Abstract
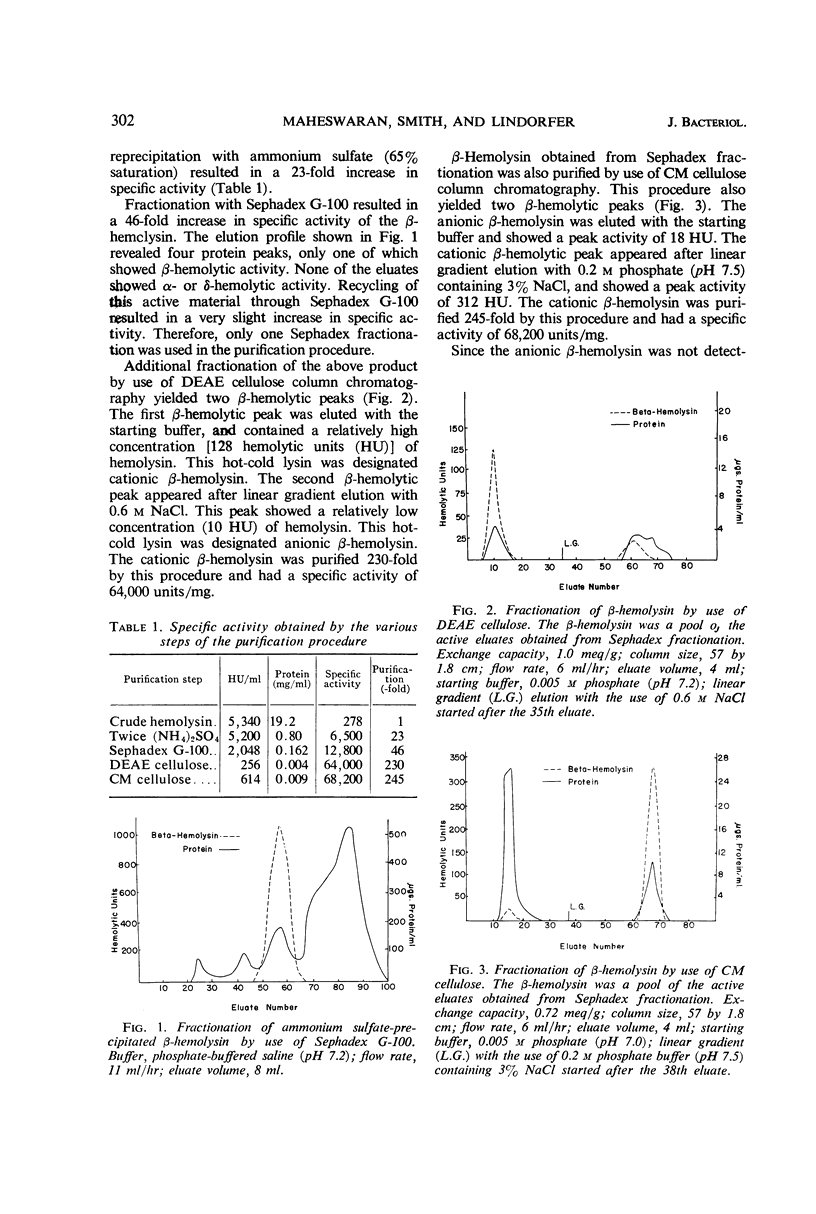
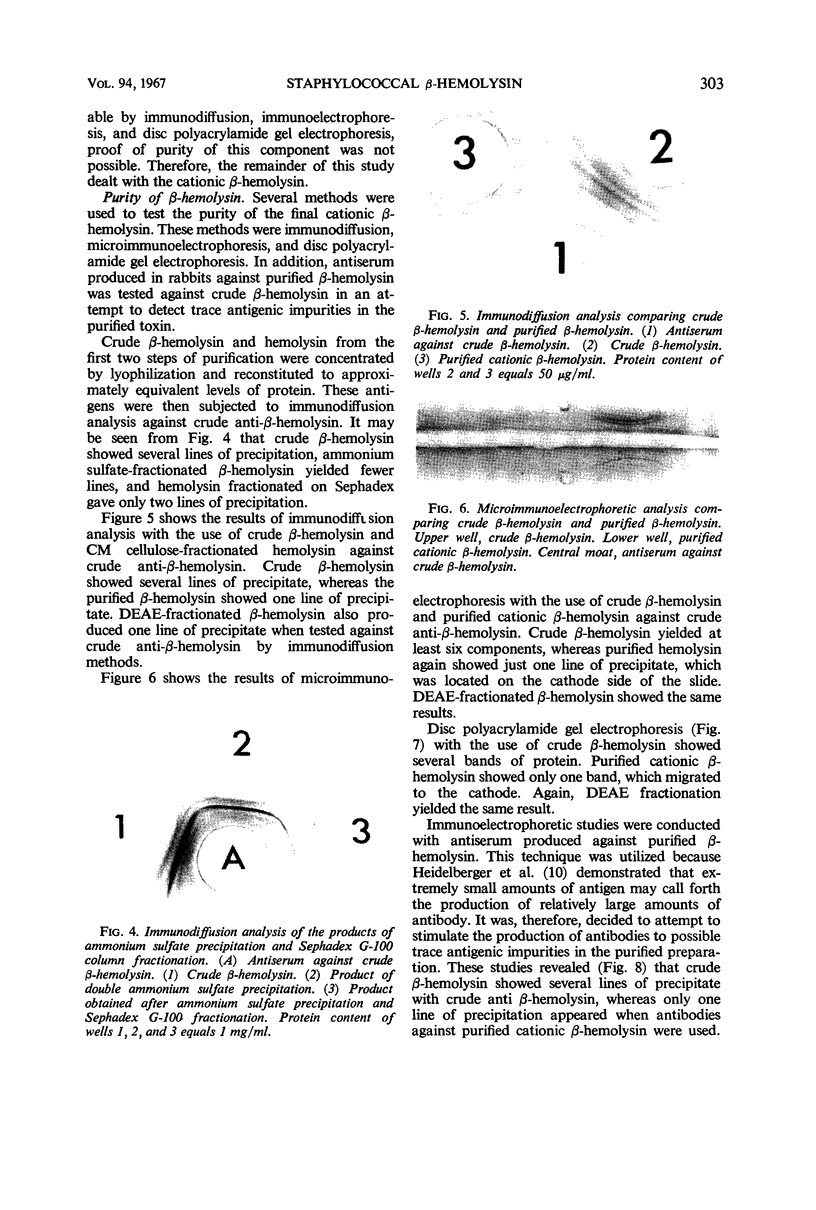
The purification of staphylococcal β-hemolysin was accomplished by the successive use of three protein fractionation methods. The first method employed was a double precipitation with the use of ammonium sulfate at 65% saturation. The second phase of purification used Sephadex G-100 column fractionation. The third phase utilized either carboxymethyl cellulose or diethylaminoethyl cellulose fractionation. The last two fractionation methods both resulted in the separation of a relatively high concentration of cationic hot-cold lysin and a low concentration of anionic hot-cold lysin. Because of the low concentration of the anionic component, its purity could not be assessed. However, the purity of the cationic component was demonstrated by immunodiffusion, microimmunoelectrophoresis, and by disc polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In addition, antisera against purified cationic β-hemolysin yielded one line of precipitate when tested against the original crude β-hemolysin. The purified cationic β-hemolysin was stable in the lyophilized state. Crude β-hemolysin was dermonecrotic, whereas purified cationic β-hemolysin was not dermonecrotic even after Mg++ activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHESBRO W. R., HEYDRICK F. P., MARTINEAU R., PERKINS G. N. PURIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL BETA-HEMOLYSIN AND ITS ACTION ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:378–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.378-389.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER L. Z., MADOFF M. A., WEINSTEIN L. HEMOLYSIS OF RABBIT ERYTHROCYTES BY PURIFIED STAPHYLOCOCCAL ALPHA-TOXIN. I. KINETICS OF THE LYTIC REACTION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:127–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.127-135.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. A nomogram for ammonium sulphate solutions. Biochem J. 1953 Jun;54(3):457–458. doi: 10.1042/bj0540457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. Distribution of haemolysins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):541–554. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUND J. The effect of paraffin oil and mycobacteria on antibody formation and sensitization; a review. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Jul;21(7):645–656. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.7.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNGOLD L., LIPARI R. Tissue antigens of human tumors grown in rats, hamsters, and eggs. Cancer Res. 1955 Mar;15(3):159–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOKEN K. I., HOYT H. H. Studies on bovine staphylococcic mastitis. I. Characterization of staphylococci. Am J Vet Res. 1962 May;23:534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar M., Kumar S., Lindorfer R. K. Heat reactivation of the alpha-hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal activities of crude and purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1681-1685.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASMAN A., VAN DER SLOT J. On a new method of preparing staphylococcus toxin and toxoid. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1953;19(3):256–266. doi: 10.1007/BF02594852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISEMAN G. M. SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BETA-HAEMOLYSIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:187–207. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]