Abstract
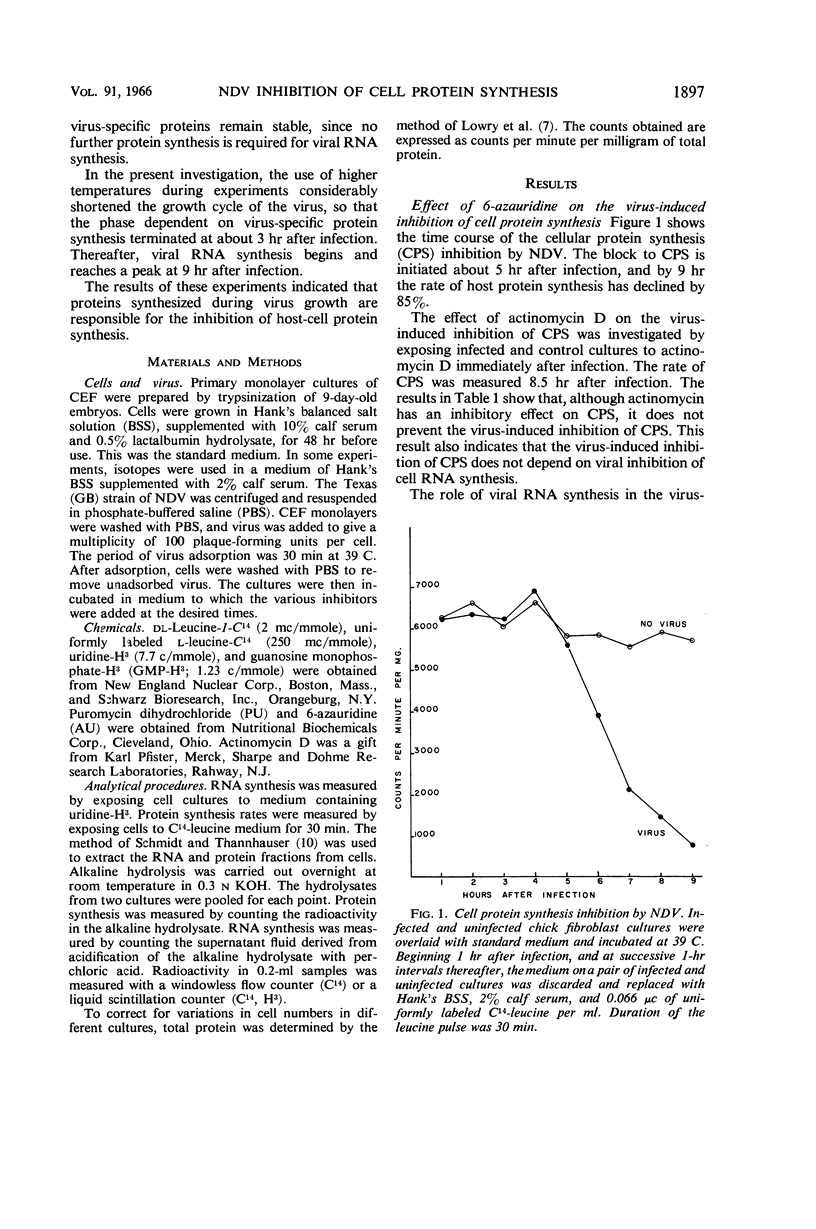
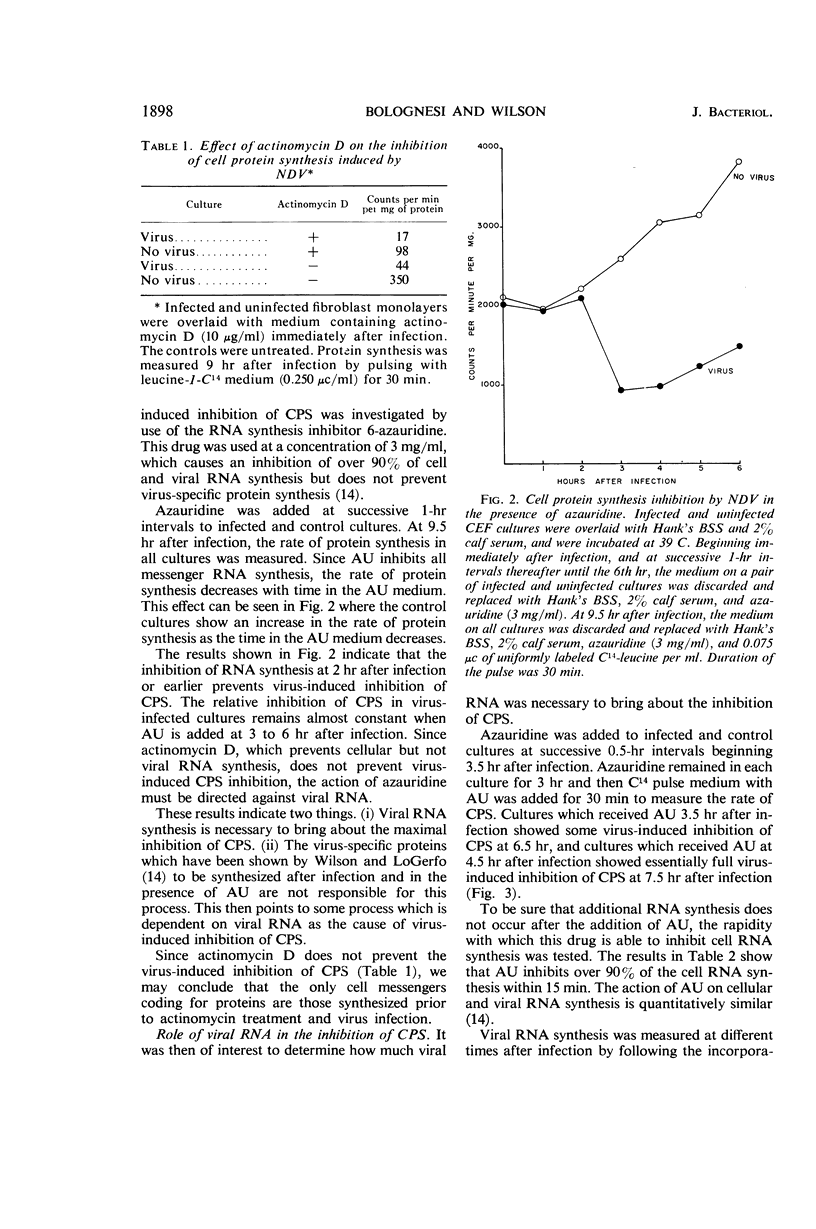
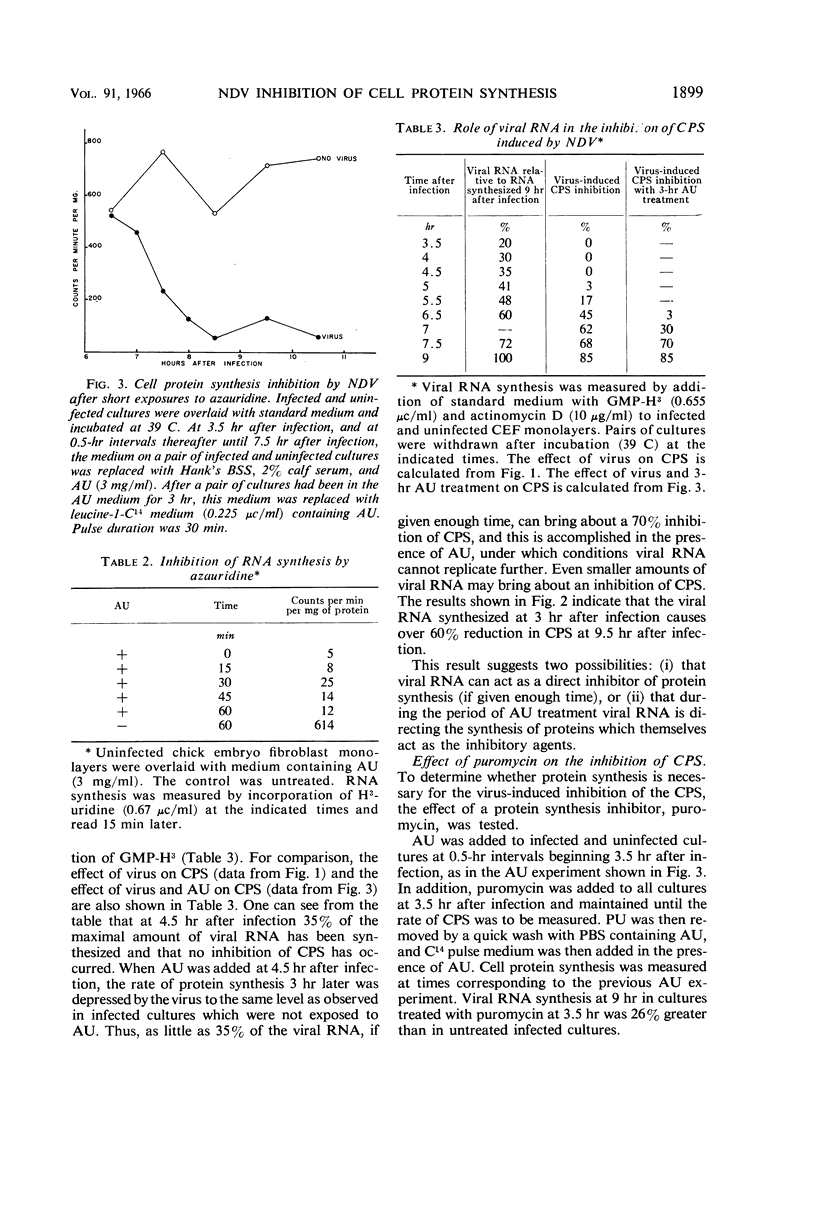
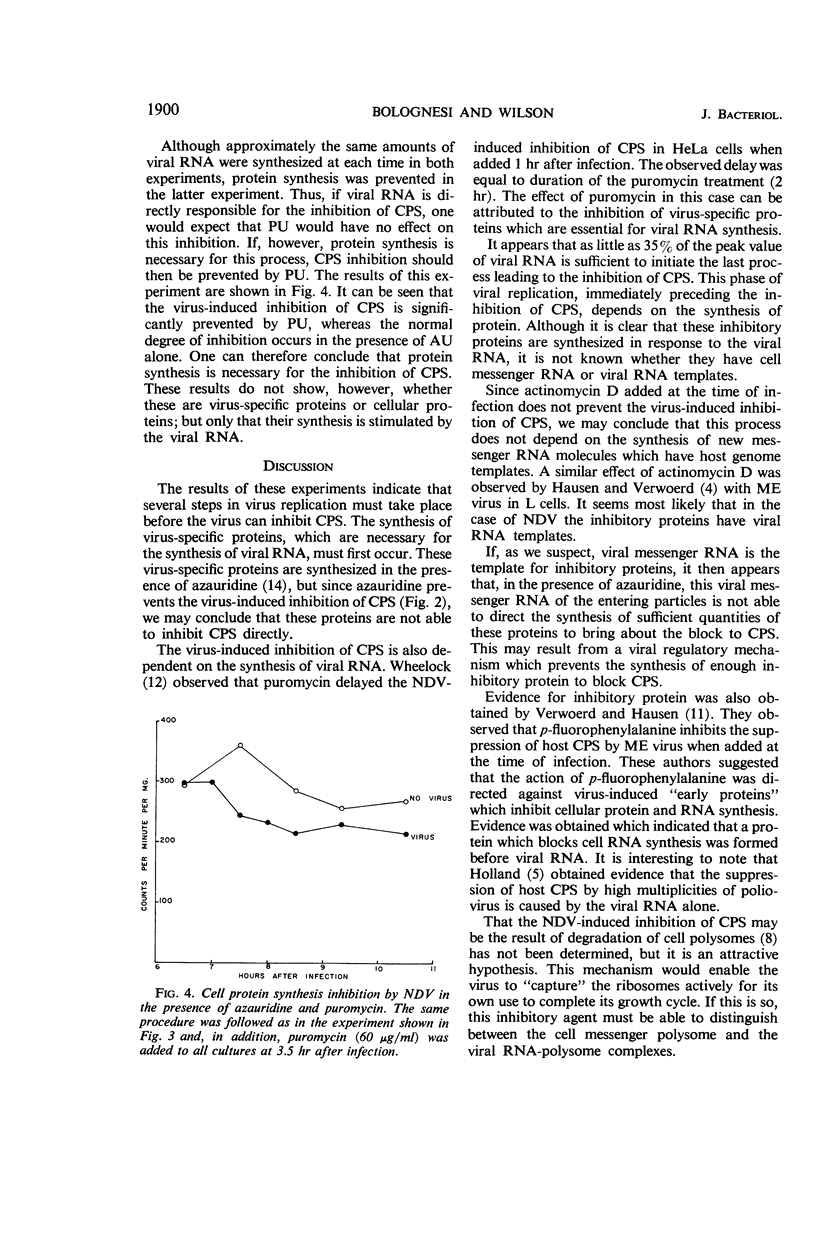
Bolognesi, D. P. (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, N.Y.), and D. E. Wilson. Inhibitory proteins in the Newcastle disease virus-induced suppression of cell protein synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 91:1896–1901. 1966.—Infection by Newcastle disease virus brings about a rapid and marked inhibition of cell protein synthesis (CPS) in chick embryo fibroblast monolayers. The block to CPS is initiated about 5 hr after infection, and by 9 hr about 85% of the host protein synthesis is shut off. Azauridine (3 mg/ml), a ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis inhibitor, prevents the virus-induced inhibition of CPS when added at the time of infection; but it does not prevent the inhibition when added at 3 hr after infection. When puromycin (60 μg/ml), a protein synthesis inhibitor, was added at 3.5 hr after infection, viral RNA was synthesized in normal amounts, but the virus-induced inhibition of CPS was prevented. Actinomycin D added at the time of infection does not, however, prevent the virus-induced inhibition of CPS. The results of these experiments indicate that proteins synthesized during Newcastle disease virus replication are responsible for the inhibition of host-cell protein synthesis. The synthesis of these inhibitory proteins depends on the prior synthesis of viral RNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DARNELL J. E., Jr Early events in poliovirus infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:149–158. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARNELL J. E., Jr, LEVINTOW L. Poliovirus protein: source of amino acids and time course of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jan;235:74–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., BALTIMORE D. Patterns of macromolecular synthesis in normal and virus-infected mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:175–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSEN P., VERWOERD D. W. STUDIES ON THE MULTIPLICATION OF A MEMBER OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP (ME VIRUS) IN L CELLS. III. ALTERATION OF RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHETIC PATTERNS IN VIRUS-INFECTED CELLS. Virology. 1963 Dec;21:617–627. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. INHIBITION OF HOST CELL MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS BY HIGH MULTIPLICITIES OF POLIOVIRUS UNDER CONDITIONS PREVENTING VIRUS SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:574–581. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PETERSON J. A. NUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DURING POLIOVIRUS INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:556–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICH A., PENMAN S., BECKER Y., DARNELL J., HALL C. POLYRIBOSOMES: SIZE IN NORMAL AND POLIO- INFECTED HELA CELLS. Science. 1963 Dec 27;142(3600):1658–1663. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3600.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALZMAN N. P., LOCKART R. Z., Jr, SEBRING E. D. Alterations in HeLa cell metabolism resulting from poliovirus infection. Virology. 1959 Oct;9:244–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERWOERD D. W., HAUSEN P. STUDIES ON THE MULTIPLICATION OF A MEMBER OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP (ME VIRUS) IN L CELLS. IV. ROLE OF "EARLY PROTEINS" IN VIRUS INDUCED METABOLIC CHANGES. Virology. 1963 Dec;21:628–635. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELOCK E. F., TAMM I. Biochemical basis for alterations in structure and function of HeLa cells infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:617–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELOCK E. F. The role of protein synthesis in the eclipse period of newcastle disease virus multiplication in HeLa cells as studied with puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1358–1366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON D. E., LOGERFO P. INHIBITION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN NEWCASTLE DISEASE VIRUS-INFECTED CELLS BY PUROMYCIN AND 6-AZAURIDINE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1550–1555. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1550-1555.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN E. F., HEETER M., DARNELL J. E. RNA synthesis in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


