Abstract
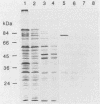
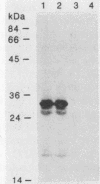
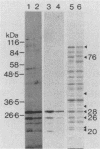
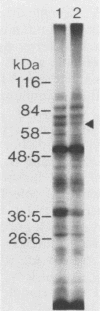
A library of Streptococcus gordonii DL1-Challis DNA was constructed in lambda gt11. Phage plaques were screened for production of antigens that reacted with antiserum to S. gordonii cell surface proteins. A recombinant phage denoted lambda gt11-cp2 was isolated that carried 1.85 kb of S. gordonii DNA and that expressed an antigen with a molecular mass of 29 kDa in Escherichia coli. Antibodies that reacted with the expression product were affinity purified and were shown to react with a single polypeptide antigen with a molecular mass of 76 kDa in S. gordonii DL1-Challis. A segment (0.85 kb) of the cloned DNA within the transcription unit was ligated into a nonreplicative plasmid carrying an erythromycin resistance determinant and transformed into S. gordonii DL1-Challis. The plasmid integrated onto the chromosome, and expression of the 76-kDa polypeptide antigen was abolished. The gene inactivation had no obvious effect on bacterial growth or on a number of phenotypic properties, including hydrophobicity and adherence. However, it abolished serum-induced cell aggregation, mutant cells had reduced aggregation titers in saliva and in colostrum immunoglobulin A, and it also reduced coaggregation with some Actinomyces species. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles of cell envelope proteins from wild-type and mutant strains showed that as well as lacking the surface-exposed 76-kDa polypeptide, mutant cell envelopes were deficient in several other polypeptides, including those that bound to immunoglobulin A. Expression of the gene encoding the 76-kDa polypeptide in S. gordonii appeared to be critical for functional conformation of the cell surface.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Rosan B. Cell surface proteins of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.245-250.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan R. A., Jenkinson H. F. Glucosyltransferase production by Streptococcus sanguis Challis and comparison with other oral streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Apr;5(2):63–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassels F. J., London J. Isolation of a coaggregation-inhibiting cell wall polysaccharide from Streptococcus sanguis H1. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4019-4025.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimasoni G., Song M., McBride B. C. Effect of crevicular fluid and lysosomal enzymes on the adherence of streptococci and bacteroides to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1484–1489. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1484-1489.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demuth D. R., Davis C. A., Corner A. M., Lamont R. J., Leboy P. S., Malamud D. Cloning and expression of a Streptococcus sanguis surface antigen that interacts with a human salivary agglutinin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2484-2490.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Mechanism of integrating foreign DNA during transformation of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. IV. Complexing between non-mucin glycoproteins, immunoglobulins and mucins in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(1):46–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenno J. C., LeBlanc D. J., Fives-Taylor P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a type 1 fimbrial gene of Streptococcus sanguis FW213. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3527–3533. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3527-3533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Cloning of a Streptococcus sanguis adhesin which mediates binding to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1150–1157. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1150-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty D. W., Handley P. S. Expression of the surface properties of the fibrillar Streptococcus salivarius HB and its adhesion deficient mutants grown in continuous culture under glucose limitation. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Oct;135(10):2611–2621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-10-2611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg M. C., Gong K., MacFarlane G. D., Erickson P. R., Soberay A. H., Krebsbach P. H., Manjula G., Schilling K., Bowen W. H. Phenotypic characterization of Streptococcus sanguis virulence factors associated with bacterial endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.515-522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussen C., Dowdle E. B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Carter D. A. Cell surface mutants of Streptococcus sanguis with altered adherence properties. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1988 Jun;3(2):53–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1988.tb00081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F. Cell-surface proteins of Streptococcus sanguis associated with cell hydrophobicity and coaggregation properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1575–1589. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Mandelstam J. Cloning of the Bacillus subtilis lys and spoIIIB genes in phage phi 105. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2229–2240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F. Novobiocin-resistant mutants of Streptococcus sanguis with reduced cell hydrophobicity and defective in coaggregation. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1909–1918. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F. Properties of a phosphocarrier protein (HPr) extracted from intact cells of Streptococcus sanguis. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3183–3197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregations and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(2):137–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laible N. J., Germaine G. R. Adsorption of lysozyme from human whole saliva by Streptococcus sanguis 903 and other oral microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):148–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.148-159.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M. Characterization of an adhesion antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2417–2423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2417-2423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Erdos G. W., Piacentini D. A., Ayakawa G. Y., Crowley P. J., Bleiweis A. S. Construction and characterization of isogenic mutants of Streptococcus mutans deficient in major surface protein antigen P1 (I/II). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3306–3313. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3306-3313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G., Ofstehage J. C. Aggregation and adherence of Streptococcus sanguis: role of human salivary immunoglobulin A. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1104-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to conformationally specific determinants in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2279-2285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Jones K. R., Wood P. H. Chimeric streptococcal plasmids and their use as molecular cloning vehicles in Streptococcus sanguis (Challis). J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1425–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1425-1435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Crosby L. K., Vatter A. E., Cisar J. O., McNeil M. R., Bush C. A., Tjoa S. S., Fennessey P. V. A polysaccharide from Streptococcus sanguis 34 that inhibits coaggregation of S. sanguis 34 with Actinomyces viscosus T14V. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2229–2235. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2229-2235.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., McBride B. C. Cell surface components of Streptococcus sanguis: relationship to aggregation, adherence, and hydrophobicity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):255–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.255-262.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Identification and preliminary characterization of a Streptococcus sanguis fibrillar glycoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.164-171.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite: evidence for two binding sites. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis by a neuraminidase-sensitive component of serum and crevicular fluid. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1073–1080. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1073-1080.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins L. D., Lee L. N., LeBlanc D. J. Evidence for a disseminated erythromycin resistance determinant mediated by Tn917-like sequences among group D streptococci isolated from pigs, chickens, and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):439–444. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M., Berman R., Lamont R. J., Demuth D. R. Cloning and expression of an adhesin antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):531–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Golub E. Characteristic differences between saliva-dependent aggregation and adhesion of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.86-90.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundegren J., Arnold R. R. Differentiation and interaction of secretory immunoglobulin A and a calcium-dependent parotid agglutinin for several bacterial strains. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):288–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.288-292.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Strunk R. W., Balian G., Calderone R. A. Microbial adhesion to fibronectin in vitro correlates with production of endocarditis in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Dec;180(3):474–482. doi: 10.3181/00379727-180-42205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]