Abstract
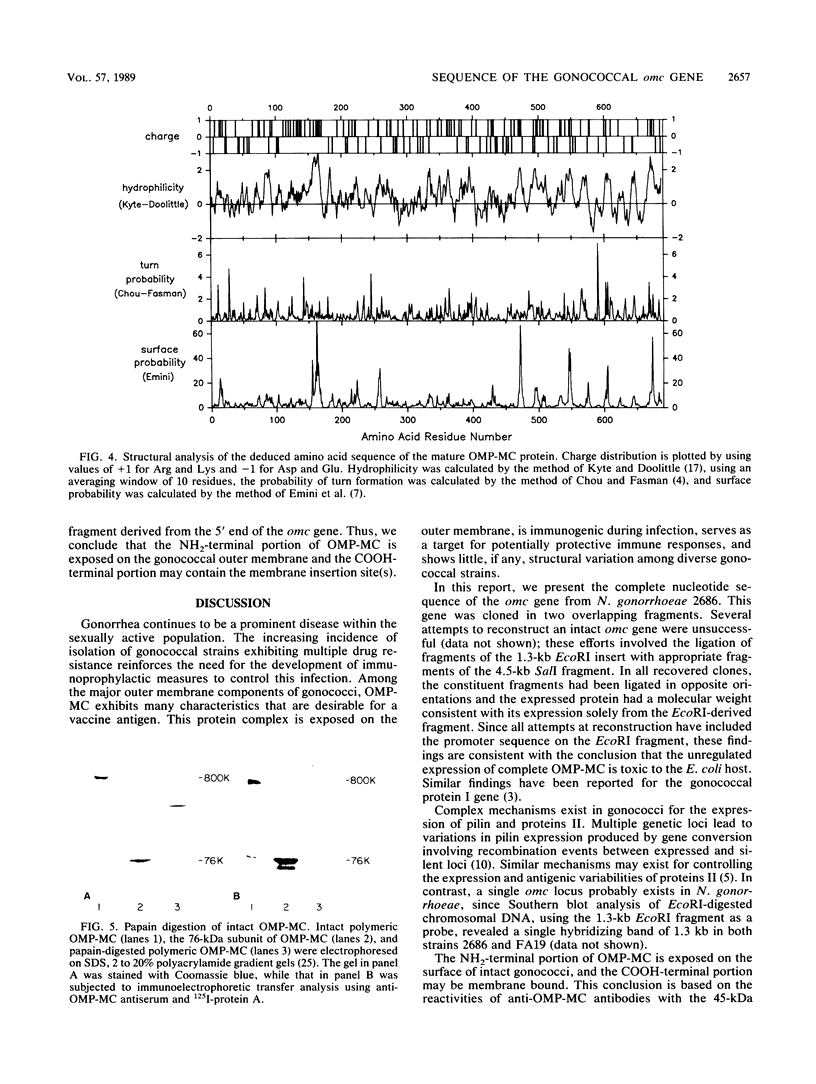
The omc gene, encoding the outer membrane protein-macromolecular complex (OMP-MC), was cloned in two pieces from Neisseria gonorrhoeae 2686. The 5' fragment of the omc gene included a promoter sequence, as indicated by its unregulated expression in Escherichia coli. Attempts to reconstruct an intact omc gene were unsuccessful, suggesting that expression of the complete OMP-MC protein was toxic to E. coli. Complete sequence determination revealed a coding sequence of 2,133 nucleotides; the deduced amino acid sequence indicated a mature protein of 687 amino acids with an NH2-terminal signal peptide of 24 amino acids. Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence revealed that the NH2-terminal half of OMP-MC is generally hydrophilic, while the COOH-terminal portion contains alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Serological analyses demonstrated that the NH2-terminal portion of OMP-MC is exposed on the gonococcal surface and the COOH-terminal portion is membrane associated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Gagliardi N. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of the non-serogroup antigen structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):870–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.870-874.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetti N. H., Sparling P. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of the structural gene for protein I, the major outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9084–9088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Black W. J., Kawula T. H., Barritt D. S., Dempsey J. A., Kverneland K., Jr, Stephenson A., Schepart B. S., Murphy G. L., Cannon J. G. Recombination among protein II genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae generates new coding sequences and increases structural variability in the protein II family. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Meyer T. F. The repertoire of silent pilus genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: evidence for gene conversion. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. V., Wilde C. E., 3rd Conservation of peptide structure of outer membrane protein-macromolecular complex from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.839-845.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. Structural comparison of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.736-742.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd R. C. 125I-peptide mapping of protein III isolated from four strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):622–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.622-631.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Sparling P. F. Multiple antibiotic resistance due to a single mutation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):321–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride H. M., Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., Watt P. J. The role of outer membrane proteins in the survival of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9 within guinea-pig subcutaneous chambers. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Sep;126(1):63–67. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Sawyer W. D., Haak R. A. High-molecular-weight antigenic protein complex in the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.475-482.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Vayo H. E., Tam M. R., Blake M. S. Immunoglobulin G antibodies directed against protein III block killing of serum-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immune serum. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1735–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Clark V. L. Genetic loci and linkage associations in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S92–103. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. P., Johnston K. H. One-dimensional peptide mapping of the major outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):739–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.739-745.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. P., Black J. R., Barritt D. S., Connell T. D., Cannon J. G. Resistance to meningococcemia apparently conferred by anti-H.8 monoclonal antibody is due to contaminating endotoxin and not to specific immunoprotection. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1927–1928. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1927-1928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak K., Diaz J. L., Jackson D., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: detection of antibodies to surface proteins in sera of patients with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):166–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]