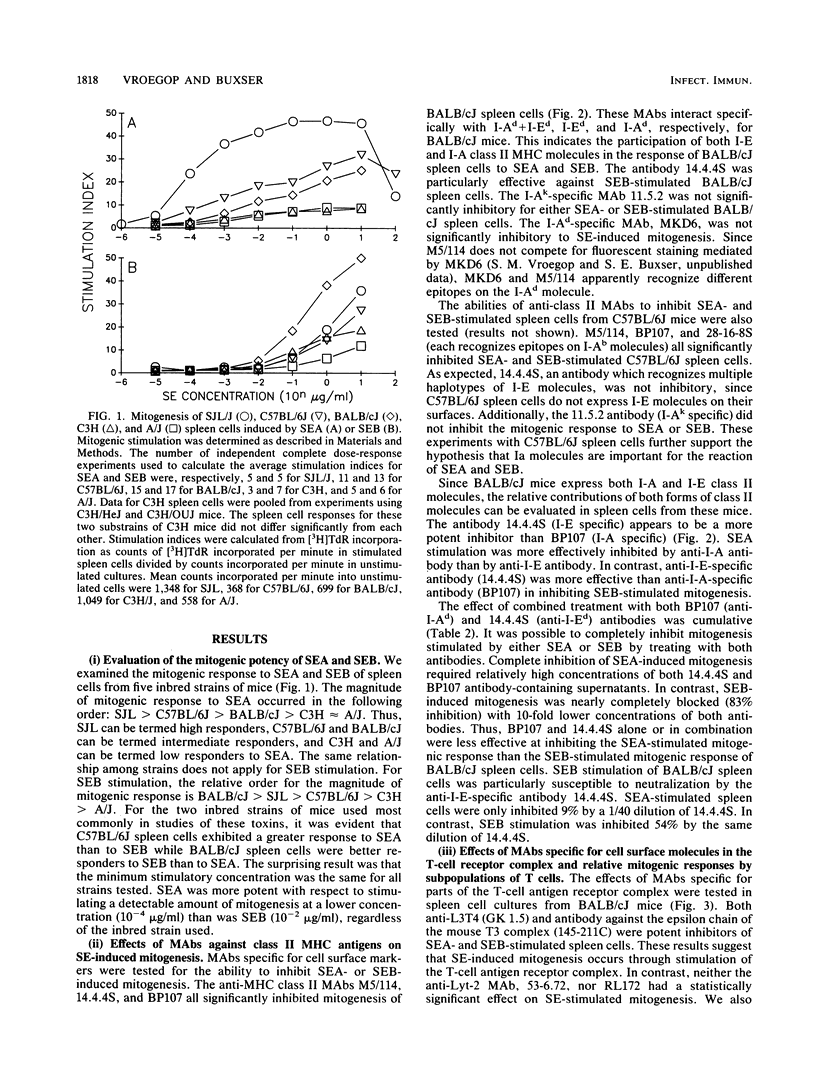
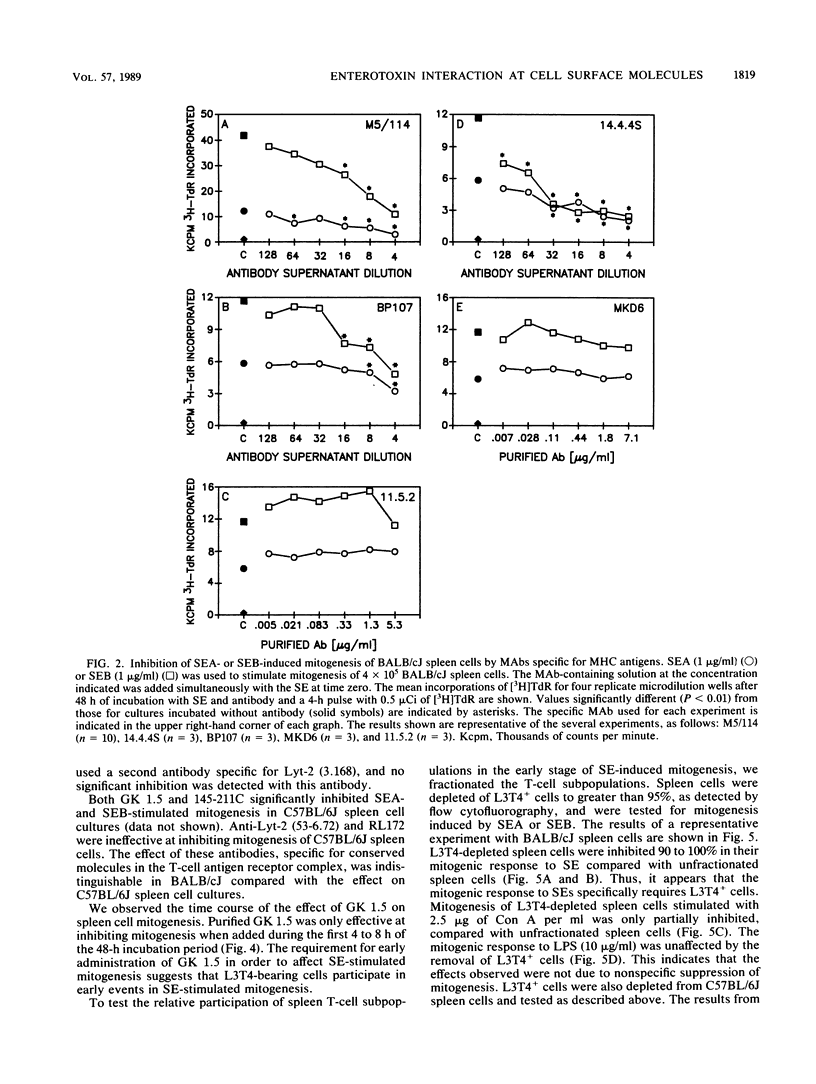
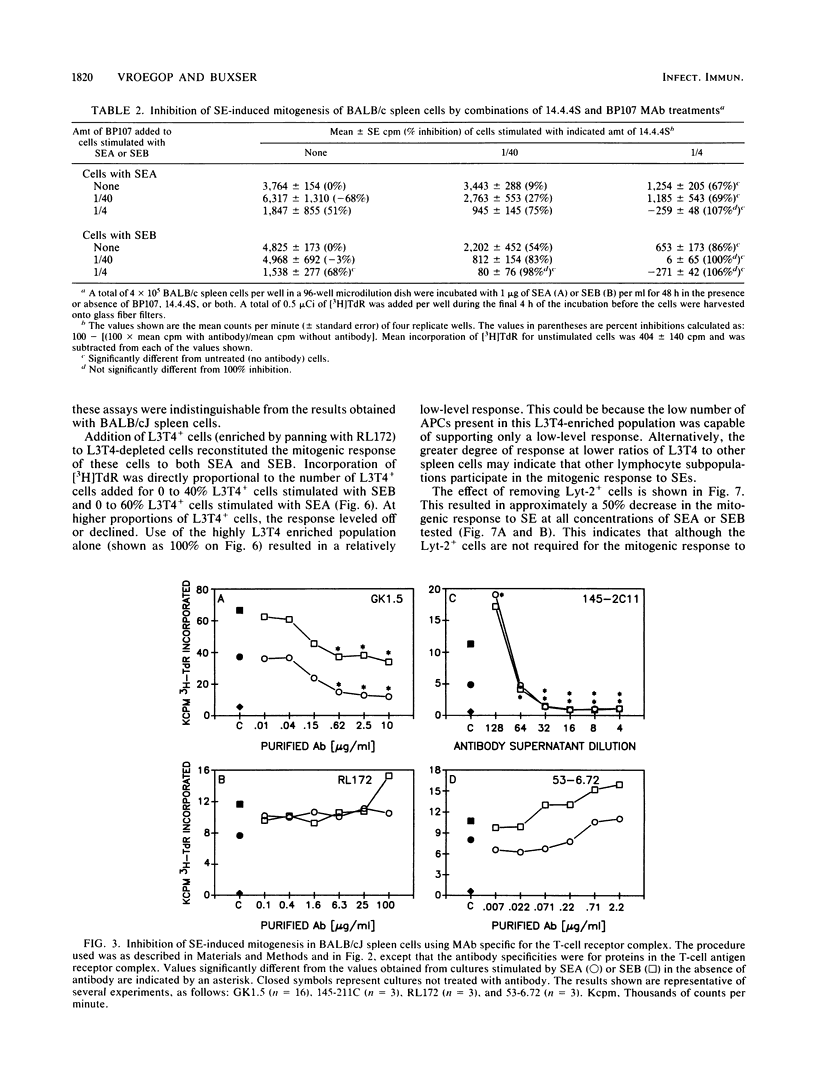
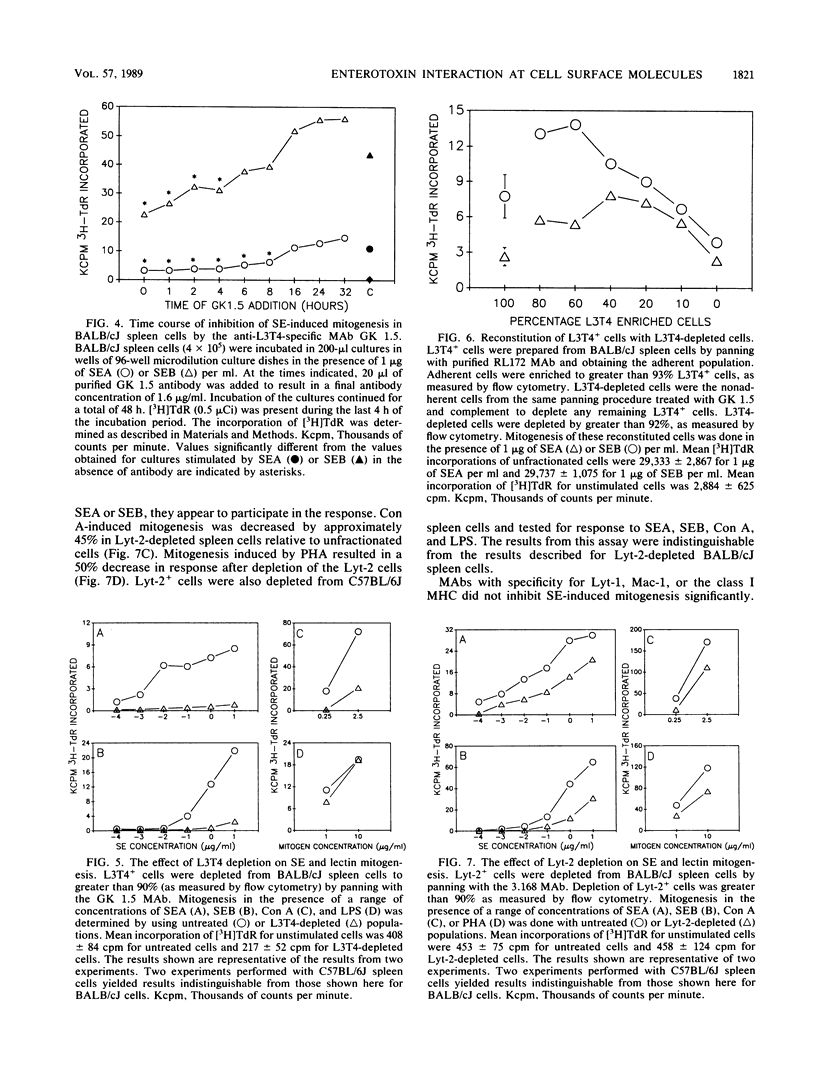
We tested the mitogenic response to staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) type A and SE type B in spleen cells from five strains of mice and found consistent and significant differences among the strains. We chose to study the mitogenic responses of two of these strains, C58BL/6J and BALB/cJ, in greater detail. We investigated the effects of specific monoclonal antibodies to cell surface determinants on SE-induced mitogenesis. Monoclonal antibodies against Ia (class II major histocompatibility complex) determinants blocked SE-induced mitogenesis. Both I-A and I-E molecules can participate in the stimulation, and in BALB/cJ mice which express both types of class II molecules both must be blocked to prevent mitogenesis. Mitogenesis was not inhibited by monoclonal antibodies specific for class I major histocompatibility complex antigens or monoclonal antibodies specific for Mac-1, Lyt-1, or Lyt-2 cell surface proteins. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the T-cell surface antigens L3T4 and T3 also substantially inhibited SE-induced mitogenesis. This implicates participation of the T-cell antigen receptor complex in stimulation induced by the SEs. Elimination of L3T4+ helper-inducer T cells abolished the mitogenic response of spleen cells to SE. Reconstitution of L3T4-depleted spleen cells with L3T4+ T cells showed that the level of the mitogenic response was directly proportional to the number of L3T4+ cells added. Elimination of Lyt-2+ cells resulted in a 50% decrease in the response to SEs. These results indicate that L3T4+ T cells are required for the mitogenic response to SE, but both L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ T cells participate in SE-induced mitogenesis. Our results suggest that both Ia and the T-cell antigenic receptor complex are involved in SE-induced mitogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Dialynas D. P., Strominger J. L., Smith J. A., Owen F. L., Seidman J. G., Ip S., Rosen F., Krangel M. S. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):145–149. doi: 10.1038/322145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxser S., Bonventre P. F., Archer D. L. Specific receptor binding of staphylococcal enterotoxins by murine splenic lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):827–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.827-833.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Fischer H., Sjögren H. O. Binding of staphylococcal enterotoxin A to accessory cells is a requirement for its ability to activate human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2484–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Sjögren H. O. Kinetics of IL-2 and interferon-gamma production, expression of IL-2 receptors, and cell proliferation in human mononuclear cells exposed to staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. P., Rogers T. J. Immunosuppression induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):166–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H. T cell stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Clonally variable response and requirement for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on accessory or target cells. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1697–1707. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G., Doenhoff M. Selective triggering of human T and B lymphocytes in vitro by polyclonal mitogens. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Bergdoll M. S. The primary structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. 3. The cyanogen bromide peptides of reduced and aminoethylated enterotoxin B, and the complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3518–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Hughes J. L., Bergdoll M. S., Schantz E. J. Complete amino acid sequence of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7006–7013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Relative ability of mitogens to stimulate production of interferon by lymphoid cells and to induce suppression of the in vitro immune response. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jan;154(1):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Gutman G. A., Lewis D. E., Griswold S. T., Warner N. L. Monoclonal antibodies against rat immunoglobulin kappa chains. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Patel M. R., Linna T. J., Rogers T. J. Suppression of cytolytic T-cell activity by staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced suppressor cells: role of interleukin 2. Cell Immunol. 1986 Nov;103(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Kappler J., Tax W. J., Terhorst C. Characterization of the two heavy chains of the T3 complex on the surface of human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12039–12048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto M., Torten M., Birnbaum S. C. Suppression of the in vivo humoral and cellular immune response by staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Transplantation. 1978 Jun;25(6):320–323. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197806000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Oleszak E. L., Good R. A. Immunomodulation of human leukocytes by staphylococcal enterotoxin A: augmentation of natural killer cells and induction of suppressor cells. Cell Immunol. 1986 Feb;97(2):371–385. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Acuto O., Schlossman S. F. Comparison of T3-associated 49- and 43-kilodalton cell surface molecules on individual human T-cell clones: evidence for peptide variability in T-cell receptor structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saizawa K., Rojo J., Janeway C. A., Jr Evidence for a physical association of CD4 and the CD3:alpha:beta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):260–263. doi: 10.1038/328260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. J., Spero L. The complete amino acid sequence of staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6300–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. G., Johnson H. M. The effect of staphylococcal enterotoxins on the primary in vitro immune response. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. R., Leatherman D. L., Metzger J. F. Evidence for cell-receptor activity in lymphocyte stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxin. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi-Willner T., Berke G. The mitogenic activity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB): a monovalent T cell mitogen that stimulates cytolytic T lymphocytes but cannot mediate their lytic interaction. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


