Abstract
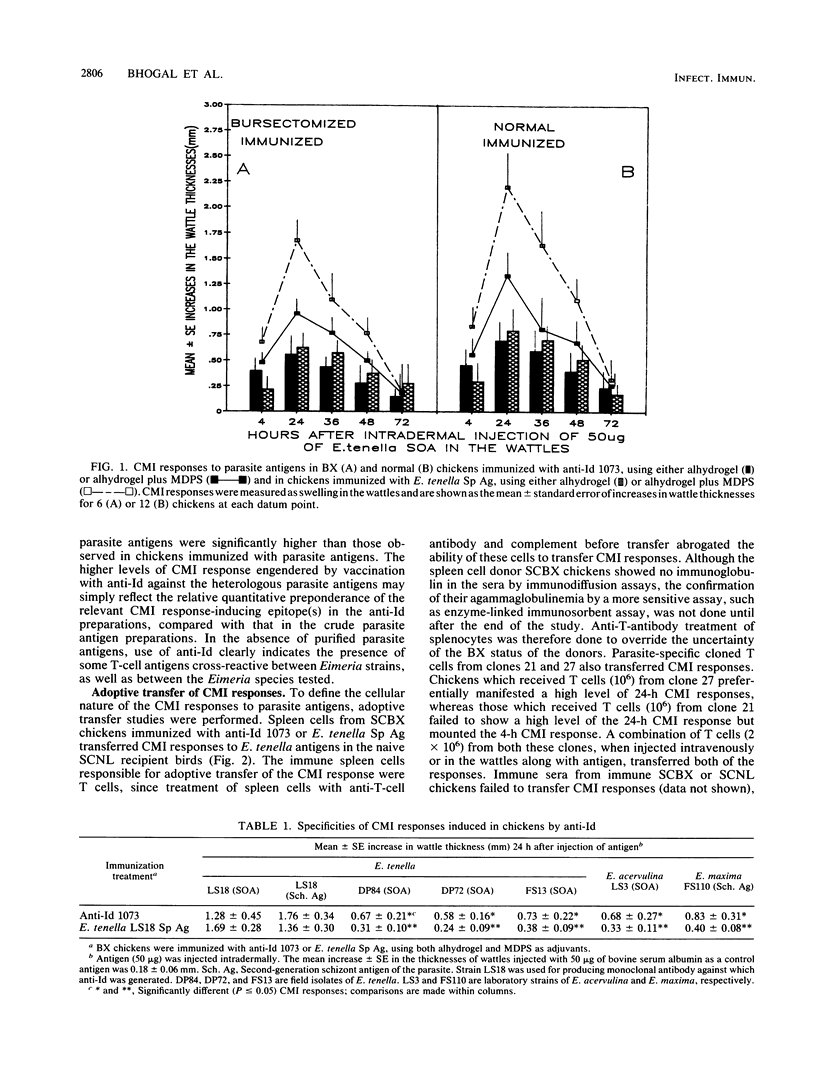
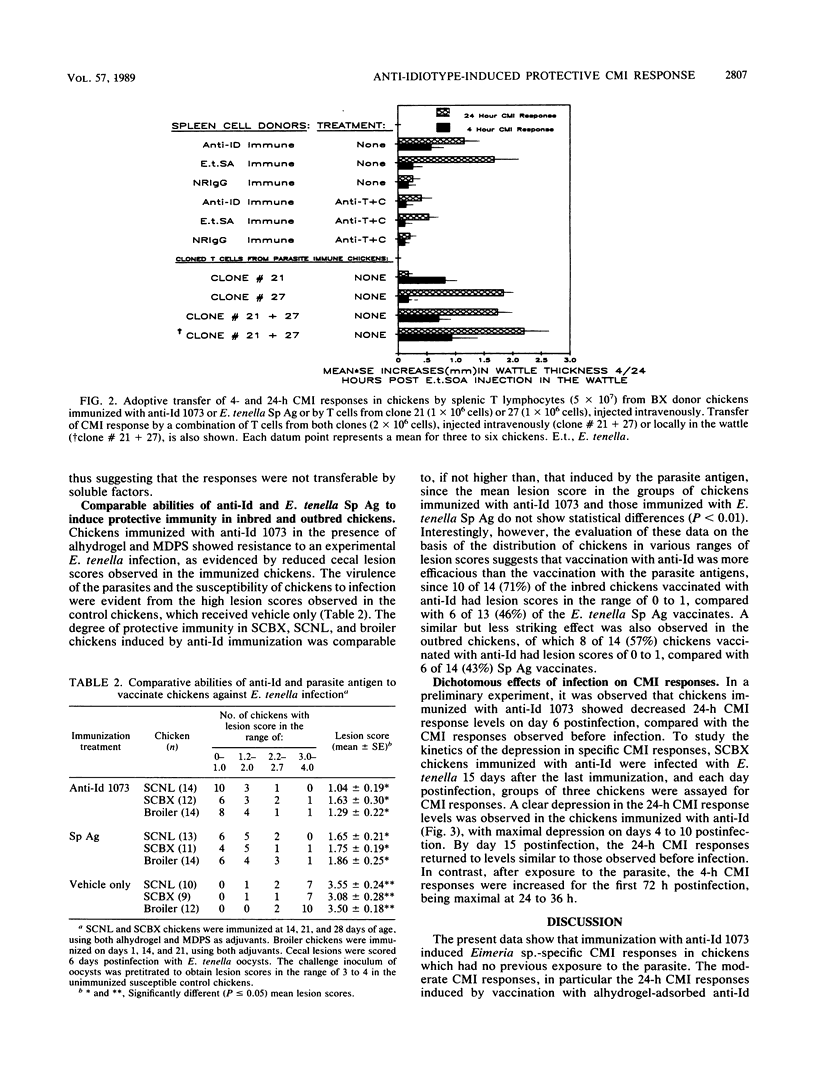
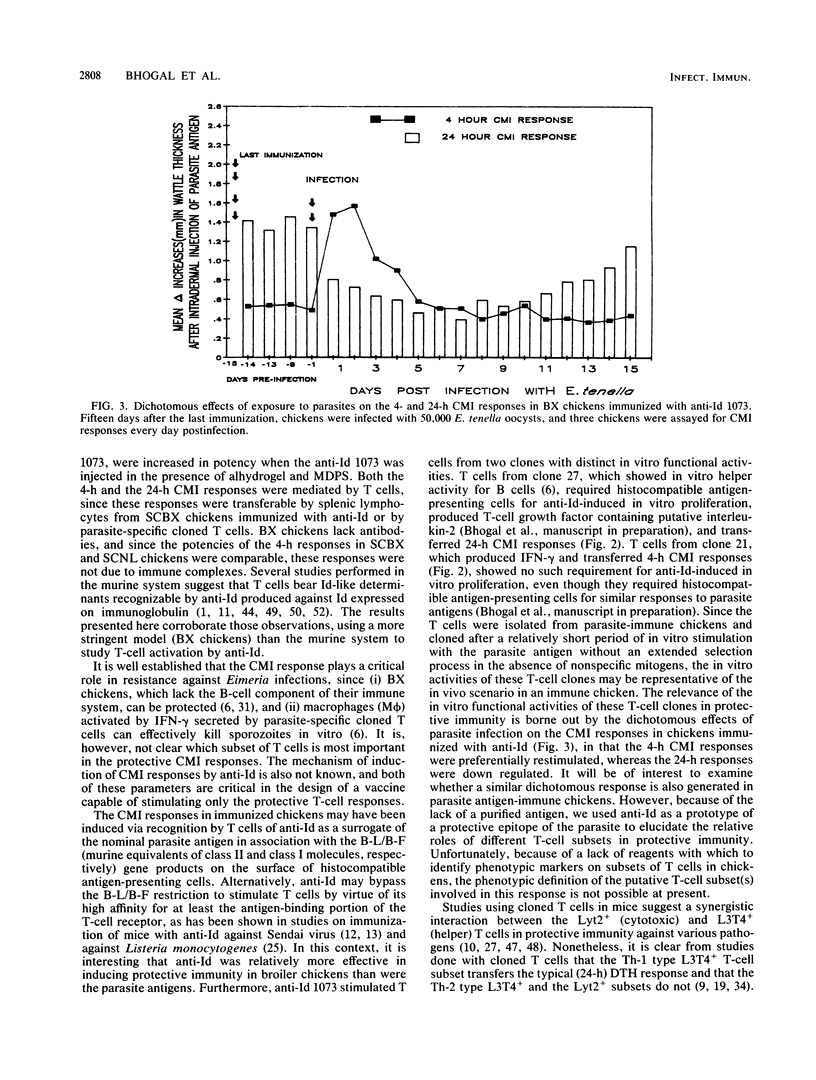
Polyclonal anti-idiotype 1073 (anti-Id 1073), raised against a monoclonal antibody specific for the protective epitope(s) of Eimeria tenella sporozoites, induced cell-mediated immune (CMI) responses in bursectomized chickens. Whereas alhydrogel-adsorbed anti-Id 1073 was sufficient to engender the CMI response at 4 h after injection, induction of the CMI response at 24 h required both alhydrogel and muramyl dipeptide sterol. Exposure of immunized chickens to live parasites prompted a dichotomous effect on the CMI response engendered by anti-Id in that the 4-h CMI response was preferentially stimulated and the 24-h CMI response was down regulated. Both types of CMI response were transferable to naive chickens by T cells from anti-Id 1073 immune donors or by parasite-specific T cells from clones 21 and 27. These T-cell clones were generated from chickens immunized by repeated infections with E. tenella and showed in vitro proliferative responses to anti-Id 1073. The abilities of T cells from clone 21 to selectively transfer the 4-h CMI response and to generate gamma interferon to activate macrophages for their cytotoxic effects on Eimeria sporozoites correlate with the preferential stimulation by parasites of the 4-h CMI response in chickens immunized with anti-Id 1073. These data show that anti-Id 1073 mimics the protective epitope(s) of the parasite and primes chickens for protective CMI responses. Cytotoxic T cells, equivalent to the mammalian T-cell subset of the Lyt2+ phenotype, appear to be the primary effector T cells in the CMI response engendered by anti-Id 1073 against Eimeria parasites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold B., Wallich R., Hämmerling G. J. Elicitation of delayed-type hypersensitivity to phosphorylcholine by monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies in an allogeneic environment. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):670–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berche P., Decreusefond C., Theodorou I., Stiffel C. Impact of genetically regulated T cell proliferation on acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):932–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal B. S., Miller G. A., Anderson A. C., Jessee E. J., Strausberg R., McCandliss R., Strausberg S. Vaccination of chickens with recombinant E. tenella antigen alone or in combination with a subclinical exposure induces cross protective immunity against coccidiosis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;307:131–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal B. S., Nagy L. K., Walker P. D. Neutrophil mediated and IgA dependent antibacterial immunity against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in the porcine intestinal mucosa. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jan;14(1):23–44. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal B. S., Nollstadt K. H., Karkhanis Y. D., Schmatz D. M., Jacobson E. B. Anti-idiotypic antibody with potential use as an Eimeria tenella sporozoite antigen surrogate for vaccination of chickens against coccidiosis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1113–1119. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1113-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal B. S., Tse H. Y., Jacobson E. B., Schmatz D. M. Chicken T lymphocyte clones with specificity for Eimeria tenella. I. Generation and functional characterization. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3318–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgault I., Gomez A., Gomard E., Picard F., Levy J. P., Gomrad E. A virus-specific CD4+ cell-mediated cytolytic activity revealed by CD8+ cell elimination regularly develops in uncloned human antiviral cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):252–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. M., Chen C. L., Ager L. L., Cooper M. D. Identification of the avian homologues of mammalian CD4 and CD8 antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2133–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cher D. J., Mosmann T. R. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. II. Delayed-type hypersensitivity is mediated by TH1 clones. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3688–3694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiplunkar S., De Libero G., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterium leprae-specific Lyt-2+ T lymphocytes with cytolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):793–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.793-797.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Rajewsky K. Induction of T and B cell immunity by anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):661–666. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H. C., Finberg R. W. Sendai virus-specific T-cell clones: induction of cytolytic T cells by an anti-idiotypic antibody directed against a helper T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Schofield L., Enea V., Schellekens H., van der Meide P., Collins W. E., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of development of exoerythrocytic forms of malaria parasites by gamma-interferon. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):881–884. doi: 10.1126/science.3085218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzych J. M., Capron M., Lambert P. H., Dissous C., Torres S., Capron A. An anti-idiotype vaccine against experimental schistosomiasis. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):74–76. doi: 10.1038/316074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiernaux J., Bona C., Baker P. J. Neonatal treatment with low doses of anti-idiotypic antibody leads to the expression of a silent clone. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):1004–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein S., Curtis J., Akuffo H., Turk J. L. Dissociation between delayed-type hypersensitivity and resistance to pathogenic mycobacteria demonstrated by T-cell clones. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):564–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.564-567.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., DeBlois L. A. Induction of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni by a nonliving vaccine. II. Response of mouse strains with selective immune defects. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3864–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Salzman C., Pearce E. J. Induction of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni by a non-living vaccine. VI. Antigen recognition by non-responder mouse strains. Parasite Immunol. 1988 Jan;10(1):71–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Roland J., Cazenave P. A. Recurrent idiotopes and internal images. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):243–247. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J., Reid W. M. Anticoccidial drugs: lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Aug;28(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Eichmann K., Müller I., Wrazel L. J. Vaccination against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes with a clonotypic antiserum. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4123–4127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hahn H., Berger R., Kirchner H. Interferon-gamma production by Listeria monocytogenes-specific T cells active in cellular antibacterial immunity. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Mar;13(3):265–268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., Väth U., Müller I. Effective protection against Listeria monocytogenes and delayed-type hypersensitivity to listerial antigens depend on cooperation between specific L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):263–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.263-266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Adler-Storthz K., Henkel R. D., Sanchez Y., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen: enhancement by prior injection of antibodies to the idiotype. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.6603657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Dreesman G. R. Enhancement of the immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen. In vivo administration of antiidiotype induces anti-HBs that expresses a similar idiotype. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):655–665. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj H. S. Effects of immunosuppression on avian coccidiosis: cyclosporin A but not hormonal bursectomy abrogates host protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1616–1621. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1616-1621.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara M. K., Ward R. E., Kohler H. Monoclonal idiotope vaccine against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1325–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.6505692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Bhogal B. S., Anderson A. C., Jessee E. J., McCandliss R., Likel M., Strasser J., Strausberg S., Strausberg R. Application of a novel recombinant Eimeria tenella antigen in a vaccine to protect broiler chickens from coccidiosis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;307:117–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino M. A., Grebenau M. D., Thorbecke G. J. Requirements for induction of delay hypersensitivity in the chicken. Dev Comp Immunol. 1978 Feb;2(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(78)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Joysey H. S., Hesketh P., Grencis R. K., Wakelin D. Mediation of immunity to Eimeria vermiformis in mice by L3T4+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1760–1765. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1760-1765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Esser K. M., Sher A. Immunization of mice against African trypanosomiasis using anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1108–1119. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Shigekane V. M., Fisher W. L., Locksley R. M. Cellular and humoral immunity to Leishmania major in genetically susceptible mice after in vivo depletion of L3T4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1303–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz D. M., Crane M. S., Murray P. K. Purification of Eimeria sporozoites by DE-52 anion exchange chromatography. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):181–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Gaulton G. N., McDade K. K., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Syngeneic monoclonal antiidiotype can induce cellular immunity to reovirus. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1195–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Söderström T. Neonatal administration of idiotype or antiidiotype primes for protection against Escherichia coli K13 infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1001–1011. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbeck M. J., Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Activation of bovine neutrophils by recombinant interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1986 Mar;98(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. J., Oca M. J., Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Murray H. W. Role of L3T4+ and LyT-2+ cells in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3971–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Remington J. S. Dual regulation of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii infection by Lyt-2+ and Lyt-1+, L3T4+ T cells in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3943–3946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Bach B. A., Dohi Y., Nisonoff A., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Antigen- and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. I. Induction of suppressor T cells with anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1216–1228. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Brown A. R., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Antigen- and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. III. Induction of delayed type hypersensitivity to azobenzenearsonate with anti-cross-reactive idiotypic antibodies. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):896–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L., Scott D. W. Initial induction of immunity, followed by suppression of responses to parasite antigens during Trypanosoma cruzi infection of mice. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Sep;9(5):579–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. R., Morahan G., Walker I. D., Miller J. F. Induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity to azobenzenearsonate by a monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):743–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ceredig R., Cerottini J. C., Louis J. A. Therapeutic effect of anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody GK1.5 on cutaneous leishmaniasis in genetically-susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbain J., Wikler M., Franssen J. D., Collignon C. Idiotypic regulation of the immune system by the induction of antibodies against anti-idiotypic antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5126–5130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


