ABSTRACT
Gram-negative outer membrane (OM) integrity is maintained in part by Mg2+ cross-links between phosphates on lipid A and on core sugars of adjacent lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecules. In contrast to other Gram-negative bacteria, waaP, encoding an inner-core kinase, could not be inactivated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. To examine this further, expression of the kinases WaaP or WapP/WapQ/PA5006 was placed under the control of the arabinose-regulated pBAD promoter. Growth of these strains was arabinose dependent, confirming that core phosphorylation is essential in P. aeruginosa. Transmission electron micrographs of kinase-depleted cells revealed marked invaginations of the inner membrane. SDS-PAGE of total LPS from WaaP-depleted cells showed accumulation of a fast-migrating band. Mass spectrometry (MS) analysis revealed that LPS from these cells exhibits a unique truncated core consisting of two 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acids (Kdo), two l-glycero-d-manno-heptoses (Hep), and one hexose but completely devoid of phosphates, indicating that phosphorylation by WaaP is necessary for subsequent core phosphorylations. MS analysis of lipid A from WaaP-depleted cells revealed extensive 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose modification. OM prepared from these cells by Sarkosyl extraction of total membranes or by sucrose density gradient centrifugation lacked truncated LPS. Instead, truncated LPS was detected in the inner membrane fractions, consistent with impaired transport/assembly of this species into the OM.
IMPORTANCE
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane (OM) comprised of a phospholipid inner leaflet and a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer leaflet. The OM protects cells from toxic molecules and is important for survival during infection. The LPS core kinase gene waaP can be deleted in several Gram-negative bacteria but not in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We used a controlled-expression system to deplete WaaP directly in P. aeruginosa cells, which halted growth. WaaP depletion also caused gross changes in cell morphology and led to the accumulation of an aberrant LPS lacking several core sugars and all core phosphates. The aberrant LPS failed to reach the OM, suggesting that WaaP is essential in P. aeruginosa because it is required to produce the full-length LPS that is recognized by the OM transport/assembly machinery in this organism. Therefore, WaaP may constitute a good target for the development of novel antipseudomonal agents.
Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the third most common agent of nosocomial infections in the United States (1) and is associated with a variety of infections, perhaps most notably in the lungs of those with cystic fibrosis (2). P. aeruginosa also exhibits intrinsic resistance to antibiotics, mediated in part by its comparatively impermeable outer membrane (OM) working in conjunction with multiple efflux pumps (3). Options for treating P. aeruginosa infections are limited and becoming less effective due to increased antibiotic resistance (4, 5), necessitating the development of new antimicrobials. The intrinsic resistance engendered by efflux/OM also severely hampers the identification and development of new antibiotics with sufficient whole-cell potency to be clinically useful. One approach to this has been to target the synthesis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the major component defining the OM. Targeting OM biogenesis is attractive because the OM is essential for viability and mediates virulence as well as resistance to toxic agents and antibacterials (6, 7). The OM is an asymmetric bilayer, with a phospholipid inner leaflet and an LPS outer leaflet. The basic structure of LPS (reviewed in references 8 and 9; also see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) includes a relatively conserved molecule of the membrane anchor lipid A (endotoxin), covalently attached to a more variable polysaccharide unit, composed of two independently synthesized carbohydrate regions. These are the core oligosaccharide and the O-antigen repeating unit, which extend outward from the cell surface. Potent inhibitors of LpxC, involved in lipid A biosynthesis, that have antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa have been identified (10–12).
Biosynthesis of LPS itself is well understood, but there has been recent interest in dissecting the downstream mechanisms for transport and assembly of LPS into the outer leaflet of the OM (9, 13–15). The process emerging has several interesting features; lipid A-core, synthesized on the inner leaflet of the inner membrane (IM), is flipped across the IM by the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter MsbA (16, 17). On the periplasmic side, LPS is first extracted from the outer leaflet of the IM by LptC in coordination with the LptBFG transporter complex and then conveyed by the periplasmic protein LptA to the LptDE complex, which inserts fully assembled LPS to the outer leaflet of the OM through an as-yet-uncharacterized process (13, 18). The transporters studied to date are essential for viability in Escherichia coli, and their downregulation leads to morphological changes consistent with interruption of LPS transport/assembly (15, 19, 20). Coincident with the improved understanding of the LPS transport/assembly process, a recent report (21) described a peptide-based inhibitor of LptD with very potent cellular activity against P. aeruginosa.
OM integrity is maintained in part by cross-linking of LPS between negative charges of phosphates on lipid A and inner core with Mg2+ ions (22, 23). The first l-glycero-d-manno-heptose (HepI) residue of the inner core in E. coli and Salmonella enterica LPS contains a single phosphate at the O-4 position that is not essential for growth. However, deletion of the gene encoding the WaaP (previously RfaP) kinase responsible for addition of this phosphate engenders the so-called deep-rough phenotype (24–26), typical of that caused by mutational loss of inner-core sugars. This phenotype includes hypersensitivity to hydrophobic antibiotics and loss of virulence, reflecting disruption of the OM permeability barrier (22). WaaP phosphorylates nascent lipid A-core at the cytoplasmic side of the IM prior to MsbA-mediated transport of lipid A-core to the periplasmic side of the IM (27, 28).
The inner core of P. aeruginosa LPS (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) is heavily phosphorylated, with 3 to 6 phosphates (29, 30). Reflecting this, P. aeruginosa waaP occurs within a gene cluster containing LPS sugar transferase genes waaF, waaC, and wapG; two other LPS kinase genes, wapP and wapQ; and a putative LPS kinase gene, PA5006 (8, 23) (Fig. 1A). In contrast to E. coli and S. enterica, waaP and wapP were inferred to be essential, based on an inability to inactivate either gene in P. aeruginosa (23). P. aeruginosa waaP can mediate the phosphorylation of the HepI O-4 position when introduced into a Salmonella waaP-knockout strain (23). The second essential HepI phosphate of P. aeruginosa LPS is thought to be added by WapP (23, 28). Transformation of either waaP or wapP into a Salmonella waaP-knockout strain dramatically increased resistance to sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and novobiocin (23), consistent with LPS core phosphorylation. The inability to create genetic deletions of waaP in P. aeruginosa suggested a role for LPS phosphorylation beyond OM cross-linking, but its requirement for viability precluded further studies in P. aeruginosa. Here, we employed an arabinose-inducible expression system (pBAD) to characterize the cellular impact of depletion of WaaP and WapP/WapQ/PA5006 directly in the native P. aeruginosa PAO1 (K767) background.
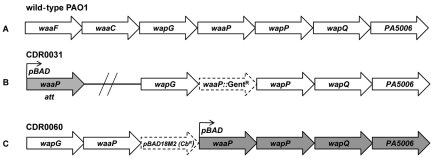
FIG 1 .
Genetic organization of waaP in wild type, CDR0031, and CDR0060. (A) The four proposed LPS kinase genes waaP, wapP, wapQ, and PA5006 are annotated as a single operon among other LPS synthesis genes in P. aeruginosa PAO1. (B and C) Genetic arrangement of arabinose-regulated LPS kinase strains; the arabinose promoter (pBAD) controls expression of waaP in strain CDR0031 (B) and expression of wapP, wapQ, and PA5006 in strain CDR0060 (C). The arabinose-regulated copy of waaP in CDR0031 was inserted at a nonessential chromosomal att site, and the native copy of waaP was insertionally inactivated by a gentamicin resistance cartridge. Expression of waaP in CDR0060 is controlled by its native promoter upstream of waaF as in panel A, and a second waaP copy, generated by pBAD18M2 integration into the chromosome, is arabinose controlled.
RESULTS
WaaP is essential for growth in P. aeruginosa PAO1.
To characterize the role of inner-core kinases of P. aeruginosa PAO1, we regulated the expression of waaP (CDR0031) and wapP/wapQ/PA5006 (CDR0060) using an arabinose-inducible promoter system (pBAD) in a single copy on the chromosome. Growth of strains CDR0031 and CDR0060 required supplementation of the medium with l-arabinose (Fig. 2), directly demonstrating that WaaP and at least one other kinase (WapP, WapQ, or PA5006) are essential for growth in P. aeruginosa. A genetic knockout of wapQ was reported, while attempts to inactivate WapP proved unsuccessful (23), suggesting that the failure of CDR0060 to grow resulted from loss of WapP. However, some contribution to viability might be provided from the putative kinase PA5006.
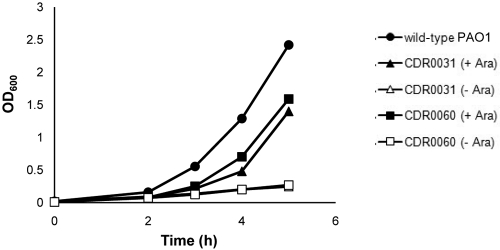
FIG 2 .
Growth of CDR0031 and CDR0060 is dependent on l-arabinose. Growth of wild-type PAO1 and l-arabinose-controlled-expression waaP (CDR0031) and wapP/wapQ/PA5006 (CDR0060) strains was measured by monitoring OD600 after their subculture with (+) and without (−) 0.2% l-arabinose. Strains CDR0031 and CDR0060 cultured with l-arabinose grow slightly slower than wild-type PAO1, suggesting that wild-type expression levels of waaP or wapP/wapQ/PA5006 were not achieved with full induction.
Core kinase depletion causes accumulation of LPS having a truncated core.
When cultured without l-arabinose, strains CDR0031 and CDR0060 stopped growing after several generations, allowing isolation of kinase-depleted cells that presumably accumulate LPS lacking one or more core HepI phosphates. Total LPS isolated from kinase-depleted cells had an additional band of LPS compared to wild-type LPS (Fig. 3A, lanes 3 and 5). These species migrated faster than did the wild-type lipid A-core band and slightly slower than the truncated lipid A-core band of a defined P. aeruginosa galU knockout (Fig. 3A, lane 6). GalU is the glucose-1-phosphate uridylyl transferase needed to synthesize UDP-glucose. Correspondingly, LPS from the galU mutant terminates at the galactosamine residue due to loss of the distal outer-core glucoses depicted in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material (29, 31). The truncated LPS species observed from WapP/WapQ/PA5006 depletion (CDR0060) migrated slightly faster than that from WaaP depletion (CDR0031; compare lanes 3′ and 5′ in Fig. 3A).
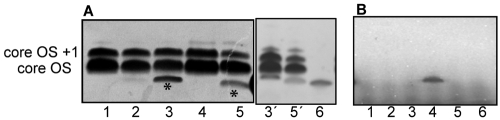
FIG 3 .
LPS derived from CDR0031 and CDR0060 contains truncated LPS. (A) Total LPS was isolated and visualized by silver staining after SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, wild-type PAO1; lane 2, CDR0031 + Ara; lanes 3 and 3′, CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted); lane 4, CDR0060 + Ara; lanes 5 and 5′, CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted); lane 6, galU knockout (PAO1). Note the accumulation of truncated LPS species (*, lanes 3 and 5) when waaP or wapP/wapQ/PA5006 was downregulated (−Ara). (B) WaaP kinase (lanes 2, 4, and 6) and control (lanes 1, 3, and 5) reaction mixtures with total LPS and [γ-33P]ATP. Lanes 1 and 2, wild-type PAO1 LPS; lanes 3 and 4, CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted) LPS; lanes 5 and 6, CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted) LPS.
To determine whether the truncated LPS from the WaaP-depleted strain lacked the HepI 4-phosphate, purified P. aeruginosa WaaP kinase and [γ-33P]ATP were incubated with the total LPS isolated from strain CDR0031. A strong 33P-labeled band (Fig. 3B) was observed at the position of the truncated LPS species (Fig. 3A, lane 3), suggesting that only the truncated LPS lacked the HepI 4-phosphate normally added by WaaP. We observed no 33P incorporation with the truncated LPS derived from CDR0060 in the in vitro WaaP reaction, consistent with this species already having the HepI 4-phosphate.
Truncated LPS with unphosphorylated core is not transported to the OM.
Since WaaP is uniquely essential in P. aeruginosa, we surmised that truncated LPS lacking core phosphates might not be recognized by downstream transport/assembly machinery and would fail to reach the OM. Supporting this, LPS from OM prepared by Sarkosyl extraction of total membranes lacked the truncated LPS bands (Fig. 4A). Sucrose density gradient separation of the IM and OM confirmed that the truncated LPS species for both kinase-depleted strains were localized primarily in the IM fraction (Fig. 4B). A faint band of truncated LPS was visible in OM fractions from both procedures when the LPS sample was overloaded. This may represent low levels of transport of truncated LPS to the OM and/or minor contamination of IM in the OM preparation. Nonetheless, the presence of the truncated LPS overwhelmingly in the IM fraction implies failure of the downstream LPS transport machinery to recognize this species.
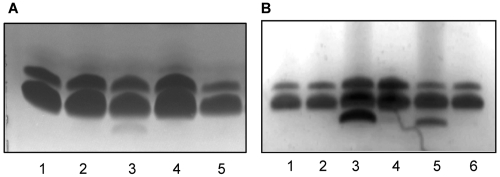
FIG 4 .
Truncated LPS of CDR0031 and CDR0060 is localized to the IM. SDS-PAGE of LPS isolated from Sarkosyl-extracted OM (A) or from IM and OM fractions (B). (A) Lane 1, wild-type PAO1; lane 2, CDR0031 + Ara; lane 3, CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted); lane 4, CDR0060 + Ara; lane 5, CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted). (B) Lane 1, wild-type PAO1 IM LPS; lane 2, wild-type PAO1 OM LPS; lane 3, CDR0031 IM LPS (−Ara, WaaP-depleted); lane 4, CDR0031 OM LPS (−Ara, WaaP-depleted); lane 5, CDR0060 IM LPS (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted); lane 6, CDR0060 OM LPS (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted).
Cellular depletion of core kinases leads to an abnormal IM.
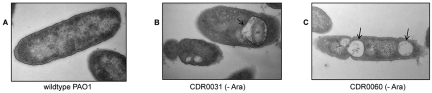
Cells depleted of WaaP or WapP/WapQ/PA5006 revealed gross morphological defects, including severe IM invaginations (standard transmission electron microscopy [TEM] [Fig. 5] and high-pressure-freeze [HPF]-substitution TEM [see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material]). The IM invaginations form large membrane-bound or “vacuole-like” compartments that appear to contain periplasmic material, reminiscent of plasmolysis induced by severe osmotic shock (32, 33). It is noteworthy that the kinase-depleted cells were isolated directly from rich growth medium and immediately fixed or processed for freeze substitution. The cells were not exposed to conditions of osmotic shock, and the similar images obtained using two different electron microscopy (EM) techniques suggest that this phenomenon is not an artifact of EM preparative procedures.
FIG 5 .
Morphological changes to P. aeruginosa cells upon depletion of LPS core kinases. Cells were examined by standard TEM. (A) Wild-type PAO1; (B) CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted); (C) CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted). Severe perturbations (lengthening and invaginations) of the IM (indicated by arrows) were observed for WaaP- and WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted cells, consistent with accumulation of truncated LPS which is not exported to the OM.
Identification of truncated LPS core species from kinase-depleted cells.
To characterize the truncated LPS species accumulating in strains depleted of core kinase activity, LPS was isolated from the IM fractions obtained from wild-type PAO1, WaaP-depleted (CDR0031), and WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted (CDR0060) cells. Core oligosaccharides were isolated and analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). For wild-type PAO1, CDR0031, and CDR0060 LPS, core peaks consistent with the expected uncapped-core glycoforms (8, 30, 34) were detected (see Table S1 and Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). The peaks were consistent with the [M-2H]2− and [M-3H + Na]2− ions of the expected wild-type LPS cores lacking O antigen (Table S1). The mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) values of most peaks were consistent with Rha-Glc4-GalN(Ala)-Hep(Cm)-Hep-Kdo (Cm is carbamoyl and Kdo is 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid) with a range of 2 to 5 phosphates. The absence of phosphoethanolamine is consistent with the LPS isolation procedure used as noted previously (29). The detection of core in the IM fraction of wild-type PAO1 is consistent with Fig. 4B.
The ESI-MS spectrum for core isolated from WaaP-depleted, IM-derived LPS (enriched for the truncated species) had major novel peaks at m/z 783.2 and 765.2 (Table 1; see also Fig. S3B in the supplemental material). The exact masses of these singly-charged species are consistent with the [M-H]− ion of the unique truncated core: Hex-Hep2-Kdo and its anhydro-Kdo derivative, respectively (35). Assuming the presence of two Kdo units before hydrolysis, this putative pentasaccharide core lacks all phosphates. The carbamate and alanine moieties present on wild-type and galU mutant core (Table S1) (8, 29) are also absent. The proposed core composition of Hex-Hep2-Kdo also indicates that the outer-core galactosamine (GalN), usually linked to HepII, is missing and an as-yet-unidentified hexose is present in the core. The identity, linkage analysis, and anomeric configuration of this hexose remain to be determined. Minor novel peaks at m/z 853.3 and 835.3 were also detected (Table 1; see also Fig. S3B). The exact masses of these singly-charged species are consistent with the [M-H]− ion of the unique truncated core: GalN(Ala)-Hep2-Kdo and its anhydro-Kdo derivative, respectively. This minor pentasaccharide core also lacks all phosphates and carbamate moieties.
TABLE 1 .
Observed masses and proposed compositions for truncated cores observed by ESI-MS
| Strain | Proposed structureb | Calculated m/z | Observed m/za |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDR0031 (WaaP-depleted) | [HexHep2Kdo-H]− | 783.24 | 783.2 |
| [HexHep2anhydroKdo-H]− | 765.23 | 765.2 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep2Kdo-H]− | 853.29 | 853.3 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep2anhydroKdo-H]− | 835.28 | 835.3 | |
| CDR0060 (WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted) | [HexHep2Kdo-H]− | 783.24 | 783.2 |
| [HexHep2anhydroKdo-H]− | 765.23 | 765.2 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepPKdo-H]− | 976.27 | 976.3 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepPKdo-2H]2− | 487.63 | 487.6c | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepPanhydroKdo-H]− | 958.26 | 958.3 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepPanhydroKdo-2H]2− | 478.62 | 478.6c | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepP2Kdo-2H]2− | 527.61 | 527.6 | |
| [GalN(Ala)Hep(Cm)HepP2anhydroKdo-2H]2− | 518.61 | 518.6 |
Peaks identified by negative-ion ESI-MS with an m/z scan (60 to 2,200) were subject to enhanced-resolution ESI-MS to determine exact mass and charge state (data not shown).
Only assignable peaks with unambiguous exact masses and charge states are listed.
A second Kdo residue, which is cleaved as a result of acid hydrolysis during core preparation (35), would be present in the intact core.
Peaks observed by enhanced-resolution ESI-MS but not shown in Fig. S3C in the supplemental material.
ESI-MS examination of IM-derived LPS core isolated from the wapP/wapQ/PA5006-downregulated strain CDR0060 (Table 1; see also Fig. S3C in the supplemental material) revealed peaks consistent with truncated cores with compositions of GalN(Ala)-HepII(Cm)-HepI-P-Kdo and GalN(Ala)-HepII(Cm)-HepI-P2-Kdo (and their corresponding anhydro-Kdo derivatives). These species are similar to those observed in the galU mutant (29) except with only 1 or 2 core phosphates, instead of 3 to 6. The presence of phosphates in the core suggests that WaaP is active in the CDR0060 background. The second core phosphate present could reflect nonuniform downregulation of the three kinases in this strain or phosphorylation by an unidentified kinase. The additional negative charge(s) may explain the faster migration of the truncated LPS from strain CDR0060 compared to that from CDR0031 (Fig. 3A). Unexpectedly, the major nonphosphorylated, truncated core species seen upon WaaP depletion (see above) were also seen here (Table 1; see also Fig. S3C), and this remains unexplained.
Kinase depletion induces lipid A modification.
To see if lipid A modification systems are activated upon WaaP depletion, lipid A was isolated from wild-type PAO1 and WaaP-depleted CDR0031 cells and analyzed by ESI-MS. Wild-type PAO1 LPS (see Fig. S4A in the supplemental material) had both penta-acylated species (m/z 722.5 and 730.5) and hexa-acylated species (m/z 807.6 and 815.6) as expected (8) (see also Fig. S5). Interestingly, loss of WaaP leads to modification of the lipid A species by 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose (l-Ara4N), singly and doubly (Fig. S4B), at the 1- and/or 4′-phosphate of the lipid A diglucosamine backbone (Fig. S5). This modification is mediated by ArnT on the periplasmic leaflet of the IM (8). Modification was also observed for WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted cells (data not shown). Although decreases in OM stability/lipid perturbations have been shown to lead to secondary acylation (palmitate addition) of lipid A (21, 36), data from ESI-MS analysis showed no significant differences in acylation between wild-type and WaaP-depleted cells.
IM and OM phospholipid and lipid A analysis.
IM and OM samples from wild-type and WaaP-depleted cells have similar amounts of normal LPS (Fig. 4B), with the additional truncated species present only in the IM from strain CDR0031. The presence of penta-acylated lipid A in the IM fraction (see Fig. S6A in the supplemental material) is diagnostic of OM contamination because penta-acylated LPS is formed in the OM by the action of PagL (8, 37). ESI-MS spectra for lipid A from WaaP-depleted cells showed a significant amount of l-Ara4N-modified lipid A in both IM and OM fractions (Fig. S6). Therefore, l-Ara4N modification is not specific to the truncated LPS localized in the IM fraction. The WaaP-deficient cells should have more LPS in their IM fractions than should the wild-type cells, due to the presence of the additional truncated LPS species. Reflecting this, the ratio of lipid A to phospholipid in the IM is larger for WaaP-depleted cells than for wild-type cells (Fig. S6A); however, the IM did not have a comparatively lower fraction of l-Ara4N-modified lipid A, suggesting that the truncated LPS was also l-Ara4N modified at the periplasmic leaflet of the IM.
Effect of core kinase depletion on EDTA and antibiotic susceptibility.
To see if depletion of WaaP compromised the OM in P. aeruginosa, we tested the susceptibilities of CDR0031 and CDR0060 to EDTA, the hydrophobic antibiotic novobiocin, and a polycationic antimicrobial peptide, polymyxin B, in media supplemented with high (0.2%) or low (0.04%) l-arabinose (Table 2). CDR0031 supplemented with low l-arabinose was 32-fold more sensitive to EDTA and 4-fold more sensitive to novobiocin than was wild-type PAO1. Wild-type susceptibility to both compounds was restored with addition of 0.2% l-arabinose. We also noted an increase in sensitivity to polymyxin B (ca. 16-fold) upon waaP downregulation in P. aeruginosa. Strain CDR0060 also became more susceptible to antibiotics under low-l-arabinose conditions; however, this effect appeared to be less pronounced than for strain CDR0031.
TABLE 2 .
MIC determinationsa
| Strain | MIC of: |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA (mM) | Novobiocin (µg/ml) | Polymyxin B (µg/ml) | |
| PAO1 | 10 | 625–1,250 | 0.5–1 |
| CDR0031 + 0.2% Ara | 5–10 | 625 | 0.25 |
| CDR0031 + 0.04% Ara | 0.3125–0.625 | 156 | 0.03125–0.0625 |
| CDR0060 + 0.2% Ara | 0.625–0.125 | 625 | 0.25 |
| CDR0060 + 0.04% Ara | 0.3125–0.625 | 312–625 | 0.125 |
Values are from at least two determinations. Because of a high frequency of reversion to wild type, MIC testing with the wapP/wapQ/PA5006-regulated strain CDR0060 was supplemented with 300 µg/ml carbenicillin to maintain arabinose-controlled expression of LPS kinases.
DISCUSSION
Phosphorylation of the LPS inner core by WaaP is important for maintaining the OM permeability barrier of E. coli and S. enterica (23, 25, 26). Loss of waaP in E. coli R1 strain F470 (lacking O antigen) and in S. enterica also caused loss of HepIII, loss of inner-core phosphates on HepI and HepII, and decreased efficiency in O-antigen attachment (S. enterica) (25, 26). Altered core structure and reduced O-antigen attachment were also reported for transposon-mediated disruption of waaP in Shigella flexneri (38). These waaP mutants were, however, viable, and for S. enterica, production of full-length LPS was noted without a growth defect (25). In contrast, attempts to inactivate waaP in P. aeruginosa were unsuccessful (23). Here, we show directly that WaaP is essential for growth using a recombinant P. aeruginosa strain harboring an l-arabinose-inducible waaP gene. This allowed the depletion of WaaP, which caused the accumulation of a truncated species of LPS. MS analysis of core showed that loss of WaaP prevents all core phosphorylation and blocks completion of full-length core. It was suggested that the P. aeruginosa OM was uniquely dependent on maintaining LPS cross-links and that their loss would destabilize the membrane of P. aeruginosa, accounting for the essential nature of WaaP (23). However, our data support an alternative explanation, i.e., that the altered LPS produced in the absence of WaaP is not recognized by the LPS transport and OM assembly machinery. EM images of these cells revealed gross changes to the IM, consistent with a defect in LPS trafficking or, alternatively, continued synthesis of IM (containing the aberrant LPS) after cessation of OM synthesis. Similar observations with a strain downregulated for WapP/WapQ/PA5006 suggest that the HepI 4-phosphate transferred by WaaP may not be the specific factor mediating recognition by the transport machinery. Nonetheless, our data clearly showed that WaaP is a prerequisite for synthesis of efficiently transportable LPS in P. aeruginosa.
The P. aeruginosa OM is less permeable than that of other Gram-negative bacteria (39). It is difficult to assess the direct impact of WaaP depletion on the OM itself, which appears largely intact in several cells examined by EM. However, loss of WaaP appears to increase sensitivity to the hydrophobic antibiotic novobiocin (Table 2). This increase is relatively small compared to that reported for waaP genetic knockouts created in E. coli and S. enterica (23, 25, 26, 28), but this may reflect partial WaaP loss due to downregulation. Sensitivity to EDTA may result from a general defect in new LPS reaching the OM, providing less cross-linked LPS overall, increasing susceptibility to Mg2+ chelation.
Reduction in LPS negative charge via l-Ara4N decoration of the lipid A moiety has been linked to reduced susceptibility to cationic peptides, including polymyxin B (40). Lipid A from an S. enterica waaP knockout lacked l-Ara4N modification (25), whereas we show that lipid A from the WaaP-depleted P. aeruginosa cells was modified. Susceptibility to polymyxin B was increased in both cases, suggesting that any contribution of lipid A modification to polymyxin resistance in P. aeruginosa is outweighed by the loss of core phosphates. Perhaps consistent with this, the membrane-defective hypersusceptible P. aeruginosa strain Z61 also had l-Ara4N modification of the LPS and increased susceptibility to polymyxin B (41).
The precise location of the aberrant LPS resulting from loss of core phosphates is not known. There is no obvious accumulation of membranous material in the periplasm in our EM images as observed for E. coli strains downregulated for Lpt components (15) and for P. aeruginosa cells treated with an inhibitor of LptD (21). The truncated LPS was isolated primarily in the IM fraction, and the apparent lengthening of the IM is more consistent with specific IM localization. P. aeruginosa lipid A-core chemically stripped of all phosphates (including the lipid A phosphates) failed to stimulate the ATPase activity of isolated P. aeruginosa MsbA in vitro (16), but this could not be attributed to a particular phosphate(s). In our electron micrographs, there was no obvious blebbing on the inner leaflet of the IM previously seen with MsbA temperature-sensitive mutants of E. coli (20). This suggests that the LptBCFG complex may not recognize the truncated LPS. Furthermore, the evidence for l-Ara4N modification of the truncated LPS, which is reported to occur at the outer leaflet of the IM (40), implies that this species could be trapped in the periplasmic leaflet; however, the specific location and the underlying basis for the proposed LPS transport defect await further investigation.
Taken together, our data indicate that WaaP is necessary for the completion of LPS synthesis and OM assembly in P. aeruginosa and may therefore be a good target for the discovery of novel therapeutics targeting P. aeruginosa.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and growth media.
All bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers used in this study are listed in Tables S2 and S3 in the supplemental material. Lysogeny broth (L broth) (tryptone, 10 g/liter; yeast extract, 5 g/liter; NaCl, 10 g/liter) or L agar was used for routine growth of E. coli and P. aeruginosa at 37°C unless otherwise specified. l-Arabinose-dependent strains CDR0031 (gentamicin resistant) and CDR0060 (carbenicillin resistant) are derivatives of the wild-type P. aeruginosa strain PAO1. As necessary, 0.2% l-arabinose and gentamicin (10 µg/ml for E. coli and 100 µg/µl for P. aeruginosa), ampicillin (100 µg/ml for E. coli), carbenicillin (300 µg/µl for P. aeruginosa), or tetracycline (10 µg/ml for E. coli or 100 µg/ml for P. aeruginosa) were added to growth medium.
DNA manipulations.
Oligonucleotides were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. (Coralville, IA), and DNA sequencing was carried out by Agencourt Inc. (Bedford, MA). PCR was carried out using AccuPrime GC DNA polymerase (Invitrogen), Vent DNA polymerase (NEB), or Phusion High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (NEB), according to the supplier’s instructions. DNA fragments were purified using QIAquick PCR cleanup or gel extraction kits (Qiagen).
Construction of pMini-CTX derivative with pBAD-waaP expression system.
Plasmid pBAD18M2 is a derivative of pBAD18 with an altered ribosome binding site (RBS) and HindIII site addition to the araC-pBAD promoter segment as described previously for plasmid pBEM10 (12). The waaP gene was PCR amplified with primers waaPupHind and waaPrevXmaI, using Phusion DNA polymerase (NEB) to generate blunt ends. This fragment was digested with HindIII and ligated into pBAD18M2 that had been cut with XhoI, blunt ended, and then cut with HindIII. The resultant plasmid pBADM2-waaP had waaP with 132 bp of upstream untranslated sequence, placed in the correct orientation for regulated expression from the pBAD promoter, with an XmaI site introduced downstream of waaP. A mini-CTX derivative of the pBAD-regulated waaP construct, for placement on the P. aeruginosa genome, was then made as follows. Plasmid pRC7 was constructed as a general mini-CTX vector for placing pBAD-regulated constructs into the genome. For this, the luxCDABE genes from mini-CTX-lux (42) were removed with SalI-EcoRV and swapped with an XhoI-HpaI fragment encompassing an araC-pBAD promoter fragment derived from a synthetic plasmid, pGA18-pBAD (GeneArt AG, Burlingame, CA). The final construct used for placing a regulated copy of waaP into the att site (pRC8) was made by swapping an EcoRV-XmaI fragment from pBAD18M2-waaP (encompassing part of araC through waaP) into the pRC7 vector from which the corresponding partial araC-pBAD fragment had been removed by digestion with EcoRV and XmaI.
Construction of the WaaP controlled-expression strain CDR0031.
The pBAD-waaP construct was inserted into the genome of P. aeruginosa PAO1, using the E. coli mobilizer strain S17-1, and confirmed as described previously (43, 44). The native waaP gene was then inactivated as follows: the waaP gene was generated from PAO1 using primers waaPforHind and waaPrevBam, digested with HindIII and BamHI, and ligated into similarly digested pEX18Tc (45). The aacC1 gentamicin resistance cartridge (isolated from pUCGm [46] with SalI) was ligated into the unique XhoI site within waaP in the same orientation as the waaP gene to generate plasmid pRC10. Plasmid pRC10 was used to disrupt waaP on the genome of P. aeruginosa as described previously (47), using the E. coli mobilizer strain S17-1 (44). Recombinants lacking plasmid backbone were isolated by streaking merodiploid colonies onto L agar with 5% sucrose, 0.2% l-arabinose, and 100 µg/ml gentamicin. Colonies were tested for gentamicin resistance and tetracycline sensitivity. To identify native waaP inactivation, the location of aacC1 was determined using PCR with primer pairs waaPXhoI and waaPoutr (native) and PaaraC and PawaaPXho (pBAD regulated). One isolate, CDR0031, had the aacC1 cartridge within the native waaP copy and retained the intact pBAD-regulated copy with a 132-bp upstream leader sequence (Fig. 1B).
Construction of the WapP/WapQ/PA5006 controlled-expression strain CDR0060.
Strain CDR0060 was constructed using a procedure based on that reported previously for creation of a controlled-regulation strain for LpxC (12). Plasmid pBAD18M2-waaP, described above, was introduced into PAO1 using electroporation (48). Plasmid pBAD18M2-waaP cannot replicate in P. aeruginosa, and therefore, carbenicillin-resistant colonies arise from integration of the plasmid into the chromosome. Because pBAD18M2-waaP has the entire waaP gene rather than a partial fragment, it will generate an insertion, leaving the native copy of waaP intact and having waaP, wapP, wapQ, and PA5006 under the control of the pBAD promoter (Fig. 1C). Since the native waaP is preserved, only wapP, wapQ, and PA5006 are regulated by the pBAD promoter. Putative regulated strains were identified by testing for arabinose-dependent growth, and for one such colony (CDR0060), the presence of the regulated waaP gene was confirmed by colony PCR using primers PaaraC and waaPoutf.
Cellular depletion of LPS kinases from strains CDR0031 and CDR0060.
Cultures of wild-type PAO1, CDR0031 (gentamicin, 100 µg/µl), and CDR0060 (carbenicillin, 300 µg/µl), with 0.2% l-arabinose added for CDR0031 and CDR0060, were grown overnight. These were then subcultured into fresh medium (with and without 0.2% l-arabinose) to a starting optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.01 (CDR0060) or 0.02 (PAO1 and CDR0031). Growth was monitored by OD600 over time. Typically, growth of the arabinose-dependent CDR0031 and CDR0060 cultures substantially leveled off at an OD600 of ~0.4 (at 5 h) in arabinose-free medium, compared to the wild-type PAO1 strain or CDR0031 and CDR0060 in arabinose-containing cultures, which continued to grow normally (Fig. 2). Presumably, culture growth leveled off due to the gradual depletion of the kinase proteins during cell doublings. For characterization of cells depleted of WaaP or WapP/WapQ/PA5006, the cells were harvested by centrifugation (at 3,000 × g, 10 min) from cultures without l-arabinose after leveling off to an OD600 of ~0.4 (5 h). For comparisons, cells from wild-type PAO1 cultures were always harvested at a similar OD600 as that of LPS kinase-depleted cells.
Total LPS isolation and analysis by SDS-PAGE.
Wild-type PAO1, CDR0031, and CDR0060 were grown and harvested as described above. Cell pellets were resuspended in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) containing 2 mM MgCl2, DNase (100 µg/ml), and RNase (25 µg/ml) and lysed in a French pressure cell (2 passes at 15,000 lb/in2). Total LPS was isolated as previously described (49). LPS samples were analyzed after being resolved by SDS-PAGE in precast 12% bis-Tris NuPAGE gels (Invitrogen) and visualized by silver staining (Bio-Rad).
Sarkosyl-extracted OM preparation and LPS isolation.
Outer membranes were prepared as described previously (50, 51) from cells prepared and lysed as described above. Unbroken cells were removed by low-speed centrifugation (at 3,000 × g, 10 min), and the IM was solubilized by addition of 1% Sarkosyl and incubation for 1 h at 30°C. OM was isolated by centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 1 h and resuspended in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0). Proteins were removed from isolated OM by digestion with proteinase K (200 µg/ml) overnight at 37°C. LPS was analyzed as described above.
Sucrose density gradient separation of IM and OM and LPS isolation.
Cell pellets were resuspended in cold 20% (wt/vol) sucrose in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 µg/ml DNase I, and frozen at −80°C. Cell lysate was prepared as described above, and separation of IM and OM was carried out as described previously (52). Briefly, overnight ultracentrifugation (260,000 × g) of the cell lysate over a 2-step sucrose gradient of 4 ml 70% (wt/vol) sucrose cushion layered with 4 ml 60% (wt/vol) sucrose separated IM (reddish) and OM (white) fractions. IM and OM fractions were collected separately and diluted with water to a final sucrose concentration of <20% and centrifuged again (260,000 × g, 1 h) to pellet membranes. For crude LPS isolation, IM or OM samples were resuspended in water and digested with proteinase K (0.25 μg/μl) in 1× NuPAGE loading buffer (Invitrogen) for 3 h at 60°C. IM or OM LPS was analyzed as described above.
Phosphorylation of LPS using [γ-33P]ATP and purified P. aeruginosa WaaP.
Kinase reaction mixtures (15 µl total) contained 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 15 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1.0 µCi [γ-33P]ATP diluted with 10 µM unlabeled ATP, and ~3.5 µg total LPS isolated from wild-type PAO1, CDR0031, and CDR0060, depleted of LPS kinases. Reactions were initiated by addition of 750 ng purified P. aeruginosa WaaP (see Text S1 in the supplemental material), reaction mixtures were incubated for 2 h at room temperature, and reactions were stopped by addition of 5 µl 4× NuPAGE sample loading buffer (Invitrogen). For separation of LPS species after incubation with WaaP (or water), the total volume of each kinase reaction mixture was loaded on a 10-well precast 12% bis-Tris NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen) run at 200 V for 45 min, followed by drying of the gel for 45 min at 80°C. Incorporation of [γ-33P]ATP into LPS was detected by exposure of the gel to Kodak BioMax XAR film for 30 h and development with a Kodak X-OMAT 2000A film processor.
Lipid A isolation.
Lipid A was isolated from cell pellets based on a previous protocol (53) (see details in Text S1 in the supplemental material) and stored at −20°C until needed. For IM and OM samples, the pooled IM or OM fractions from sucrose density gradient centrifugation were directly hydrolyzed with 1% acetic acid to release the lipid A and then extracted with chloroform (as described in Text S1). The samples contain both phospholipids and lipid A.
ESI-MS of lipid A.
Lipid A mass spectra were acquired on a 4000 QTRAP hybrid triple-quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer equipped with a Turbo V ion source (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) utilizing the TurboIonSpray probe for ESI (full method details in Text S1 in the supplemental material). Briefly, spectra were collected in the negative-ion mode over a full-scan m/z from 60 to 2,200 with a quadrupole 3 (Q3) scan (0.2-atomic-mass-unit [amu] step size, 4.3 s/scan, acquired for 1 to 4 min/sample). To determine each peak’s exact mass with isotopic resolution, the default enhanced-resolution scan was employed (acquisition time, 1 to 4 min/sample), centered on the m/z for the peak of interest. With exact masses identified for peaks of interest, tandem MS spectra were acquired with the default product ion (MS2) scan of the appropriate m/z range for each species (0.1- to 0.2-amu step size, 1 to 5 s/scan, acquisition time of 1 to 4 min/sample). Data acquisition and analysis were performed with Analyst 1.4.2 software (Applied Biosystems).
ESI-MS of LPS core.
To isolate the core oligosaccharide, IM LPS samples (isolated as described above from 500-ml cultures; OD600 of 0.4 to 0.5) were incubated with 1.5% acetic acid for 2 h at 100°C (final volume, 1 ml), cooled to room temperature, and centrifuged (16,200 × g, 10 min) to pellet the aggregated free lipid A released by mild acid hydrolysis. The supernatant, containing the core, was removed and stored at −80°C until needed. For ESI-MS analysis, the samples containing the free core were thawed and diluted (generally 5- to 50-fold, as needed) with water to a volume of 500 µl and piperidine was added to a final concentration of 1% (vol/vol). Each sample was analyzed with ESI-MS as described for lipid A (see Text S1 in the supplemental material) with minor modifications: declustering potential (DP) was −60 V and the nebulizer gas (GS1) was 35 lb/in2. Enhanced-resolution and tandem MS were then performed as described for lipid A. Data acquisition and analysis utilized Analyst 1.4.2 software (Applied Biosystems).
Electron microscopy.
Cells were harvested at an OD600 of ~0.4 and fixed with a mixture of 2.5% glutaraldehyde and 2% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer (CB), pH 7.4, for 2 h at room temperature. Chemically fixed samples were washed in 0.1 M CB and postfixed with 1% osmium tetroxide (OsO4)-1.5% potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN6)]) for 1 h, washed in water three times, and incubated in 1% aqueous uranyl acetate for 1 h and dehydrated in ascending grades of ethanol. The samples were then infiltrated and embedded in TAAB Epon (Marivac Canada Inc., St. Laurent, Canada) and polymerized at 60°C for 48 h. Ultrathin sections (60 to 80 nm) were cut, stained with lead citrate, and observed at 80 kV in a JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope. Images were recorded using an AMT 2k charge-coupled device (CCD) camera. Methods for HPF-substitution TEM are described in Text S1 in the supplemental material.
MIC determinations.
MIC values were determined according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines (54) with the following modification. The BBL Prompt kit (Difco) was used according to the provided protocol to prepare an inoculum of 1.5 × 108 CFU/ml from stationary-phase cells, which corresponds to a McFarland turbidity standard of 0.5. L broth was used instead of Mueller-Hinton broth, and l-arabinose was added, as indicated in Table 2, for growth of strains CDR0031 and CDR0060. Growth was assessed after approximately 18 h at 37°C.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplemental methods and references for supplemental tables. Download Text S1, PDF file, 0.147 MB.
Observed masses and proposed compositions for full-length cores observed by ESI-MS.
Bacterial strains and plasmids.
Oligonucleotide primers.
General structure for the capped-core glycoform of P. aeruginosa serotype 05 (PAO1) LPS. Dashed lines reflect nonstoichiometric substitutions. Note that the only inner-core phosphate whose position has been confirmed is that added by WaaP at position 4 of HepI. The uncapped core differs from the capped core in the arrangement of the outer core; the uncapped core is never substituted with O antigen, and the Rha residue is linked to GlcII instead of GlcI and contains a fourth outer-core Glc linked to Rha. Ala, alanine; Cm, carbamoyl; EtnP, phosphoethanolamine; GalN, 2-amino-2-deoxygalactose; Glc, glucose; Hep, l-glycero-d-manno-heptose; Kdo, 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid; Rha, rhamnose; P, phosphate. Download Figure S1, PDF file, 0.06 MB.
Morphological changes to P. aeruginosa cells upon depletion of LPS core kinases. Cells were examined by high-pressure freeze-substitution TEM. (A) Wild-type PAO1. (B) CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted). (C) CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted). Severe perturbations (lengthening and invaginations) of the IM (indicated by arrows) were observed for WaaP- and WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted cells, consistent with accumulation of truncated LPS which is not exported to the OM. Download Figure S2, PDF file, 1.739 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of the core species from IM LPS. Inner membrane LPS preparation, core isolation, and broad-scan ESI-MS (m/z, 60 to 2,200) for wild-type PAO1 (A), CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted) (B), and CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted) (C) are described in Materials and Methods. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown). The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each molecular ion, as summarized in Table 1 and Table S1 in the supplemental material. Only assignable peaks with unambiguous exact masses and charge states are annotated. The blue asterisk is consistent with a singly, negatively-charged dimer of SDS [M-H]−, as confirmed by enhanced-resolution ESI-MS and ESI-tandem MS. SDS is likely present as a contaminant from the preparation of LPS. Peaks annotated in red (B and C) correspond to proposed truncated core species. Proposed compositions for the annotated peaks are listed in Table 1 and Table S1. Download Figure S3, PDF file, 0.448 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of lipid A for wild-type PAO1 and CDR0031. Lipid A isolation and ESI-MS for wild-type PAO1 (A) and CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted) (B) are described in Materials and Methods. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown.) The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each lipid A molecular ion as described in Text S1 in the supplemental material. All annotated peaks are doubly negatively-charged [M-2H]2− and are consistent with known lipid A species (Fig. S5). In panel B, the peaks annotated with one or two asterisks are consistent with the presence of one or two l-Ara4N modifications, respectively. Download Figure S4, PDF file, 0.271 MB.
Pseudomonas lipid A structural variation. The invariant lipid A is shown in black. In red are the variable l-Ara4N modifications at the 1- or 4′-phosphates that are induced by LPS kinase depletion. In blue is the 3-O-acyl chain that can be removed by the outer membrane lipase, PagL, to yield 3-O-deacyl-lipid A. In green are the 2-hydroxyl units that can be added by LpxO homologs at the 2 and 2′ secondary acyl chains. These various modifications give rise to a diverse set of lipid A species. The predicted m/z values for all detected lipid A species [M-2H]2− ions are summarized in the box. The localization of the first l-Ara4N and/or 2-hydroxy modification, if there is any specificity, has not been determined. Download Figure S5, PDF file, 0.176 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of total lipids from wild-type PAO1 and CDR0031. The membrane preparation, separation, lipid isolation, and ESI-MS for inner membranes (A) and outer membranes (B) of wild-type PAO1 (blue trace) and CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted, red trace) are described in Materials and Methods. The lipid samples contained both phospholipids and free lipid A. The spectra in each panel were normalized (percentage of highest ion from full scan, 60 to 2,200 m/z), aligned, and overlaid with Analyst 1.4.2. The range below m/z 770 is not shown. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown). The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each lipid A molecular ion previously identified in Fig. S4 and described in Fig. S5. Peaks that are not annotated are singly, negatively-charged ions, and these are consistent with phospholipid species (phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine) of various acyl chain lengths. Download Figure S6, PDF file, 0.304 MB.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Maria Ericsson (Harvard Medical School EM Facility) and Dianne Moyles (University of Guelph) for TEM sample preparation and imaging, Xiaoyu Shen (NIBR) for plasmid pBAD18M2, Mohindra Seepersaud (NIBR) for assistance with lipid isolation, and Gregg Chenail (NIBR) for assistance with mass spectrometry. We also thank Lili Xie, Brian Vash, Rajiv Chopra, Travis Stams, Doriano Fabbro, Sovanda Som, and Lionel Muller (Novartis) for helpful discussions.
J.S.L. holds a Canada Research Chair in Cystic Fibrosis and Microbial Glycobiology, and research in his laboratory is funded by operating grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-14687) and Cystic Fibrosis Canada.
Footnotes
Citation DeLucia AM, et al. 2011. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inner-core phosphates are required for complete LPS synthesis and transport to the outer membrane in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. mBio 2(4):e00142-11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00142-11
REFERENCES
- 1. Rossolini GM, Mantengoli E. 2005. Treatment and control of severe infections caused by multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 11(Suppl. 4):17–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Govan JR, Deretic V. 1996. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol. Rev. 60:539–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Poole K. 2004. Efflux-mediated multiresistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10:12–26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Giamarellou H. 2010. Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: how to treat and for how long. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 36(Suppl. 2):S50–S54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hirsch EB, Tam VH. 2010. Impact of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection on patient outcomes. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 10:441–451 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Behrens-Kneip S. 2010. The role of SurA factor in outer membrane protein transport and virulence. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 300:421–428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Fito-Boncompte L, et al. 2011. Full virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires OprF. Infect. Immun. 79:1176–1186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. King JD, Kocincova D, Westman EL, Lam JS. 2009. Review: lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innate Immun. 15:261–312 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Raetz CR, Whitfield C. 2002. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:635–700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Anderson MS, et al. 1993. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli. The first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. J. Biol. Chem. 268:19858–19865 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. McClerren AL, et al. 2005. A slow, tight-binding inhibitor of the zinc-dependent deacetylase LpxC of lipid A biosynthesis with antibiotic activity comparable to ciprofloxacin. Biochemistry 44:16574–16583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Mdluli KE, et al. 2006. Molecular validation of LpxC as an antibacterial drug target in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:2178–2184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chng SS, Gronenberg LS, Kahne D. 2010. Proteins required for lipopolysaccharide assembly in Escherichia coli form a transenvelope complex. Biochemistry 49:4565–4567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ruiz N, Kahne D, Silhavy TJ. 2009. Transport of lipopolysaccharide across the cell envelope: the long road of discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7:677–683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Sperandeo P, et al. 2008. Functional analysis of the protein machinery required for transport of lipopolysaccharide to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 190:4460–4469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ghanei H, Abeyrathne PD, Lam JS. 2007. Biochemical characterization of MsbA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 282:26939–26947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Zhou Z, White KA, Polissi A, Georgopoulos C, Raetz CR. 1998. Function of Escherichia coli MsbA, an essential ABC family transporter, in lipid A and phospholipid biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 273:12466–12475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Chng SS, Ruiz N, Chimalakonda G, Silhavy TJ, Kahne D. 2010. Characterization of the two-protein complex in Escherichia coli responsible for lipopolysaccharide assembly at the outer membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107:5363–5368 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Braun M, Silhavy TJ. 2002. Imp/OstA is required for cell envelope biogenesis in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1289–1302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Doerrler WT, Reedy MC, Raetz CR. 2001. An Escherichia coli mutant defective in lipid export. J. Biol. Chem. 276:11461–11464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Srinivas N, et al. 2010. Peptidomimetic antibiotics target outer-membrane biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science 327:1010–1013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Schnaitman CA, Klena JD. 1993. Genetics of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in enteric bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 57:655–682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Walsh AG, et al. 2000. Lipopolysaccharide core phosphates are required for viability and intrinsic drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 35:718–727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Nagy G, et al. 2006. Down-regulation of key virulence factors makes the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium rfaH mutant a promising live-attenuated vaccine candidate. Infect. Immun. 74:5914–5925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Yethon JA, et al. 2000. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium waaP mutants show increased susceptibility to polymyxin and loss of virulence in vivo. Infect. Immun. 68:4485–4491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Yethon JA, Heinrichs DE, Monteiro MA, Perry MB, Whitfield C. 1998. Involvement of waaY, waaQ, and waaP in the modification of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide and their role in the formation of a stable outer membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 273:26310–26316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Yethon JA, Whitfield C. 2001. Purification and characterization of WaaP from Escherichia coli, a lipopolysaccharide kinase essential for outer membrane stability. J. Biol. Chem. 276:5498–5504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Zhao X, Lam JS. 2002. WaaP of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a novel eukaryotic type protein-tyrosine kinase as well as a sugar kinase essential for the biosynthesis of core lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4722–4730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Choudhury B, Carlson RW, Goldberg JB. 2005. The structure of the lipopolysaccharide from a galU mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serogroup-O11. Carbohydr. Res. 340:2761–2772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sadovskaya I, et al. 2000. Structural characterization of the outer core and the O-chain linkage region of lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O5. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:1640–1650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Dean CR, Goldberg JB. 2002. Pseudomonas aeruginosa galU is required for a complete lipopolysaccharide core and repairs a secondary mutation in a PA103 (serogroup O11) wbpM mutant. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 210:277–283 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Cook WR, MacAlister TJ, Rothfield LI. 1986. Compartmentalization of the periplasmic space at division sites in Gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 168:1430–1438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Lewenza S, Mhlanga MM, Pugsley AP. 2008. Novel inner membrane retention signals in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoproteins. J. Bacteriol. 190:6119–6125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Poon KK, Westman EL, Vinogradov E, Jin S, Lam JS. 2008. Functional characterization of MigA and WapR: putative rhamnosyltransferases involved in outer core oligosaccharide biosynthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 190:1857–1865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Olsthoorn MM, Haverkamp J, Thomas-Oates JE. 1999. Mass spectrometric analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ssp. pneumoniae rough strain R20 (O1-: K20-) lipopolysaccharide preparations: identification of novel core oligosaccharide components and three 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulopyranosonic artifacts. J. Mass Spectrom. 34:622–636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Smith AE, et al. 2008. PagP activation in the outer membrane triggers R3 core oligosaccharide truncation in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Biol. Chem. 283:4332–4343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Trent MS, Pabich W, Raetz CR, Miller SI. 2001. A PhoP/PhoQ-induced lipase (PagL) that catalyzes 3-O-deacylation of lipid A precursors in membranes of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 276:9083–9092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Rathman M, et al. 2000. The development of a FACS-based strategy for the isolation of Shigella flexneri mutants that are deficient in intercellular spread. Mol. Microbiol. 35:974–990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Hancock RE. 1998. Resistance mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other nonfermentative Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27(Suppl. 1):S93–S99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Raetz CR, Reynolds CM, Trent MS, Bishop RE. 2007. Lipid A modification systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76:295–329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Conrad RS, Boll M, Radziejewska-Lebrecht J, Galanos C. 1999. The occurrence of 4-amino-4-deoxy-arabinose in LPS of supersusceptible strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa Z61: noncorrelation with polymyxin resistance. Curr. Microbiol. 38:228–232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Becher A, Schweizer HP. 2000. Integration-proficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa vectors for isolation of single-copy chromosomal lacZ and lux gene fusions. Biotechniques 29:948–952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hoang TT, Kutchma AJ, Becher A, Schweizer HP. 2000. Integration-proficient plasmids for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: site-specific integration and use for engineering of reporter and expression strains. Plasmid 43:59–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Priefer UB, Simon R, Pühler A. 1985. Extension of the host range of Escherichia coli vectors by incorporation of RSF1010 replication and mobilization functions. J. Bacteriol. 163:324–330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP. 1998. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Schweizer HD. 1993. Small broad-host-range gentamycin resistance gene cassettes for site-specific insertion and deletion mutagenesis. Biotechniques 15:831–834 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Dean CR, et al. 1999. Characterization of the serogroup O11 O-antigen locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103. J. Bacteriol. 181:4275–4284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Choi KH, Kumar A, Schweizer HP. 2006. A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J. Microbiol. Methods 64:391–397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Darveau RP, Hancock RE. 1983. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J. Bacteriol. 155:831–838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Dean CR, Visalli MA, Projan SJ, Sum PE, Bradford PA. 2003. Efflux-mediated resistance to tigecycline (GAR-936) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:972–978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Masuda N, Sakagawa E, Ohya S. 1995. Outer membrane proteins responsible for multiple drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39:645–649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Hancock RE, Carey AM. 1979. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- and 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J. Bacteriol. 140:902–910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Six DA, Carty SM, Guan Z, Raetz CR. 2008. Purification and mutagenesis of LpxL, the lauroyltransferase of Escherichia coli lipid A biosynthesis. Biochemistry 47:8623–8637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. CLSI 2008. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 18th informational supplement, M100–MS18 CLSI, Wayne, PA [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental methods and references for supplemental tables. Download Text S1, PDF file, 0.147 MB.
Observed masses and proposed compositions for full-length cores observed by ESI-MS.
Bacterial strains and plasmids.
Oligonucleotide primers.
General structure for the capped-core glycoform of P. aeruginosa serotype 05 (PAO1) LPS. Dashed lines reflect nonstoichiometric substitutions. Note that the only inner-core phosphate whose position has been confirmed is that added by WaaP at position 4 of HepI. The uncapped core differs from the capped core in the arrangement of the outer core; the uncapped core is never substituted with O antigen, and the Rha residue is linked to GlcII instead of GlcI and contains a fourth outer-core Glc linked to Rha. Ala, alanine; Cm, carbamoyl; EtnP, phosphoethanolamine; GalN, 2-amino-2-deoxygalactose; Glc, glucose; Hep, l-glycero-d-manno-heptose; Kdo, 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid; Rha, rhamnose; P, phosphate. Download Figure S1, PDF file, 0.06 MB.
Morphological changes to P. aeruginosa cells upon depletion of LPS core kinases. Cells were examined by high-pressure freeze-substitution TEM. (A) Wild-type PAO1. (B) CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted). (C) CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted). Severe perturbations (lengthening and invaginations) of the IM (indicated by arrows) were observed for WaaP- and WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted cells, consistent with accumulation of truncated LPS which is not exported to the OM. Download Figure S2, PDF file, 1.739 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of the core species from IM LPS. Inner membrane LPS preparation, core isolation, and broad-scan ESI-MS (m/z, 60 to 2,200) for wild-type PAO1 (A), CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted) (B), and CDR0060 (−Ara, WapP/WapQ/PA5006-depleted) (C) are described in Materials and Methods. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown). The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each molecular ion, as summarized in Table 1 and Table S1 in the supplemental material. Only assignable peaks with unambiguous exact masses and charge states are annotated. The blue asterisk is consistent with a singly, negatively-charged dimer of SDS [M-H]−, as confirmed by enhanced-resolution ESI-MS and ESI-tandem MS. SDS is likely present as a contaminant from the preparation of LPS. Peaks annotated in red (B and C) correspond to proposed truncated core species. Proposed compositions for the annotated peaks are listed in Table 1 and Table S1. Download Figure S3, PDF file, 0.448 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of lipid A for wild-type PAO1 and CDR0031. Lipid A isolation and ESI-MS for wild-type PAO1 (A) and CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted) (B) are described in Materials and Methods. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown.) The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each lipid A molecular ion as described in Text S1 in the supplemental material. All annotated peaks are doubly negatively-charged [M-2H]2− and are consistent with known lipid A species (Fig. S5). In panel B, the peaks annotated with one or two asterisks are consistent with the presence of one or two l-Ara4N modifications, respectively. Download Figure S4, PDF file, 0.271 MB.
Pseudomonas lipid A structural variation. The invariant lipid A is shown in black. In red are the variable l-Ara4N modifications at the 1- or 4′-phosphates that are induced by LPS kinase depletion. In blue is the 3-O-acyl chain that can be removed by the outer membrane lipase, PagL, to yield 3-O-deacyl-lipid A. In green are the 2-hydroxyl units that can be added by LpxO homologs at the 2 and 2′ secondary acyl chains. These various modifications give rise to a diverse set of lipid A species. The predicted m/z values for all detected lipid A species [M-2H]2− ions are summarized in the box. The localization of the first l-Ara4N and/or 2-hydroxy modification, if there is any specificity, has not been determined. Download Figure S5, PDF file, 0.176 MB.
ESI-MS characterization of total lipids from wild-type PAO1 and CDR0031. The membrane preparation, separation, lipid isolation, and ESI-MS for inner membranes (A) and outer membranes (B) of wild-type PAO1 (blue trace) and CDR0031 (−Ara, WaaP-depleted, red trace) are described in Materials and Methods. The lipid samples contained both phospholipids and free lipid A. The spectra in each panel were normalized (percentage of highest ion from full scan, 60 to 2,200 m/z), aligned, and overlaid with Analyst 1.4.2. The range below m/z 770 is not shown. Peak annotations are derived from follow-up enhanced-resolution ESI-MS, which provided baseline resolution of the isotopic peaks (data not shown). The enhanced-resolution spectra were utilized to determine the exact monoisotopic mass and charge state for each lipid A molecular ion previously identified in Fig. S4 and described in Fig. S5. Peaks that are not annotated are singly, negatively-charged ions, and these are consistent with phospholipid species (phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine) of various acyl chain lengths. Download Figure S6, PDF file, 0.304 MB.