Abstract
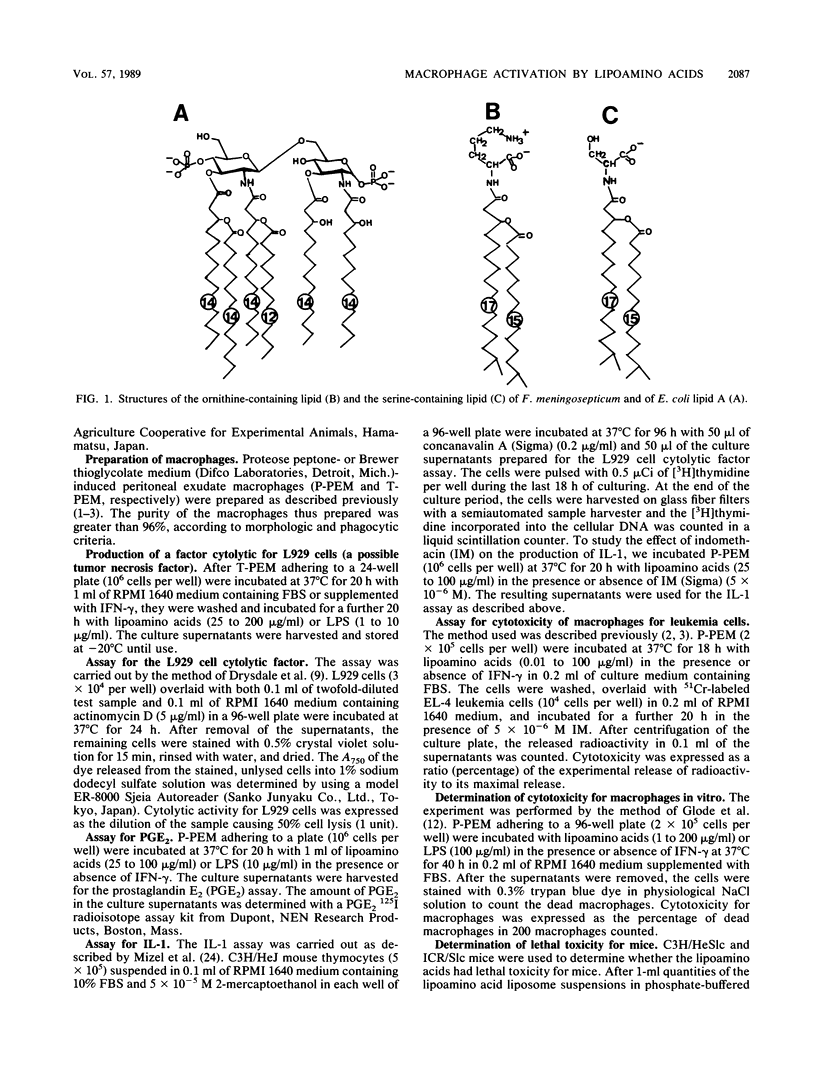
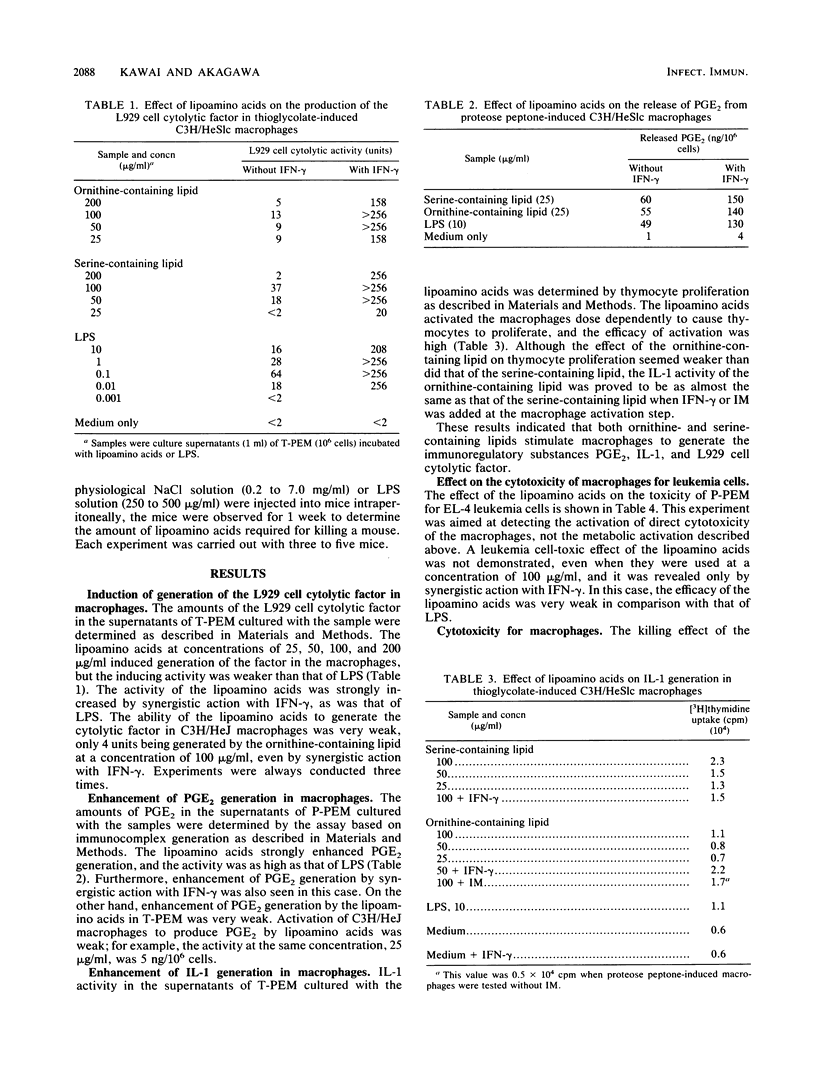
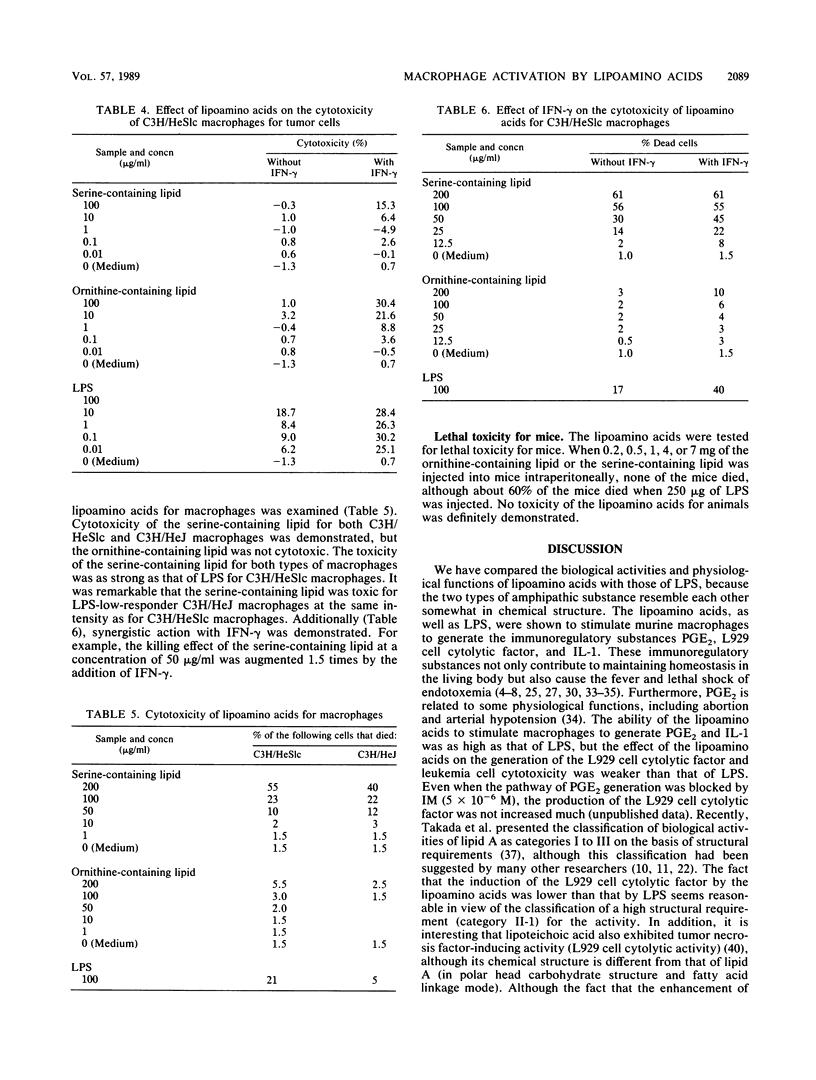
alpha-N-(3-Acyloxyacyl)-ornithine (or -serine) is the structure of lipoamino acids obtained by us previously from some gram-negative bacteria (Y. Kawai and I. Yano, Eur. J. Biochem. 136:531-538, 1983; Y. Kawai, I. Yano, and K. Kaneda, Eur. J. Biochem. 171:73-80, 1988; Y. Kawai, I. Yano, K. Kaneda, and E. Yabuuchi, Eur. J. Biochem. 175:633-641, 1988). The 3-acyloxyacylamide structure is present in both the lipoamino acids and lipid A of lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin). The efficacy of lipoamino acids (an ornithine-containing lipid and a serine-containing lipid) in activating C3H/HeSlc mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages was compared with that of bacterial lipopolysaccharide, because the two types of substances were expected to exhibit similar biological activities and physiological functions on the basis of their structural similarities. Actually, the lipoamino acids, as well as lipopolysaccharide, strongly activated the macrophages to generate the immunoregulatory substances prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-1, but their effect on the induction of L929 cell cytolytic factor (a possible tumor necrosis factor), another immunoregulatory substance, was weaker than that of lipopolysaccharide. The effect of lipoamino acids on the cytotoxicity of macrophages for EL-4 leukemia cells was very weak. However, all of these activities, as far as tested, were strongly enhanced by synergistic action with gamma interferon. Only the serine-containing lipid killed both C3H/HeSlc and C3H/HeJ macrophages to almost the same degree as endotoxin killed C3H/HeSlc macrophages. On the other hand, lethal toxicity for mice was not found with either the ornithine-containing lipid or the serine-containing lipid, even when 7 mg of compound was injected into a mouse. These studies suggest that the lipoamino acids are nontoxic characteristic immunoactivators.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagawa K. S., Kamoshita K., Onodera S., Tokunaga T. Restoration of lipopolysaccharide-mediated cytotoxic macrophage induction in C3H/HeJ mice by interferon-gamma or a calcium ionophore. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Mar;78(3):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagawa K. S., Tokunaga T. Appearance of a cell surface antigen associated with the activation of peritoneal macrophages in mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(9):831–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagawa K. S., Tokunaga T. Lack of binding of bacterial lipopolysaccharide to mouse lung macrophages and restoration of binding by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1444–1459. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale B. E., Zacharchuk C. M., Shin H. S. Mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity: production of a soluble cytotoxic factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2362–2367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T., Westphal O., Brade H., Brade L., Freudenberg M., Schade U., Imoto M., Yoshimura H. Synthetic and natural Escherichia coli free lipid A express identical endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Jacques A., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Resistance of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice to the in vitro cytotoxic effects of endotoxin. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y. Characteristic cellular fatty acid composition and an ornithine-containing lipid as a new type of hemagglutinin in Bordetella pertussis. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y. Hemagglutinating activity of phosphatidylserine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Moribayashi A. Characteristic lipids of Bordetella pertussis: simple fatty acid composition, hydroxy fatty acids, and an ornithine-containing lipid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):996–1005. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.996-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Moribayashi A., Yano I. Ornithine-containing lipid of Bordetella pertussis that carries hemagglutinating activity. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):907–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.907-910.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Suzuki K., Hagiwara T. Phosphatidylserine and ornithine-containing lipids of Bordetella, hemagglutinins of lipoamino acid structure, and their control in biomembranes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):367–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Yano I., Kaneda K. Various kinds of lipoamino acids including a novel serine-containing lipid in an opportunistic pathogen Flavobacterium. Their structures and biological activities on erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Yano I., Kaneda K., Yabuuchi E. Ornithine-containing lipids of some Pseudomonas species. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):633–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Yano I. Ornithine-containing lipid of Bordetella pertussis, a new type of hemagglutinin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 15;136(3):531–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoche H. W., Shively J. M. The structure of an ornithine-containing lipid from Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Ikeda T., Otsuka K., Shimauchi H., Kasai N., Mashimo J. Synthetic lipid A with endotoxic and related biological activities comparable to those of a natural lipid A from an Escherichia coli re-mutant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):225–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.225-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa Y., Nakatsuka M., Takimoto H., Furuya T., Nagumo T., Yamamoto A., Homma Y., Inada K., Yoshida M., Kiso M. Importance of fatty acid substituents of chemically synthesized lipid A-subunit analogs in the expression of immunopharmacological activity. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.149-155.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by the macrophage cell line, P388D1. I. Enhancement of LAF production by activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C. Bacterial endotoxins and pathogenesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S733–S747. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Morita T., Iwanaga S., Niwa M., Takahashi K. A sensitive substrate for the clotting enzyme in horseshoe crab hemocytes. J Biochem. 1977 May;81(5):1567–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Amano F., Akamatsu Y., Akagawa K., Tokunaga T., Raetz C. R. Macrophage activation by monosaccharide precursors of Escherichia coli lipid A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki M., Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. A new endotoxin sensitive factor associated with hemolymph coagulation system of horseshoe crab (Limulidae). FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 3;120(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Will J. A., Burhop K. E., Raetz C. R. Protection of mice against lethal endotoxemia by a lipid A precursor. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):905–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.905-907.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Purcell S., Takayama K. Molecular requirements for B-lymphocyte activation by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4624–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Schade U., Jensen M., Wollenweber H. W., Lüderitz O., Greisman S. G. Bacterial endotoxins: chemical structure, biological activity and role in septicaemia. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:8–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. H., Terry A., Raetz C. R. Induction of kappa light chain synthesis in 70Z/3 B lymphoma cells by chemically defined lipid A precursors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5098–5103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kotani S., Tanaka S., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Tsujimoto M., Komuro T., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Kusunose N. Structural requirements of lipid A species in activation of clotting enzymes from the horseshoe crab, and the human complement cascade. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):573–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanamoto K., Zähringer U., McKenzie G. R., Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Biological activities of synthetic lipid A analogs: pyrogenicity, lethal toxicity, anticomplement activity, and induction of gelation of Limulus amoebocyte lysate. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):421–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.421-426.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele O. W., Biswas C. J., Hunneman D. H. Isolation and characterization of an ornithine-containing lipid from Paracoccus denitrificans. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Usami H., Nagamuta M., Sugawara Y., Hamada S., Yamamoto T., Kato K., Kokeguchi S., Kotani S. The use of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) from Streptococcus pyogenes to induce a serum factor causing tumour necrosis. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):739–742. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


