Abstract
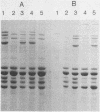
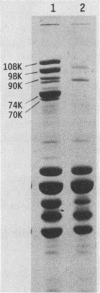
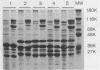
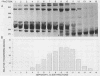
The iron-regulated proteins (IRPs) of five group B meningococcal strains expressing class 2 outer membrane proteins were compared with those of five strains expressing class 3 proteins. Three to four high-molecular-weight IRPs were expressed by each strain, but their molecular sizes varied between strains and were not related to class 2 or 3 protein expression. Transferrin and hemoglobin could be used as a sole iron source. By using anti-human transferrin antibodies, it was shown that meningococcal cells and purified outer membranes bound transferrin. Growth under conditions of iron limitation caused a several-fold increase in the amount of transferrin bound to the cell surface. The transferrin-binding protein was detergent solubilized from outer membranes and partially purified. The isolated protein bound human transferrin and had an apparent molecular mass of 70 kilodaltons. To evaluate the potential of vaccines containing IRPs, we prepared outer membrane vaccines from strains M986-NCV-1 (M986) (--:2a: P1.2) and 44/76-M25 (44/76) (--:15:P1.15) grown to fully express their IRPs. Both vaccines induced significant anti-IRP antibodies as measured by enzyme immunoassay and by Western immunoblot with both M986 and 44/76 outer membranes. By Western blot analysis, the M986 vaccine induced antibodies to two different IRPs, one of which was shared with 44/76. Since the IRPs are major in vivo-expressed outer membrane proteins and are required for survival in vivo, these proteins should be evaluated for their usefulness in a group B meningococcal vaccine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Dyer D. W., Thompson M. K., Sparling P. F. Human immune response to iron-repressible outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):710–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.710-713.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., McKenna W., Thompson S. A., Sparling P. F. A pleiotropic iron-uptake mutant of Neisseria meningitidis lacks a 70-kilodalton iron-regulated protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):977–983. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.977-983.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Robbins J. D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. III. Immunogenicity of serotype 2 vaccines and specificity of protection in a guinea pig model. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Zahradnik J. M., Wang L. Y., Mocca L. F., Tsai C. M. Antibody response of adults to an aluminum hydroxide-adsorbed Neisseria meningitidis serotype 2b protein-group B polysaccharide vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):710–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietzner T. A., Bolan G., Schoolnik G. K., Morse S. A. Purification and characterization of the major iron-regulated protein expressed by pathogenic Neisseriae. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1041–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel typing system for characterization of Neisseria meningitidis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.240-244.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Gonzalez G. C. Comparison of the abilities of different protein sources of iron to enhance Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2425–2429. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2425-2429.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Lee B. C. Comparative analysis of the transferrin and lactoferrin binding proteins in the family Neisseriaceae. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Mar;35(3):409–415. doi: 10.1139/m89-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Trivett T., DeVoe I. W. Energy-independent uptake of iron from citrate by isolated outer membranes of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.547-553.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E. Immunotype epitopes of Neisseria meningitidis lipooligosaccharide types 1 through 8. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1652–1656. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1652-1656.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Loss of transferrin receptor activity in Neisseria meningitidis correlates with inability to use transferrin as an iron source. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3132–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3132-3138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Frasch C. E. Development of a Neisseria meningitidis group B serotype 2b protein vaccine and evaluation in a mouse model. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):408–414. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.408-414.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]