Abstract
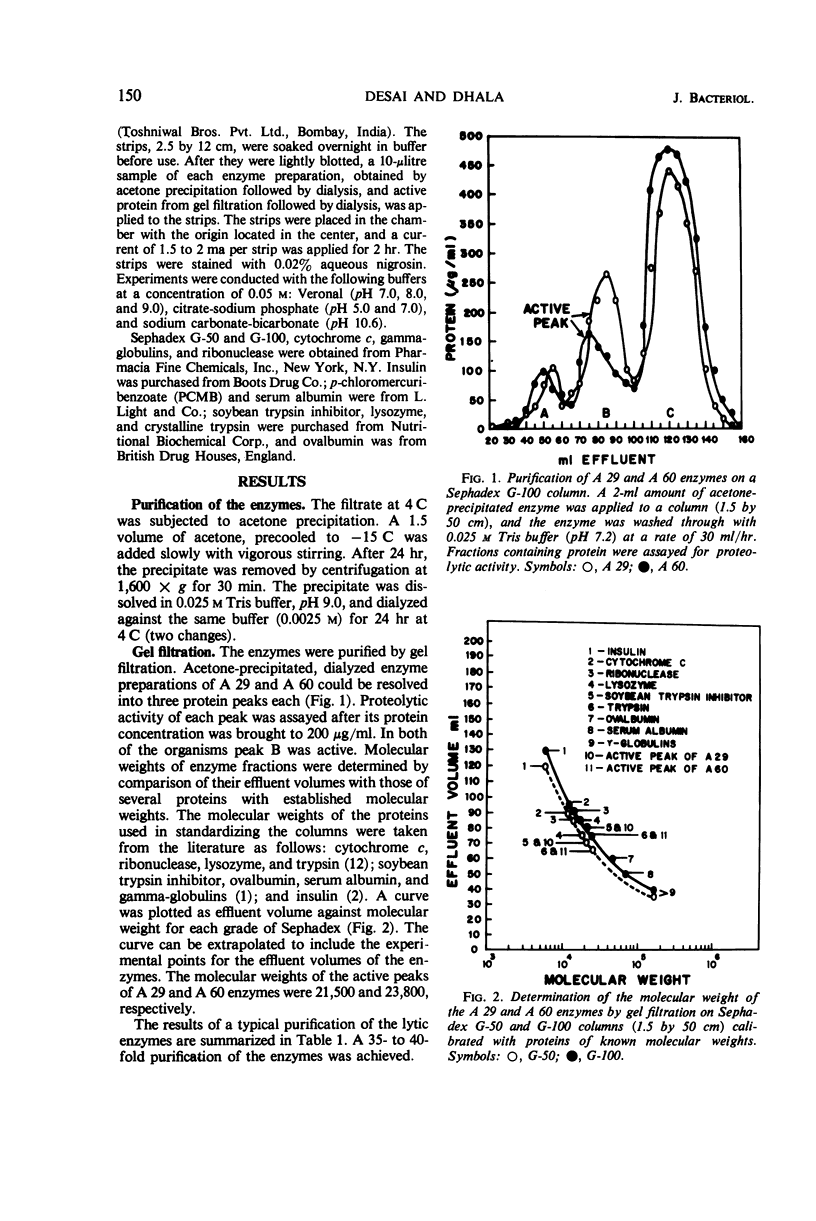
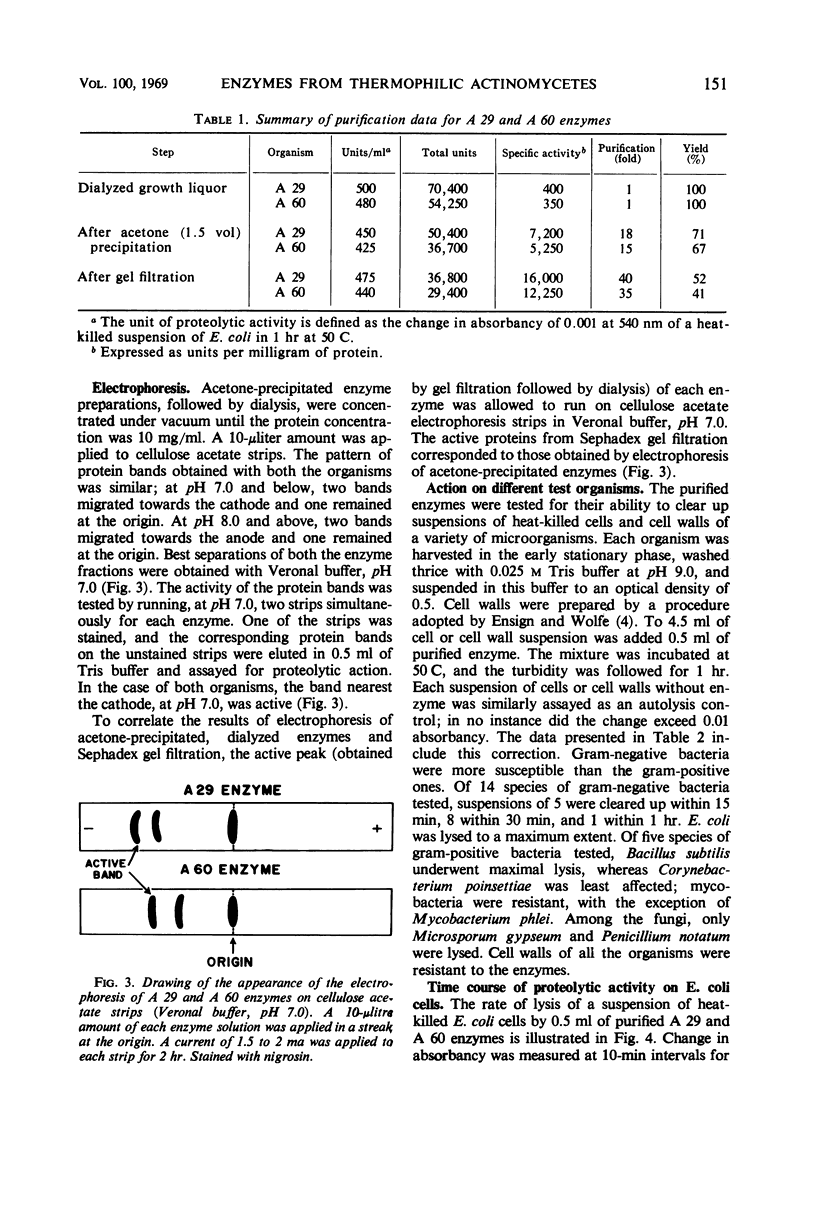
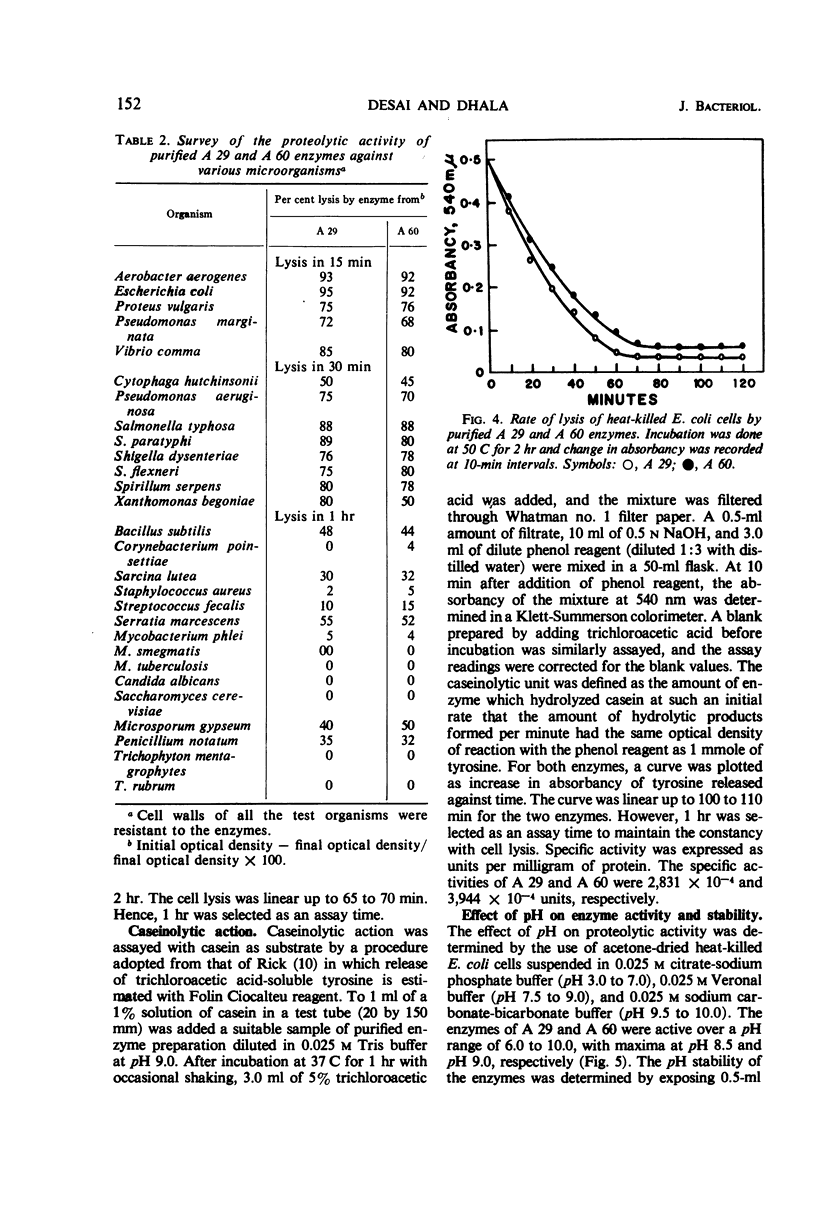
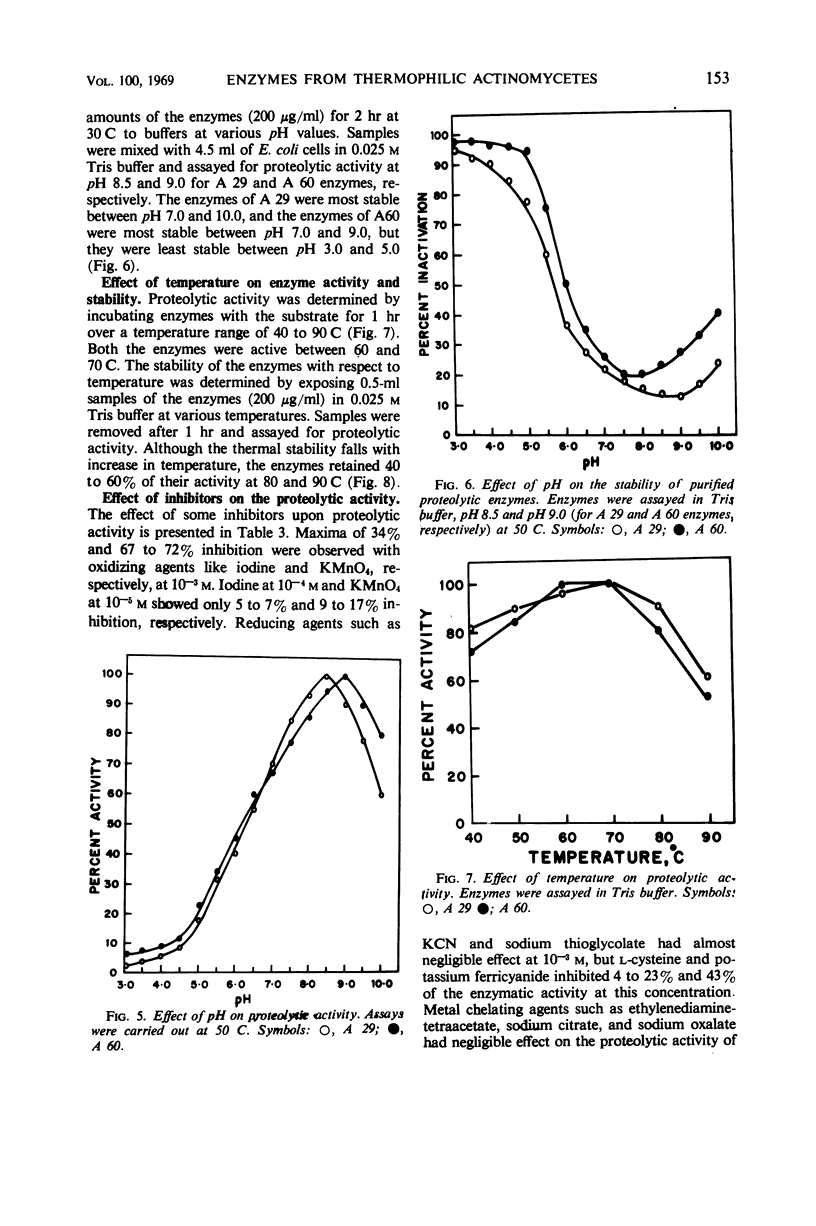
The enzymes isolated from two selected cultures of thermophilic actinomycetes—Thermomonospora fusca (A 29) and Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (A 60)—possess proteolytic activity. The enzymes were purified more than 35- to 40-fold and showed three bands each upon cellulose acetate electrophoresis at several pH values. Based upon Sephadex gel filtration, molecular weights of 21,500 and 23,800 were calculated for the active peaks of the enzymes. The purified enzymes lysed heat-killed cells of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, mycobacteria, and fungi and also hydrolyzed casein. The enzymes were most active between a temperature range of 60 and 70 C and pH 8.0 and 9.0, and were significantly inhibited by potassium permanganate, potassium ferricyanide, and iodine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai A. J., Dhala S. A. Bacteriolysis by thermophilic actinomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1967;33(1):56–62. doi: 10.1007/BF02045534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensign J. C., Wolfe R. S. Characterization of a small proteolytic enzyme which lyses bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):524–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.524-534.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSMACHEV A. E. Ob antagonisticheskikh svoistvakh termofil'nykh aktinomitsetov. Mikrobiologiia. 1956 Sep-Oct;25(5):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. I. Production and fractionation of the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):555–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. II. Nature of the cellular substrate attacked by the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):569–580. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTAGUE M. D. THE ENZYME DEGRADATION OF CELL WALLS OF STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:588–595. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somkuti G. A., Babel F. J. Purification and properties of Mucor pusillus acid protease. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1407–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1407-1414.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON W. T., TOVE S. B., SPECK M. L. EXTRACELLULAR PROTEINASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:49–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.49-53.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


