Abstract
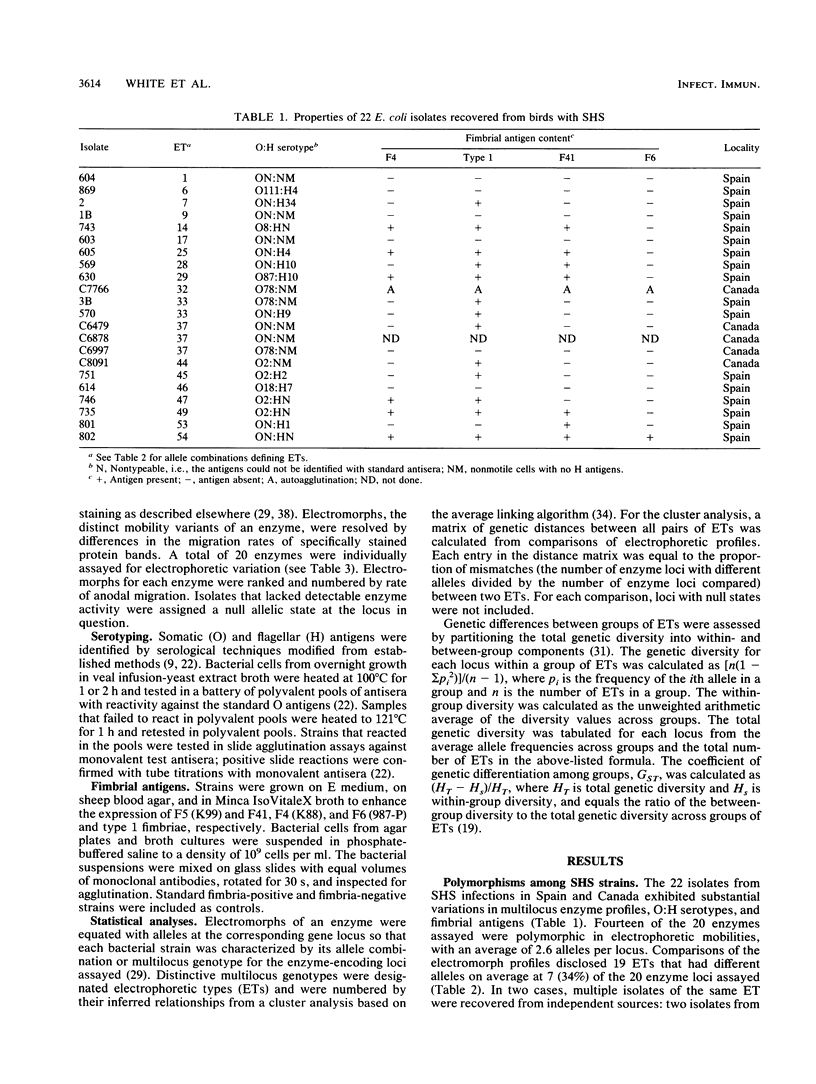
Genetic diversity among 22 Escherichia coli strains isolated from chickens with swollen-head syndrome (SHS), an acute respiratory disease of domestic poultry, and 93 strains isolated from birds with colibacillosis was assessed on the basis of allelic variation at 20 enzyme-encoding loci detected by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. SHS isolates from Spain and Canada were polymorphic at 14 loci and were classified into 19 multilocus genotypes, defining clones that differed on average at 34% of the loci. In most cases, SHS isolates of different clonal genotypes were distinct in O:H serotype and expressed different fimbrial antigens. Comparisons with 93 isolates obtained from birds with colibacillosis revealed enzyme polymorphisms at 17 of 20 loci, with an average of 3.5 alleles per locus. In the total sample, 56 clonal genotypes were distinguished, with 27 (23%) of the isolates belonging to one of three common clones. Both SHS and colibacillosis isolates were genetically diverse, with an average single-locus diversity of 0.36, indicating that a wide variety of naturally occurring bacterial clones is associated with these acute avian infections. Six previously defined groups of clones identified in diseased birds from the United States were represented in isolates from Spain, indicating that similar clones occur in widely separated geographic areas. In addition, one group of SHS isolates was closely related to a recognized widespread clone complex incriminated in human septicemia and meningitis. The results suggest that certain strains implicated in SHS infections belong to a clone complex whose members have special attributes that promote involvement in invasive diseases in humans and animals.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Heuzenroeder M., Kusecek B., Ochman H., Caugant D., Selander R. K., Väisanen-Rhen V., Korhonen T. K., Stuart S., Orskov F. Clonal analysis of Escherichia coli O2:K1 isolated from diseased humans and animals. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.268-276.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Pluschke G. Clonal analysis of descent and virulence among selected Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:185–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Musser J. M., Helmuth R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Frerichs W. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Ferris K., McWhorter A. C., Wells J. G., Cravioto A. Toward a population genetic analysis of Salmonella: genetic diversity and relationships among strains of serotypes S. choleraesuis, S. derby, S. dublin, S. enteritidis, S. heidelberg, S. infantis, S. newport, and S. typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brée A., Dho M., Lafont J. P. Comparative infectivity for axenic and specific-pathogen-free chickens of O2 Escherichia coli strains with or without virulence factors. Avian Dis. 1989 Jan-Mar;33(1):134–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Lidin-Janson G., Whittam T. S., Svanborg Edén C., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships among strains of Escherichia coli in the intestine and those causing urinary tract infections. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:203–227. doi: 10.1159/000318331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloud S. S., Rosenberger J. K., Fries P. A., Wilson R. A., Odor E. M. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian Escherichia coli. I. Serotypes, metabolic activity, and antibiotic sensitivity. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1084–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff S. R., Hocking P. M., Randall C. J., MacKenzie G. Head swelling of traumatic aetiology in broiler breeding fowl. Vet Rec. 1989 Aug 5;125(6):133–134. doi: 10.1136/vr.125.6.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren E. Een 'nieuwe ziekte' in de kip; diagnostische bevindingen. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1985 Dec 15;110(24):1076–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Valtonen M. V., Parkkinen J., Väisänen-Rhen V., Finne J., Orskov F., Orskov I., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.486-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafont J. P., Dho M., D'Hauteville H. M., Bree A., Sansonetti P. J. Presence and expression of aerobactin genes in virulent avian strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):193–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.193-197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J. S., Cook J. K. Turkey rhinotracheitis: preliminary investigations. Vet Rec. 1986 Feb 22;118(8):206–207. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.8.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley A. J., Thomson D. K. Swollen-head syndrome in broiler chickens. Avian Dis. 1984 Jan-Mar;28(1):238–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Schlievert P. M., Chow A. W., Ewan P., Kreiswirth B. N., Rosdahl V. T., Naidu A. S., Witte W., Selander R. K. A single clone of Staphylococcus aureus causes the majority of cases of toxic shock syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. D. Swollen head syndrome in broiler breeders. Vet Rec. 1985 Dec 7;117(23):619–620. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.23.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Evidence for clonal population structure in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):198–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison M., Chettle N., Randall C. J., Wyeth P. J. Observations on swollen head syndrome in broiler and broiler breeder chickens. Vet Rec. 1989 Aug 26;125(9):229–231. doi: 10.1136/vr.125.9.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelman B., Meroz M., Samberg Y. 'Swollen head syndrome' in broiler breeders in Israel. Vet Rec. 1988 Oct 22;123(17):444–444. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.17.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picault J. P., Giraud P., Drouin P., Guittet M., Bennejean G., Lamande J., Toquin D., Gueguen C. Isolation of a TRTV-like virus from chickens with swollen-head syndrome. Vet Rec. 1987 Aug 8;121(6):135–135. doi: 10.1136/vr.121.6.135-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mercer A., Kusećek B., Pohl A., Achtman M. Induction of bacteremia in newborn rats by Escherichia coli K1 is correlated with only certain O (lipopolysaccharide) antigen types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):599–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.599-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger J. K., Fries P. A., Cloud S. S., Wilson R. A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian Escherichia coli. II. Factors associated with pathogenicity. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1094–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Williams P. H., Pattison P. E., Caugant D. A. Genetic relationships and clonal structure of strains of Escherichia coli causing neonatal septicemia and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.213-222.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Musser J. M., Caugant D. A., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Population genetics of pathogenic bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanichkul A., Panigrahy B. Biological and immunological characterization of pili of Escherichia coli serotypes O1, O2, and O78 pathogenic to poultry. Avian Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;30(4):781–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wilson R. A. Genetic relationships among pathogenic Escherichia coli of serogroup O157. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2467–2473. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2467-2473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wilson R. A. Genetic relationships among pathogenic strains of avian Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2458–2466. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2458-2466.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wolfe M. L., Wilson R. A. Genetic relationships among Escherichia coli isolates causing urinary tract infections in humans and animals. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Feb;102(1):37–46. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyeth P. J., Chettle N. J., Gough R. E., Collins M. S. Antibodies to TRT in chickens with swollen head syndrome. Vet Rec. 1987 Mar 21;120(12):286–287. doi: 10.1136/vr.120.12.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellen G. Ontario. Swollen-head Syndrome in Broiler Chickens. Can Vet J. 1988 Mar;29(3):298–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


