Abstract
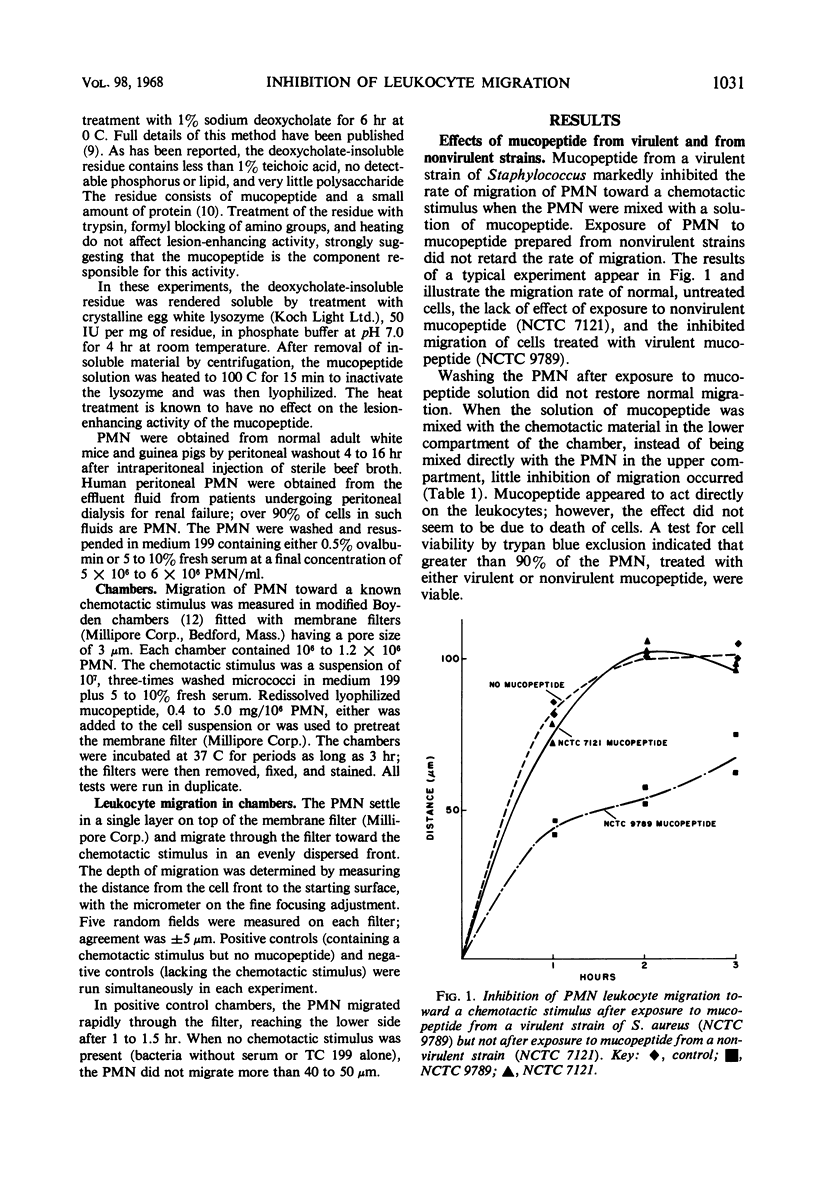
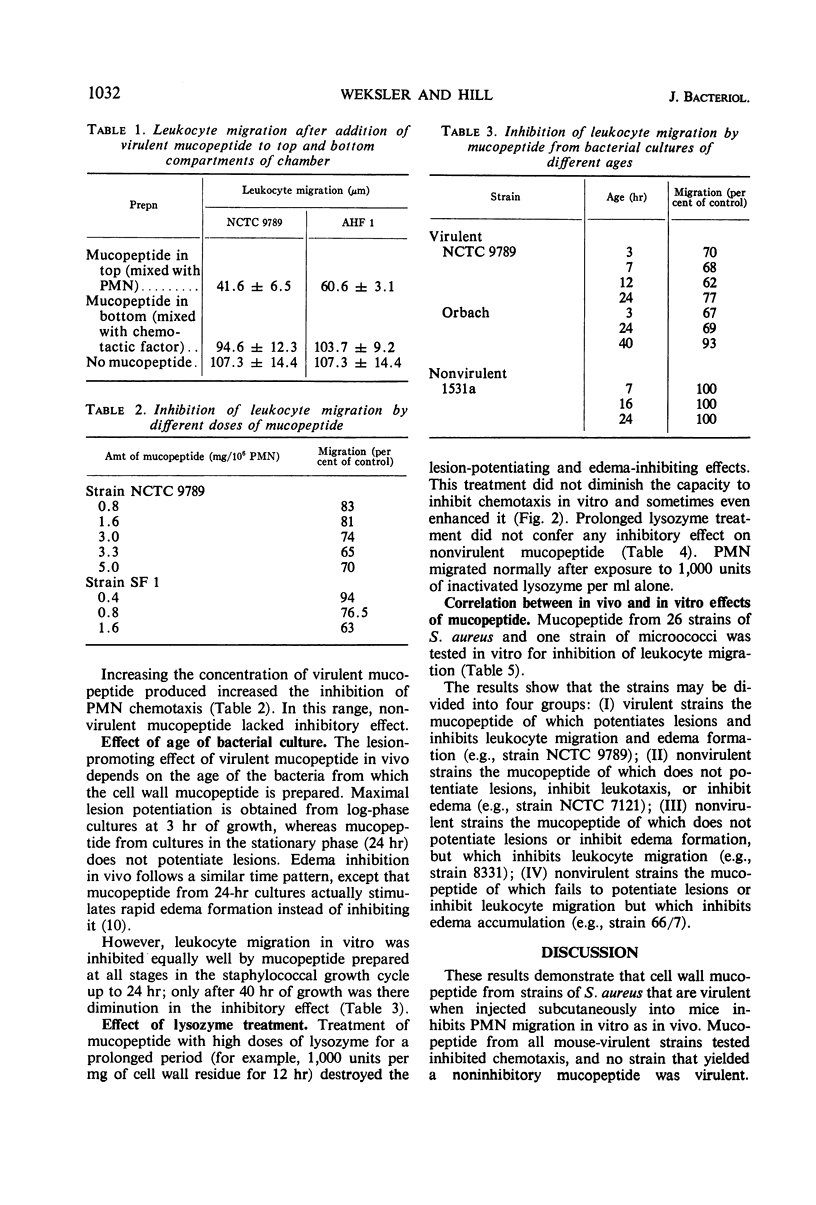
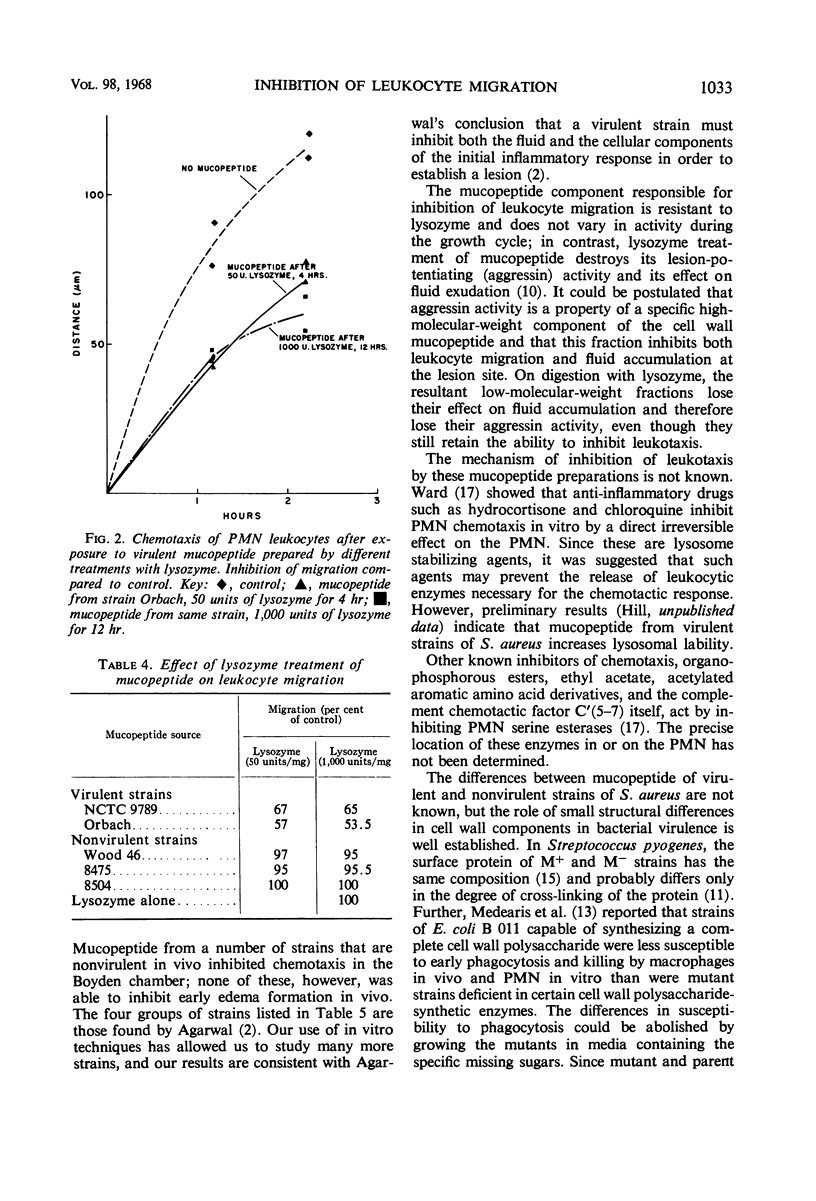
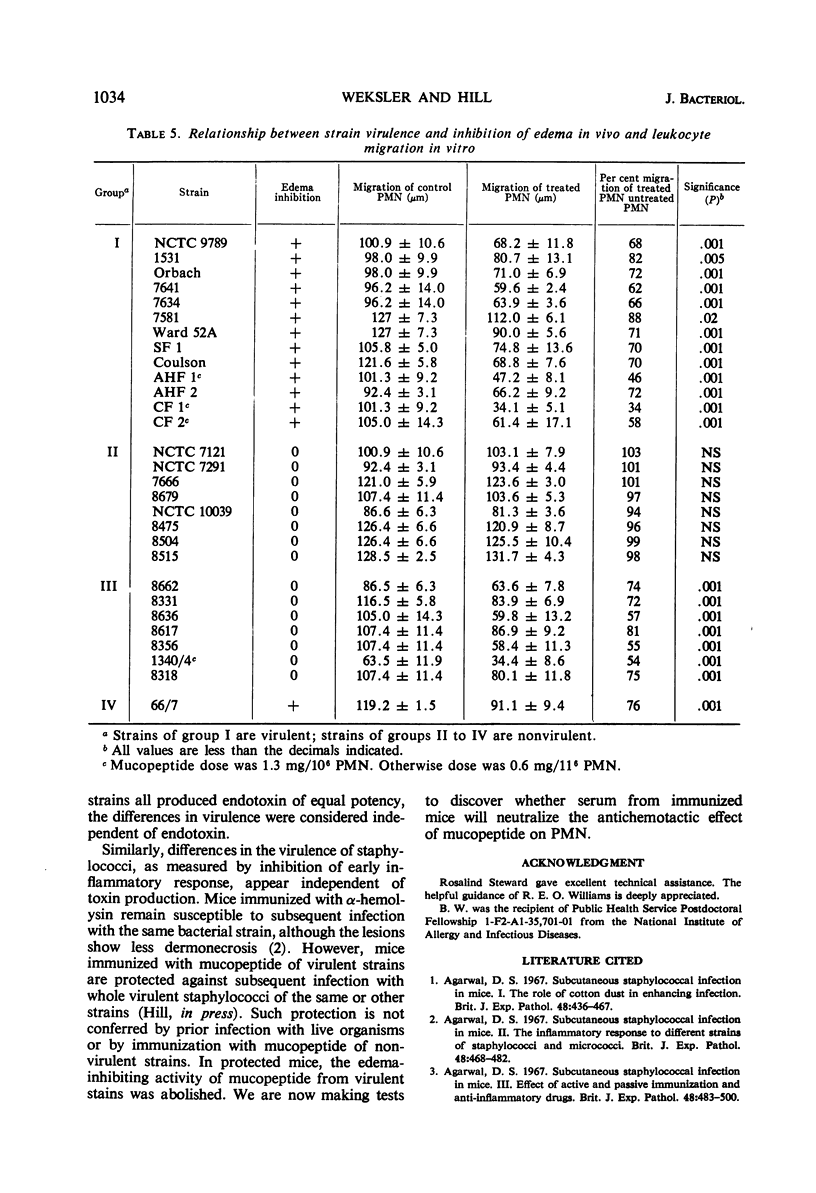
Cell wall mucopeptide isolated from virulent strains of Staphylococcus aureus has previously been found to potentiate subcutaneous staphylococcal lesions in mice. This cell wall fraction was found to inhibit the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes toward a chemotactic stimulus, as tested by the micropore filter chamber technique. A close correlation was shown to exist between in vivo “mouse virulence” of staphylococcal strains and the in vitro inhibition of leukocyte migration by the cell wall factor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal D. S. Subcutaneous staphylococcal infection in mice. 3. Effect of active and passive immunization and anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Oct;48(5):483–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal D. S. Subcutaneous staphylococcal infection in mice. I. The role of cotton-dust in enhancing infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Aug;48(4):436–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal D. S. Subcutaneous staphylococcal infection in mice. II. The inflammatory response to different strains of staphylococci and micrococci. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Oct;48(5):468–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andriole V. T., Lytton B. The effect and critical duration of increased tissue pressure on susceptibility to bacterial infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Jun;46(3):308–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE J. F., MILES A. A. The sequence of vascular events in early infective inflammation. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Determinants of infection in the peritoneal cavity. I. Response to and fate of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus albus in the mouse. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Aug;35:12–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Determinants of infection in the peritoneal cavity. II. Factors influencing the fate of Staphylococcus aureus in the mouse. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Aug;35:29–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER S. EXPERIMENTAL STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTION OF THE SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE OF THE MOUSE. 3. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE CELLULAR AGGRESSIN OF COAGULASE-PRODUCING STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Infect Dis. 1965 Jun;115:285–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL M. J., JAMES A. M., MAXTED W. R. SOME PHYSICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF THE BEHAVIOUR OF BACTERIAL SURFACES. IX. STUDIES ON THE STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:402–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLEY J. V. Incubation of serum with tissue extracts as a cause of chemotaxis of granulocytes. Nature. 1963 Jun 22;198:1212–1213. doi: 10.1038/1981212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J. A staphylococcal aggressin. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):31–43. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J. Action of bile salts on bacterial cell walls. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1152–1154. doi: 10.1038/2141152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., MILES E. M., BURKE J. The value and duration of defence reactions of the skin to the primary lodgement of bacteria. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Feb;38(1):79–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPER B. S., HAYASHI J. A., BARKULIS S. S. Studies of streptococcal cell walls. V. Amino acid composition of cell walls of virulent and avirlent group A hemolytic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:33–38. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.1.33-38.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Mechanisms of the inhibition of chemotaxis by phosphonate esters. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1001–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


