Abstract
A heat-stable, particulate, lipopolysaccharide-protein antigenic complex has been isolated from a virulent, encapsulated strain of Pasteurella multocida by extraction with cold, formalinized saline, and centrifugation at 105,000 × g. The original bacterial culture had been obtained from a bison that died of hemorrhagic septicemia, an infectious disease of cattle and buffalo. Injection of fractional milligram amounts of the antigen into mice, rabbits, and calves produced toxic reactions which frequently resulted in death of the host. The surviving animals demonstrated a high degree of immunity to challenge with live, virulent organisms. Two injections with 15 μg of the antigen produced a high degree of immunity in mice without the development of any signs of toxicity. The gross chemical composition and toxicity of the antigen were similar to those reported for endotoxins obtained by the Boivin or Westphal procedure. Although strong serological cross-reactions were obtained in Ouchterlony plates between the 105,000 × g antigens from the bison strain and an avian strain with antisera to these strains, these antisera agglutinated only the bacterial cells of the homologous strain. The active immunity obtained in mice by the injection of the 105,000 × g antigens of each strain was specific and could be correlated with the agglutination tests.
Full text
PDF

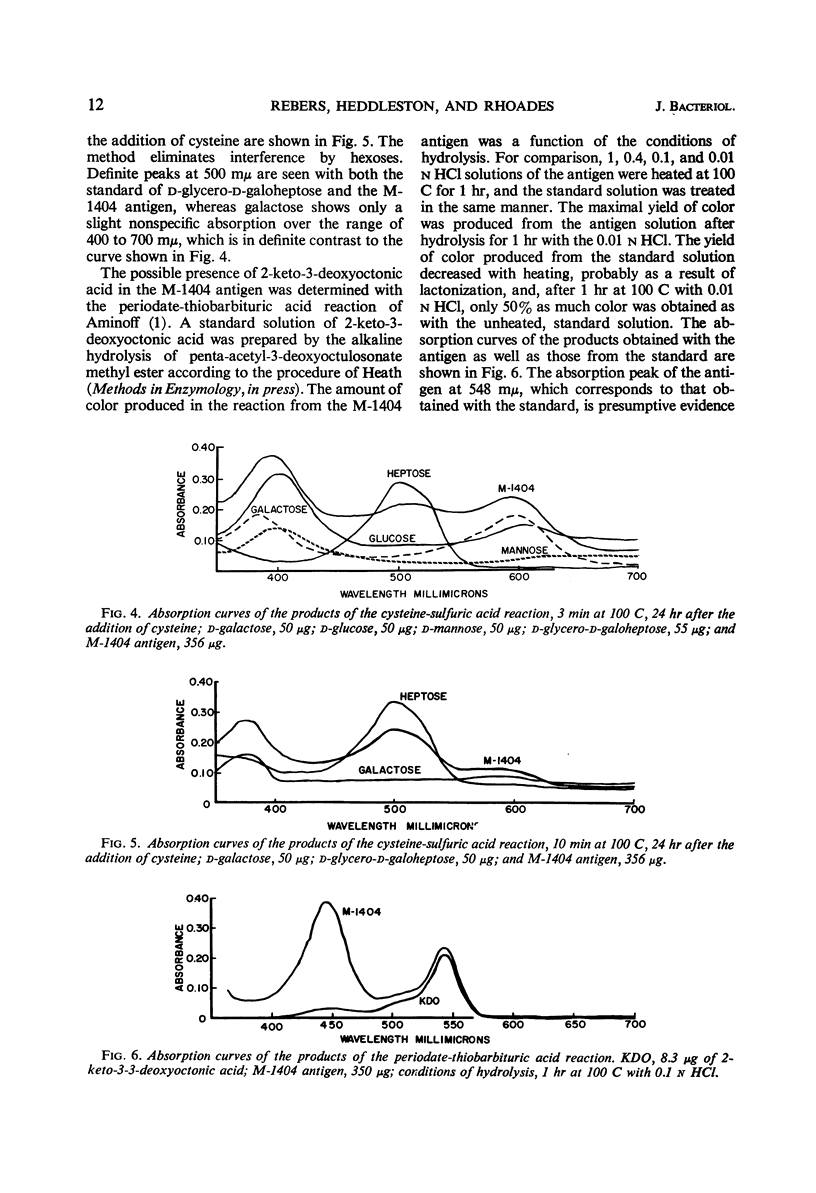
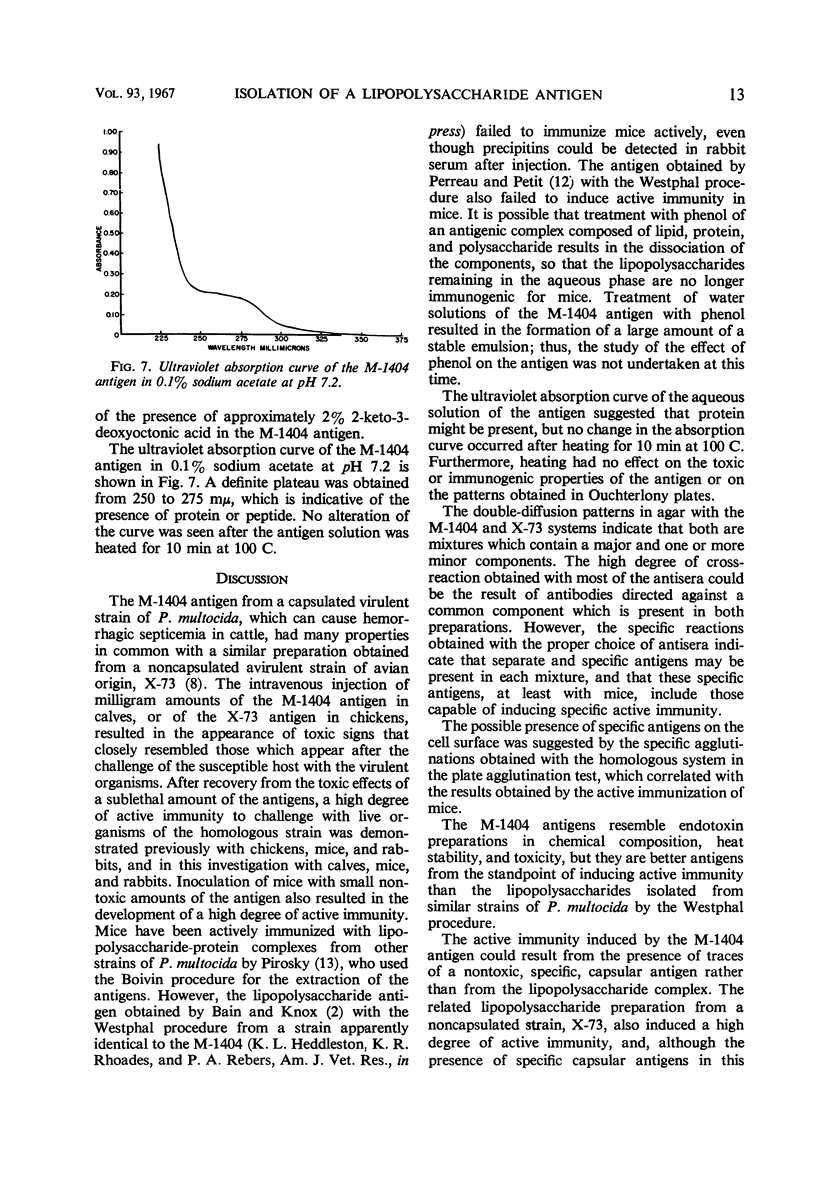

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIN R. V., KNOX K. W. The antigens of Pasteurella multocida type I. II. Lipopolysaccharides. Immunology. 1961 Apr;4:122–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYER R. L., TAMMES A. R., ROUTH J. I. The determination of phosphorus and phosphatase with N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddleston K. L. Immunologic and serologic comparison of three strains of Pasteurella multocida. Cornell Vet. 1966 Apr;56(2):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]