Abstract
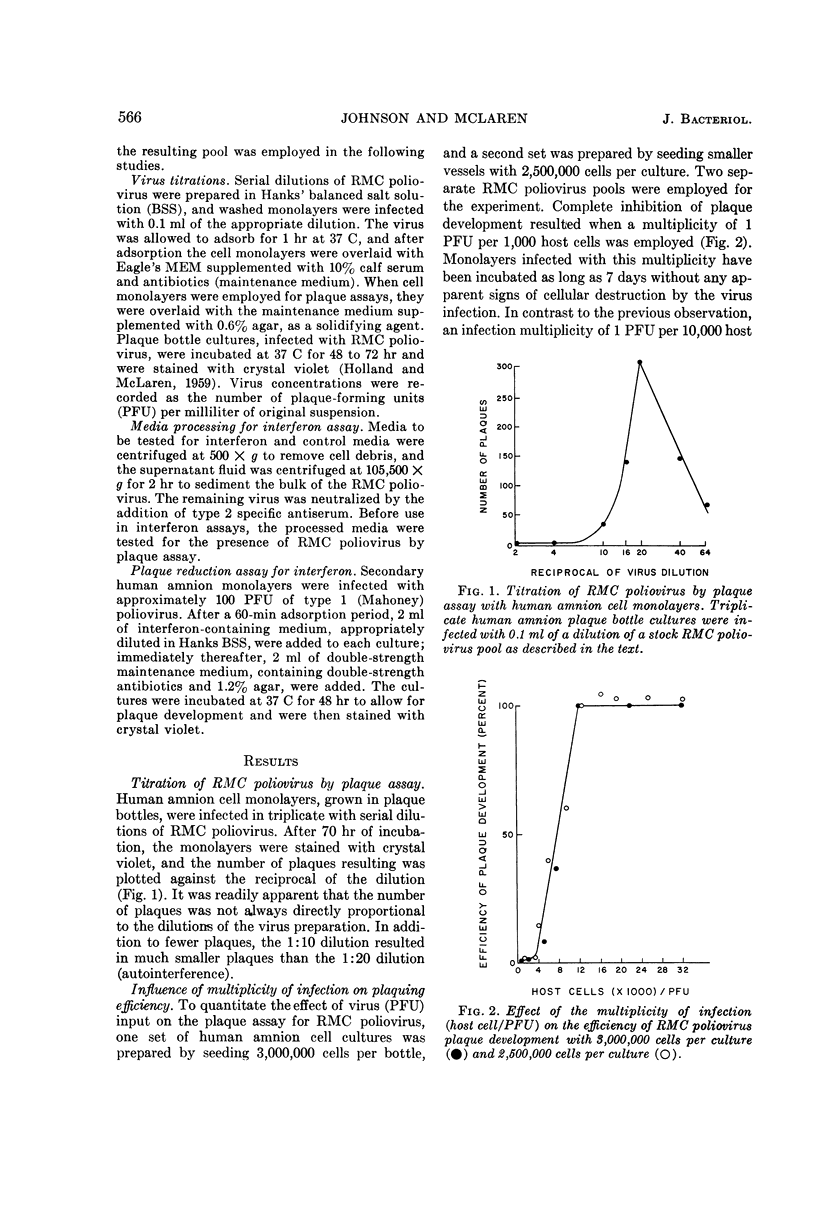
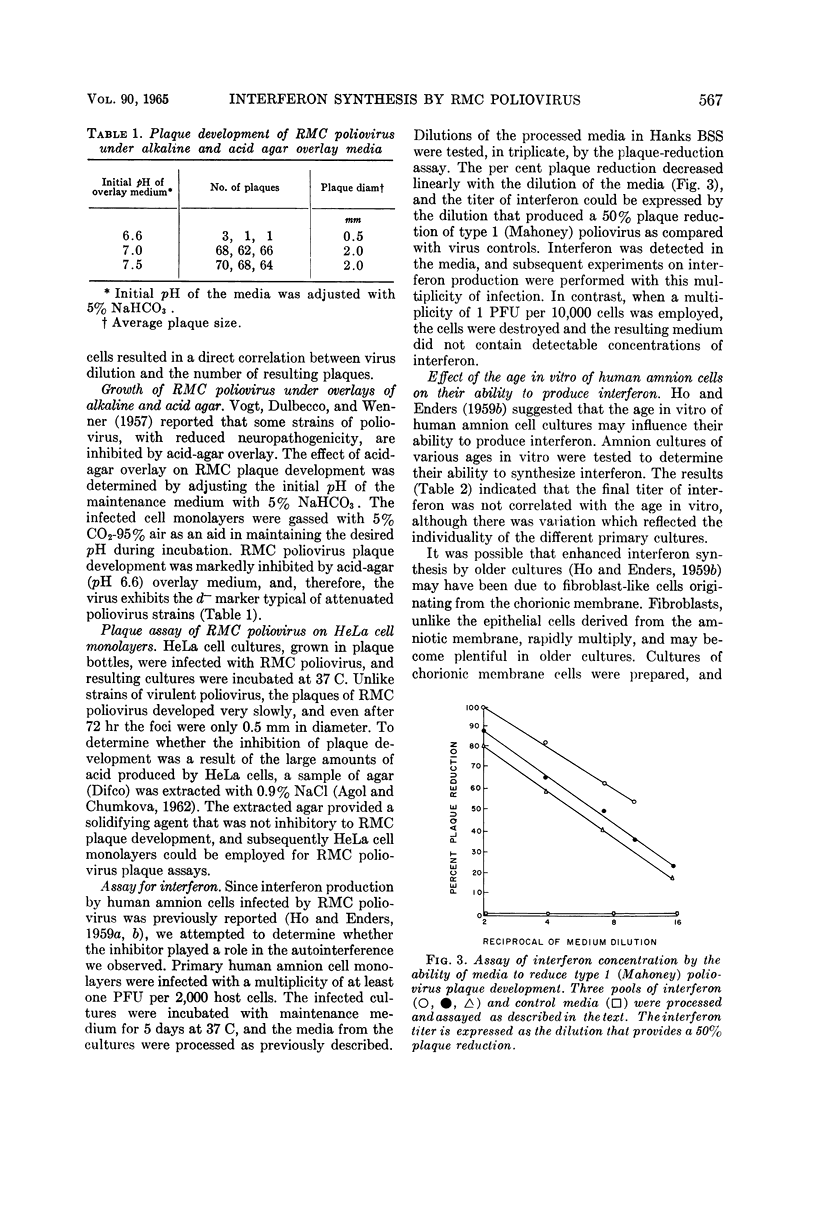
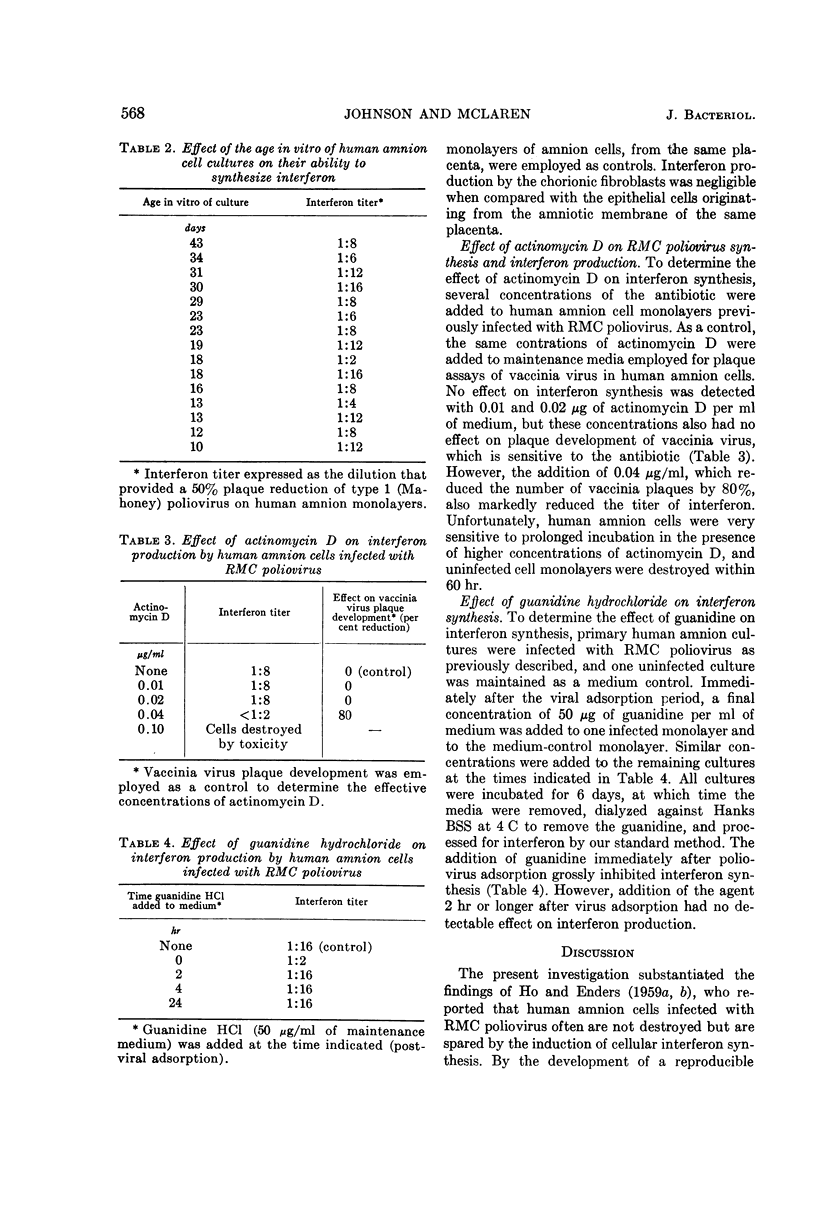
Johnson, Terry C. (University of Minnesota, Minneapolis), and Leroy C. McLaren. Plaque development and induction of interferon synthesis by RMC poliovirus. J. Bacteriol. 90:565–570. 1965.—Plaque development by RMC poliovirus on human amnion cell monolayers was investigated with regard to autointerference and to the effect of acid-agar overlay on plaquing efficiency. The virus was inhibited by acid-agar overlay, thereby exhibiting the d− marker typical of attenuated poliovirus strains. In addition, a lack of RMC poliovirus plaque development on HeLa cell monolayers was shown to be the result of an agar inhibitor which could be removed by NaCl extraction. By use of a simplified plaque reduction assay, it was shown that interferon production was responsible for the autointerference phenomenon. Interferon synthesis did not correlate with the ages in vitro of human amnion cell cultures. Fibroblasts originating from the chorionic membrane produced negligible amounts of the inhibitor. Interferon synthesis by human amnion cells infected with RMC poliovirus was inhibited by actinomycin D. The addition of guanidine hydrochloride to infected cultures immediately after RMC poliovirus adsorption markedly inhibited interferon synthesis, although after 2 hr (postadsorption) guanidine had no effect on interferon production.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOL V. I., CHUMAKOVA M. Ia. An agar polysaccharide and d marker of poliovirus. Virology. 1962 May;17:221–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWTHER D., MELNICK J. L. Studies of the inhibitory action of guanidine on poliovirus multiplication in cell cultures. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:65–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIFFORD G. E., HELLER E. EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D ON INTERFERON PRODUCTION BY 'ACTIVE' AND 'INACTIVE' CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS IN CHICK CELLS. Nature. 1963 Oct 5;200:50–51. doi: 10.1038/200050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Inhibition of DNA-primed RNA synthesis during poliovirus infection of human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C. Improved method for staining cell monolayers for virus plaque counts. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:596–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.4.596-597.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M., ENDERS J. F. Further studies on an inhibitor of viral activity appearing in infected cell cultures and its role in chronic viral infections. Virology. 1959 Nov;9:446–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Interferons. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jun 21;266:1313–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196206212662506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Enders J. F. AN INHIBITOR OF VIRAL ACTIVITY APPEARING IN INFECTED CELL CULTURES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Mar;45(3):385–389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINKO N., MELNICK J. L. Interference between poliomyelitis viruses in tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1954 Sep 1;100(3):247–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHMANN-GRUBE F. Preparation of cell cultures from human amniotic membranes. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1961;11:258–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01241690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B. [Inhibition of the in vitro multiplication of poliomyelitis viruses using guanidine]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1961 May 15;37:395–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Effect of actinomycin D on cellular nucleic acid synthesis and virus production. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):556–557. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUMEL Action of actinomycin D on animal cells and viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1238–1245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R., WENNER H. A. Mutants of poliomyelitis viruses with reduced efficiency of plating in acid medium and reduced neuropathogenicity. Virology. 1957 Aug;4(1):141–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


