Abstract
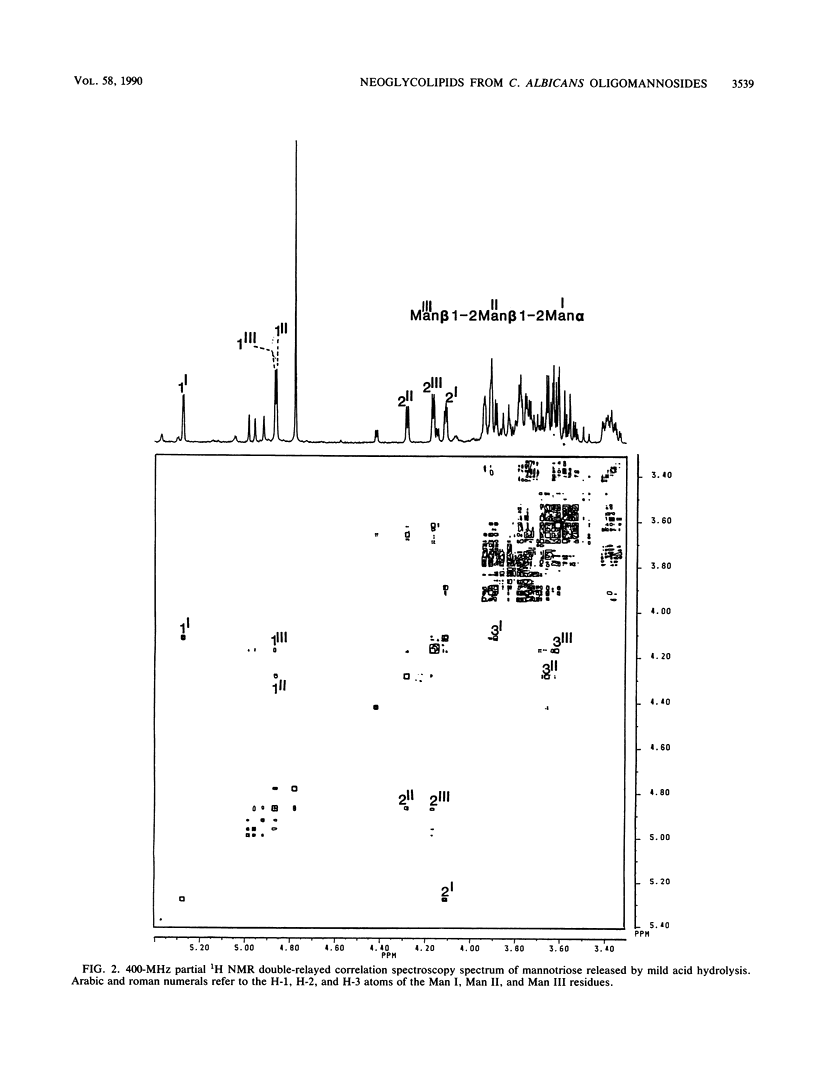
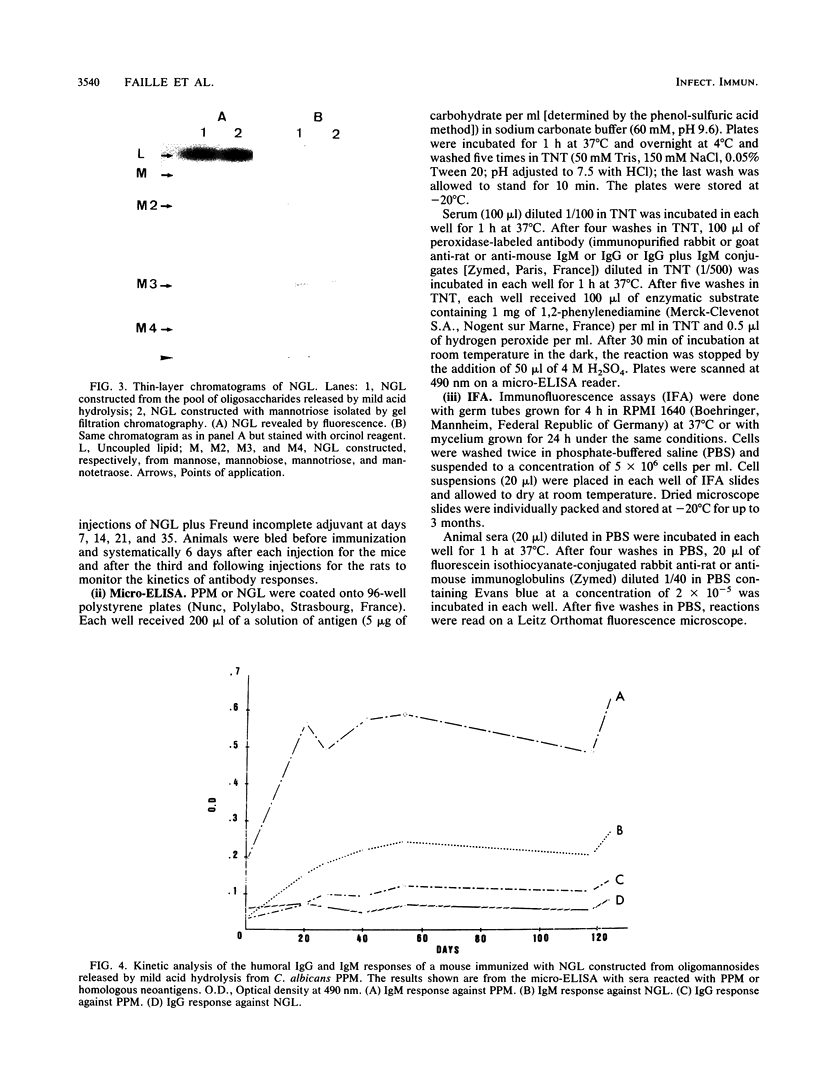
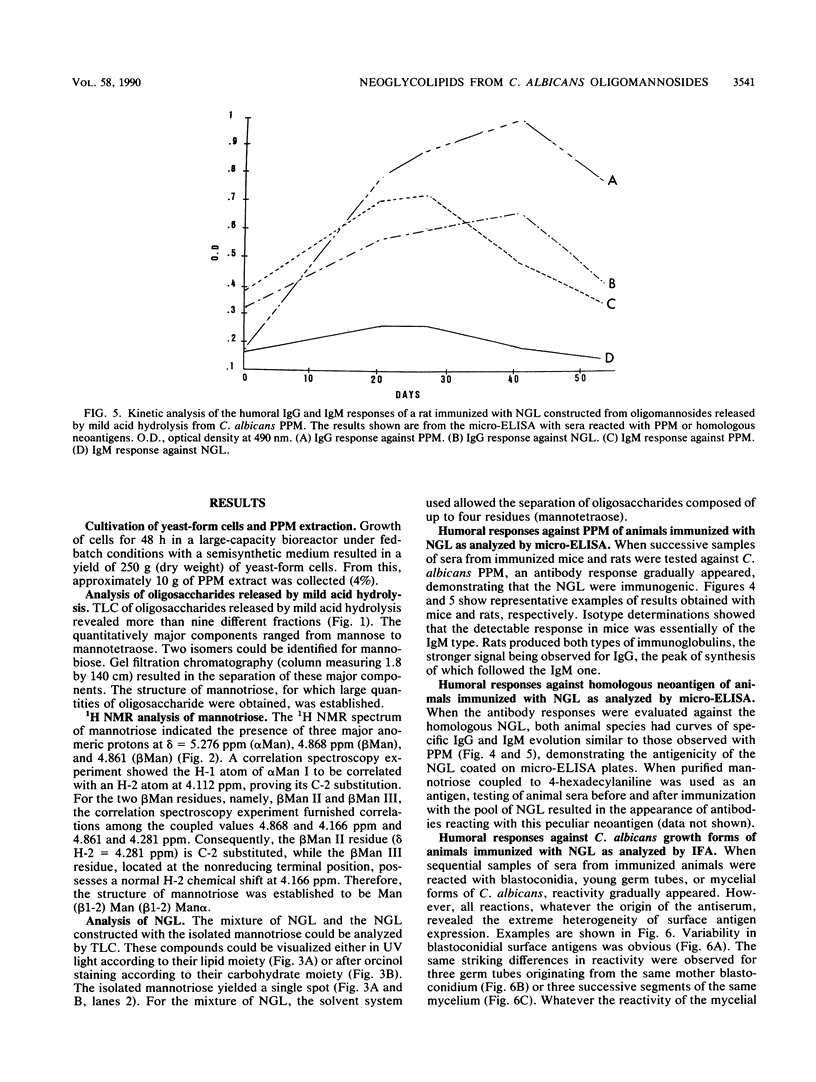
To establish a model to study the immunoreactivity of oligosaccharidic structures from the Candida albicans cell wall, we attempted to construct neoglycolipids with these residues by using oligomannosides released after mild acid hydrolysis of the phosphopeptidomannans isolated from yeast forms. From a mixture of manno-oligosaccharides ranging from mannobiose to mannononaose, the structure of a quantitatively major component (mannotriose) was determined to be Man (beta 1-2) Man (beta 1-2) Man alpha by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. After coupling of the pool of oligosaccharides to a lipid (4-hexadecylaniline), the synthesized molecules were injected into mice and rats. Antibody responses were detected on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay plates coated with either phosphopeptidomannans or neoglycolipids. The hybrid molecules exhibited both immunogenicity and antigenicity. The kinetics of antibody responses as well as immunofluorescence patterns observed on whole C. albicans cells strongly mimicked results from the immunization of animals with natural antigens. Construction of neoglycolipids could therefore provide an interesting approach to the study of specific oligosaccharides of C. albicans and their recognition by the host immune system.
Full text
PDF




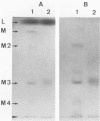
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou C. E. Some aspects of the structure, immunochemistry, and genetic control of yeast mannans. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;40(0):239–270. doi: 10.1002/9780470122853.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of a cell surface determinant on Candida albicans as evidenced by an agglutinating monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):966–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.966-972.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of cell surface antigens of Candida albicans during morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.337-343.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardès T., Piechaczyk M., Cavaillès V., Salhi S. L., Pau B., Bastide J. M. Production and partial characterization of anti-Candida monoclonal antibodies. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1986 Mar-Apr;137C(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/s0771-050x(86)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. E., Ballou C. E. Linkage and sequence analysis of mannose-rich glycoprotein core oligosaccharides by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4345–4358. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier B., Hopwood V., Poulain D. Electric and chemical fusions for the production of monoclonal antibodies reacting with the in-vivo growth phase of Candida albicans. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Dec;27(4):239–245. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-4-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruit J., Cailliez J. C., Odds F. C., Poulain D. Expression of an epitope by surface glycoproteins of Candida albicans. Variability among species, strains and yeast cells of the genus Candida. J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(3):241–252. doi: 10.1080/02681219080000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood V., Poulain D., Fortier B., Evans G., Vernes A. A monoclonal antibody to a cell wall component of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.222-227.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Mitobe H., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural study of phosphomannan of yeast-form cells of Candida albicans J-1012 strain with special reference to application of mild acetolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 1;272(2):364–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Suzuki S. Acetolysis of Pichia pastoris IFO 0948 strain mannan containing alpha-1,2 and beta-1,2 linkages using acetolysis medium of low sulfuric acid concentration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Mar;245(2):494–503. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Shibata N., Yonezu T., Suzuki S. Structural study of phosphomannan-protein complex of Citeromyces matritensis containing beta-1,2 linkage. Application of partial acid degradation and acetolysis techniques under mild conditions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jul;256(1):381–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocourek J., Ballou C. E. Method for fingerprinting yeast cell wall mannans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1175–1181. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1175-1181.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan G., Pavliak V., Masler L. Structural studies of mannans from the cell walls of the pathogenic yeasts Candida albicans serotypes A and B and Candida parapsilosis. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Feb 1;172(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90858-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kagaya K., Fukazawa Y., Soe G. Production and characterization of agglutinating monoclonal antibodies against predominant antigenic factors for Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):881–886. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.881-886.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Loveless R. W., Lawson A. M., Chai W., Lachmann P. J., Childs R. A., Thiel S., Feizi T. A library of oligosaccharide probes (neoglycolipids) from N-glycosylated proteins reveals that conglutinin binds to certain complex-type as well as high mannose-type oligosaccharide chains. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13834–13839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo Y., Ichikawa T., Suzuki S. Relationship between phosphate content and immunochemical properties of subfractions of bakers' yeast mannan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.63-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Hopwood V., Vernes A. Antigenic variability of Candida albicans. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):223–270. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Tronchin G., Vernes A., Popeye R., Biguet J. Antigenic variations of Candida albicans in vivo and in vitro--relationships between P antigens and serotypes. Sabouraudia. 1983 Jun;21(2):99–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERS D. F., GROLLMAN A. P., HASENCLEVER H. F. POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF CANDIDA CELL WALL. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Fukasawa S., Kobayashi H., Tojo M., Yonezu T., Ambo A., Ohkubo Y., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of phospho-D-mannan-protein complexes isolated from yeast and mold form cells of Candida albicans NIH A-207 serotype A strain. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Apr 15;187(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Ichikawa T., Tojo M., Takahashi M., Ito N., Okubo Y., Suzuki S. Immunochemical study on the mannans of Candida albicans NIH A-207, NIH B-792, and J-1012 strains prepared by fractional precipitation with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Dec;243(2):338–348. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata N., Kobayashi H., Tojo M., Suzuki S. Characterization of phosphomannan-protein complexes isolated from viable cells of yeast and mycelial forms of Candida albicans NIH B-792 strain by the action of Zymolyase-100T. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Plessas N., Goldstein I. J. Production and characterization of antisera raised to the manninotrionate group [alpha-D-Galp-(1----6)-alpha-D-Galp-(1----6)-D-gluconate]. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Jun 15;189:301–307. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)84106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snippe H., van Dam J. E., van Houte A. J., Willers J. M., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F. Preparation of a semisynthetic vaccine to Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):842–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.842-844.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Mizuochi T., Childs R. A., Feizi T. Improved procedure for the construction of neoglycolipids having antigenic and lectin-binding activities, from reducing oligosaccharides. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):661–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2560661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Fukazawa Y. Immunochemical characterization of Candida albicans cell wall antigens: specific determinant of Candida albicans serotype A mannan. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(5):387–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. W., Gool H. C., Hardy M., Lee Y. C., Feizi T. Novel approach to the study of the antigenicities and receptor functions of carbohydrate chains of glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):474–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Shibata N., Kobayashi M., Mikami T., Suzuki M., Suzuki S. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies reactive with beta-1,2-linked oligomannosyl residues in the phosphomannan-protein complex of Candida albicans NIH B-792 strain. Clin Chem. 1988 Mar;34(3):539–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Fukazawa Y., Taguchi M., Nakase T., Shinoda T. Serologic aspects on yeast classification. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Aug 30;53(1):77–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02127199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterrowd G. E., Cutler J. E. Candida albicans-induced agglutinin and immunoglobulin E responses in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):33–38. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.33-38.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies of conjugates of isomaltosyl oligosaccharides to lipid: fractionation of rabbit antibodies to stearyl-isomaltosyl oligosaccharides and a study of their combining sites by a competitive binding assay. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90367-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]