Abstract
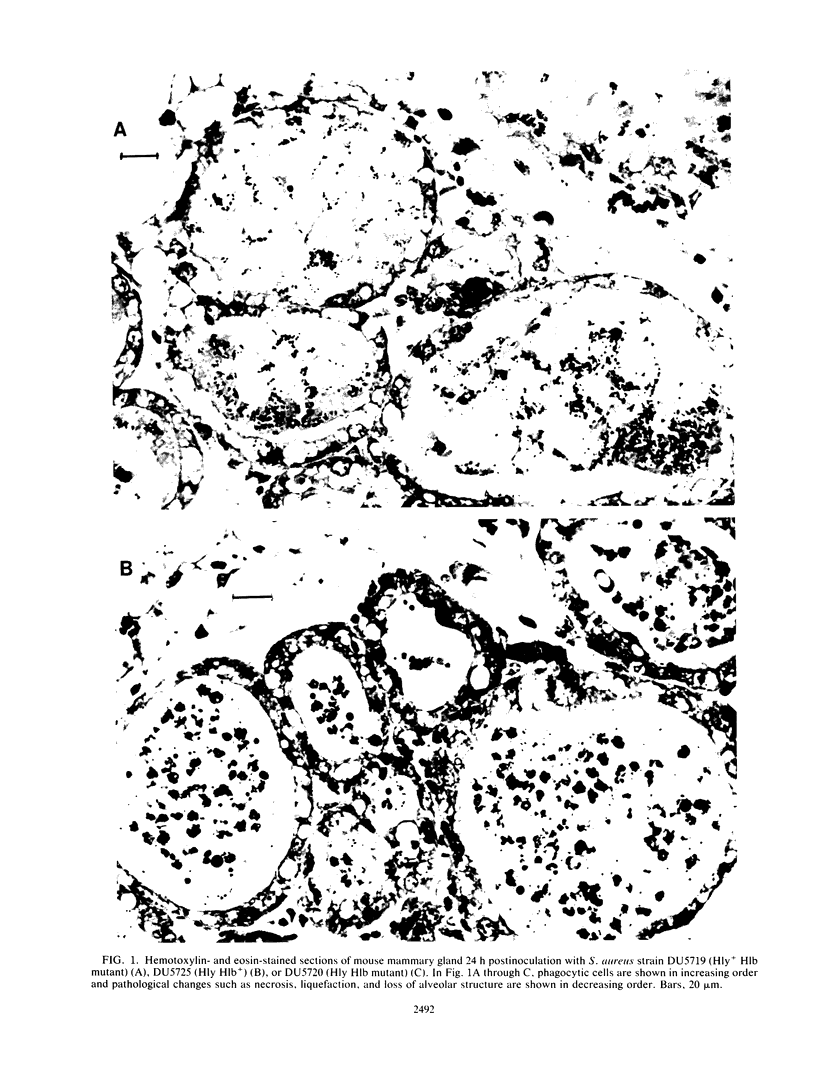
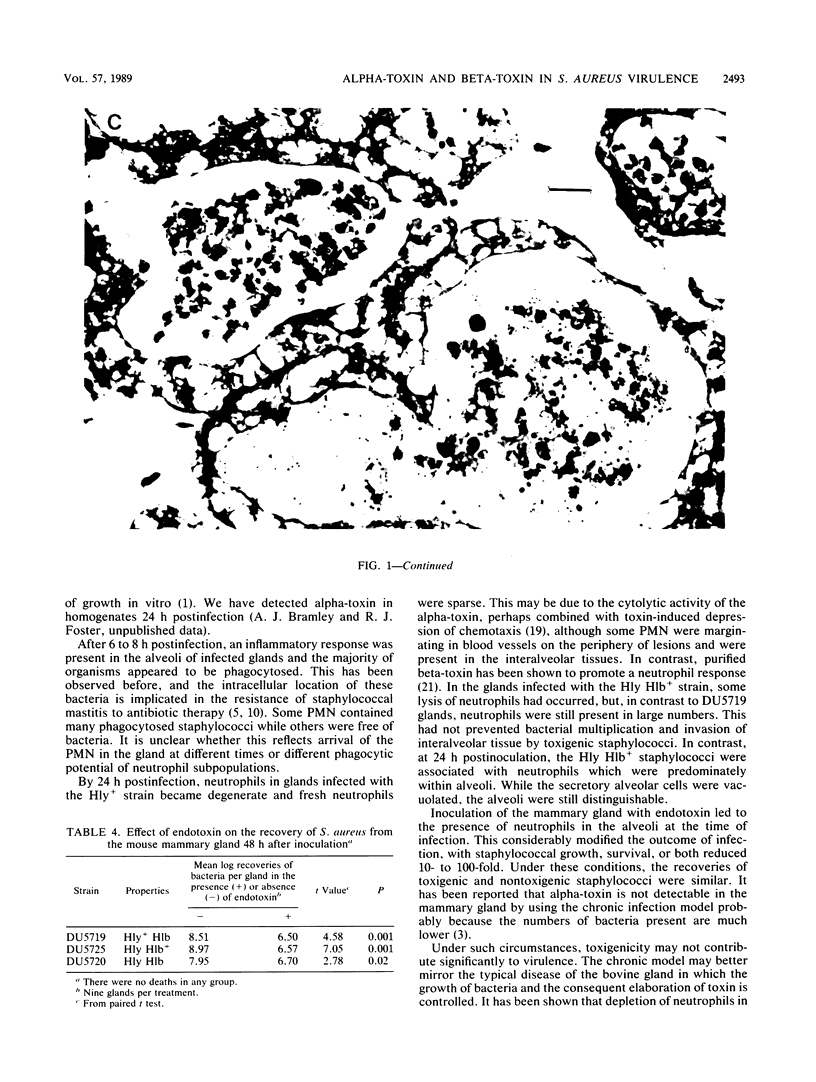
Mutants of Staphylococcus aureus which fail to express alpha-toxin (Hly), beta-toxin (Hlb), or both have been constructed by site-specific mutagenesis. The virulence of the mutants was compared with that of wild-type toxigenic strains by intramammary inoculation of lactating mice. A bovine strain, M60, and a laboratory strain, 8325-4, caused acute mastitis and death within 48 h for 60% of the mice inoculated. Animals inoculated with Hly mutants also developed acute mastitis, but no deaths occurred. Comparisons of Hly- or Hlb-positive strains with the double mutation Hly Hlb showed that both toxins led to a significantly higher recovery of S. aureus from the gland 48 h postinfection. Histopathological examination of mammary glands showed that phagocytosis of bacteria occurred irrespective of toxigenicity, but toxigenic strains, particularly those which were Hly+, continued to multiply, invaded the interalveolar tissues, and produced severe lesions. Stimulation of an inflammatory response by inoculation of the mammary gland with endotoxin prior to challenge with S. aureus reduced recovery of the bacteria 10- to 100-fold and, under these conditions, neither alpha-toxin nor beta-toxin contributed significantly to growth and survival.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas-ali B., Coleman G. The characteristics of extracellular protein secretion by Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46) and their relationship to the regulation of alpha-toxin formation. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):277–282. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adlam C., Ward P. D., McCartney A. C., Arbuthnott J. P., Thorley C. M. Effect immunization with highly purified alpha- and beta-toxins on staphylococcal mastitis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):250–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.250-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. C., Adlam C., Knights J. M. The effect of staphylocoagulase in the mammary gland of the mouse. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Jun;63(3):336–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. C. Experimental staphylococcal mastitis in the mouse: the induction of chronic mastitis and its response to antibiotic therapy. J Comp Pathol. 1977 Oct;87(4):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. C. Pathogenesis of experimental mastitis in the mouse caused by a strain of Staphylococcus aureus of low virulence and its modification by endotoxin. J Comp Pathol. 1975 Oct;85(4):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(75)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. C. Progressive pathology of staphylococcal mastitis with a note on control, immunisation and therapy. Vet Rec. 1982 Apr 17;110(16):372–376. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.16.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. C., Arbuthnott J. P., Pomeroy H. M., Birkbeck T. H. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus of the beta-lysin determinant from Staphylococcus aureus: evidence that bacteriophage conversion of beta-lysin activity is caused by insertional inactivation of the beta-lysin determinant. Microb Pathog. 1986 Dec;1(6):549–564. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven N., Anderson J. C. Experimental acute staphylococcal mastitis in the mouse: the influence of pathological changes on the kinetics and therapeutic action of cloxacillin. J Comp Pathol. 1982 Oct;92(4):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(82)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. The nature of discrepancies between haemolysins in culture filtrates and plate haemolysin patterns of staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):31–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson P., Lindberg M., Haraldsson I., Wadström T. Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in a mouse mastitis model: studies of alpha hemolysin, coagulase, and protein A as possible virulence determinants with protoplast fusion and gene cloning. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):765–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.765-769.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M., de Azavedo J. C., Kennedy S., Foster T. J. Inactivation of the alpha-haemolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4 by site-directed mutagenesis and studies on the expression of its haemolysins. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Nowlan P., Weavers E. D., Foster T. Virulence of protein A-deficient and alpha-toxin-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus isolated by allele replacement. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3103–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3103-3110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. J., Wilkinson P. C., McInroy R. J., McKay S., McCartney A. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Effects of staphylococcal products on locomotion and chemotaxis of human blood neutrophils and monocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):433–439. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm O. W., Lasmanis J., Jain N. C. Conversion of chronic staphylococcal mastitis to acute gangrenous mastitis after neutropenia in blood and bone marrow produced by an equine anti-bovine leukocyte serum. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Aug;37(8):885–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. D., Adlam C., McCartney A. C., Arbuthnott J. P., Thorley C. M. A histopathological study of the effects of highly purified staphlococcal alpha and beta toxins on the lactating mammary gland and skin of the rabbit. J Comp Pathol. 1979 Apr;89(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(79)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]