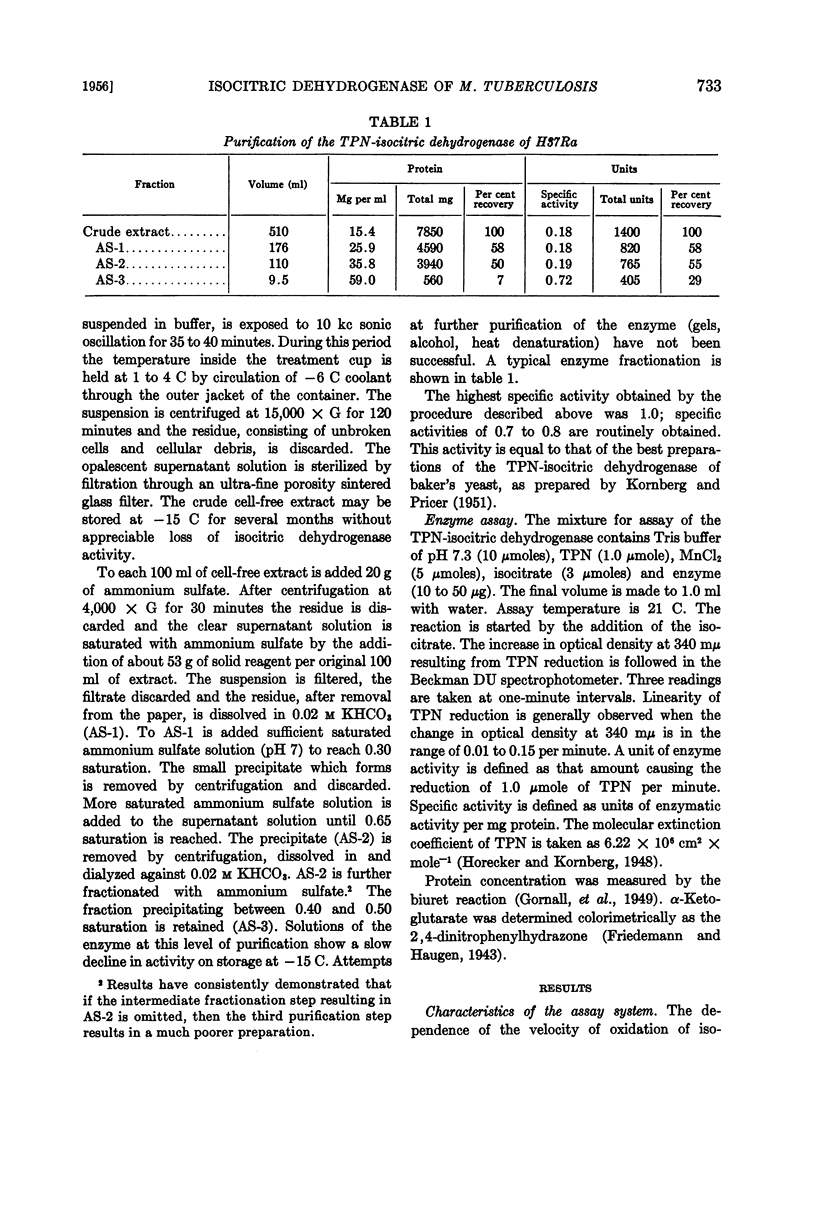
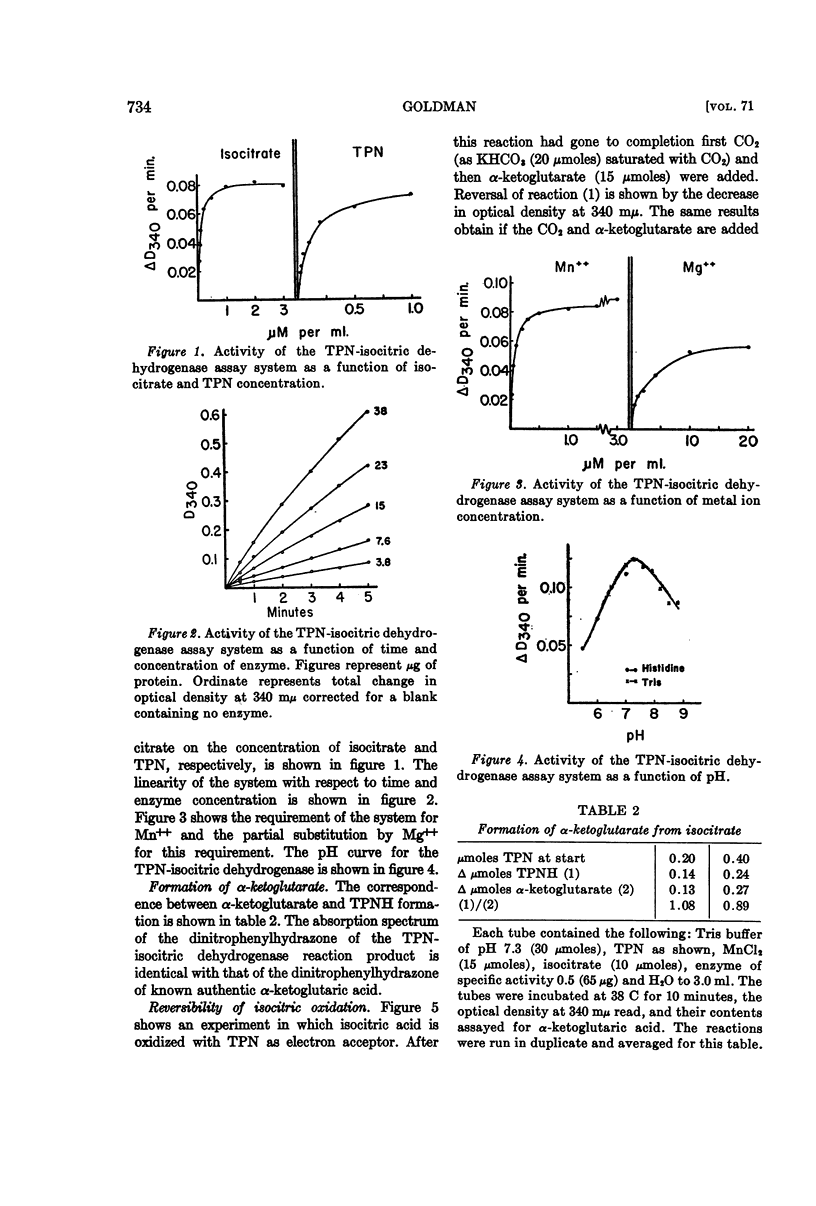
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler E., Euler H. V., Günther G., Plass M. isoCitric dehydrogenase and glutamic acid synthesis in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1939 Jun;33(6):1028–1045. doi: 10.1042/bj0331028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAFFLIN A. L., OCHOA S. Partial purification of isocitric dehydrogenase and oxalosuccinic carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG A., PRICER W. E., Jr Di- and triphosphopyridine nucleotide isocitric dehydrogenases in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1951 Mar;189(1):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLMAN I., YOUMANS G. P. Studies on the metabolism of mycobacterim tuberculosis. VII. Terminal respiratory activity of an avirulent strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1954 Oct;68(4):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.4.411-418.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLMAN I., YOUMANS G. P. The characterization of the terminal respiratory enzymes of the H37Ra strain of mycobacterium tuberculosis var. hominis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.320-325.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYLE J., DIXON M. The identity of TPN-linked isocitric dehydrogenase and oxalosuccinic carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Mar;16(3):434–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHOA S., STERN J. R., SCHNEIDER M. C. Enzymatic synthesis of citric acid. II. Crystalline condensing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1951 Dec;193(2):691–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


