Abstract
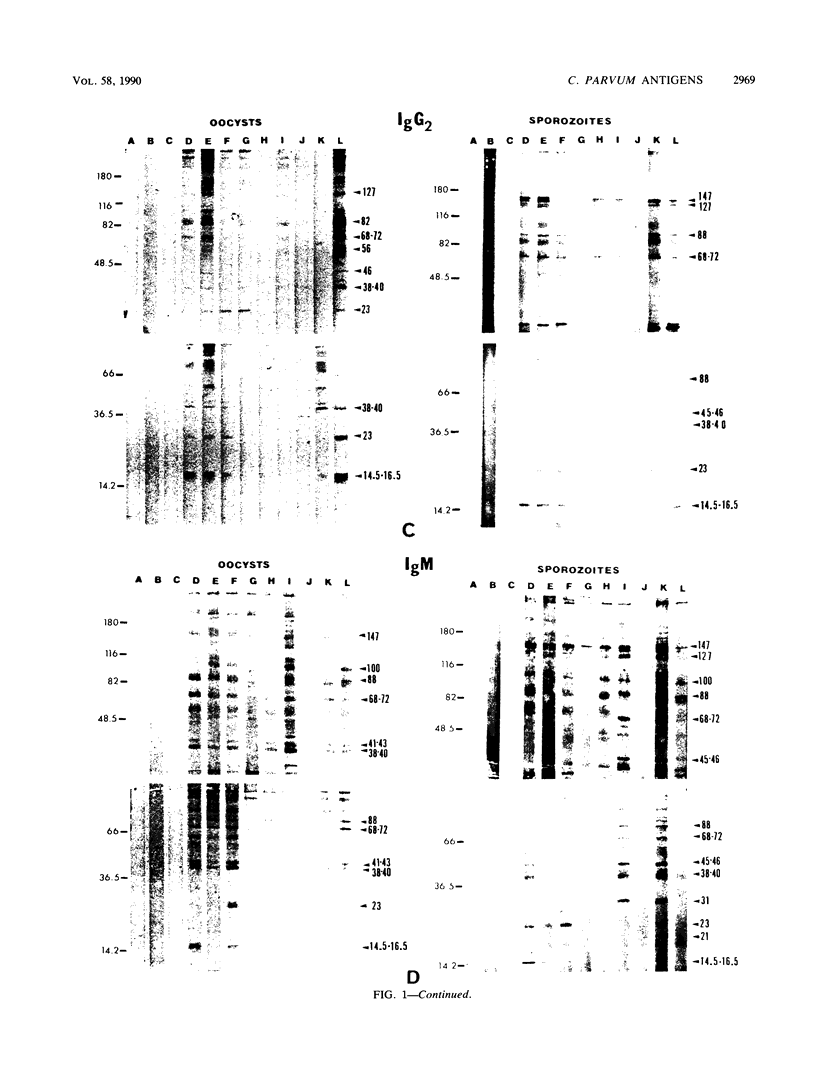
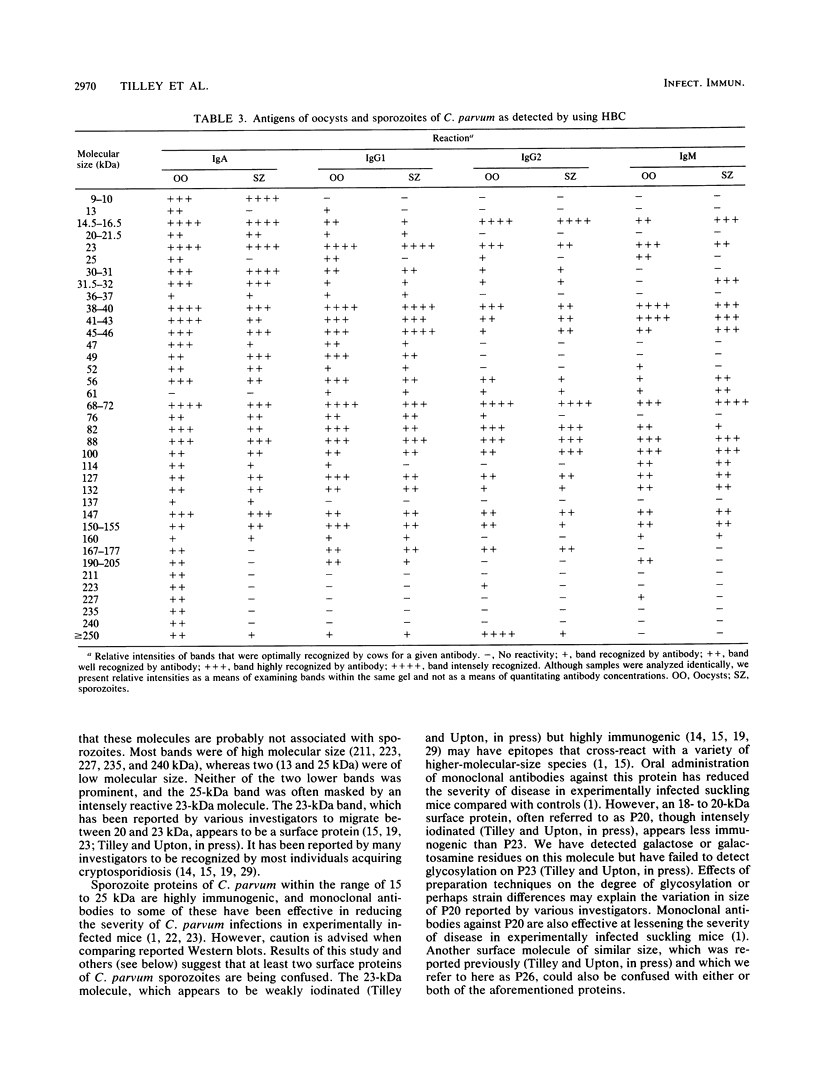
Colostral whey from seven hyperimmunized and two control cows (hyperimmune bovine colostrum) was examined by Western immunoblotting for the presence of antibody against oocysts and sporozoites of Cryptosporidium parvum, using rabbit anti-bovine immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgG1, IgG2, and IgM antibodies, followed by a horseradish peroxidase goat anti-rabbit polyvalent antibody. Although considerable variation was found in binding activity between cows on different immunization protocols, IgA and IgG1 in whey recognized a greater variety of C. parvum antigens than did IgG2 and IgM. A band at 9 to 10 kilodaltons appeared unique in that it was recognized only by IgA.
Full text
PDF
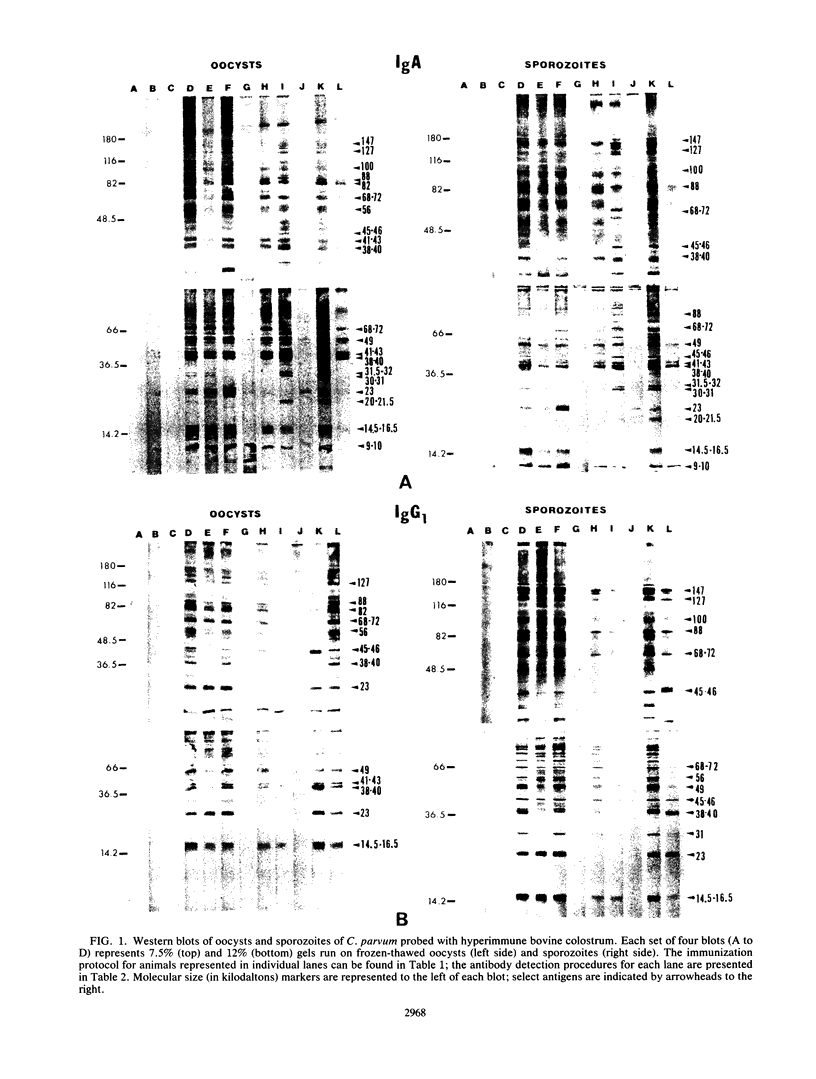

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrowood M. J., Mead J. R., Mahrt J. L., Sterling C. R. Effects of immune colostrum and orally administered antisporozoite monoclonal antibodies on the outcome of Cryptosporidium parvum infections in neonatal mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2283–2288. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2283-2288.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Cano F., Càceres P., Chew F., Pareja G. Infection and diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium sp. among Guatemalan infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):88–91. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.88-91.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Andrews C., Ungar B. L., Blagburn B. Efficacy of hyperimmune bovine colostrum for prophylaxis of cryptosporidiosis in neonatal calves. J Parasitol. 1989 Jun;75(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Guidry A., Blagburn B. L. Immunotherapeutic efficacy of bovine colostral immunoglobulins from a hyperimmunized cow against cryptosporidiosis in neonatal mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2962–2965. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2962-2965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Perryman L. E., Riggs M. W. Hyperimmune bovine colostrum neutralizes Cryptosporidium sporozoites and protects mice against oocyst challenge. J Parasitol. 1989 Feb;75(1):151–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guderian R. H., Sandoval C. A., Mackenzie C. D. Cryptosporidiosis in Ecuadorian children with acute diarrhoea. J Trop Pediatr. 1986 Dec;32(6):290–292. doi: 10.1093/tropej/32.6.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harp J. A., Woodmansee D. B., Moon H. W. Effects of colostral antibody on susceptibility of calves to Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Dec;50(12):2117–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højlyng N., Mølbak K., Jepsen S. Cryptosporidium spp., a frequent cause of diarrhea in Liberian children. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1109-1113.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo A., Barriga O. O., Redman D. R., Bech-Nielsen S. Identification by transfer blot of antigens reactive in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in rabbits immunized and a calf infected with Cryptosporidium sp. Vet Parasitol. 1986 Aug;21(3):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(86)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. W., Allen S. D., Mitchell J., Quinn M. Rotavirus and Cryptosporidium shedding in dairy calf feces and its relationship to colostrum immune transfer. J Dairy Sci. 1988 May;71(5):1288–1294. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(88)79685-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Payne D., Woodmansee D., Kim C. W. Characterization of the Cryptosporidium antigens from sporulated oocysts of Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2436–2441. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2436-2441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb R., Lanser J. A., O'Donoghue P. J. Electrophoretic and immunoblot analysis of Cryptosporidium oocysts. Immunol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct-Dec;66(Pt 5-6):369–376. doi: 10.1038/icb.1988.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb R., Smith P. S., Davies R., O'Donoghue P. J., Atkinson H. M., Lanser J. A. Localization of a 23,000 MW antigen of Cryptosporidium by immunoelectron microscopy. Immunol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;67(Pt 4):267–270. doi: 10.1038/icb.1989.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L., Bolaños H., Pizarro D., Vives M. Criptosporidiosis en niños de Costa Rica: estudio transveral y longitudinal. Rev Biol Trop. 1984 Jun;32(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L., Bolaños H., Pizarro D., Vives M. Cryptosporidiosis in children from some highland Costa Rican rural and urban areas. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):24–29. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan M. M., Venkatesan S., George R., Mathew M., Mathan V. I. Cryptosporidium and diarrhoea in southern Indian children. Lancet. 1985 Nov 23;2(8465):1172–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. R., Arrowood M. J., Sterling C. R. Antigens of Cryptosporidium sporozoites recognized by immune sera of infected animals and humans. J Parasitol. 1988 Feb;74(1):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Woodmansee D. B., Harp J. A., Abel S., Ungar B. L. Lacteal immunity to enteric cryptosporidiosis in mice: immune dams do not protect their suckling pups. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):649–653. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.649-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape J. W., Levine E., Beaulieu M. E., Marshall F., Verdier R., Johnson W. D., Jr Cryptosporidiosis in Haitian children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Mar;36(2):333–337. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman L. E., Riggs M. W., Mason P. H., Fayer R. Kinetics of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoite neutralization by monoclonal antibodies, immune bovine serum, and immune bovine colostrum. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):257–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.257-259.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. W., McGuire T. C., Mason P. H., Perryman L. E. Neutralization-sensitive epitopes are exposed on the surface of infectious Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1340–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. W., Perryman L. E. Infectivity and neutralization of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2081–2087. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2081-2087.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Weinstein W. Oral administration of bovine colostrum anti-cryptosporidia antibody fails to alter the course of human cryptosporidiosis. J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;73(2):413–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley M., Upton S. J., Blagburn B. L., Anderson B. C. Identification of outer oocyst wall proteins of three Cryptosporidium (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) species by 125I surface labeling. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):252–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.252-253.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Roberton D., Chapman C. Remission of diarrhoea due to cryptosporidiosis in an immunodeficient child treated with hyperimmune bovine colostrum. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 15;293(6557):1276–1277. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6557.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Roberton D., Cooper D. A., White L. Chronic cryptosporidial diarrhoea and hyperimmune cow colostrum. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):344–345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90944-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Nash T. E. Quantification of specific antibody response to Cryptosporidium antigens by laser densitometry. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.124-128.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Ward D. J., Fayer R., Quinn C. A. Cessation of Cryptosporidium-associated diarrhea in an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient after treatment with hyperimmune bovine colostrum. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):486–489. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90842-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Burden D. J. Measurement of class specific antibody against cryptosporidium in serum and faeces from experimentally infected calves. Res Vet Sci. 1987 Sep;43(2):264–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Richter J. M., Waldron M. A., Weber D. J., McCarthy D. M., Hopkins C. C. Cryptosporidiosis in immunocompetent patients. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1278–1282. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]