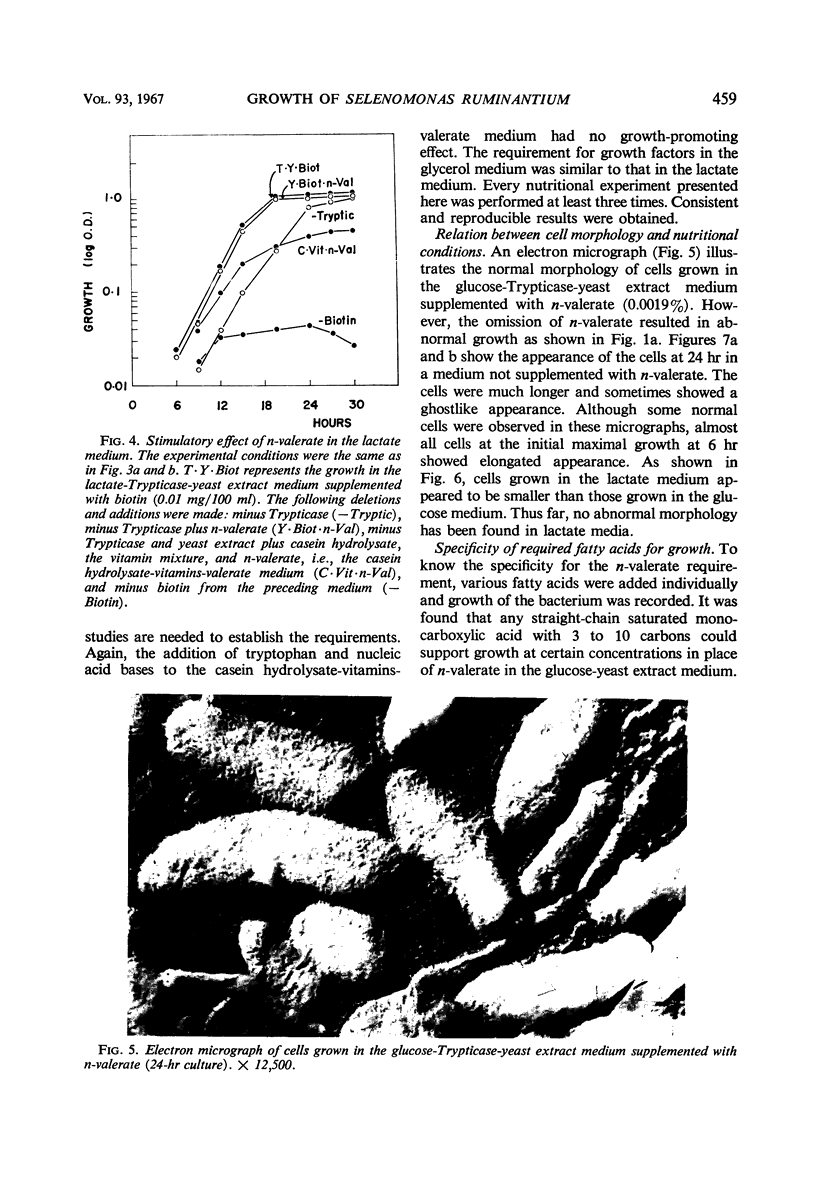
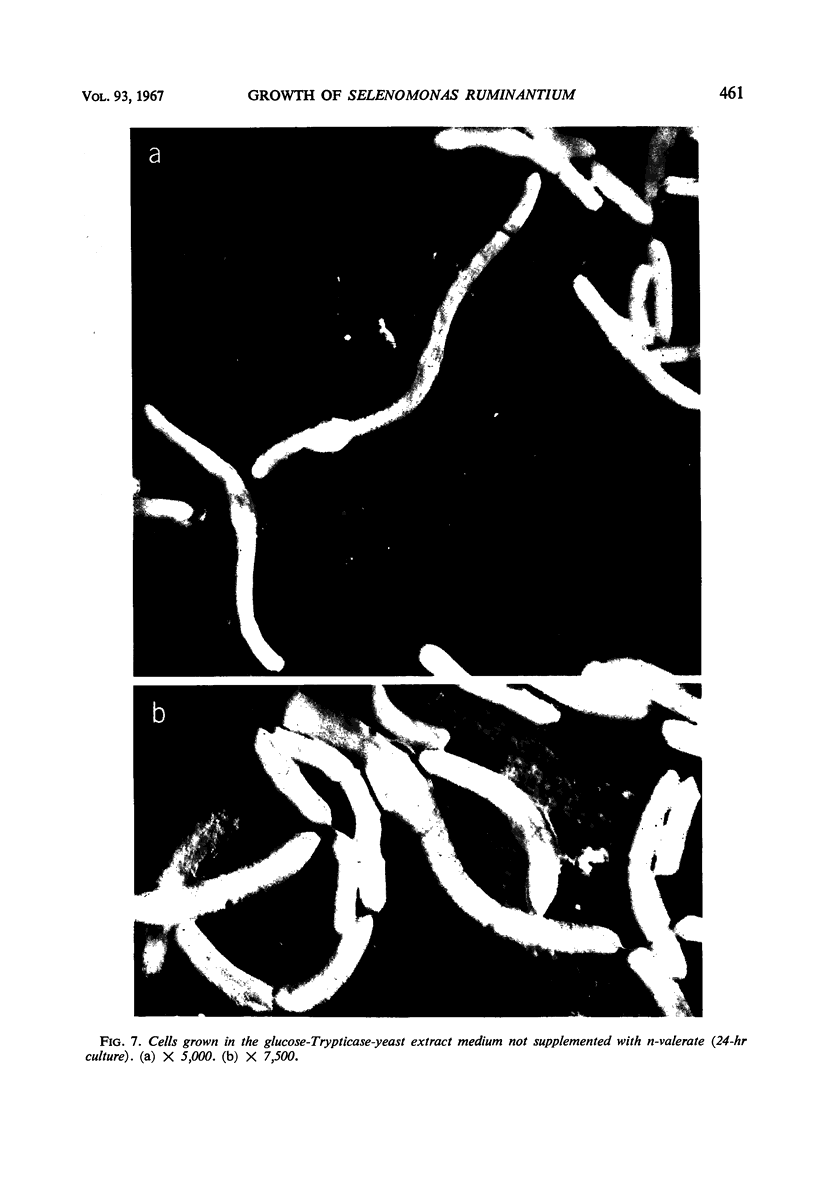
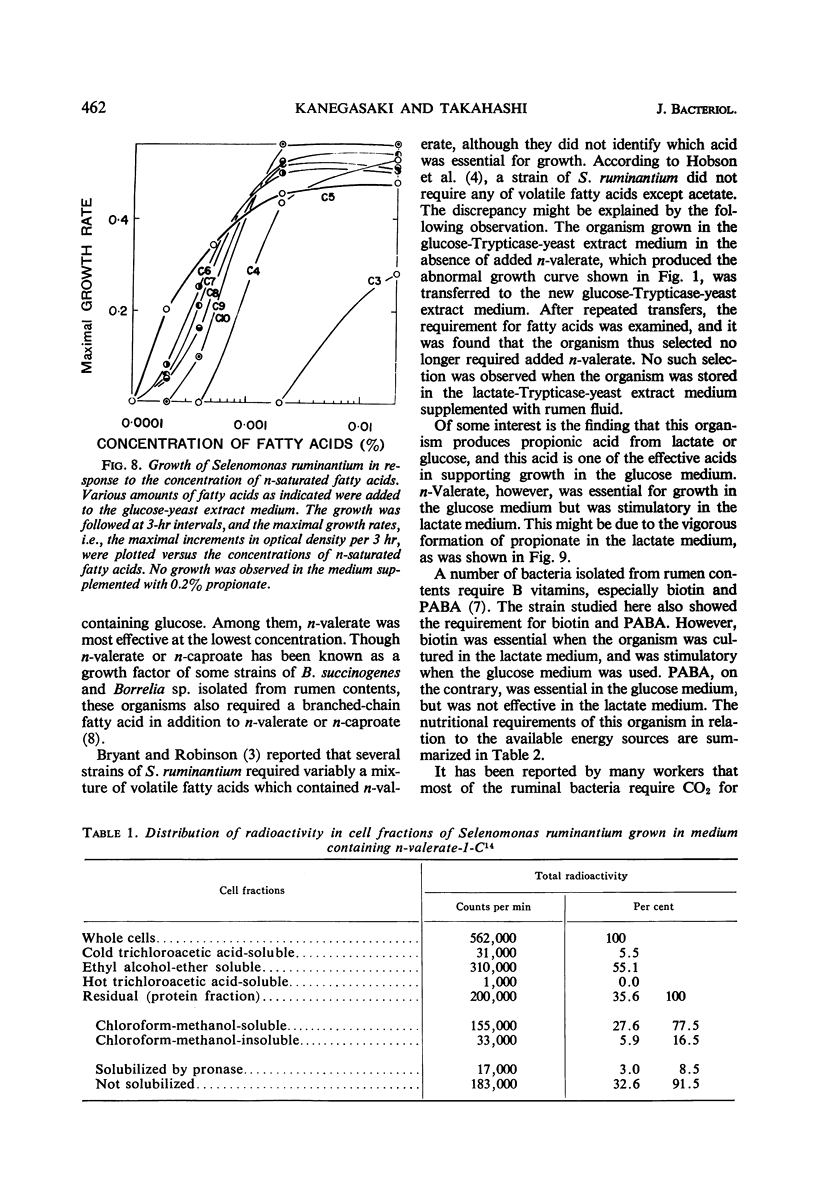
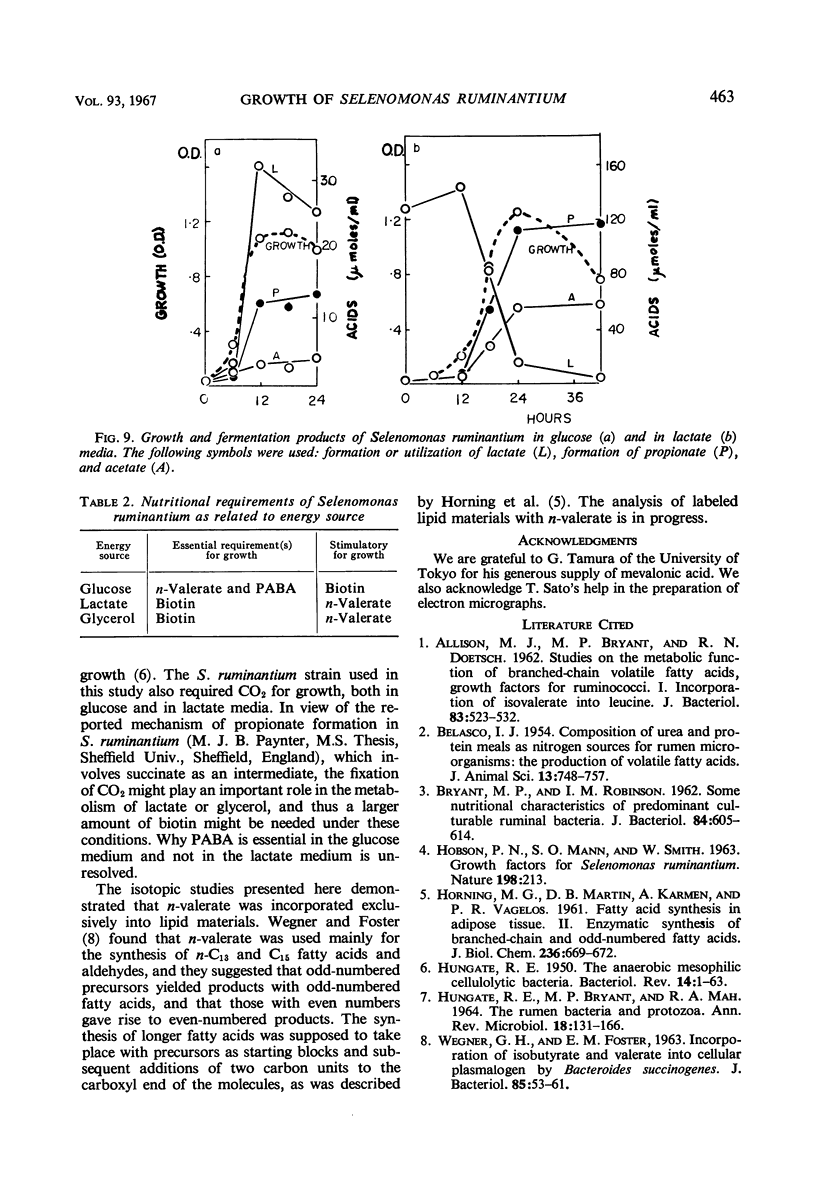
Abstract
Nutritional characteristics of Selenomonas ruminantium var. lactilytica isolated from a sheep rumen were studied. The organism required for growth the addition of a clarified rumen fluid to a Trypticase-yeast extract medium with either lactate or glucose as an energy source. The requirement for rumen fluid was found to be satisfied by volatile fatty acids in glucose media and by biotin in lactate media. Straight-chain saturated fatty acids with C3 to C10 carbon skeleton had been found to be effective. Among them, n-valerate was most effective at the lowest concentration. An abnormal morphology was observed with n-valerate-deficient glucose media. n-Valerate was essential in glucose media, and it was stimulatory in lactate media. Fermentation products from glucose were lactate, propionate, and acetate, and fermentation products from lactate were propionate and acetate. When cells were grown in a glucose medium containing n-valerate-C14, the label was present in cell fractions. Almost all of the activity was found in lipid materials.
Full text
PDF
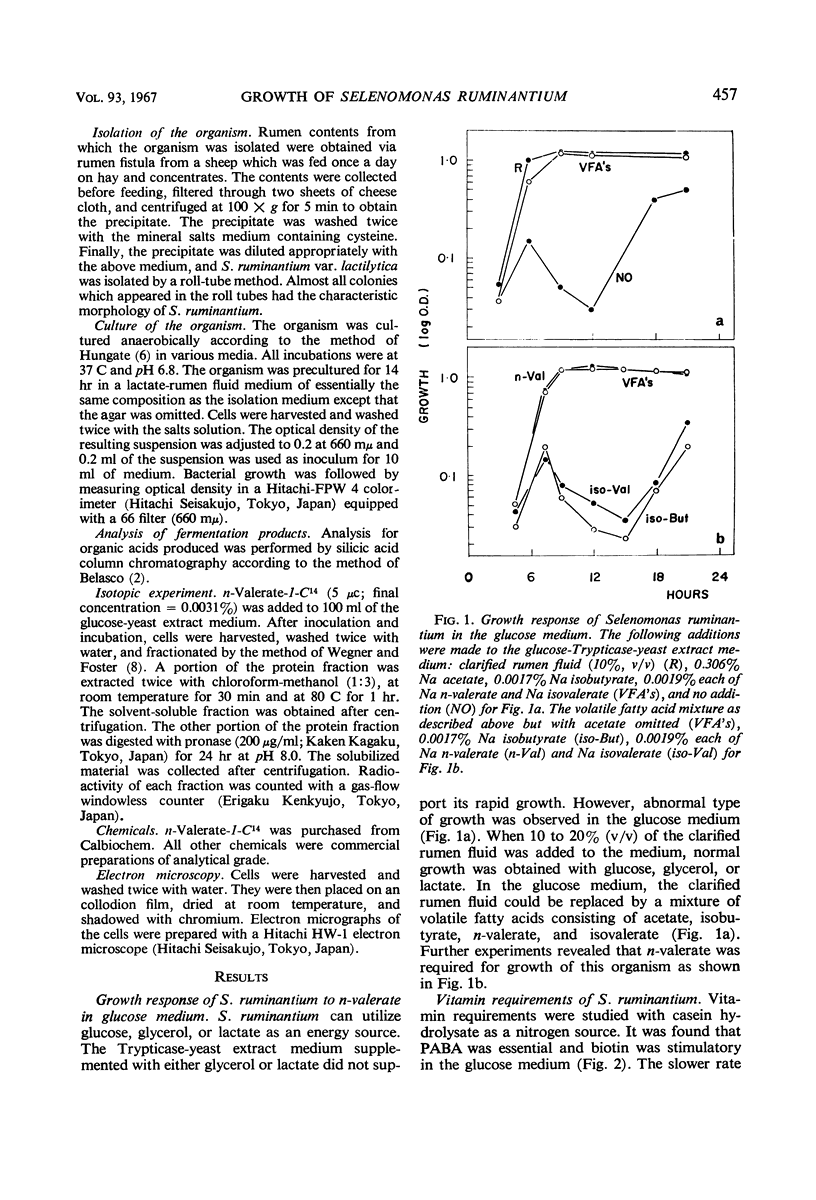
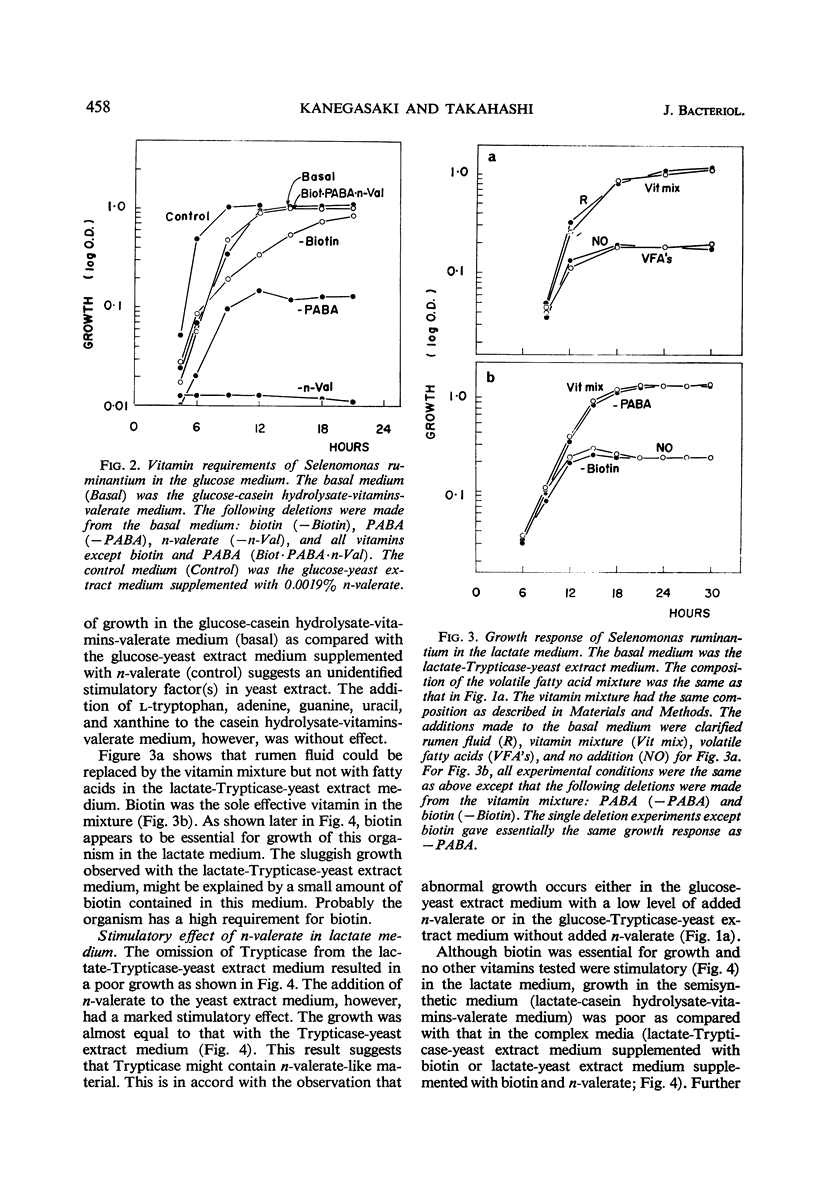

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON M. J., BRYANT M. P., DOETSCH R. N. Studies on the metabolic function of branched-chain volatile fatty acids, growth factors for ruminococci. I. Incorporation of isovalerate into leucine. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:523–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.523-532.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N., MANN S. O., SMITH W. Growth factors for Selenomonas ruminantium. Nature. 1963 Apr 13;198:213–213. doi: 10.1038/198213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNING M. G., MARTIN D. B., KARMEN A., VAGELOS P. R. Fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue. II. Enzymatic synthesis of branched chain and odd-numbered fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:669–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., BRYANT M. P., MAH R. A. THE RUMEN BACTERIA AND PROTOZOA. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:131–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEGNER G. H., FOSTER E. M. Incorporation of isobutyrate and valerate into cellular plasmalogen by Bacteroides succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:53–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.53-61.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]