Abstract
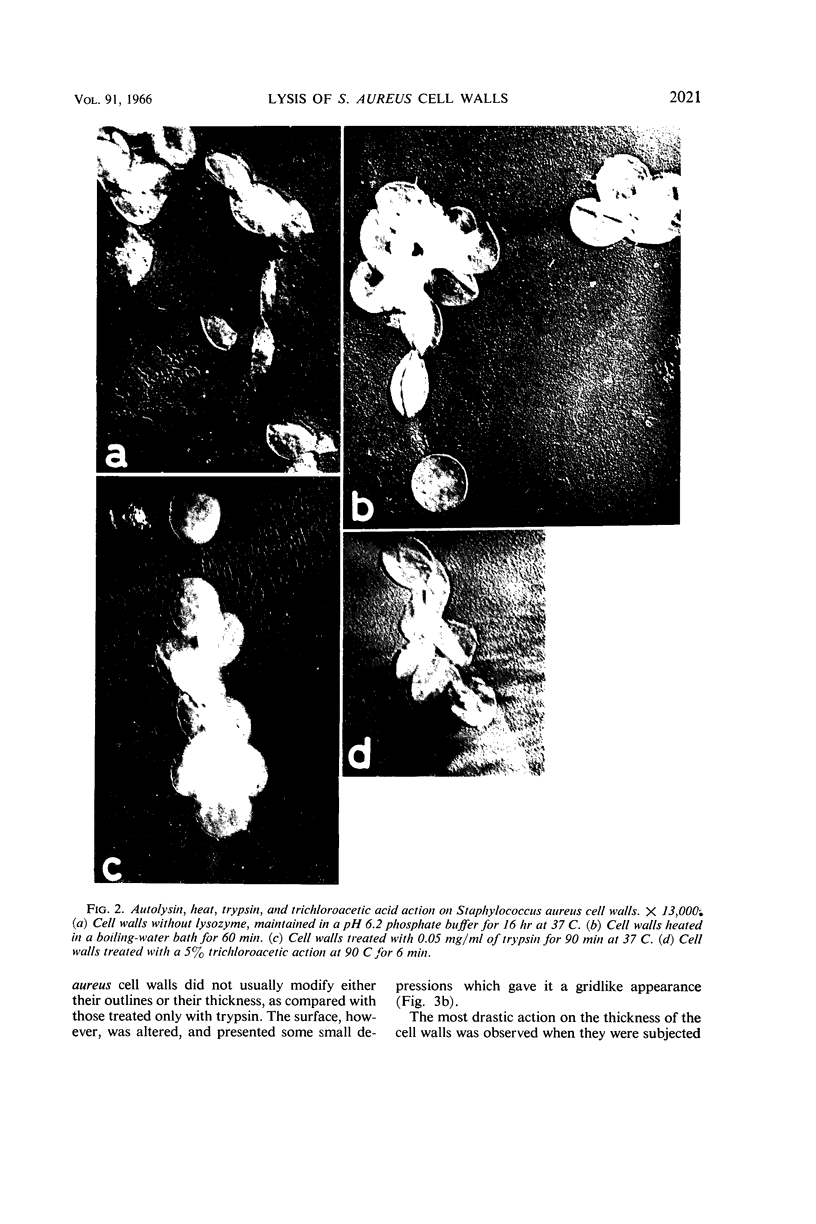
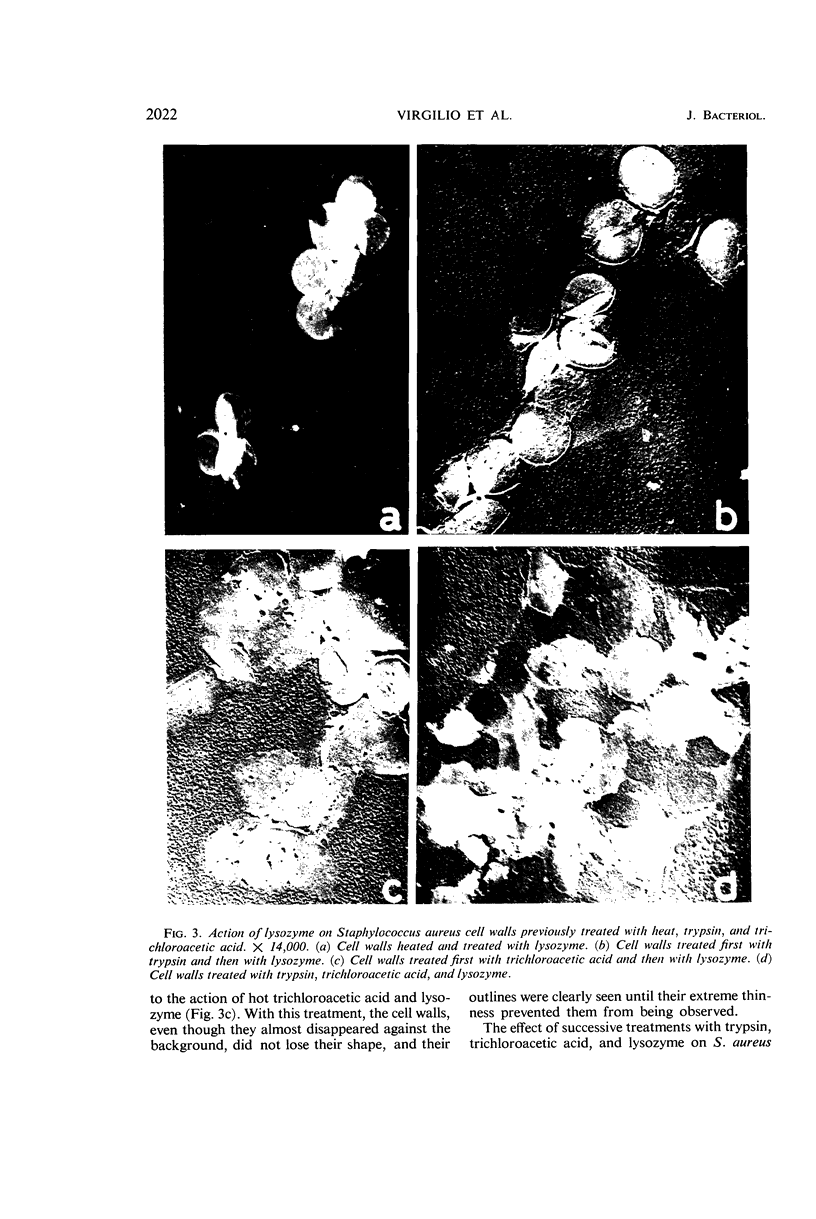
Virgilio, Rafael (Escuela de Química y Farmacia, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile), C. González, Nubia Muñoz, and Silvia Mendoza. Electron microscopy of Staphylococcus aureus cell wall lysis. J. Bacteriol. 91:2018–2024. 1966.—A crude suspension of Staphylococcus aureus cell walls (strain Cowan III) in buffer solution was shown by electron microscopy to lyse slightly after 16 hr, probably owing to the action of autolysin. The lysis was considerably faster and more intense after the addition of lysozyme. A remarkable reduction in thickness and rigidity of the cell walls, together with the appearance of many irregular protrusions in their outlines, was observed after 2 hr; after 16 hr, there remained only a few recognizable cell wall fragments but many residual particulate remnants. When autolysin was previously inactivated by trypsin, there was a complete inhibition of the lytic action of lysozyme; on the other hand, when autolysin was inactivated by heat and lysozyme was added, a distinct decrease in the thickness of the cell walls was observed, but there was no destruction of the walls. The lytic action of lysozyme, after treatment with hot 5% trichloroacetic acid, gave rise to a marked dissolution of the structure of the cell walls, which became lost against the background, without, however, showing ostensible alteration of wall outlines. From a morphological point of view, the lytic action of autolysin plus lysozyme was quite different from that of trichloroacetic acid plus lysozyme, as shown by electron micrographs, but in both cases it was very intense. This would suggest different mechanisms of action for these agents.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRICH K. M., SWORD C. P. METHICILLIN-INDUCED LYSOZYME-SENSITIVE FORMS OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:690–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.690-695.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. The study of cell rupture in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):199–206. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERN R. A., KINGKADE M. J., KERN S. F., BEHRENS O. K. Characterization of the action of lysozyme on Staphylococcus aureus and on Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.171-178.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Studies on the chemistry and immunochemistry of cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:229–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEDING P. Observations on the sensitization of erythrocytes with staphylococcal polysaccharide products. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;41(5):435–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1957.tb01046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. R. Chemical structure and biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:18–55. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.18-55.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., MCIVOR M. CELL-WALL LYSINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS STRAINS INDUCED BY SPECIFIC TYPING PHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.667-675.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J. STAPHYLOCOCCAL SENSITIZATION: SPECIFIC BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF PHAGE K ON THE BACTERIAL CELL WALL IN LYSIS-FROM-WITHOUT. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1185–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1185-1193.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Cell structure and the enzymic lysis of bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):512–523. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R., PAVLIK J. G. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. VI. Wall composition and sensitivity to lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:398–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. The properties of lysozyme and its action on microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Jun;21(2):82–100. doi: 10.1128/br.21.2.82-100.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]