Abstract
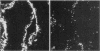
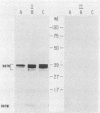
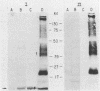
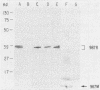
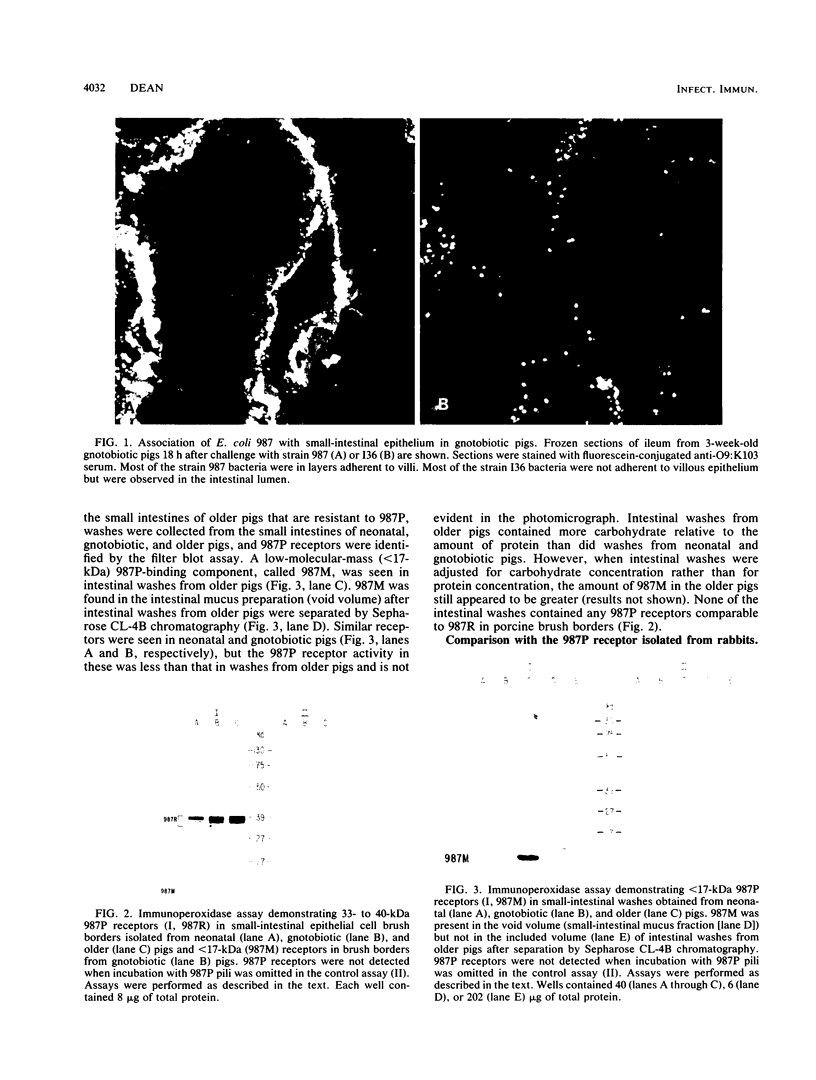
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates that express 987P pili colonize the small intestine and cause diarrhea in neonatal (less than 6-day-old) but not in older (greater than 3-week-old) pigs. However, 987P+ E. coli isolates adhere in vitro to small-intestinal epithelial cells from pigs of both ages. This indicates that older pigs as well as neonatal pigs contain receptors for 987P pili and that resistance in older pigs is not due to a lack of intestinal receptors for 987P pili. In this study, we demonstrated that 3-week-old gnotobiotic pigs, like neonatal pigs, were colonized and developed diarrhea when challenged with 987P+ E. coli. We compared 987P receptors in small-intestinal epithelial cell brush borders and in intestinal washes (luminal contents) from less than 1-day-old, 3-week-old gnotobiotic, and 3- to 4-week-old weaned pigs. Samples were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted onto nitrocellulose filters, and 987P binding was demonstrated by immunoassay using purified 987P pili. Multiple 987P-binding components ranging from 33 to 40 kDa were found in brush borders from both 987P-susceptible (neonatal and gnotobiotic) and 987P-resistant (older) pigs: 987P binding to these receptors, which we called 987R, did not correlate with 987P susceptibility. A less than 17-kDa 987P receptor, 987M, was found in the mucus fraction of intestinal washes from 987P-resistant older pigs. Only trace amounts of 987M were detected in 987P-susceptible neonatal and gnotobiotic pigs. 987M comigrated with the 987P receptor previously isolated from adult rabbits. Receptors for 987P in the mucus of older pigs may inhibit 987P-mediated intestinal colonization by preventing the attachment of 987P+ enterotoxigenic E. coli to intestinal epithelial receptors for 987P.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertschinger H. U., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Association of Escherichia coli with the small intestinal epithelium. I. Comparison of enteropathogenic and nonenteropathogenic porcine strains in pigs. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):595–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.595-605.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. In vitro adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli to small intestinal villous epithelial cells from rabbits and the identification of a soluble 987P pilus receptor-containing fraction. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1192-1198.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Location and distribution of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli in small intestines. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.345-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Isaacson R. E. Purification and characterization of a receptor for the 987P pilus of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):98–105. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.98-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W. Age-specific colonization of porcine intestinal epithelium by 987P-piliated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.82-87.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Roberton A. M., Sherman P. M. Inhibition of attachment of Escherichia coli RDEC-1 to intestinal microvillus membranes by rabbit ileal mucus and mucin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2437–2442. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2437-2442.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W., Lefkowitz J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Nagy B., Moon H. W. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: colonization and adhesion factors of pig enteropathogens that lack K88. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):531–539. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Richter P. Escherichia coli 987P pilus: purification and partial characterization. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.784-789.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Sojka W. J., Wells G. A. K99 and 987P adhesins on Escherichia coli enteropathogenic for piglets. Vet Rec. 1982 Aug 21;111(8):165–166. doi: 10.1136/vr.111.8.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine intestine by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: selection of piliated forms in vivo, adhesion of piliated forms to epithelial cells in vitro, and incidence of a pilus antigen among porcine enteropathogenic E. coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.344-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: ileal colonization and adhesion by pig enteropathogens that lack K88 antigen and by some acapsular mutants. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1214–1220. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1214-1220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnels P. L., Moon H. W., Schneider R. A. Development of resistance with host age to adhesion of K99+ Escherichia coli to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):298–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.298-300.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento J. I., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Postweaning diarrhea in swine: experimental model of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1154–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. M., Boedeker E. C. Pilus-mediated interactions of the Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 with mucosal glycoproteins in the small intestine of rabbits. Gastroenterology. 1987 Oct;93(4):734–743. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Robinson I. M., Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Matthews P. J., Alexander T. J. Pathogenic synergism between Treponema hyodysenteriae and other selected anaerobes in gnotobiotic pigs. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1042–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1042-1047.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]