Abstract
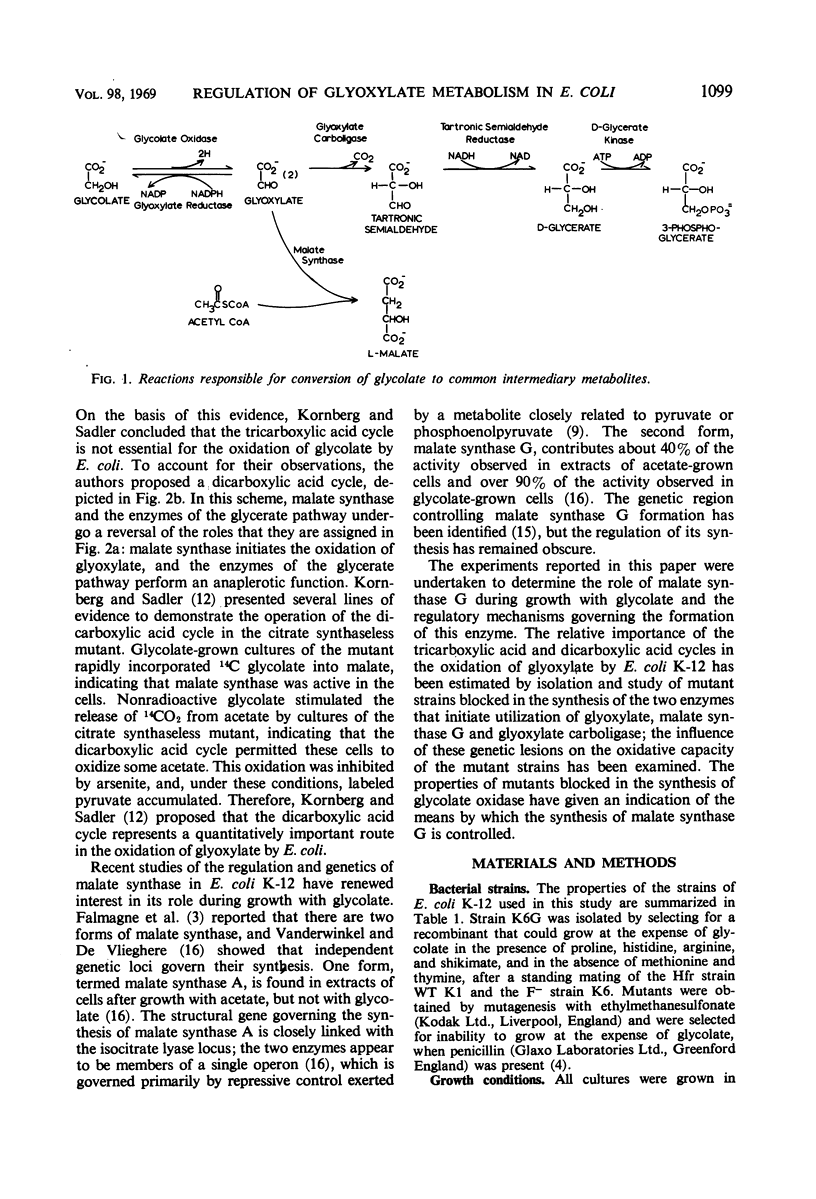
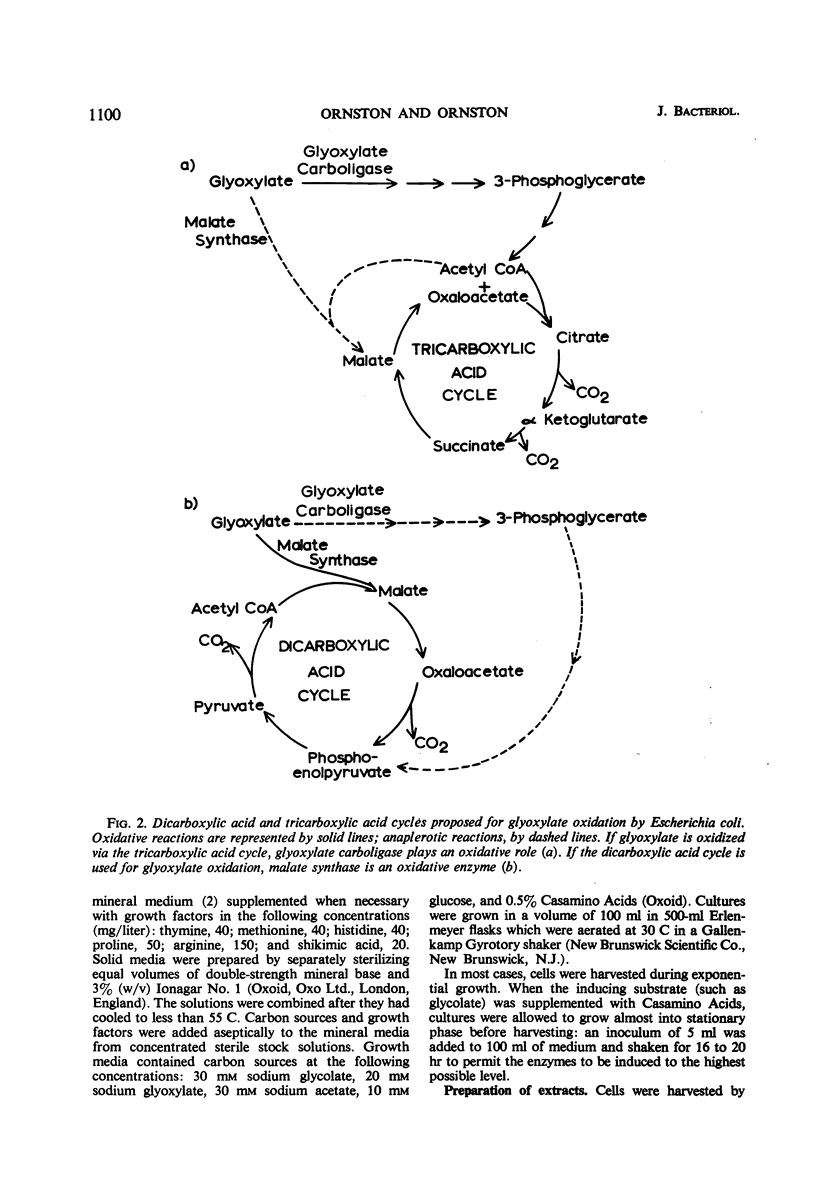
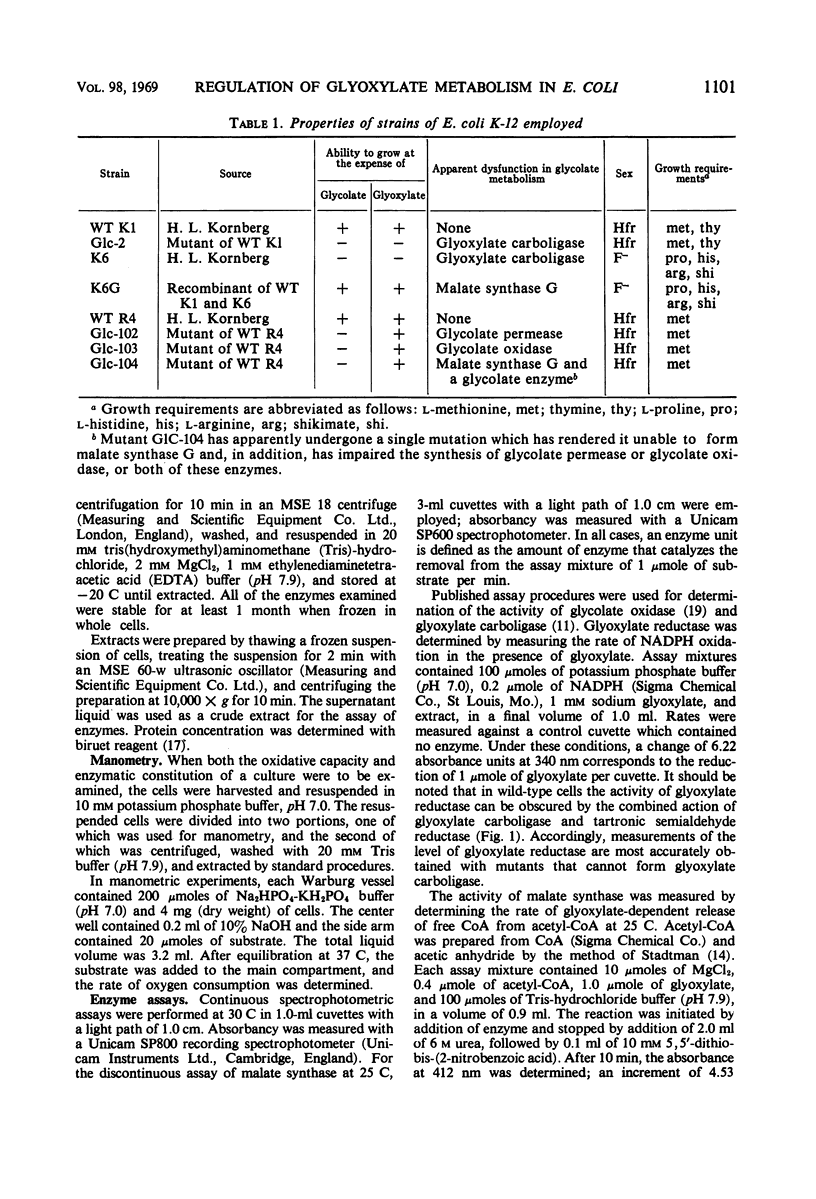
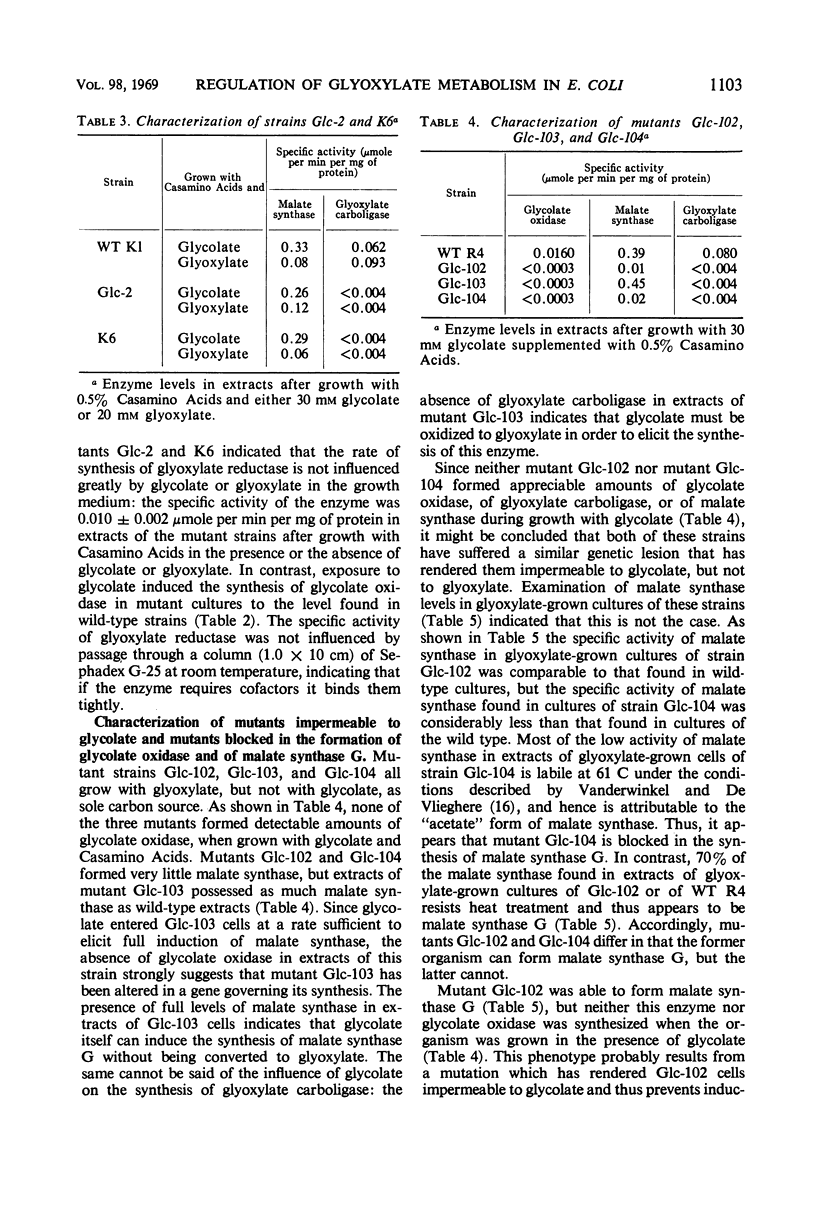
The relative contributions of the dicarboxylic acid and the tricarboxylic acid cycles to the oxidative catabolism of glyoxylate in Escherichia coli K-12 were deduced by analysis of mutant strains that were blocked in the formation of glyoxylate carboligase and of malate synthase G (the “glycolate form” of malate synthase). Mutant strains unable to form malate synthase G were unimpaired in their ability to oxidize glyoxylate. Hence, the dicarboxylic acid cycle does not appear to play an essential role in this process. Organisms blocked in the synthesis of glyoxylate carboligase did not oxidize glyoxylate at a detectable rate, indicating that wild-type organisms convert glyoxylate to acetyl-coenzyme A and oxidize it via the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The foregoing evidence indicates that malate synthase G plays an anaplerotic role during growth with glycolate or acetate as the carbon source. The in vivo activity of malate synthase G was not detectable when the intracellular concentration of acetyl-coenzyme A was low, suggesting that this substrate or a closely related metabolite exerts a sensitive positive control over the enzyme. The synthesis of malate synthase G appears to be induced directly by glycolate which may be formed by a constitutive reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent glyoxylate reductase in glyoxylate- or acetate-grown cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH J. M., KORNBERG H. L. FINE CONTROL OF THE GLYOXYLATE CYCLE BY ALLOSTERIC INHIBITION OF ISOCITRATE LYASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 9;73:519–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90457-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth J. M., Kornberg H. L. The anaplerotic fixation of carbon dioxide by Escherichia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Aug 16;165(999):179–188. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKULIS S. S., KRAKOW G. Conversion of glyoxylate to hydroxypyruvate by extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):593–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALMAGNE P., VANDERWINKEL E., WIAME J. M. MISE EN EVIDENCE DE DEUX MALATE SYNTHASES CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 18;99:246–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KAUFMAN H. Selecting bacterial mutants by the penicillin method. Science. 1960 Feb 26;131(3400):604–605. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3400.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTO A. M., KORNBERG H. L. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 7. Preparation and properties of crystalline tartronic semialdehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:273–284. doi: 10.1042/bj0810273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSEN R. W., HAYASHI J. A. Glycolate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:679–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.679-687.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 6. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycollate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:69–82. doi: 10.1042/bj0780069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., SADLER J. R. The metabolism of C2-compounds in micro-organisms. VIII. A dicarboxylic acid cycle as a route for the oxidation of glycollate by Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:503–513. doi: 10.1042/bj0810503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L. Selective utilization of metabolic routes by Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:257–260. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L. The role and control of the glyoxylate cycle in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj0990001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDERWINKEL E., LIARD P., RAMOS F., WIAME J. M. Genetic control of the regulation of isocitritase and malate synthase in Escherichia coli K 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 18;12:157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinkel E., De Vlieghere M. Physiologie et génétique de l'isocitritase et des malate synthases chez Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jun;5(1):81–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELITCH I., OCHOA S. Oxidation and reduction of glycolic and glyoxylic acids in plants. I. Glycolic and oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):707–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


