Abstract
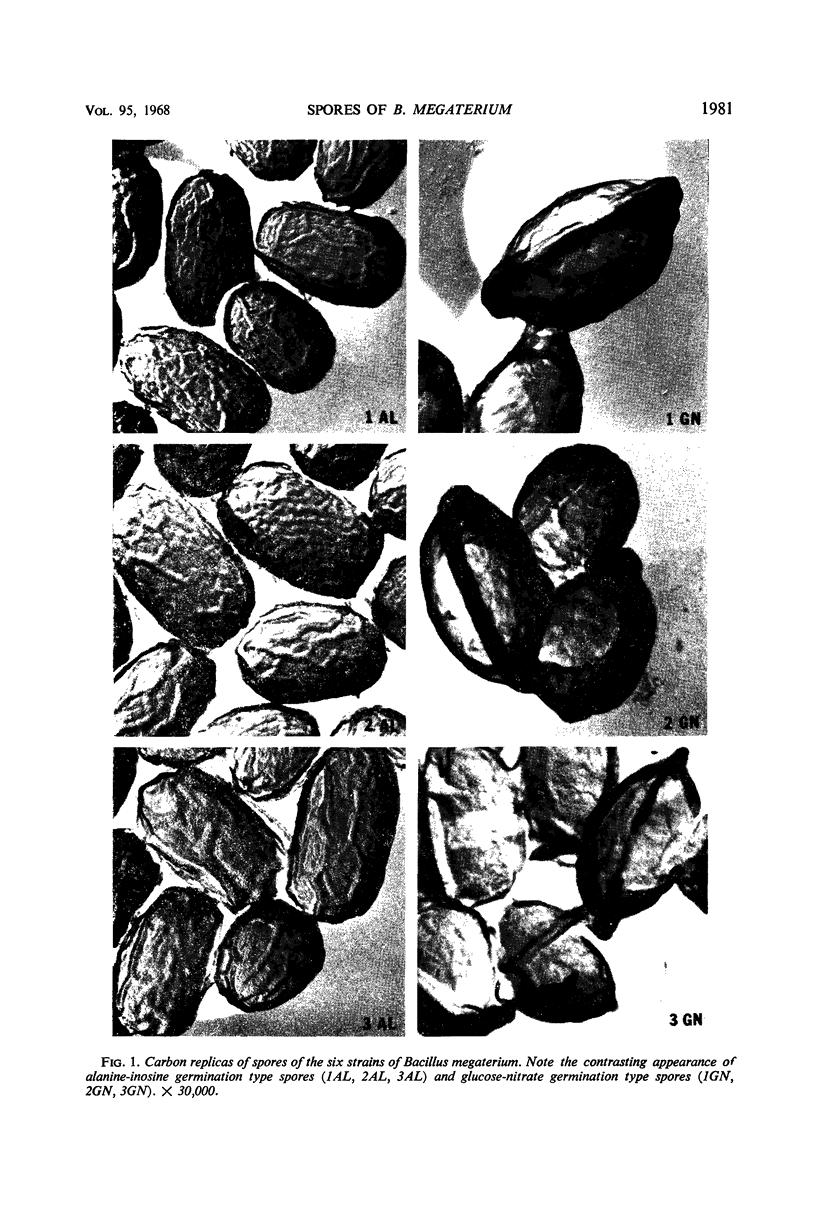
The spores of six strains of Bacillus megaterium were divided into two distinct groups on the basis of germination. Three of the strains germinated in a mixture of l-alanine and inosine (AL type spores), and three strains germinated in a mixture of glucose and potassium nitrate (GN type spores); recriprocal germination in the respective solutions did not occur. The AL spores and the GN spores were morphologically distinct. Other differences between the two spore groups included germination inhibition characteristics, dipicolinic acid content, hexosamine content, phosphorus and magnesium content, spore coat features, ion exchange properties, and heat resistance. A correlation appears to exist between spore morphology and certain other spore properties in strains of B. megaterium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDERTON G., SNELL N. Base exchange and heat resistance in bacterial spores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jan 31;10:139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran H. R., Evans F. R. Heat Activation Inducing Germination in the Spores of Thermotolerant and Thermophilic Aerobic Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1945 Apr;49(4):335–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.4.335-346.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthit H. A., Halvorson H. O. Satellite deoxyribonucleic acid from Bacillus cereus strain T. Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):182–183. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz-James P. C., Young I. E. CYTOLOGICAL COMPARISON OF SPORES OF DIFFERENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78(6):755–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.755-764.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD G. W., HITCHINS A. D. SENSITIZATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES TO LYSOZYME AND TO HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WITH AGENTS WHICH RUPTURE DISULPHIDE BONDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:413–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYATT M. T., LEVINSON H. S. Interaction of heat, glucose, L-alanine, and potassium nitrate in spore germination of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1961 Feb;81:204–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.2.204-211.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., DeCourcy S. J., Jr, Mudd S. An immunologically active cell-wall peptide polymer obtained from the culture filtrates of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 26;121(1):210–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90378-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMMERS J., VASSEUR E. Influence of sugars and amines on the colorimetric hexosamine method of elson and morgan and its possible elimination. Nature. 1950 Jun 3;165(4205):898–898. doi: 10.1038/165898a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Foster J. W. Chemical and electron microscope studies on fractions prepared from coats of Bacillus spores. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):257–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSON H. S., HYATT M. T. EFFECT OF SPORULATION MEDIUM ON HEAT RESISTANCE, CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, AND GERMINATION OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:876–886. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.876-886.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson H. S., Wrigley A. S. Spore Germination and Emergence of Bacillus megaterium. Science. 1960 May 6;131(3410):1382–1382. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3410.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSSAL P. M. A mechanical cell disintegrator. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Dec;31(6):583–589. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. Factors affecting the germination of thick suspensions of bacillus subtilis spores in L-alanine solution. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):330–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope L., Yolton D. P., Rode L. J. Appendages of Clostridium bifermentans spores. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1206-1215.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. GASEOUS HYDROCARBONS AND THE GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:31–38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Germination of bacterial spores with alkyl primary amines. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:768–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.768-779.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Ionic and non-ionic compounds in the germination of spores of Bacillus megaterium Texas. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:201–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00406436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Ionic germination of spores of Bacillus megaterium QM B 1551. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:183–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00406435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Influence of exchangeable ions on germinability of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1582–1588. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1582-1588.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Quantitative aspects of exchangeable calcium in spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1589–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1589-1593.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Williams M. G. Utility of sodium hypochlorite for ultrastructure study of bacterial spore integuments. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1772–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1772-1778.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS L. E., BAILEY G. F. DRY RUPTURE OF BACTERIAL SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:720–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.720-721.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEPECKY R. A. INHIBITION OF SPORULATION AND GERMINATION OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM BY PHENETHYL ALCOHOL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:369–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARKA J., CASLAVSKA J. SPORULATION OF PROTOPLASTS. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1964 Jan;23:21–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02875896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., DARK F. A. A cell-wall lytic enzyme associated with spores of Bacillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):236–249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks L. E. Adenine and 2,6-diaminopurine as germinants for Bacillus macerans spores. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1789–1790. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1789-1790.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER H. W., MATCHES J. R., AYRES J. C. Chemical composition and heat resistance of some aerobic bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:960–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.960-966.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTH A. D., OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Location and composition of spore mucopeptide in Bacillus species. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:593–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolton D. P., Pope L., Williams M. G., Rode L. J. Further electron microscope characterization of spore appendages of Clostridium bifermentans. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.231-238.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




