Abstract
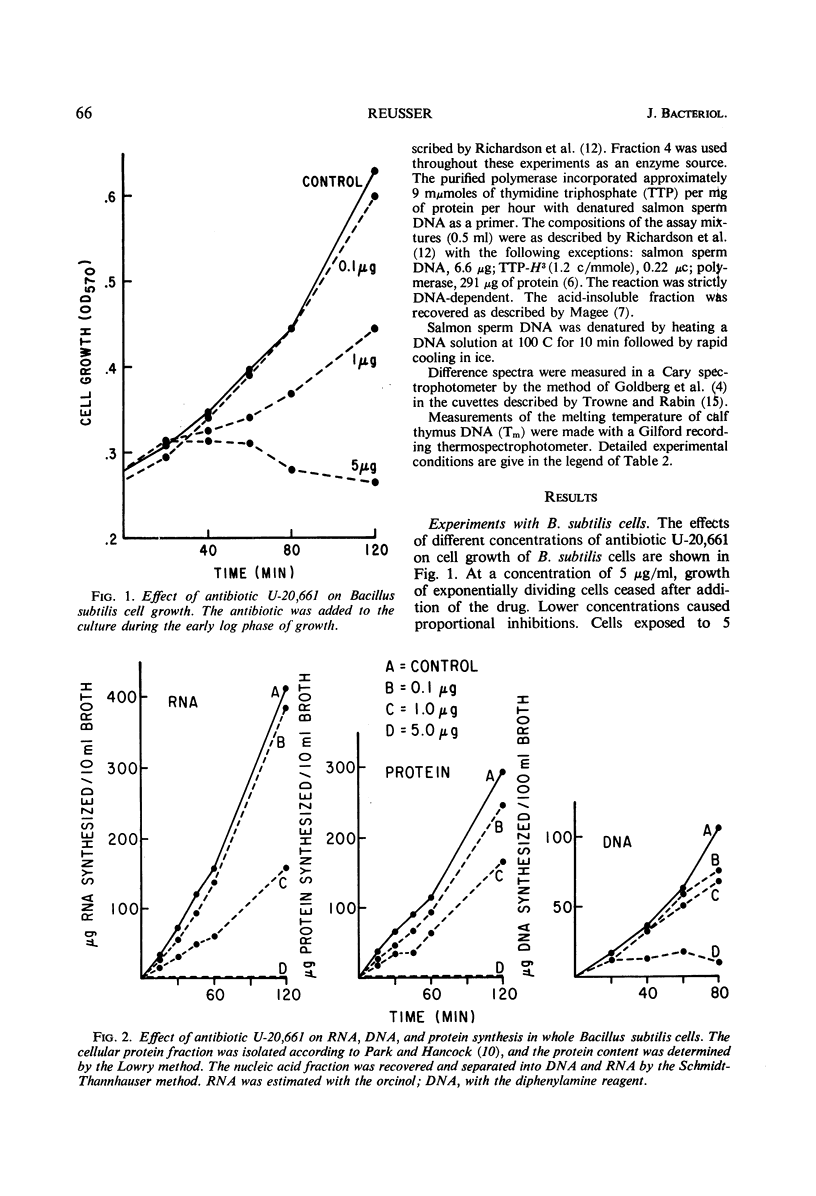
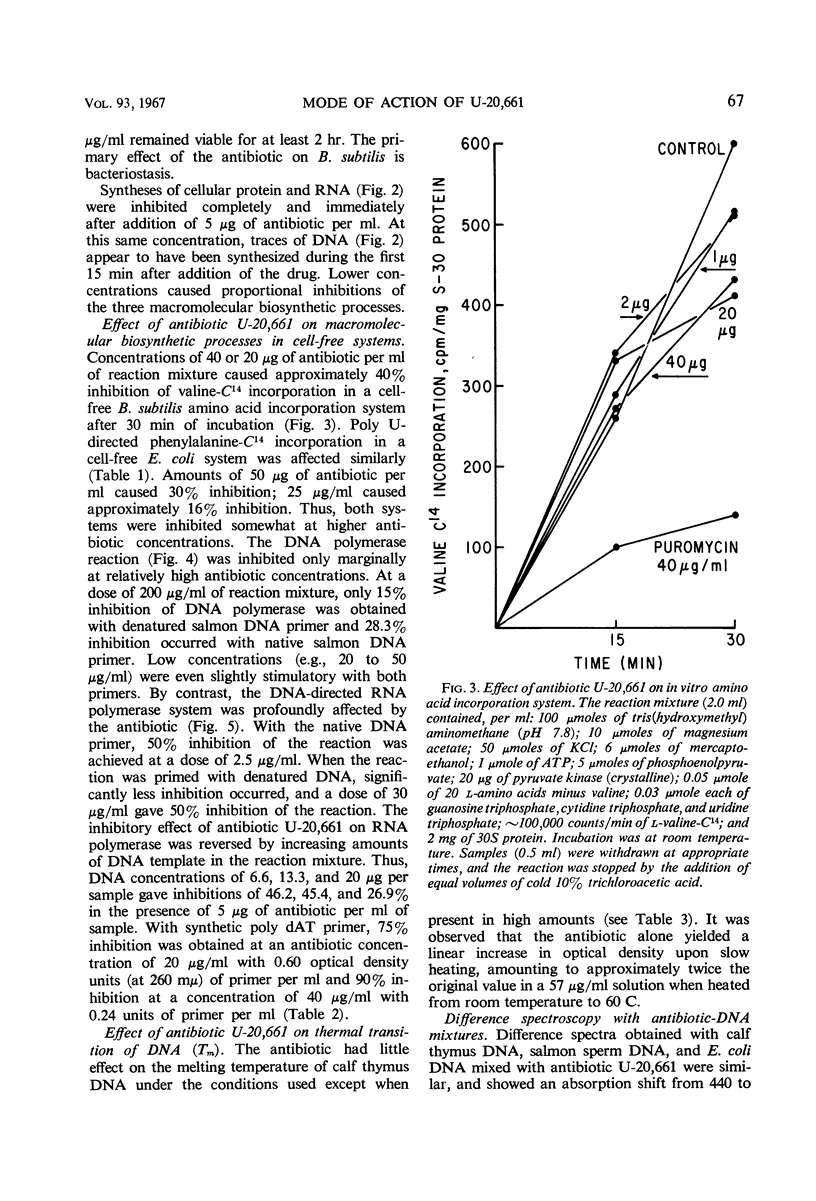
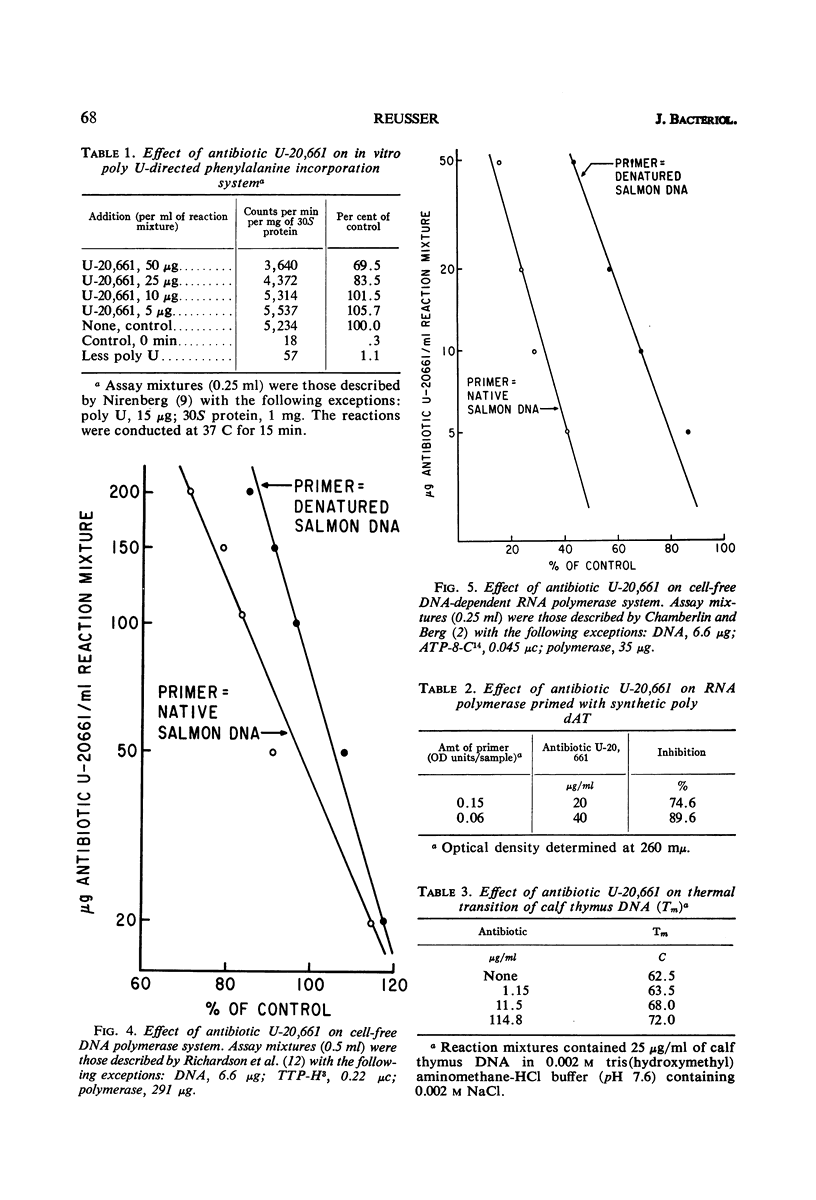
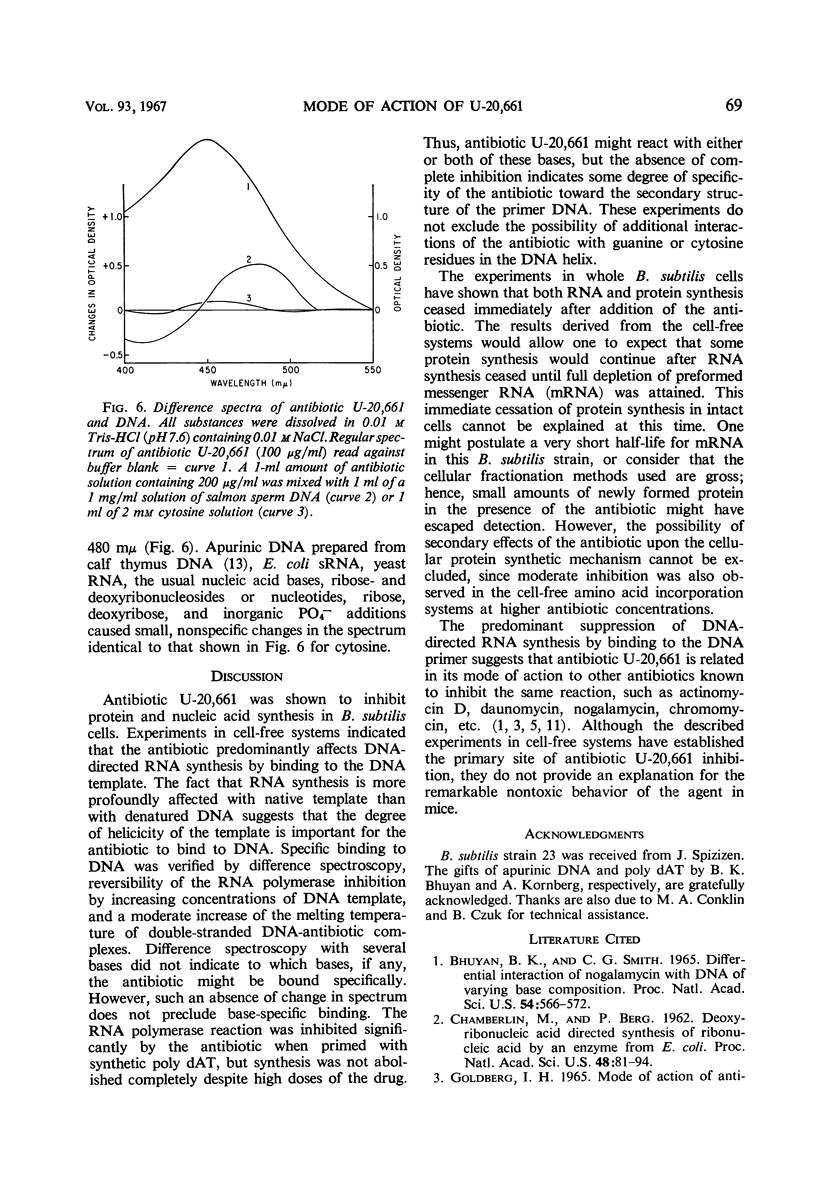
Antibiotic U-20,661 was shown to inhibit predominantly deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-directed ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis by binding to the double-stranded DNA template. Specific binding to DNA was verified by difference spectroscopy, reversal of the RNA polymerase inhibitory effect by increasing concentrations of DNA template, and by moderately increasing the melting temperature of double-stranded DNA in the presence of the antibiotic. The RNA polymerase reaction primed with synthetic poly dAT was inhibited considerably, but not completely even with high concentrations of antibiotic. Thus, the agent might bind to adenine or thymidine or both bases in the double-stranded DNA helix.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuyan B. K., Smith C. G. Differential interaction of nogalamycin with DNA of varying base composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):566–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. Deoxyribo ucleic acid-directed synthesis of ribonucleic acid by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:81–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M., REICH E. Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2094–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten W., Kersten H., Szybalski W. Physicochemical properties of complexes between deoxyribonucleic acid and antibiotics which affect ribonucleic acid synthesis (actinomycin, daunomycin, cinerubin, nogalamycin, chormomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGEE W. E. DNA polymerase and deoxyribonucleotide kinase activities in cells infected with vaccinia virus. Virology. 1962 Aug;17:604–607. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., SCHILDKRAUT C. L., APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. XIV. FURTHER PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich E., Goldberg I. H. Actinomycin and nucleic acid function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:183–234. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60742-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM C., HODES M. E., CHARGAFF E. The formation apurinic acid from the desoxyribonucleic acid of calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):49–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROWN P. W., RABIN B. R. THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CARBOXYDISMUTASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:88–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


