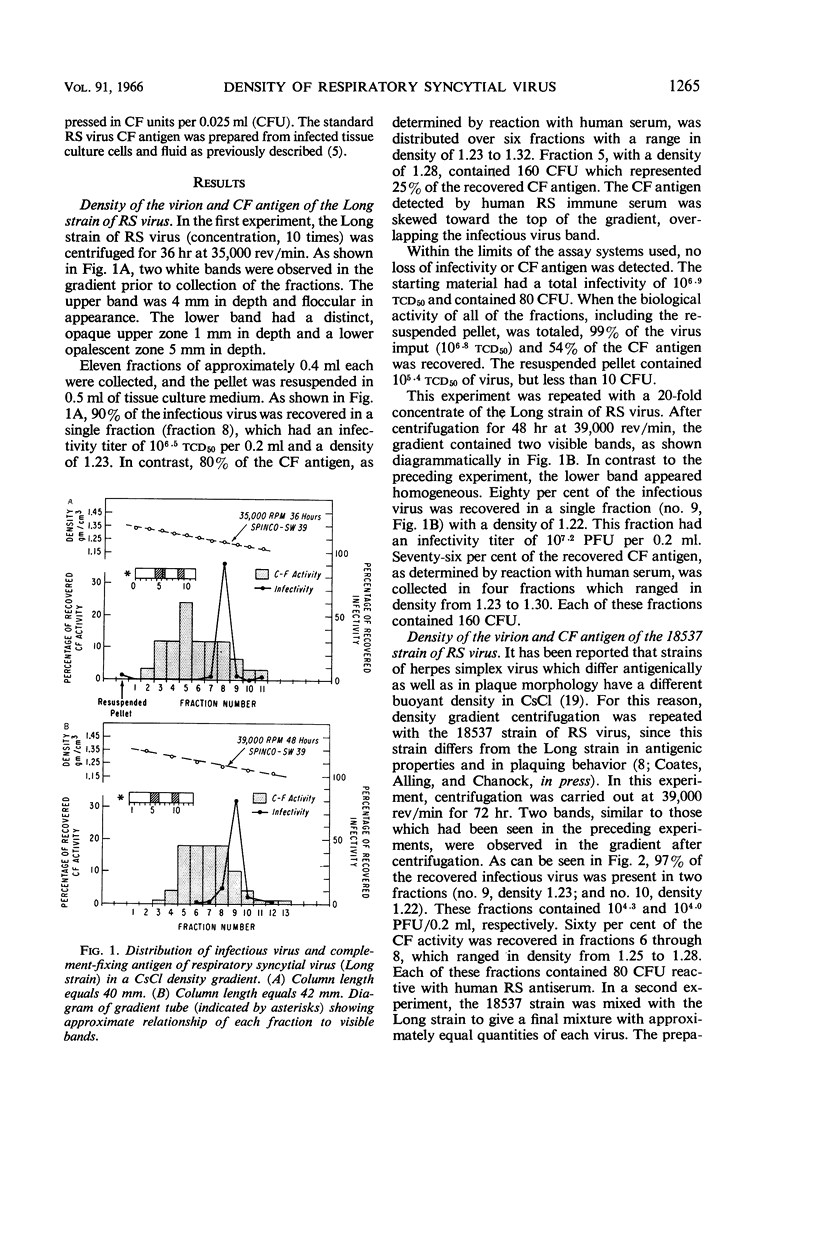
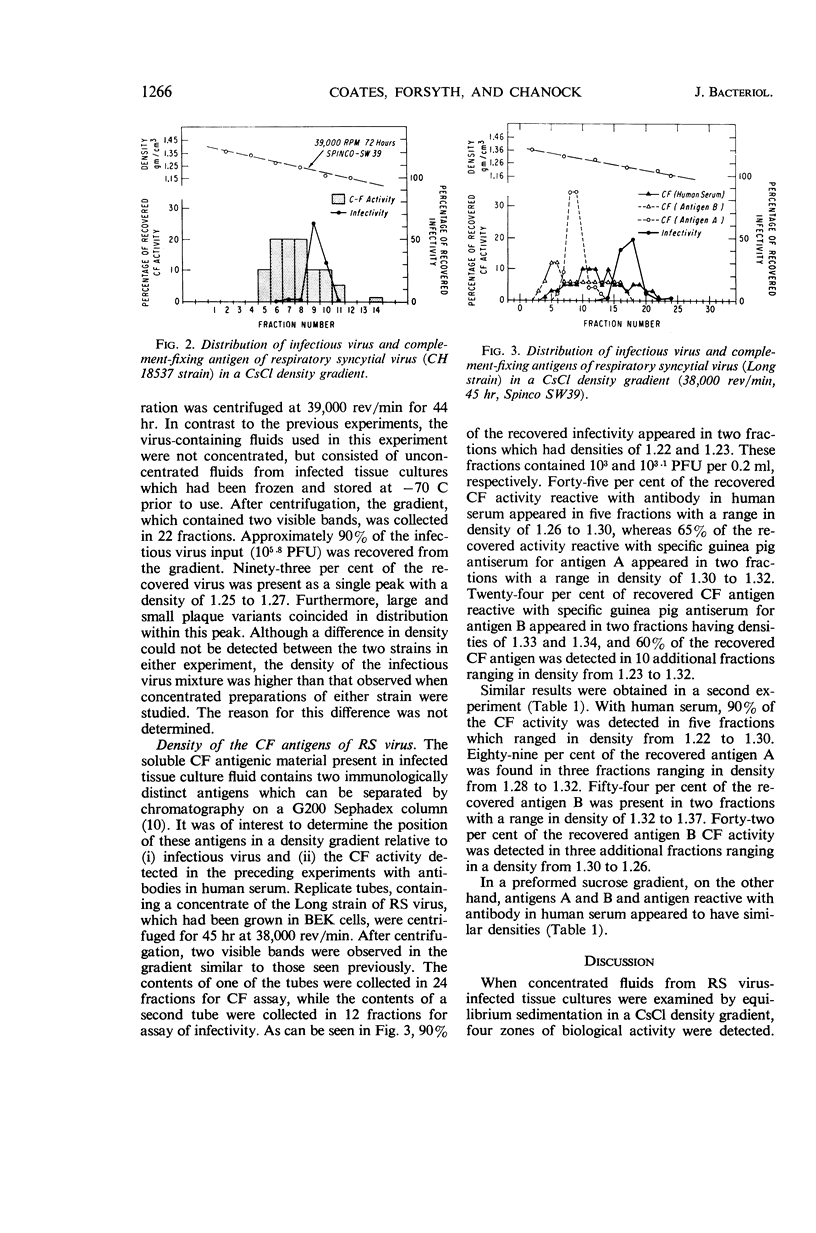
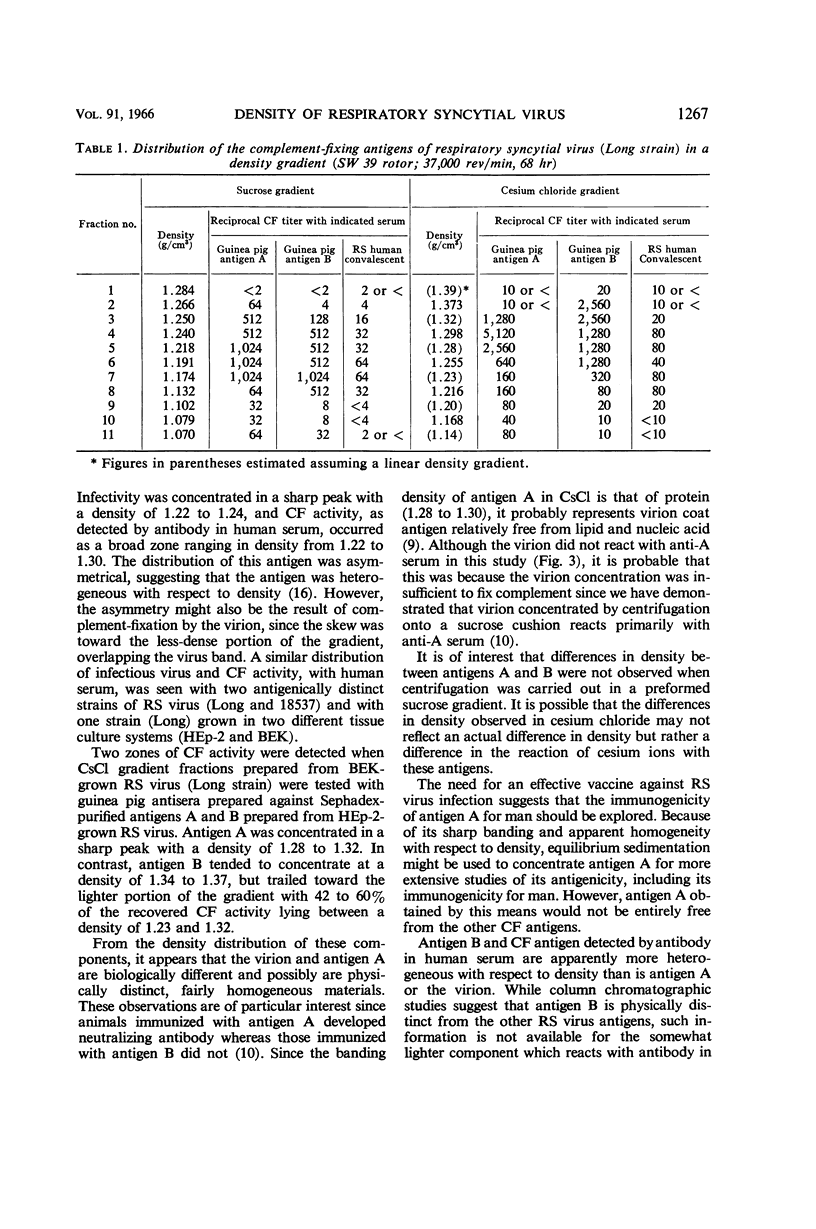
Abstract
Coates, Helen V. (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.), Ben R. Forsyth, and R. M. Chanock. Biophysical studies of respiratory syncytial virus. I. Density of respiratory syncytial virus and associated complement-fixing antigens in a cesium chloride density gradient. J. Bacteriol. 91:1263–1269. 1966.—Concentrated fluids from respiratory syncytial (RS) virus-infected tissue cultures (HEp-2 and BEK) were subjected to equilibrium sedimentation in cesium chloride. When two antigenically distinct strains of RS virus (Long and 18537) were tested, approximately 90% of the infectious virus was recovered in a sharp, symmetrical peak with a density of 1.22 to 1.24. In a similar study, unconcentrated virus had a density of 1.25 to 1.27. Two immunologically distinguishable complement-fixing antigens (antigens A and B) were detected at densities of 1.28 to 1.32 and 1.23 to 1.37. In addition, the existence of a third antigen (density of 1.22 to 1.30) was suggested. The possible origin of these antigens is discussed relative to the known properties of RS virus and the other myxoviruses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., PERRY B. T. Properties of the nucleic acid of the Ryan strain of filamentous influenza virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):40–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADA G. L., PERRY B. T. Studies on the soluble complement fixing antigens of influenza virus. 3. The nature of the antigens. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1954 Apr;32(2):177–185. doi: 10.1038/icb.1954.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D. Equilibrium sedimentation of influenza virus in caesium chloride density gradients. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Dec;38:499–507. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT C. R., Jr, HAMRE D. Growth and serological characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:8–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., KIM H. W., VARGOSKO A. J., DELEVA A., JOHNSON K. M., CUMMING C., PARROTT R. H. Respiratory syncytial virus. I. Virus recovery and other observations during 1960 outbreak of bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and minor respiratory diseases in children. JAMA. 1961 May 27;176:647–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., PARROTT R. H., COOK K., ANDREWS B. E., BELL J. A., REICHELDERFER T., KAPIKIAN A. Z., MASTROTA F. M., HUEBNER R. J. Newly recognized myxoviruses from children with respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jan 30;258(5):207–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195801302580502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R., ROIZMAN B., MYERS R. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). I. Isolation, properties and characterization. Am J Hyg. 1957 Nov;66(3):281–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COATES H. V., KENDRICK L., CHANOCK R. M. Antigenic differences between two strains of respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Apr;112:958–964. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., RUBIN H., DAVIS C. A. The production, purification, and properties of Newcastle disease virus labeled with radiophosphorus. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):96–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth B. R., Coates H. V., Chanock R. M. Biophysical studies of respiratory syncytial virus. II. Identification of two soluble complement-fixing antigens of respiratory syncytial virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1270–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1270-1276.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBNER R. J., CHANOCK R. M., RUBIN B. A., CASEY M. J. INDUCTION BY ADENOVIRUS TYPE 7 OF TUMORS IN HAMSTERS HAVING THE ANTIGENIC CHARACTERISTICS OF SV40 VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1333–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON K. M., CHANOCK R. M., RIFKIND D., KRAVETZ H. M., KNIGHT V. Respiratory syncytial virus. IV. Correlation of virus shedding, serologic response, and illness in adult volunteers. JAMA. 1961 May 27;176:663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISCH A. L., JOHNSON K. M., CHANOCK R. M. Immunofluorescence with respiratory syncytial virus. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:177–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Stahl F. W., Vinograd J. EQUILIBRIUM SEDIMENTATION OF MACROMOLECULES IN DENSITY GRADIENTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):581–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRBY E. SEPARATION OF MEASLES VIRUS COMPONENTS BY EQUILIBRIUM CENTRIFUGATION IN CSCL GRADIENTS. I. CRUDE AND TWEEN AND ETHER TREATED CONCENTRATED TISSUE CULTURE MATERIAL. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1964;14:306–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01555823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., ROANE P. R., Jr A physical difference between two strains of herpes simplex virus apparent on sedimentation in cesium chloride. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:75–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLUEDERBERG A. E., ROIZMAN B. Separation of multiple antigenic components of measles virus by equilibrium sedimentation in cesium chloride. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:80–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


