Abstract
Background: Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a zinc-finger transcription factor with diverse regulatory functions in proliferation, differentiation, and development. KLF4 also plays a role in inflammation, tumorigenesis, and reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. To gain insight into the mechanisms by which KLF4 regulates these processes, we conducted DNA microarray analyses to identify differentially expressed genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) wild type and null for Klf4. Methods: Expression profiles of fibroblasts isolated from mouse embryos wild type or null for the Klf4 alleles were examined by DNA microarrays. Differentially expressed genes were subjected to the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). The microarray data were also interrogated with the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) for pathway identification. Results obtained from the microarray analysis were confirmed by Western blotting for select genes with biological relevance to determine the correlation between mRNA and protein levels. Results: One hundred and sixty three up-regulated and 88 down-regulated genes were identified that demonstrated a fold-change of at least 1.5 and a P-value < 0.05 in Klf4-null MEFs compared to wild type MEFs. Many of the up-regulated genes in Klf4-null MEFs encode proto-oncogenes, growth factors, extracellular matrix, and cell cycle activators. In contrast, genes encoding tumor suppressors and those involved in JAK-STAT signaling pathways are down-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs. IPA and GSEA also identified various pathways that are regulated by KLF4. Lastly, Western blotting of select target genes confirmed the changes revealed by microarray data. Conclusions: These data are not only consistent with previous functional studies of KLF4's role in tumor suppression and somatic cell reprogramming, but also revealed novel target genes that mediate KLF4's functions.
Keywords: KLF4, microarray, MEF, DAVID, GSEA, IPA, SAM, FDR
Introduction
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) [1, 2] is a member of the KLF family of zinc finger transcription factors that are involved in diverse biological processes including proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and development [3-7]. KLF4 also plays an important role in pathological conditions such as tumorigenesis and inflammation [8-14]. Moreover, recent studies indicate that KLF4 is involved in the reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells [15-20]. The finding that KLF4 overexpression prevents mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell differentiation suggests that KLF4 contributes to ES cell self-renewal [21].
Mice deficient for Klf4 have been generated. Klf4-null (Klf4-/-) mice die shortly after birth and exhibit defects in terminal differentiation of epithelial tissues such as the epidermis and colon [22, 23]. Mice with tissue-specific deletion of Klf4 also have perturbed homeostasis in tissues from which the gene was deleted including the conjunctiva and stomach [24, 25]. In contrast, mice heterozygous for Klf4 (Klf4+/-) are normal but have increased tumor burden in the intestine when bred to ApcMin mice that are genetically predisposed to develop intestinal adenomas [10]. Conversely, inhibition of oncogenic Notch signaling in ApcMin mice results in an increase in Klf4 expression accompanied by a reduction in intestinal tumor burden [9]. These results are highly suggestive of a tumor suppressive function for KLF4 in the intestinal epithelium. Recent studies demonstrating that mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) null for the Klf4 alleles are genetically unstable as evidenced by the presence of aneuploidy, chromosome aberration, and centrosome amplification are consistent with this notion [26].
Despite growing evidence that KLF4 mediates many important physiological processes as exemplified above, the biochemical mechanisms by which KLF4 exerts many of its functions are not well established. Previous studies involving transcriptional profiling of KLF4 when it is overexpressed in a colon cancer cell line indicate that KLF4 has a global inhibitory effect on macromolecular biosynthesis and the cell cycle [27, 28]. However, no systemic evaluation has been conducted to examine the global expression profiles of KLF4 in untransformed cells. Here we compared the expression profiles of KLF4 between MEFs wild type and null for the Klf4 alleles in an attempt to gain further insight into the mechanism of action of KLF4 in a physiological context.
Materials and methods
Isolation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and cell culture
Mice heterozygous for the Klf4 alleles (Klf4+/-) on a C57BL/6 background [23] were crossbred. MEFs wild type (Klf4+/+), heterozygous (Klf4+/-), or null (Klf4-/-) for Klf4 were derived from day 13.5 embryos using the 3T3 protocol as previously described [29]. Briefly, 106 MEFs were plated on 10-cm dishes and maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37°C in atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Cells were passed every 3 days at a density of 106 cells per 10-cm dish. The breeding of mice and isolation of MEFs from mice were approved by the Emory University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol number 098-2007).
Purification and preparation of RNA
RNA was processed from cells that had reached 80-90 confluency. Total RNA from cultured wild type and Klf4-null MEFs in triplicate was extracted using Trizol reagent as recommended by the manufacturer (Invitrogen; Carlsbad, CA). RNA was subjected to DNase I treatment in order to remove any contaminating genomic DNA. Final purification was performed on RNAeasy columns (Qiagen; Valencia, CA), according to the manufacturer's recommendations. The integrity of total RNA was confirmed by formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis. The RNA was quantified by spectrophotometric reading at 260 and 280 nm and RNA with OD260 /OD280 > 1.8 was submitted for microarray analysis.
Microarray expression analysis
Purified RNA was shipped to the Emory Bio-marker Service Center, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, for microarray analysis. Concentration of the RNA was quantified by a Nanodrop spec-trophotometer (Wilmington, DE) and quality was assessed using the Agilent Bioanalyzer (Foster City, CA). Samples with the RNA integrity number of > 7 were used for further microarray analysis. RNA was amplified into cRNA and labeled by in vitro transcription using Illumina TotalPrep RNA Amplification Kit (Ambion, Applied Biosystems; Foster City, CA). Samples were then hybridized to the Mouse WG-6 v2.0 Expression Beadchip that queries 45,281 transcripts that cover over 19,000 unique, curated genes in the NCBI RefSeq database (Build 36, Release 22). The chips were processed as per manufacturer's instructions without any modification. The arrays were scanned using the BeadStation 500 Instrument (Illumina Inc.; San Diego, CA) and data were normalized using the GenomeStudio v1.0.2 (Illumina Inc.; San Diego, CA). The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI's) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and are accessible through GEO series accession number GSE21768.
Data normalization and statistical analysis
The background subtraction, expression summary, normalization, and log base 2 transformation of gene signals were carried out using Illumina Beadchip software (Illumina Inc.; San Diego, CA). Significant genes were identified using the significance analysis of microarrays (SAM) software [30], for which 1,000 random class assignment permutations estimated a false discovery rate (FDR) rate of 1%. This resulted in the identification of 6,218 genes with significant changes in expression between Klf4+/+ and Klf4-/- MEFs.The 6,218 differentially expressed genes were annotated and biological processes were analyzed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) (www.david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov). A fold-change of > 1.5 or < -1.5 and P < 0.05 were used as the criteria for significant gene expression changes between the Klf4+/+ and Klf4-/- cells. This narrowed the number of significant genes down to 251 genes, including 163 up-regulated and 88 down-regulated ones, in Klf4-null cells.
Pathway analyses were conducted on the 6,218 differentially expressed genes with a FDR of 1% identified above using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA; www.broad.mit.edu/gsea) and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA; www.ingenity.com). GSEA, based on the Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic, was performed as described [31]. GSEA is a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles, using 1,000 trials with randomly permuted class label to estimate a P-value. For each gene set, the ES (enrichment score) were normalized to account for differences in gene set size. The false discovery rate (FDR) was then calculated relative to the normalized enrichment score (NES) values to determine the false-positive rate. Significant FDR and P-values were less than 25% and 0.001, respectively, in accordance with GSEA recommendations.
IPA assigns biological functions to genes using the Ingenuity Pathways Knowledge Base (Ingenuity Systems, Inc., Redwood City, CA). In this, genes could be sorted several times to different groups, if their function is known as to be multimodal. The dataset containing the gene identifiers and fold-changes were uploaded into the web-based application and each gene identifier was mapped to its corresponding gene object in the Ingenuity Pathways Knowledge Base. After the analysis, generated biological function genes are ordered by P-value of significance and maximum number of genes.
Western blot analysis
Following protein extraction, Western blot analysis was conducted using primary antibodies against CDK2, MMP3, SUMO3, and β-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), STAT3, pSTAT3 and SOCS3 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA). The blots were incubated with appropriate horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. The antibody-antigen complex was visualized by ECL chemiluminescence (Amersham, Pittsburgh, PA, USA).
Results
Changes in global gene expression patterns between wild type and Klf4-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts
To identify differentially expressed genes between wild type and Klf4-null MEFs, complimentary RNAs in triplicate were hybridized to the Illumina Mouse WG-6 v2.0 Expression BeadChip containing 45,218 probes that represent over 19,000 unique, curated mouse genes in the NCBI RefSeq database (Build 36, Release 22). Significance analysis of microarray (SAM) was used to analyze the original normalized dataset. This revealed a total of 6,218 genes that were differentially expressed in the Klf4-null cells compared to wild type MEFs with a false discovery rate (FDR) equal to or less than 1% (1% chance of genes falsely identified as differentially expressed). Among this group, 163 up-regulated and 88 down-regulated genes in Klf4-null compared to wild type MEFs exhibited at least a 1.5 fold-change in expression levels and a P-value < 0.05. Both the up- and down-regulated differentially expressed genes were submitted to DAVID (Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery), a web-based application (david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov) that allows access to a relational database of functional annotation [32, 33]. Shown in Tables 1 and 2 are examples of the up-regulated and down-regulated genes in Klf4-null cells, respectively, that have identifiable molecular functions. Moreover, many of these genes can be clustered into major functional categories. For example, up-regulated genes in Klf4-null cells encode cell cycle activators, extracellular matrix proteins, proto-oncogenes, growth factors, and proteins involved in ubiquitination and inflammatory responses (Table 1). In contrast, a distinct group of genes is down-regulated in Klf4-null cells and includes those encoding JAK-STAT signaling proteins, homeobox proteins, glutathione metabolism, and ephrins (Table 2). The full lists of up- and down-regulated genes in Klf4 -null MEFs are provided as supplementary materials (Tables S1 and S2, respectively).
Table 1.
Examples of functional annotation clustering of genes up-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs
| ILLUMINA_ID | Gene Symbol | Gene Name (Description) | P-Value | Fold-change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Cycle | 8.00E-03 | |||
| ILMN_1217331 | Mcm6 | MINICHROMOSOME MAINTENANCE DEFICIENT 6 | 40.36 | |
| ILMN_2723931 | E2f6 | E2F TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR 6 | 26.8 | |
| ILMN_1218470 | Cdk2 | CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE 2 | 9.32 | |
| ILMN_2652909 | Ddit3 | DNA-DAMAGE INDUCIBLE TRANSCRIPT 3 | 2.07 | |
| ILMN_2742152 | Gadd45a | GROWTH ARREST AND DNA-DAMAGE-INDUCIBLE 45 ALPHA | 1.92 | |
| ILMN_1227009 | Gas2l1 | GROWTH ARREST-SPECIFIC 2 LIKE 1 | 1.74 | |
| ILMN_1220454 | Anapc13 | ANAPHASE PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 13 | 1.61 | |
| ILMN_1216213 | Incenp | INNER CENTROMERE PROTEIN | 1.56 | |
| ILMN_1256301 | Rcc2 | REGULATOR OF CHROMOSOME CONDENSATION 2 | 1.53 | |
| Extracellular Matrix | 5.80E-06 | |||
| ILMN_2735184 | Col18a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE XVIII, ALPHA 1 | 51.5 | |
| ILMN_1223997 | Crtap | CARTILAGE ASSOCIATED PROTEIN | 32.74 | |
| ILMN_2753809 | Mmp3 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 3 | 31.08 | |
| ILMN_2747959 | Dcn | DECORIN | 21.44 | |
| ILMN_2737685 | Mmp13 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 13 | 13.86 | |
| ILMN_1258629 | Col3a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE III, ALPHA 1 | 5.65 | |
| ILMN_2619952 | Mmp10 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 10 | 5.32 | |
| ILMN_1254546 | Col5a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE V, ALPHA 2 | 3.42 | |
| ILMN_1238215 | Ctgf | CONNECTIVE TISSUE GROWTH FACTOR | 2.28 | |
| ILMN_2687880 | Col1a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE I, ALPHA 1 | 2.06 | |
| ILMN_1258759 | Col6a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE VI, ALPHA 2 | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_2678218 | Mmp2 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 2 | 1.75 | |
| ILMN_1217071 | Mmp16 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 16 | 1.67 | |
| Ubiquitin | 1.40E-02 | |||
| ILMN_2662401 | Sumo3 | SMT3 SUPPRESSOR OF MIF TWO 3 HOMOLOG 3 (YEAST) | 70.01 | |
| ILMN_1225261 | Uchl1 | UBIQUITIN CARBOXY-TERMINAL HYDROLASE L1 | 3.02 | |
| ILMN_1229019 | Fbxo44 | F-BOX PROTEIN 44 | 2.12 | |
| ILMN_2749911 | Ube2q2 | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2Q (PUTATIVE) 2 | 1.96 | |
| ILMN_2417991 | Ube2i | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2I | 1.79 | |
| ILMN_1227863 | Ube2n | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2N | 1.53 | |
| Proto-oncogenes | 2.70E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2655260 | Ptp4a3 | PROTEIN TYROSINE PHOSPHATASE 4A3 | 4.0 | |
| ILMN_1233424 | Lbcl1 | RHO/RAC GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE FACTOR (GEF) 2 | 2.03 | |
| ILMN_1224526 | Lck | LYMPHOCYTE PROTEIN TYROSINE KINASE | 2.0 | |
| ILMN_1237241 | Araf | V-RAF MURINE SARCOMA 3611 VIRAL ONCOGENE HOMOLOG | 1.83 | |
| ILMN_1212787 | Pttg1 | PITUITARY TUMOR-TRANSFORMING 1 | 1.8 | |
| ILMN_2481071 | Hras1 | HARVEY RAT SARCOMA VIRUS ONCOGENE 1 | 1.78 | |
| ILMN_1251669 | Evi2a | ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE 2A | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_2492264 | Wisp1 | WNT1 INDUCIBLE SIGNALING PATHWAY PROTEIN 1 | 1.76 | |
| ILMN_1221750 | Mycl1 | LUNG CARCINOMA MYC RELATED ONCOGENE 1 | 1.66 | |
| Growth Factors | 2.30E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1238547 | Areg | AMPHIREGULIN | 21.43 | |
| ILMN_1215252 | Bmp4 | BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEIN 4 | 14.31 | |
| ILMN_2745480 | Fgf13 | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 13 | 6.53 | |
| ILMN_2710698 | Fgf21 | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 21 | 5.51 | |
| ILMN_1236725 | Gdf1 | GROWTH DIFFERENTIATION FACTOR 1 | 2.53 | |
| ILMN_2484527 | Vegfa | VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR A | 1.97 | |
| ILMN_2736496 | Fgf10 | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 10 | 1.73 | |
| Chemotaxis | 1.50E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1231814 | Ccl5 | CHEMOKINE (C-C MOTIF) LIGAND 5 | 13.25 | |
| ILMN_2763243 | Cxcl1 | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 1 | 8.46 | |
| ILMN_2658910 | Cxcl12 | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 12 | 6.78 | |
| ILMN_1245710 | Ccl2 | CHEMOKINE (C-C MOTIF) LIGAND 2 | 5.47 | |
| ILMN_1214419 | Cxcl10 | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 10 | 2.94 | |
| Inflammatory Response | 1.60E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1230789 | C3 | COMPLEMENT COMPONENT 3 | 8.8 | |
| ILMN_2763243 | Cxcl1 | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 1 | 8.46 | |
| ILMN_2742075 | Cd14 | CD14 ANTIGEN | 2.68 | |
| ILMN_1254383 | Atrn | ATTRACTIN | 1.99 | |
| ILMN_1259252 | Anxa1 | ANNEXIN A1 | 1.99 | |
| Other Genes | ||||
| ILMN_1218967 | Kif2c | KINESIN FAMILY MEMBER 2C | 37.42 | |
| ILMN_2611181 | Ccdc3 | COILED-COIL DOMAIN CONTAINING 3 | 36.32 | |
| ILMN_2703267 | Nes | NESTIN | 18.5 | |
| ILMN_1245451 | Rab6b | RAB6B, MEMBER RAS ONCOGENE FAMILY | 14.71 | |
| ILMN_2713285 | Fhl1 | FOUR AND A HALF LIM DOMAINS 1 | 14.19 | |
| ILMN_2606660 | Card10 | CASPASE RECRUITMENT DOMAIN FAMILY, MEMBER 10 | 10.23 | |
| ILMN_2686327 | Gas6 | GROWTH ARREST SPECIFIC 6 | 8.94 | |
| ILMN_2689998 | Fjx1 | FOUR JOINTED BOX 1 (DROSOPHILA) | 8.81 | |
| ILMN_1247646 | H1fx | H1 HISTONE FAMILY, MEMBER X | 6.91 | |
| ILMN_1217159 | Lmo7 | LIM DOMAIN ONLY 7 | 5.51 | |
| ILMN_1214327 | S100a13 | S100 CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN A13 | 5.19 | |
| ILMN_1242829 | Prdx2 | PEROXIREDOXIN 2 | 5.10 | |
| ILMN_2868133 | Gata6 | GATA BINDING PROTEIN 6 | 4.75 | |
| ILMN_1227993 | Vav3 | VAV 3 ONCOGENE | 2.67 | |
| ILMN_2714361 | Cd34 | CD34 ANTIGEN | 2.32 | |
| ILMN_2687880 | Col1a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE I, ALPHA 1 | 2.02 | |
| ILMN_1214227 | Krt1-10 | KERATIN COMPLEX 1, ACIDIC, GENE 1-10 | 1.84 |
The criteria for Functional Annotation Clustering of Gene analysis was set at P < 0.05 and fold-change 3 1.5. Shown are functional clusters of genes that were up-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs.
Table 2.
Examples of functional annotation clustering of genes down-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs
| ILLUMINA_ID | Gene Symbol | Gene Name (Description) | P-Value | Fold-change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAT-STAT Signaling | 1.90E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1219155 | Jak3 | JANUS KINASE 3 | -3.448 | |
| ILMN_2698046 | Stat3 | SIGNAL TRANSDUCER AND ACTIVATOR OF TRANSCRIPTION 3 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_2618176 | Socs3 | SUPPRESSOR OF CYTOKINE SIGNALING 3 | -1.538 | |
| Homeobox | 4.20E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2860958 | Dlx2 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 2 | -14.286 | |
| ILMN_1219807 | Hoxd4 | HOMEO BOX D4 | -6.667 | |
| ILMN_1242977 | Hoxb5 | HOMEO BOX B5 | -5.263 | |
| ILMN_2636480 | Hoxa5 | HOMEO BOX A5 | -4 | |
| Glutathione Metabolism | 2.90E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2773022 | Gsta4 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, ALPHA 4 | -9.091 | |
| ILMN_2624854 | Gstm2 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 2 | -5 | |
| ILMN_1228233 | Gstm1 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 1 | -2.564 | |
| ILMN_2705777 | Gstm5 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 5 | -2.439 | |
| ILMN_2641807 | Gstm6 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 6 | -2.326 | |
| Ephrin | 2.60E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1257372 | Efnb1 | EPHRIN B1 | -2.041 | |
| ILMN_1217493 | Efna4 | EPHRIN A4 | -1.639 | |
| ILMN_2716212 | Efnb2 | EPHRIN B2 | -1.515 | |
| Other Genes | ||||
| ILMN_2771738 | Dlk1 | DELTA-LIKE 1 HOMOLOG (DROSOPHILA) | -307.819 | |
| ILMN_1256371 | Fez1 | FASCICULATION AND ELONGATION PROTEIN ZETA 1 | -37.299 | |
| ILMN_2724942 | Ptgis | PROSTAGLANDIN I2 (PROSTACYCLIN) SYNTHASE | -33.333 | |
| ILMN_1224866 | Ptgs1 | PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASE 1 | -12.5 | |
| ILMN_1260020 | Pcdh1 | PROTOCADHERIN 1 | -8.362 | |
| ILMN_3163581 | En1 | ENGRAILED 1 | -7.692 | |
| ILMN_2699052 | Nrn1 | NEURITIN 1 | -4.387 | |
| ILMN_1246282 | Tcfap2a | TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR AP-2, ALPHA | -3.658 | |
| ILMN_2628178 | Socs2 | SUPPRESSOR OF CYTOKINE SIGNALING 2 | -3.226 | |
| ILMN_2729197 | Hic1 | HYPERMETHYLATED IN CANCER 1 | -3.587 | |
| ILMN_1240677 | Gadd45gip1 | GROWTH ARREST AND DNA-DAMAGE-INDUCED GAMMA INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 | -3.026 | |
| ILMN_2623578 | Nid1 | NIDOGEN 1 | -2.71 | |
| ILMN_2677332 | Hic2 | HYPERMETHYLATED IN CANCER 2 | -2.515 | |
The criteria for Functional Annotation Clustering of Gene analysis was set at P < 0.05 and fold-change 3 1.5. Shown are functional clusters of genes that were down-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs.
Ingenuity biological functional analyses of the genes in wild type and Klf4-null MEFs
We next used Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA; www.ingenuity.com) to test for enrichment of known gene function. IPA groups significant genes according to biological processes in which they function. The program displays the genes' significance values, the other genes with which it interacts, and how the genes' products directly and indirectly act on each other. The criteria applied for the search of major biological function categories were maximum number of genes and the P-value of significance. A range of P-values between 3.18 ×10-14 to 5.75 × 10-03 is considered statistically significant. Table 3 shows the most significant results of analysis of 6,218 differentially expressed genes with a FDR less than or equal to 1% identified by SAM. As shown, top biological functions regulated by KLF4 include tumorigenesis, cell death, neoplasia, cancer, apoptosis, proliferation and growth of cells. This result is consistent with previous findings that KLF4 is involved in tumor suppression, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis. Interestingly, one particularly large gene set is involved in neurological disorder (1,016 genes) although the P-value just reached statistical significance (Supplementary Table S3).
Table 3.
Top high-level functions identified by Ingenuity global function analysis of genes regulated by Klf4
| Biological Function Classification | Number of Genes | Significance (P-value) |
|---|---|---|
| Tumorigenesis | 802 | 2.42E-06 |
| Cell death | 753 | 3.18E-14 |
| Neoplasia | 751 | 2.45E-06 |
| Cancer | 719 | 5.29E-06 |
| Apoptosis | 659 | 5.53E-15 |
| Proliferation of cells | 614 | 6.31E-06 |
| Growth of cells | 525 | 4.10E-12 |
| Development of cells | 342 | 1.78E-07 |
| Migration of cells | 333 | 9.54E-06 |
The criteria applied for the search of major biological function categories were maximum number of genes and the P-value of significance. P-values in the range of 3.18 ×10-14to 5.75 × 10-03 indicated statistical significance.
Functional pathway analysis with Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
We also used the GSEA functional enrichment analysis to interrogate molecular pathways enriched in the two MEFs. In this exercise, 6,218 differentially expressed genes were analyzed for gene sets enriched in Klf4-null and wild type cells. A total of 47 pathway gene sets, 23 in Klf4 -null and 24 in wild type cells, were significantly enriched with a P-value < 0.05 and FDR < 0.25. Tables 4 and 5 show the lists of gene sets enriched in Klf4-null and wild type MEFs, respectively. The complete dataset is provided as Supplementary Table S4, which also includes the specific genes in the pathway gene sets that were enriched in the Klf4-null or wild type MEFs. In addition, snapshots of the enriched pathways in Klf4-null and wild type cells are provided as Supplementary Figures S1 and S2, respectively.
Table 4.
Gene sets enriched in Klf4-null cells Identified by GSEA
| Gene sets | Size | ES | NES | FDR q-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bile acid biosynthesis | 21 | -0.572 | -1.844 | 0.213 |
| The 50 most downregulated genes in primary invasive breast dutcal carcinoma or metastatic breast carcinoma isolated from lymph nodes, as compared to normal mammary epithelium. | 25 | -0.642 | -1.787 | 0.062 |
| Genes up-regulated in multiple myeloma cells exposed to the pro-proliferative cytokine IL-6 versus those with N-ras-activating mutations | 19 | -0.577 | -1.775 | 0.133 |
| Genes involved in hematopoietic cell lineage | 65 | -0.524 | -1.739 | 0.130 |
| B cell antigen receptors (BCRs) activate tyrosine kinases and transiently increase tyrosine phosphorylation on binding to antigen. | 33 | -0.533 | -1.735 | 0.111 |
| Genes down-regulated in hepatoma tissue of Myc+E2f1 transgenic mice | 54 | -0.505 | -1.690 | 0.131 |
| Genes involved in ERBB signaling pathway | 82 | -0.426 | -1.684 | 0.118 |
| Genes with spiked expression in subsets of MM PCs from newly diagnosed patients | 21 | -0.725 | -1.684 | 0.109 |
| Genes involved in regulation of autophagy | 23 | -0.570 | -1.664 | 0.102 |
| Genes involved in type I diabetes mellitus | 19 | -0.471 | -1.661 | 0.097 |
| Genes expressed in classic medulloblastomas. | 35 | -0.498 | -1.661 | 0.093 |
| Genes down-regulated in hepatoma tissue of Myc+Tgfa transgenic mice | 54 | -0.556 | -1.660 | 0.104 |
| Genes involved in nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 21 | -0.701 | -1.654 | 0.099 |
| Any process involved in the controlled movement of a cell. | 48 | -0.479 | -1.644 | 0.091 |
| Tyrosine metabolism | 27 | -0.494 | -1.636 | 0.108 |
| Inflammatory response pathway | 15 | -0.792 | -1.621 | 0.093 |
| Genes involved in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 209 | -0.466 | -1.619 | 0.109 |
| Down-regulated at 6-12 hours following treatment of WS1 human skin fibroblasts with UVC at a low dose | 15 | -0.601 | -1.615 | 0.116 |
| Any series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of an extracellular ligand to a receptor on the surface of the target cell | 117 | -0.470 | -1.601 | 0.122 |
| Genes involved in Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 96 | -0.508 | -1.600 | 0.118 |
| Genes involved in Hedgehog signaling pathway | 54 | -0.601 | -1.593 | 0.122 |
| Reactive oxidative species related genes curated from GO | 27 | -0.565 | -1.581 | 0.130 |
| Genes down-regulated in hepatoma tissue of E2f1 transgenic mice | 51 | -0.506 | -1.580 | 0.127 |
All genes were ranked by differential expression between Klf4-null and wild type MEFs using enrichment score; enrichment score normalized for differences in gene set size; and false discovery rate. Size equals the number of genes in the gene list mapped to the dataset. ES: enrichment score; NES: normalized enrichment score; FDR q-value: false discovery rate—multiple comparisons correction (q-value). The criteria for the GSEA analysis was P < 0.05 and false discovery rate (FDR) < 25%.
Table 5.
Gene sets enriched in wild type cells Identified by GSEA
| Gene sets | Size | ES | NES | FDR q-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostaglandin and leukotriene metabolism | 28 | 0.628 | 1.871 | 0.054 |
| The intrinsic prothrombin activation pathway is activated by traumatized blood vessels and induces clot formation | 22 | 0.659 | 1.732 | 0.095 |
| Genes involved in antigen processing and presentation | 40 | 0.514 | 1.646 | 0.134 |
| Up-regulated at 3 months of age in lungs from lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) knockout mice, which display pulmonary pathology, versus wild-type controls | 46 | 0.507 | 1.631 | 0.119 |
| Up-regulated following stable autocrine expression of human growth hormone in mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) | 150 | 0.488 | 1.627 | 0.110 |
| Genes involved in ABC transporters - general | 40 | 0.540 | 1.617 | 0.104 |
| The beta subunit of the IL-2 receptor is required for IL-2 and IL-15 signal recognition and activates JAK kinase on ligand binding | 35 | 0.545 | 1.572 | 0.134 |
| Genes highly expressed in hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma | 28 | 0.523 | 1.552 | 0.157 |
| HOX genes related to hematopoiesis | 31 | 0.500 | 1.539 | 0.159 |
| Downregulated by nickel(II) in human peripheral lung epithelial cells | 16 | 0.702 | 1.518 | 0.208 |
| Genes downregulated in multiple myeloma plasma cells that secrete the light chain immunoglobulin Ig-lambda versus those that secrete Ig-kappa. | 27 | 0.503 | 1.517 | 0.192 |
| Genes involved in JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 134 | 0.451 | 1.510 | 0.192 |
| Glutathione metabolism | 20 | 0.699 | 1.510 | 0.173 |
| Genes involved in basal transcription factors | 28 | 0.583 | 1.508 | 0.186 |
| Thrombin cleaves protease-activated receptors PAR1 and PAR4 to induce calcium influx and activate platelet aggregation, a process inhibited by aspirin | 21 | 0.500 | 1.490 | 0.199 |
| Down-regulated in mature, differentiated adipocytes following simultaneous treatment with troglitazone and TNFalpha | 25 | 0.731 | 1.482 | 0.201 |
| Up-regulated in primary human adipocytes, versus preadipocytes | 59 | 0.499 | 1.470 | 0.207 |
| Down-regulated by infection of human colon adenocarcinoma cells (SW480) with Ad-BRCA1, versus Ad-LacZ control | 16 | 0.555 | 1.466 | 0.203 |
| Downregulated by ectopic expression of NF90 in GHOST(3)CXCR4 cells | 33 | 0.612 | 1.466 | 0.194 |
| Genes involved in taste transduction | 27 | 0.485 | 1.462 | 0.192 |
| Downregulated by both Et-743 and Pt-650 in HCT116 cells | 21 | 0.438 | 1.460 | 0.190 |
| Genes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism | 40 | 0.434 | 1.454 | 0.204 |
| Summary of genes up-regulated in EFTs compared with normal body atlas | 27 | 0.499 | 1.453 | 0.200 |
All genes were ranked by differential expression between Klf4-null and wild type MEFs using enrichment score; enrichment score normalized for differences in gene set size; and false discovery rate. Size equals the number of genes in the gene list mapped to the dataset. ES: enrichment score; NES: normalized enrichment score; FDR q-value: false discovery rate—multiple comparisons correction (q-value). The criteria for the GSEA analysis was P < 0.05 and false discovery rate (FDR) < 25%.
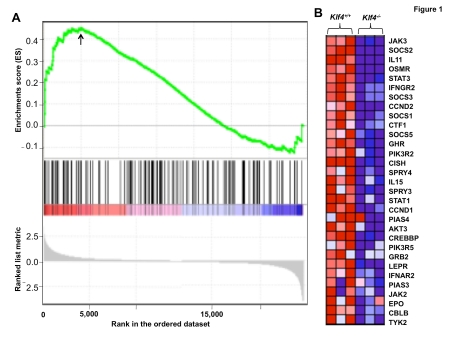
In Klf4-null MEFs, GSEA showed a significant enrichment in gene sets associated with bile acid biosynthesis, hematopoietic cell lineage, multiple myeloma, genes expressed in medulloblastomas, cell motility, cytokine receptor, cell surface receptors, autophagy, and inflammatory response. Moreover, signaling pathways including ERBB, toll like receptors, and hedgehog signaling were enriched in Klf4-null cells. On the other hand, significant enrichment in gene sets associated with antigen processing and presentation, IL-2 receptor pathway, HOX genes, JAK-STAT signaling pathways, glutathione metabolism, basal transcription factors, and adipocytes differentiation were enriched in the wild type cells. Figure 1 shows the results of enrichment of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in wild type MEFs. In this example, GSEA mapped 134 out of 1,381 genes and found a highly significant correlation between the gene list and dataset (P < 0.001 and FDR q-value = 0.192). This is consistent with the results in Table 2 showing that some of the genes involved in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway such as JAK3, STAT3, and SOCS3, are down-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs. Among these factors, STAT3 is required for embryonic stem cell maintenance and SOCS3 is involved in differentiation of embryonic stem cells [21, 34, 35].
Fiugre 1.
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) for the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. (A) Shown are enrichment scores with a ranked list metric. The arrow indicates the enrichment score of 0.45. (B) Heat map of the results of microarray analysis of 32 core enrichment genes in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in wild type (Klf4+/+) and Klf4-null (Klf4-/-) MEFs in triplicate. Red color represents up-regulated and blue color, down-regulated, genes. Significantly enriched data sets are selected according to GSEA default settings, i.e., P < 0.001 and a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.
Validation of microarray data by Western blot analysis of select genes
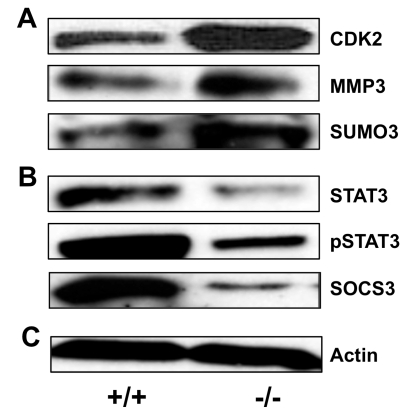
We validated some of the microarray data by Western blot analysis of select genes in wild type and Klf4-null MEFs. In the microarray analysis CDK2, MMP3, and SUMO3 mRNAs were found to be up-regulated in the Klf4-null cells (Table 1). On the other hand, STAT3 and SOCS3 mRNAs were down-regulated (Table 2). Consistent with the microarray observations, Western blot analysis of Klf4-null MEFs showed excellent correlation in changes of expression for each of these genes between wild type and Klf4-null cells (Figure 2). Interestingly, the level of phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) was also reduced in Klf4-null cells.
Figure 2.
Confirmation of select microarray data by Western blot analysis. (A) Western blot analysis of genes up-regulated in Klf4-null including CDK2, MMP3, and SUMO3. (B) Western blot analysis of genes down-regulated in Klf4-null including STAT3, pSTAT3, and SOCS3. (C) Actin loading control. Shown are the representative results of 2 independent experiments. +/+ = wild type and -/- = Klf4-null MEFs.
Discussion
Since it was initially identified some 14 years ago [1, 2], KLF4 has been shown to play an increasingly broad and important function in both physiological and pathological processes. Physiologically, KLF4 regulates proliferation, differentiation, development, apoptosis, and somatic cell reprogramming. KLF4 is also involved in disease conditions such as tumorigenesis and inflammation. Earlier studies indicate that KLF4 is a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation [1, 36] and mediates the cell cycle-checkpoint function of the tumor suppressor, p53 [37-40]. Subsequent studies confirmed this inhibitory effect by the demonstration that KLF4 exerts a tumor suppressive effect in vivo [9, 10]. Previous attempts at establishing the expression profiles of KLF4 were conducted in cultured cancer cells over-expressing KLF4 [27, 28]. These studies confirmed the cell cycle-checkpoint activity of KLF4 and provided additional evidence that KLF4 regulates both epithelial differentiation and macromolecular biosynthesis. In contrast, the present study shows for the first time the transcriptional profiles of KLF4 in a non-transformed cell system and as a result, identified many additional novel targets of KLF4 such as those involved in extracellular matrix, ubiquitin, growth factors, chemotaxis, JAK-STAT, and ephrin signaling (Tables 1 and 2). Moreover, the current study does not involve over-expression as in the previous work, thus rendering the results more physiologically relevant.
The cells used in the current study, mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), have previously been characterized [26]. Relative to wild type cells, MEFs deficient for Klf4 had both a higher rate of proliferation and apoptosis. In addition, Klf4-null cells exhibited evidence of genetic instability as evidenced by the presence of aneuploidy, chromosome aberration and centrosome amplification [26]. A mechanism underlying this genetic instability in the absence of KLF4 is likely due to elevated cyclin E levels, which are normally suppressed by KLF4 [26]. The current study provides additional supporting evidence by showing that CDK2 is significantly up-regulated in Klf4-null cells (Table 1 and Figure 2). Accompanying the increase in CDK2 levels is the up-regulation of numerous other cell cycle-promoting genes as shown in Table 1. Moreover, at least a subset of these genes such as MCM and E2F overlaps with those previously identified to be suppressed by KLF4 [27, 28]. The results of the present study therefore provide further mechanistic evidence for the observed inhibitory effect of KLF4 on proliferation.
Consistent with the tumor suppressive role for KLF4, results in Table 1 also show that numerous genes involved in tumorigenesis such as proto-oncogenes and those encoding extracellular matrix proteins, growth factors, chemokines, and inflammatory response. Many of these gene families have important roles in regulating cell growth, migration, and angiogenesis. For example, several genes encoding matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are up-regulated in Klf4-null cells (Table 1). The up-regulation of MMPs have has been implicated in the increase in proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis [41-43]. One in particular, MMP3, promotes cellular proliferation when over-expressed in transgenic mice [44]. Over-expression of MMP3 in vitro induces mesenchymal-epithelial transition (EMT) and promotes tumor progression with resultant genetic instability [45, 46]. Many of the pheno-types upon MMP3 over-expression such as genetic instability and anchorage-independent growth are shared with MEFs null for Klf4 [26]. The up-regulation of MMPs, including MMP3 (Table 1; Figure 2), in Klf4-null cells may therefore be responsible for at least some of these events.
One of the most up-regulated genes in Klf4-null MEFs from the microarray analysis is small ubiquitin-like modifier 3 (SUMO3) (Table 1). Western blot analysis confirmed its elevation in Klf4-null cells (Figure 2). Post-translational modification by SUMOs is usually transient and alters protein function by affecting protein-protein interaction [47]. Recent studies indicate that the SUMO cascade is involved in the mammalian DNA damage response from genotoxic stress [48, 49]. Klf4-null MEFs contain a high level of phos-phorylated histone H2AX (γH2AX), a marker for double-strand DNA breaks, and exhibit chromosome aberrations including dicentric chromosomes, double minute chromosomes, and chromatid breaks [26]. The elevated SUMO3 levels in these cells could therefore be a reflection of the cellular response to wide-spread DNA damage observed in Klf4-null MEFs.
KLF4 is one of several factors capable of reprogramming somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells [15-20]. However, the mechanism by which KLF4 achieves this task is not completely understood. KLF4 interacts with two other factors, Oct4 and Sox2, to promote reprogramming [50] and may form a core circuitry with other KLFs to regulate self-renewal of embryonic stem cells [51]. KLF4 also suppresses expression of the tumor suppressor gene, p53 [52], which was recently shown to be a barrier to efficient reprogramming [53-57]. In this study, we demonstrated that the JAK-STAT signaling pathway is enriched in wild type MEFs relative to Klf4-null MEFs (Tables 2 and 5; Figure 1). This could provide another mechanism by which KLF4 may influence ES cell self-renewal. A previous study showed that promotion of mouse ES cell self-renewal and maintenance of pluripotency requires leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)-stimulated STAT3 activation [21]. KLF4 is a LIF-responsive gene and overexpression of KLF4 in ES cells results in a greater capacity to self-renew [21]. A subsequent study demonstrated that KLF4 is activated by the JAK-STAT3 pathway, thus providing a mechanism by which LIF activates KLF4 [58]. It is of interest to note that both STAT3 and phospho-STAT3 levels are elevated in wild type MEFs compared to Klf4-null MEFs (Figure 2), a finding that suggests KLF4 may activate STAT3 expression, thus providing a positive feedback loop to promote ES self-renewal. Similarly, the level of SOCS3 is higher in wild type MEFs than Klf4-null cells (Figure 2). SOCS3 is also a target of LIF signaling but promotes differentiation when over-expressed [21]. KLF4 may therefore be positioned in a nodal point to mediate LIF-induced JAK-STAT signaling and to modulate the decision between self-renewal and differentiation.
In summary, our study established distinct transcriptional profiles of MEFs wild type and null for the Klf4 alleles. Functional clustering and pathway analysis identified a rich series of potential targets that may mediate KLF4's myriads of functions. In particular, our results further strengthened the previously established role of KLF4 in maintaining genetic stability and tumor suppression. Moreover, the results provided novel insights by which KLF4 may regulate somatic cell reprogramming. Studies are warranted to further substantiate the mechanisms by which KLF4 regulates these important processes.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK52230, DK64399, CA84197, and CA130308). EGH was an Emory Fellowships in Research and Science Teaching (FIRST) fellow.
Supplemental Data
Fiugre S1.
Snapshot of enriched gene sets identified by GSEA in Klf4-null MEFs.
Fiugre S2.
Snapshot of enriched gene sets identified by GSEA in wild type MEFs.
Table S1.
Functional Annotation Clustering of Genes Up-Regulated in Klf4-Null MEFs
| ILLUMINA ID | Gene Symbol | Gene Name (Description) | P-value | Fold-Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Cycle | 8.00E-03 | |||
| ILMN_1217331 | Mcm6 | MINICHROMOSOME MAINTENANCE DEFICIENT 6 | 40.36 | |
| ILMN_2723931 | E2f6 | E2F TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR 6 | 26.8 | |
| ILMN_2724570 | Mapk12 | MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE 12 | 22.19 | |
| ILMN_1218470 | Cdk2 | CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE 2 | 9.32 | |
| ILMN_1234909 | Tipin | TIMELESS INTERACTING PROTEIN | 5.3 | |
| ILMN_1212692 | Mapk13 | SAPK/ERK/KINASE 4 | 4.96 | |
| ILMN_2666690 | Cul7 | CULLIN 7 | 2.23 | |
| ILMN_2681776 | Mapk6 | MITOGEN ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE 4 | 2.11 | |
| ILMN_2652909 | Ddit3 | DNA-DAMAGE INDUCIBLE TRANSCRIPT 3 | 2.07 | |
| ILMN_2742152 | Gadd45a | GROWTH ARREST AND DNA-DAMAGE-INDUCIBLE 45 ALPHA | 1.92 | |
| ILMN_1212787 | Pttg1 | PITUITARY TUMOR-TRANSFORMING 1 | 1.8 | |
| ILMN_1216721 | Cdk5 | CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE 5 | 1.78 | |
| ILMN_1227009 | Gas2l1 | GROWTH ARREST-SPECIFIC 2 LIKE 1 | 1.74 | |
| ILMN_2663009 | Rassf5 | RAS ASSOCIATION (RALGDS/AF-6) DOMAIN FAMILY 5 | 1.64 | |
| ILMN_1220454 | Anapc13 | ANAPHASE PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 13 | 1.61 | |
| ILMN_1216213 | Incenp | INNER CENTROMERE PROTEIN | 1.56 | |
| ILMN_1256301 | Rcc2 | REGULATOR OF CHROMOSOME CONDENSATION 2 | 1.53 | |
| Extracellular Matrix | 5.80E-06 | |||
| ILMN_2735184 | Col18a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE XVIII, ALPHA 1 | 51.5 | |
| ILMN_1223997 | Crtap | CARTILAGE ASSOCIATED PROTEIN | 32.74 | |
| ILMN_2753809 | Mmp3 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 3 | 31.08 | |
| ILMN_2747959 | Dcn | DECORIN | 21.44 | |
| ILMN_2737685 | Mmp13 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 13 | 13.86 | |
| ILMN_1232899 | Smoc2 | SPARC RELATED MODULAR CALCIUM BINDING 2 | 6.91 | |
| ILMN_2727663 | Tgfbi | TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR, BETA INDUCED | 6.75 | |
| ILMN_1258629 | Col3a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE III, ALPHA 1 | 5.65 | |
| ILMN_2619952 | Mmp10 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 10 | 5.32 | |
| ILMN_2668463 | Emilin1 | ELASTIN MICROFIBRIL INTERFACER 1 | 3.99 | |
| ILMN_1230747 | Wnt9a | WINGLESS-TYPE MMTV INTEGRATION SITE 9A | 3.8 | |
| ILMN_1254546 | Col5a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE V, ALPHA 2 | 3.42 | |
| ILMN_2422848 | Wnt10b | WINGLESS RELATED MMTV INTEGRATION SITE 10B | 2.97 | |
| ILMN_2772556 | Fbn1 | FIBRILLIN 1 | 2.71 | |
| ILMN_2635784 | Gpc | GLYPICAN 1 | 2.37 | |
| ILMN_1238215 | Ctgf | CONNECTIVE TISSUE GROWTH FACTOR | 2.28 | |
| ILMN_2640248 | Lama5 | LAMININ, ALPHA 5 | 2.27 | |
| ILMN_2687880 | Col1a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE I, ALPHA 1 | 2.06 | |
| ILMN_2769917 | Timp1 | TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE 1 | 1.99 | |
| ILMN_1225835 | Mfap5 | MICROFIBRILLAR ASSOCIATED PROTEIN 5 | 1.97 | |
| ILMN_1258759 | Col6a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE VI, ALPHA 2 | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_2497957 | Epb4.1l1 | FIBULIN 1 | 1.76 | |
| ILMN_2678218 | Mmp2 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 2 | 1.75 | |
| ILMN_1217071 | Mmp16 | MATRIX METALLOPEPTIDASE 16 | 1.67 | |
| ILMN_2774596 | Lamc | LAMININ, GAMMA 1 | 1.66 | |
| ILMN_1238597 | Omd | OSTEOMODULIN | 1.53 | |
| Ubiquitin | 1.40E-02 | |||
| ILMN_2662401 | Sumo3 | SMT3 SUPPRESSOR OF MIF TWO 3 HOMOLOG 3 (YEAST) | 70.01 | |
| ILMN_2763459 | Tbcel | LEUCINE RICH REPEAT CONTAINING 35 | 3.51 | |
| ILMN_1225261 | UchM | UBIQUITIN CARBOXY-TERMINAL HYDROLASE L1 | 3.02 | |
| ILMN_1229019 | Fbxo44 | F-BOX PROTEIN 44 | 2.12 | |
| ILMN_2749911 | Ube2q2 | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2Q (PUTATIVE) 2 | 1.96 | |
| ILMN_2417991 | Ube2i | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2I | 1.79 | |
| ILMN_1246522 | Uchl3 | UBIQUITIN CARBOXYL-TERMINAL ESTERASE L3 (UBIQUITIN THIOLESTERASE) | 1.63 | |
| ILMN_2495573 | Ubqln1 | DNA SEGMENT, CHR 13, ERATO DOI 372, EXPRESSED | 1.54 | |
| ILMN_2486783 | Ube2d3 | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2D 3 (UBC4/5 HOMOLOG, YEAST) | 1.54 | |
| ILMN_1227863 | Ube2n | UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2N | 1.53 | |
| ILMN_2516699 | Ubb | UBIQUITIN B | 1.51 | |
| Proto-oncogenes | 2.70E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2655260 | Ptp4a3 | PROTEIN TYROSINE PHOSPHATASE 4A3 | 4 | |
| ILMN_1233424 | Lbcl | RHO/RAC GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE FACTOR (GEF) 2 | 2.03 | |
| ILMN_1224526 | Lck | LYMPHOCYTE PROTEIN TYROSINE KINASE | 2 | |
| ILMN_1237241 | Araf | V-RAF MURINE SARCOMA 3611 VIRAL ONCOGENE HOMOLOG | 1.83 | |
| ILMN_1212787 | Pttg1 | PITUITARY TUMOR-TRANSFORMING 1 | 1.8 | |
| ILMN_2481071 | Hras1 | HARVEY RAT SARCOMA VIRUS ONCOGENE 1 | 1.78 | |
| ILMN_1251669 | Evi2a | ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE 2A | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_2492264 | Wisp1 | WNT1 INDUCIBLE SIGNALING PATHWAY PROTEIN 1 | 1.76 | |
| ILMN_1221750 | MycM | LUNG CARCINOMA MYC RELATED ONCOGENE 1 | 1.66 | |
| Growth Factors | 2.30E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1238547 | Areg | AMPHIREGULIN | 21.43 | |
| ILMN_1215252 | Bmp4 | BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEIN 4 | 14.31 | |
| ILMN_1254114 | Artn | ARTEMIN | 8.65 | |
| ILMN_2763243 | CHEM | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 1 | 8.46 | |
| ILMN_2745480 | Fgf13 | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 13 | 6.53 | |
| ILMN_2710698 | Fgf21 | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 21 | 5.51 | |
| ILMN_1246073 | Lefty1 | LEFT RIGHT DETERMINATION FACTOR 1 | 4.72 | |
| ILMN_2659994 | Gdnf | GLIAL CELL LINE DERIVED NEUROTROPHIC FACTOR | 3.1 | |
| ILMN_1236725 | Gdf1 | GROWTH DIFFERENTIATION FACTOR 1 | 2.53 | |
| ILMN_2698449 | Hbegf | HEPARIN-BINDING EGF-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR | 2.36 | |
| ILMN_2484527 | Vegfa | VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR A | 1.97 | |
| ILMN_2697220 | Figf | C-FOS INDUCED GROWTH FACTOR | 1.74 | |
| ILMN_2736496 | FgflO | FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 10 | 1.73 | |
| Cell Adhesion | 1.80E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2774764 | Cntnap4 | CONTACTIN ASSOCIATED PROTEIN 4 | 7.88 | |
| ILMN_2627041 | Cx3cl1 | CHEMOKINE (C-X3-C MOTIF) LIGAND 1 | 2.5 | |
| ILMN_2670172 | Itga5 | INTEGRIN ALPHA 5 (FIBRONECTIN RECEPTOR ALPHA) | 2.32 | |
| ILMN_2640248 | Lama5 | LAMININ, ALPHA 5 | 2.27 | |
| ILMN_1223697 | Cd44 | CD44 ANTIGEN | 2.1 | |
| ILMN_1243254 | Adam12 | A DISINTEGRIN AND METALLOPEPTIDASE DOMAIN 12 (MELTRIN ALPHA) | 1.92 | |
| ILMN_2707976 | Cdh26 | CADHERIN-LIKE26 | 1.88 | |
| ILMN_2725411 | Cd9 | CD9 ANTIGEN | 1.84 | |
| ILMN_1257880 | Itga7 | INTEGRIN ALPHA 7 | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_2492264 | Wisp1 | WNT1 INDUCIBLE SIGNALING PATHWAY PROTEIN 1 | 1.76 | |
| ILMN_2663613 | Itgb5 | INTEGRIN BETA 5 | 1.74 | |
| ILMN_2659503 | Cdh13 | CADHERIN 13 | 1.69 | |
| ILMN_1241893 | Wisp2 | WNT1 INDUCIBLE SIGNALING PATHWAY PROTEIN 2 | 1.69 | |
| ILMN_1232768 | Vcam1 | VASCULAR CELL ADHESION MOLECULE 1 | 1.56 | |
| ILMN_1237629 | Cntn2 | CONTACTIN 2 | 1.51 | |
| Collagen | 2.10E-02 | |||
| ILMN_2735184 | Col18a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE XVIII, ALPHA 1 | 19.16 | |
| ILMN_1258629 | Col3a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE III, ALPHA 1 | 5.65 | |
| ILMN_1254546 | Col5a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE V, ALPHA 2 | 3.04 | |
| ILMN_2687880 | Col1a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE I, ALPHA 1 | 2.06 | |
| ILMN_2707616 | Col22a1 | COLLAGEN, TYPE XXII, ALPHA 1 | 1.87 | |
| ILMN_1258759 | Col6a2 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE VI, ALPHA 2 | 1.77 | |
| ILMN_1225073 | Cthrc | COLLAGEN TRIPLE HELIX REPEAT CONTAINING 1 | 1.53 | |
| Inflammatory Response | 1.60E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1230789 | C3 | COMPLEMENT COMPONENT 3 | 8.8 | |
| ILMN_2763243 | CHEM | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 1 | 8.46 | |
| ILMN_2742075 | Cd14 | CD14 ANTIGEN | 2.68 | |
| ILMN_1254383 | Atrn | ATTRACTIN | 1.99 | |
| ILMN_1259252 | Anxa1 | ANNEXINA1 | 1.99 | |
| ILMN_1255385 | Chst1 | CARBOHYDRATE (KERATAN SULFATE GAL-6) SULFOTRANSFERASE 1 | 1.82 | |
| Chemotaxis | 1.50E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1231814 | Ccl5 | CHEMOKINE (C-C MOTIF) LIGAND 5 | 13.25 | |
| ILMN_2772998 | Enpp2 | ECTONUCLEOTIDE PYROPHOSPHATASE/PHOSPHODIESTERASE 2 | 12.7 | |
| ILMN_2658910 | Cxcl12 | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 12 | 6.78 | |
| ILMN_1245710 | Ccl2 | CHEMOKINE (C-C MOTIF) LIGAND 2 | 5.47 | |
| ILMN_1253797 | Slit2 | SLIT HOMOLOG 2 (DROSOPHILA) | 3.1 | |
| ILMN_1214419 | CHEMO | CHEMOKINE (C-X-C MOTIF) LIGAND 10 | 2.94 | |
| ILMN_1235571 | Cyr61 | CYSTEINE RICH PROTEIN 61 | 2.9 | |
| ILMN_1216285 | Creb3 | CAMP RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING PROTEIN 3 | 1.55 | |
| Development | 3.10E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1234990 | Gap43 | GROWTH ASSOCIATED PROTEIN 43 | 37.4 | |
| ILMN_1226016 | Scx | SCLERAXIS | 29.89 | |
| ILMN_1215252 | Bmp4 | BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEIN 4 | 14.3 | |
| ILMN_2769657 | Picalm | PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL BINDING CLATHRIN ASSEMBLY PROTEIN | 4.98 | |
| ILMN_1246073 | Lefty1 | LEFT RIGHT DETERMINATION FACTOR 1 | 4.71 | |
| ILMN_2684289 | Sema3a | SEMA DOMAIN, IMMUNOGLOBULIN DOMAIN (IG), SHORT BASIC DOMAIN, SECRETED, | 3.89 | |
| ILMN_1230747 | Wnt9a | WINGLESS-TYPE MMTV INTEGRATION SITE 9A | 3.8 | |
| ILMN_2422848 | Wnt10b | WINGLESS RELATED MMTV INTEGRATION SITE 10B | 2.97 | |
| ILMN_2675833 | Dlx3 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 3 | 2.96 | |
| ILMN_1245731 | Hhex | HEMATOPOIETICALLY EXPRESSED HOMEOBOX | 2.82 | |
| ILMN_1238558 | Arid3b | AT RICH INTERACTIVE DOMAIN 3B (BRIGHT LIKE) | 2.35 | |
| ILMN_1225378 | Htatip2 | HIV-1 TAT INTERACTIVE PROTEIN 2, HOMOLOG (HUMAN) | 1.99 | |
| ILMN_1252870 | Rorb | RAR-RELATED ORPHAN RECEPTOR BETA | 1.89 | |
| ILMN_2722938 | Myd116 | MYELOID DIFFERENTIATION PRIMARY RESPONSE GENE 116 | 1.84 | |
| ILMN_2697220 | Figf | C-FOS INDUCED GROWTH FACTOR | 1.74 | |
| ILMN_1223414 | Ptp4a1 | PROTEIN TYROSINE PHOSPHATASE 4A1 | 1.72 | |
| ILMN_1215746 | Cchcr | COILED-COIL ALPHA-HELICAL ROD PROTEIN 1 | 1.65 | |
| ILMN_2734034 | Prrx2 | PAIRED RELATED HOMEOBOX 2 | 1.55 | |
| ILMN_2630811 | Rere | ARGININE GLUTAMIC ACID DIPEPTIDE (RE) REPEATS | 1.54 | |
| ILMN_2706755 | Foxd1 | FORKHEAD BOX D1 | 1.54 | |
| ILMN_1238875 | Strbp | SPERMATID PERINUCLEAR RNA BINDING PROTEIN | 1.54 | |
| ILMN_1253420 | Psme4 | PROTEASOME (PROSOME, MACROPAIN) ACTIVATOR SUBUNIT 4 | 1.5 | |
| Other Genes | ||||
| ILMN_1218967 | Kif2c | KINESIN FAMILY MEMBER 2C | 37.42 | |
| ILMN_2611181 | Ccdc3 | COILED-COIL DOMAIN CONTAINING 3 | 36.32 | |
| ILMN_1217009 | Rab15 | RAB15, MEMBER RAS ONCOGENE FAMILY | 33.76 | |
| ILMN_2621448 | Adh7 | ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE 7 (CLASS IV), MU OR SIGMA POLYPEPTIDE | 22.19 | |
| ILMN_1245531 | Neto2 | NEUROPILIN (NRP) AND TOLLOID (TLL)-LIKE 2 | 21.94 | |
| ILMN_1225602 | S100a1 | S100 CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN A1 | 20.27 | |
| ILMN_2703267 | Nes | NESTIN | 18.5 | |
| ILMN_1245451 | Rab6b | RAB6B, MEMBER RAS ONCOGENE FAMILY | 14.71 | |
| ILMN_2713285 | Fhl1 | FOUR AND A HALF LIM DOMAINS 1 | 14.19 | |
| ILMN_2606660 | Card 10 | CASPASE RECRUITMENT DOMAIN FAMILY, MEMBER 10 | 10.23 | |
| ILMN_2646891 | Centd1 | CENTAURIN, DELTA 1 | 9.05 | |
| ILMN_2686327 | Gas6 | GROWTH ARREST SPECIFIC 6 | 8.94 | |
| ILMN_2689998 | Fjx1 | FOUR JOINTED BOX 1 (DROSOPHILA) | 8.81 | |
| ILMN_1230080 | S100a7a | S100 CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN A15 | 6.95 | |
| ILMN_1247646 | H1fx | H1 HISTONE FAMILY, MEMBER X | 6.91 | |
| ILMN_1217159 | Lmo7 | LIM DOMAIN ONLY 7 | 5.51 | |
| ILMN_1214327 | S100a13 | S100 CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN A13 | 5.19 | |
| ILMN_1242829 | Prdx2 | PEROXIREDOXIN 2 | 5.10 | |
| ILMN_2868133 | Gata6 | GATA BINDING PROTEIN 6 | 4.75 | |
| ILMN_2614590 | Tmem45a | TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN 45A | 4.71 | |
| ILMN_1224014 | Tmem100 | TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN 100 | 4.42 | |
| ILMN_1230586 | Traf1 | TNF RECEPTOR-ASSOCIATED FACTOR 1 | 3.73 | |
| ILMN_1215807 | Glipr1 | GLI PATHOGENESIS-RELATED 1 (GLIOMA) | 3.44 | |
| ILMN_2633670 | Tmem62 | TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN 62 | 3.03 | |
| ILMN_2773901 | Glipr2 | GLI PATHOGENESIS-RELATED 2 | 3.02 | |
| ILMN_1227993 | Vav3 | VAV 3 ONCOGENE | 2.67 | |
| ILMN_2714361 | Cd34 | CD34 ANTIGEN | 2.32 | |
| ILMN_2687880 | Col1a1 | PROCOLLAGEN, TYPE I, ALPHA 1 | 2.02 | |
| ILMN_1214227 | Krt1-10 | KERATIN COMPLEX 1, ACIDIC, GENE 1-10 | 1.84 | |
The criteria for Functional Annotation Clustering of Gene analysis was set at P < 0.05 and fold-change less than or equal to 1.5. Shown are functional clusters of genes that were up-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs.
Table S2.
Functional Annotation Clustering of Genes Down-Regulated in Klf4-Null MEFs
| ILLUMINA ID | Gene Symbol | Gene Name (Description) | P-Value | Fold-Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jak-Stat Signaling Pathway | 1.90E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1256180 | Osmr | ONCOSTATIN M RECEPTOR | -4.000 | |
| ILMN_1219155 | Jak3 | JANUS KINASE 3 | -3.448 | |
| ILMN_2628178 | Socs2 | SUPPRESSOR OF CYTOKINE SIGNALING 2 | -3.226 | |
| ILMN_1243862 | IN11 | INTERLEUKIN 11 | -3.226 | |
| ILMN_2698046 | Stat3 | SIGNAL TRANSDUCER AND ACTIVATOR OF TRANSCRIPTION 3 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_2618176 | Socs3 | SUPPRESSOR OF CYTOKINE SIGNALING 3 | -1.538 | |
| Homeobox | 4.20E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2860958 | Dlx2 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 2 | -14.286 | |
| ILMN_3163581 | En1 | ENGRAILED 1 | -7.692 | |
| ILMN_1219807 | Hoxd4 | HOMEO BOX D4 | -6.667 | |
| ILMN_1242977 | Hoxb5 | HOMEO BOX B5 | -5.263 | |
| ILMN_2762935 | Rhox5 | REPRODUCTIVE HOMEOBOX 5 | -5.263 | |
| ILMN_1218266 | Meis1 | MYELOID ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE 1 | -4.348 | |
| ILMN_2636480 | Hoxa5 | HOMEO BOX A5 | -4.000 | |
| ILMN_2618302 | Hoxa2 | HOMEO BOX A2 | -3.448 | |
| ILMN_1229029 | Dlx1 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 1 | -3.030 | |
| ILMN_2621038 | Hoxa7 | HOMEO BOX A7 | -2.564 | |
| ILMN_1239460 | Onecut2 | ONE CUT DOMAIN, FAMILY MEMBER 2 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_2678094 | Prrx1 | PAIRED RELATED HOMEOBOX 1 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_2774121 | Mrg1 | MYELOID ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE-RELATED GENE 1 | -2.128 | |
| ILMN_1242943 | Mrg2 | MYELOID ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE-RELATED GENE 2 | -2.128 | |
| ILMN_2662351 | Hoxd3 | HOMEO BOX D3 | -2.083 | |
| Glutathione Metabolism | 2.90E-03 | |||
| ILMN_2773022 | Gsta4 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, ALPHA 4 | -9.091 | |
| ILMN_2624854 | Gstm2 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 2 | -5.000 | |
| ILMN_2729458 | Idh1 | ISOCITRATE DEHYDROGENASE 1 (NADP+), SOLUBLE | -2.564 | |
| ILMN_1228233 | Gstm1 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 1 | -2.564 | |
| ILMN_2705777 | Gstm5 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 5 | -2.439 | |
| ILMN_2641807 | Gstm6 | GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE, MU 6 | -2.326 | |
| ILMN_1229964 | Gstz1 | GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE ZETA 1 (MALEYLACETOACETATE ISOMERASE) | -2.174 | |
| Ephrin | 2.60E-02 | |||
| ILMN_1257372 | Efnb1 | EPHRIN B1 | -2.041 | |
| ILMN_1217493 | Efna4 | EPHRIN A4 | -1.639 | |
| ILMN_2716212 | Efnb2 | EPHRIN B2 | -1.515 | |
| Developmental protein | 3.20E-04 | |||
| ILMN_2422615 | Ebf3 | EARLY B-CELL FACTOR 3 | -18.519 | |
| ILMN_2860958 | Dlx2 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 2 | -14.286 | |
| ILMN_3163581 | En1 | ENGRAILED 1 | -7.692 | |
| ILMN_2630993 | Ppap2b | PHOSPHATIDIC ACID PHOSPHATASE TYPE 2B | -7.143 | |
| ILMN_1219807 | Hoxd4 | HOMEO BOX D4 | -6.667 | |
| ILMN_1242977 | Hoxb5 | HOMEO BOX B5 | -5.263 | |
| ILMN_2703433 | Foxc2 | FORKHEAD BOX C2 | -4.545 | |
| ILMN_1218266 | Foxc2 | MYELOID ECOTROPIC VIRAL INTEGRATION SITE 1 | -4.348 | |
| ILMN_2636480 | Hoxa5 | HOMEO BOX A5 | -4.000 | |
| ILMN_2776850 | Gas7 | GROWTH ARREST SPECIFIC 7 | -3.846 | |
| ILMN_2618302 | Hoxa2 | HOMEO BOX A2 | -3.448 | |
| ILMN_1228557 | Id2 | INHIBITOR OF DNA BINDING 2 | -3.030 | |
| ILMN_1229029 | Dlx1 | DISTAL-LESS HOMEOBOX 1 | -2.941 | |
| ILMN_2716389 | Smpd3 | SPHINGOMYELIN PHOSPHODIESTERASE 3, NEUTRAL | -2.632 | |
| ILMN_2621038 | Hoxa7 | HOMEO BOX A7 | -2.564 | |
| ILMN_2765047 | Chrd | CHORDIN | -2.381 | |
| ILMN_2624731 | Egfl7 | EGF-LIKE DOMAIN 7 | -2.326 | |
| ILMN_2721198 | Ggnbp1 | GAMETOGENETIN BINDING PROTEIN 1 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_2643531 | Angptl6 | ANGIOPOIETIN-LIKE6 | -2.273 | |
| ILMN_1234976 | Prrx1 | PAIRED RELATED HOMEOBOX 1 | -2.222 | |
| ILMN_1257372 | Efnb1 | EPHRIN B1 | -2.041 | |
| ILMN_2662351 | Hoxd3 | HOMEO BOX D3 | -2.041 | |
| ILMN_2659224 | Cspg4 | CHONDROITIN SULFATE PROTEOGLYCAN 4 | -2.000 | |
| ILMN_1232901 | Vamp5 | VESICLE-ASSOCIATED MEMBRANE PROTEIN 5 | -1.961 | |
| ILMN_2485120 | Vti1a | INHIBITOR OF DNA BINDING 1 | -1.961 | |
| ILMN_1235053 | Mlf1 | MYELOID LEUKEMIA FACTOR 1 | -1.887 | |
| ILMN_1237197 | Nrp1 | NEUROPILIN 1 | -1.887 | |
| Other Genes | ||||
| ILMN_2771738 | Dlk1 | DELTA-LIKE 1 HOMOLOG (DROSOPHILA) | -307.819 | |
| ILMN_2644350 | Thy1 | THYMUS CELL ANTIGEN 1, THETA | -67.239 | |
| ILMN_1244206 | Prl2c4 | PROLIFERIN2 | -42.157 | |
| ILMN_2661576 | BICAUD | BICAUDAL C HOMOLOG 1 (DROSOPHILA) | -37.988 | |
| ILMN_1256371 | Fez1 | FASCICULATION AND ELONGATION PROTEIN ZETA 1 (ZYGIN I) | -37.299 | |
| ILMN_2724942 | Ptgis | PROSTAGLANDIN I2 (PROSTACYCLIN) SYNTHASE | -33.333 | |
| ILMN_2661576 | BICAUD | BICAUDAL C HOMOLOG 1 (DROSOPHILA) | -33.333 | |
| ILMN_2693606 | Nr1h5 | NUCLEAR RECEPTOR SUBFAMILY 1, GROUP H, MEMBER 5 | -21.170 | |
| ILMN_2729103 | Adamts2 | A DISINTEGRIN-LIKE AND METALLOPEPTIDASE (REPROLYSIN TYPE) WITH THROMBO | -15.967 | |
| ILMN_1224866 | Ptgs1 | PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASE 1 | -12.500 | |
| ILMN_1249767 | Thbd | THROMBOMODULIN | -10.099 | |
| ILMN_1260020 | Pcdh1 | PROTOCADHERIN 1 | -8.362 | |
| ILMN_1235133 | Syn1 | SYNAPSIN I | -6.305 | |
| ILMN_1232183 | Mgmt | O-6-METHYLGUANINE-DNAMETHYLTRANSFERASE | -4.859 | |
| ILMN_2634538 | Peli2 | PELLINO2 | -4.575 | |
| ILMN_1249776 | Insl3 | INSULIN-LIKE 3 | -4.447 | |
| ILMN_2699052 | Nrn1 | NEURITIN 1 | -4.387 | |
| ILMN_2674533 | Renbp | RENIN BINDING PROTEIN | -4.011 | |
| ILMN_2674122 | Pkia | PROTEIN KINASE INHIBITOR, ALPHA | -3.780 | |
| ILMN_1246282 | Tcfap2a | TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR AP-2, ALPHA | -3.658 | |
| ILMN_2729197 | Hid | HYPERMETHYLATED IN CANCER 1 | -3.587 | |
| ILMN_1235499 | Pros1 | PROTEIN S (ALPHA) | -3.367 | |
| ILMN_1240677 | Gadd45gip1 | GROWTH ARREST AND DNA-DAMAGE-INDUCED GAMMA INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 | -3.026 | |
| ILMN_1218934 | Rdm1 | RAD52 MOTIF 1 | -3.010 | |
| ILMN_2674367 | Agrn | AGRIN | -2.932 | |
| ILMN_2623578 | Nid1 | NIDOGEN 1 | -2.710 | |
| ILMN_2624328 | Adamts7 | A DISINTEGRIN-LIKE AND METALLOPEPTIDASE (REPROLYSIN TYPE) WITH THROMBO | -2.707 | |
| ILMN_2677332 | Hic2 | HYPERMETHYLATED IN CANCER 2 | -2.515 | |
| ILMN_2677859 | Insl6 | INSULIN-LIKE 6 | -2.229 | |
| ILMN_1230145 | Acvr2b | ACTIVIN RECEPTOR IIB | -2.141 | |
The criteria for Functional Annotation Clustering of Gene analysis was set at P < 0.05 and fold-change less than or equal to 1.5. Shown are functional clusters of genes that were down-regulated in Klf4-null MEFs.
Table S3.
Functional annotation identified by Ingenuity global function analysis of genes regulated by Klf4
| Functional Annotation | P-value | Name of Genes | Number of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| neurological disorder | 5.75E-03 | ABCC4, ABCC5, ABCC10, ABCD1, ABCD4, ACADM, ACBD3, ACER3, ACP1, ACP2, ACSL1, ACSL4, ACTB, ADA, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADCY7, ADCY8, ADCY9, ADCYAP1R1, ADH7, ADRB2, AEBP1, AEBP2, AEN, AHCY, AHI1, AIG1, AIM1 (includes EG:202), AK5, | 1016 |
| tumorigenesis | 2.42E-06 | ABCA5, ABCC4, ABR, ACTB, ACTR10, ACVR1, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AHCY, AIG1, AIM2, AIM1 (includes EG:202), AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKR1B10, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH2, ALDH5A1, | 802 |
| cell death | 3.18E-14 | AAK1, ABCC4, ABCC5, ACSL4, ACTB, ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADA, ADAM12, ADAMTSL4, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIFM2, AIM2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKT3, ALCAM, ALDH2, ALDOC, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANKRD1, ANP32A, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, ANXA1, ANXA7 | 753 |
| neoplasia | 2.45E-06 | ABCA5, ABCC4, ABR, ACTB, ACTR10, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AHCY, AIG1, AIM2, AIM1 (includes EG:202), AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKR1B10, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH2, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, AMFR, | 751 |
| cancer | 5.29E-06 | ABCA5, ABCC4, ABR, ACTR10, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AHCY, AIG1, AIM2, AIM1 (includes EG:202), AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKR1B10, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH2, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, AMFR, ANGPT2, | 719 |
| apoptosis | 5.53E-15 | ACSL4, ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADA, ADAM12, ADAMTSL4, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIFM2, AIM2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKT3, ALCAM, ALDH2, ALDOC, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANKRD1, ANP32A, ANXA1, ANXA7, APBB2, APH1B, APPL1, AREG, ARF6, ARL11, ARMC10, A | 659 |
| cell death of eukaryotic cells | 1.42E-12 | AAK1, ABCC4, ACTB, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADA, ADAM12, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALDH2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, ANP32A, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, ANXA1, APH1B, AREG, ARF6, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, | 624 |
| proliferation of cells | 6.31E-06 | ABCC4, ACP1, ACSL6, ADA, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADC, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AEBP1, AFP, AGTRAP, AIM2, AKR1B1, AKT3, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANGPTL6, ANP32A, ANXA1, ANXA7, APPL1, APPL2, ARAF, ARD1A, AREG, ARHGAP24, ARHGEF2, ARIH2, ARTN, ASAH2, | 614 |
| tumor | 5.51E-04 | ABCC4, ABR, ACTR10, ACVR1, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AIG1, AIM2, AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANO6, ANP32A, ANTXR1, ANXA1, ANXA5, | 555 |
| apoptosis of eukaryotic cells | 7.67E-14 | ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADA, ADAM12, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALDH2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, ANP32A, ANXA1, APH1B, AREG, ARF6, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ASAH2, ASNS, ATF2, ATF3, ATMIN, ATP1A1, | 541 |
| growth of cells | 4.10E-12 | ABCC5, ACP1, ACTB, ACVR1B, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADFP, ADIPOR2, ADM, ADORA2B, AHCY, AHSA1, AK2, AKAP12, AKR1B1, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANP32A, ANXA1, ANXA7, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ARL3, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, | 525 |
| primary tumor | 1.00E-03 | ABCC4, ABR, ACTR10, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AIG1, AIM2, AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, ANGPT2, ANO6, ANTXR1, ANXA1, ANXA5, AQP1, AREG, ARFGEF2, ARIH2, ARL11, | 518 |
| malignant tumor | 9.24E-04 | ABCC4, ABR, ACTR10, ACY1, ADA, ADAM12, ADAMTS1, ADARB1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AIG1, AIM2, AK2, AKAP1, AKAP12, AKAP8L, AKT3, ALAD, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, ANGPT2, ANO6, ANTXR1, ANXA1, AQP1, AREG, ARFGEF2, ARIH2, ARL11, ARL4D, | 504 |
| proliferation of eukaryotic cells | 4.71E-05 | ABCC4, ACP1, ACSL6, ADA, ADAM15, ADAMTS1, ADC, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, AEBP1, AFP, AGTRAP, AIM2, AKR1B1, AKT3, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANGPTL6, ANXA1, ARD1A, AREG, ARHGAP24, ARIH2, ARTN, ATF4, ATP6V0A2, B4GALT1, BACH2 | 488 |
| transcription | 2.57E-03 | ACTR2, ACTR1B (includes EG:10120), ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADRB2, AEBP1, AEBP2, AFF4, AGRN, AMPH, ANKRD1, ANP32A, AP1G2, APBB2, APOL3 (includes EG:80833), ATF2, ATF3, ATF4, ATF7IP, ATP2C1, AZI2, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), | 468 |
| cell death of cell lines | 9.67E-15 | AAK1, ABCC4, ACTB, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADM, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALDH2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, APH1B, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ASNS, ATF2, ATF3, ATMIN, ATP2A2, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), | 467 |
| apoptosis of cell lines | 4.63E-13 | ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADM, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALDH2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, APH1B, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ASNS, ATF2, ATF3, ATMIN, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, BHLHE40, | 399 |
| differentiation of cells | 2.22E-05 | ACADM, ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADA, ADD1, ADORA2B, ADRB2, ALG5, ANXA1, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, ATF4, ATP7A, AXIN2, B4GALNT1, BAIAP2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDH2, BDNF, BHLHE40, BIN1, BLNK, BMP1, BMP4, BMPER, BSG, BTC, C5ORF13, CAND1, | 399 |
| carcinoma | 3.96E-05 | ABCC4, ACTR10, ACY1, ADAM12, ADAMTS1, ADRB2, AGPAT2, AIG1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALDH5A1, ALDOC, ANGPT2, ANO6, ANTXR1, ANXA1, AQP1, AREG, ARL11, ARRB2, ASS1, ATF2, ATP1B1, ATP2C1, AXIN2, BAT1, BCL2, BCL10, BHLHE40, BRCA2, | 382 |
| cell death of tumor cell lines | 4.67E-11 | ABCC4, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADM, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ASNS, ATF2, ATF3, ATMIN, ATP2A2, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, | 359 |
| growth of eukaryotic cells | 2.56E-06 | ABCC5, ACP1, ADAM17, ADM, AHSA1, AKAP12, AKR1B1, AKT3, ANP32A, ANXA1, ANXA7, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ATF2, ATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, BSG, BTC, C3, C8ORF4, CAMK2N1, CASP8, CAST, CBFB, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CD14, CD44, CD82, CD274, CDC7, CDCA4, CDH | 350 |
| cell death of normal cells | 9.58E-05 | ABCC4, ADA, ADAM12, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANP32A, ANXA1, ARF6, ARRB2, ASAH2, ATF2, ATF3, ATP1A1, ATP2C1, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, BID, BLNK, BMP4, BNIP3L, C3, C14ORF153, C8ORF4, | 347 |
| development of cells | 1.78E-07 | ACP1, ACVR1, ADA, ADAM17, ADD1, AFF4, AGFG1 (includes EG:3267), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANTXR1, ANXA5, ANXA7, ARHGDIG, ARHGEF2, ARRB2, ATF3, ATP1B1, ATRN, B4GALT1, BAIAP2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, BLNK, BMP4, CAPG, | 342 |
| movement of cells | 1.77E-05 | ABHD2, ACP1, ACVR1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADM, ADRB2, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANXA1, AOC3, APBB2, AREG, ARF6, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CAPNS1, CBFB, CCK, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL9, CCL13, CCL | 335 |
| migration of cells | 9.54E-06 | ABHD2, ACP1, ACVR1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADM, ADRB2, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANXA1, AOC3, APBB2, AREG, ARF6, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CAPNS1, CBFB, CCK, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL9, CCL13, CCL | 333 |
| cell division process of cells | 9.23E-06 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADM, ADORA2B, AKAP9, AKAP12, ANAPC4, ANGPTL2, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, AXIN2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BLNK, BMP4, BRCA2, BRCC3, BTC, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1 | 320 |
| apoptosis of tumor cell lines | 3.54E-11 | ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADM, AFP, AGPAT2, AHSA1, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANKRD1, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ARRB2, ASNS, ATF2, ATF3, ATMIN, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, BHLHE40, BID, | 315 |
| movement of eukaryotic cells | 3.69E-04 ACP1, ACVR1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADM, ADRB2, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANXA1, AOC3, APBB2, ARF6, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CAPNS1, CBFB, CCK, CCL5, | 302 | |
| apoptosis of normal cells | 1.80E-06 | ADA, ADAM12, ADCYAP1R1, ADM, ADRB2, ANGPT2, ANP32A, ANXA1, ARF6, ARRB2, ASAH2, ATF2, ATF3, ATP1A1, ATP2C1, B4GALNT1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BDNF, BID, BLNK, BMP4, BNIP3L, C3, C8ORF4, CABLES2, CAMK2D, CAPN1, CAPNS1, CASP2, | 301 |
| migration of eukaryotic cells | 2.34E-04 | ACP1, ACVR1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADM, ADRB2, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANXA1, AOC3, APBB2, ARF6, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CAPNS1, CBFB, CCK, CCL5, | 300 |
| developmental process of organism | 3.33E-04 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADA, ADAMTS1, ADD1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP1, ARIH2, ATF2, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP1, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCDC47, CCND1, CD164, CDH5, CDK6, CDKN1B, CDON, CHD7, CHD8, CHRD, CHST2, CHST11, | 288 |
| growth of cell lines | 1.83E-07 | ABCC5, ACP1, ADAM17, ADM, AHSA1, AKAP12, AKT3, ANP32A, ANXA1, ANXA7, AREG, ARL11, ARMC10, ATF2, ATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BMP4, BTC, C8ORF4, CAMK2N1, CAST, CBFB, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CD44, CD274, CDCA4, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, CLI | 287 |
| proliferation of cell lines | 1.32E-05 | ADC, ADM, AFP, AIM2, AKT3, ANXA1, ARD1A, AREG, ARIH2, ATP6V0A2, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCAR1, BCL2, BDNF, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BTC, BTRC, C5ORF13, CASP2, CASP8, CBFB, CCDC6, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD9, CD44, CD81, | 286 |
| death of animal | 9.24E-06 | ABCA3, ADA, ADAM12, ADH7, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ADK, ADRB2, AEBP1, AKT3, ALOX12, AMPH, ANGPT2, ANGPTL6, ANXA1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BLMH, BNIP3L, BRCA2, C3, C1GALT1, | 283 |
| developmental process of tissue | 2.24E-07 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAMTS1, ADCYAP1R1, ADRB2, AEBP1, ANGPT2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AREG, ARHGEF10, ATF3, ATP7A, B4GALNT1, B4GALT1, BACE1, BBS1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, CAPNS1, CASP9, CCNF, CD9, CD44, CD81, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A | 280 |
| death of mammalia | 7.57E-06 | ABCA3, ADA, ADAM12, ADH7, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ADK, ADRB2, AEBP1, AKT3, ALOX12, AMPH, ANGPT2, ANGPTL6, ANXA1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BLMH, BNIP3L, BRCA2, C3, C1GALT1, | 279 |
| developmental process of tumor cell lines | 4.38E-07 | ADAM17, ADM, AHSA1, AKAP12, AKT3, ALG5, ANXA1, ANXA7, AREG, ARL11, ATF2, ATF3, B4GALNT1, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDH2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CAMK2N1, CAPN1, CAST, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CD14, CD44, CD82, CD274, CDCA4, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBP | 277 |
| death of rodents | 5.72E-06 | ABCA3, ADA, ADAM12, ADH7, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ADK, ADRB2, AEBP1, AKT3, ALOX12, AMPH, ANGPT2, ANGPTL6, ANXA1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BLMH, BNIP3L, BRCA2, C3, C1GALT1, | 277 |
| death of mice | 6.21E-06 | ABCA3, ADA, ADAM12, ADH7, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ADK, ADRB2, AEBP1, AKT3, ALOX12, AMPH, ANGPT2, ANGPTL6, ANXA1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BLMH, BNIP3L, BRCA2, C3, C1GALT1, | 276 |
| survival of cells | 5.95E-05 | ACVR2B, ADK, ADORA2B, AGRN, AK5, AKAP8L, ALCAM, ALOX12, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, AREG, ARTN, ATF2, ATF4, ATP7A, AURKAIP1, BANF1, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BHLHE40, BMP4, BRCA2, BTC, C7ORF16, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CASP2, CASP6, | 256 |
| cell division process of eukaryotic cells | 2.15E-05 | ADM, ADORA2B, AKAP9, AKAP12, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, AXIN2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BLNK, BMP4, BRCA2, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CD274, CDC7, CDC2 | 254 |
| cell movement | 4.57E-03 | ACP1, ACTB, ACTR2, ADM, ALOX12, ALOX5AP, AMFR, ANGPT2, ANXA1, AOC3, ARF6, ARRB2, ARTN, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BDNF, BMP4, BSG, BTN1A1, C3, CALD1, CAMK2N2, CAPN1, CAPZB, CASP8, CAST, CBFB, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL25, CCND1, | 253 |
| cell stage | 4.52E-05 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADORA2B, AKAP9, AKAP12, ANAPC4, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, AXIN2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BRCC3, BTC, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC16, | 250 |
| developmental disorder | 1.41E-03 | ACSL4, ACTG2 (includes EG:72), ADA, ADAMTS10 (includes EG:81794), ADM, ADRB2, ANGPT2, ANKH, ARAF, ARL6, ARSA, ATF3, ATF4, ATP6AP2, ATP7A, BACE1, BBS1, BBS7, BCL2, BCOR, BDNF, BMP4, BRWD3, BTRC, C3, CACNA1C, CAMK2D, CCL13, | 250 |
| modification of protein | 1.50E-04 | ACP1, ACVR1B, ADAM17, ADM, ALG8, ALG9, ALG12, AMFR, APH1B, ARAF, ARD1A, ARRB2, ATG3, ATG10, ATG12, ATXN10, BCL2, BCL10, BMP4, BSG, CAMK2D, CAND1, CAPN1, CARD10, CAST, CCK, CCL5, CCND1, CCNE1, CCT4, CCT6A, CD9, CD34, CD44, | 248 |
| development of tissue | 3.37E-07 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ADAM12, ADAMTS1, ADCYAP1R1, ADRB2, AEBP1, ANGPT2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AREG, ARHGEF10, ATP7A, B4GALNT1, B4GALT1, BACE1, BBS1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, CAPNS1, CASP9, CCNF, CD9, CD44, CD81, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDON, CHKB, CHST11, | 239 |
| development of organ | 2.14E-04 | ABR, ACADM, ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADA, ADAMTS1, ADAMTS2, ADM, AEBP1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, AREG, ARF6, ASL, ATF3, ATP7A, BBS1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BCOR, BDNF, BMP4, BRCA2, C1GALT1, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CBFB, CCND1, CCNF, CDK5, CDK5R1, CFL1, CHD7, | 238 |
| survival of eukaryotic cells | 3.50E-05 | ACVR2B, ADK, AGRN, AK5, AKAP8L, ALOX12, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, AREG, ARTN, ATF2, ATP7A, AURKAIP1, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BHLHE40, BMP4, BRCA2, BTC, C7ORF16, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CBFB, CCL5, CCND1, CCNG1, CCRK, CD44, CD81, CD82, CDH5, | 237 |
| infectious disorder of cells | 4.84E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C3, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD44, CD93, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYA | 236 |
| development of organism | 9.75E-04 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADA, ADD1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), ARIH2, ATF2, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP1, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCDC47, CCND1, CD164, CDH5, CDK6, CDON, CHD7, CHD8, CHRD, CHST2, CHST11, CLPTM1, CNR1, COL18A1, COMMD1 (includes EG:150 | 236 |
| infection of cells | 3.10E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD44, CD93, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, C | 234 |
| infectious disorder of eukaryotic cells | 3.10E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C3, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD44, CD93, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYA | 234 |
| infection of eukaryotic cells | 1.67E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD44, CD93, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, C | 233 |
| cell stage of cells | 6.06E-05 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADORA2B, AKAP9, AKAP12, ANAPC4, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, AXIN2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BRCC3, BTC, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC16, | 229 |
| infectious disorder of cell lines | 2.08E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C3, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CSPP1, CT | 229 |
| migration of normal cells | 1.29E-03 | ACP1, ACVR1, ADAM9, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADM, ADRB2, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ANXA1, AOC3, APBB2, ARF6, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, B4GALT1, BCAR1, BDNF, BMP4, C3, CAPNS1, CCK, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL9, CCL13, CCL25, CCND1, CD9, CD34, CD44, | 229 |
| infection of cell lines | 1.28E-04 | ACADSB, AEBP2, AFG3L1, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BICD2, BMP1, C6ORF1, CAD, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCDC51, CCL5, CCT2, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLNS1A, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CSPP1, CTDP1, | 228 |
| developmental process of animal | 1.92E-03 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ADA, ADAMTS1, ADD1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP1, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCDC47, CCND1, CDH5, CDK6, CDKN1B, CDON, CHD7, CHD8, CHRD, CHST11, CNR1, COL4A2, COMMD1 (includes E | 225 |
| colorectal cancer | 2.07E-05 | ABCA5, ADAMTS1, AHCY, AIM1 (includes EG:202), AKT3, ANGPTL2, ANK3, ANTXR1, AOC3, ATP2A2, AXIN2, C14ORF143, C15ORF23, C15ORF48, C17ORF81, C9ORF167, CACNA2D1, CALD1, CAMK2N1, CAPG, CCT4, CD9, CD274, CDKN3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, | 212 |
| growth of tumor cell lines | 2.28E-05 | ADAM17, ADM, AHSA1, AKAP12, AKT3, ANXA1, ANXA7, AREG, ARL11, ATF2, ATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BTC, CAMK2N1, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CD44, CD274, CDCA4, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CLIP1, COL18A1, COL6A3, CRABP2, CREB1, CREG1, CTGF, CTSD, CUL7 ( | 212 |
| cell cycle progression | 1.38E-04 | ADORA2B, AKAP9, ANXA1, APBB2, ASNS, ATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BLNK, BMP4, BRCA2, BTC, BTRC, CALM2, CAMK2N1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCNC, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CD274, CDC7, CDC16, CDC23 | 212 |
| proliferation of tumor cell lines | 5.09E-05 | ADC, ADM, AFP, AIM2, AKT3, ANXA1, ARD1A, AREG, ARIH2, BCAR1, BCL2, BDNF, BID, BRCA2, BTC, CASP2, CASP8, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD44, CD81, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CHKA, COL1A1, CRK, CTGF, CTSB, CUL4A, CXCL12, | 200 |
| Huntington's disease | 3.11E-05 | ACADM, ACP1, ACTB, ADCY7, AEBP1, AHCY, AIG1, ALDH2, ALDH6A1, AP1S1, AQP1, ARIH2, ARL3, ATP2A2, ATP5C1, ATP5O, ATP6AP2, BAIAP2, BCL2, BCL7A, BDNF, BHLHE40, C3, C14ORF156, C4A, C5ORF13, CA11, CA12, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP6, | 199 |
| cell division process of cell lines | 5.53E-05 | ADM, AKAP9, AKAP12, APBB2, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, AXIN2, BCAR1, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCK, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CD | 199 |
| organogenesis | 2.77E-05 | ACADM, ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADAMTS1, ADM, ATF4, B4GALT1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BCOR, BDNF, BMP4, BRCA2, CASP7, CASP8, CCND1, CDKN1B, CHD7, COL18A1, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, COL8A1, CREB1, CRK, CRKL, CRYAB, CUL1, CXADR, CXCL13, DCN, DGCR6, DLC1, DLX1, DLX2, ECE1, ECE2, | 179 |
| morphogenesis of cells | 6.39E-09 | ACP1, ADD1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANTXR1, ANXA5, ANXA7, ARHGDIG, ARHGEF2, ARRB2, ATRN, BAIAP2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BDNF, BMP4, CAPG, CAPZB, CASP8, CASP9, CAST, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD82, CD151, CDC42EP1, CDC42EP2, CDH13, CDK5 | 178 |
| shape change | 1.02E-08 | ACP1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANTXR1, ANXA5, ANXA7, AP2M1, ARF6, ARHGAP17, ARHGDIG, ARRB2, ATRN, BAIAP2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BDNF, BMP4, CAPG, CASP8, CASP9, CAST, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCNE1, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD151, CDC42EP1, CDC42EP2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1B, C | 178 |
| cell stage of eukaryotic cells | 1.92E-04 | ADORA2B, AKAP9, AKAP12, ARAF, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, AXIN2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, | 177 |
| disease of tumor cell lines | 5.42E-04 | ACADSB, ADAM17, AFG3L1, ANAPC2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATF2, ATF3, ATG12, ATG16L2, BICD2, C6ORF1, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCND1, CCT2, CD82, CD151, CD274, CDKN1A, CHST1, CLNS1A, COL18A1, CSPP1, CTDP1, CTSB, CTSZ (includes EG:1522), CXADR, CYR61, DDX3X, D | 175 |
| reproductive system disorder | 4.87E-03 | ACTB, ADRB2, AIG1, ANGPT2, ANK3, ANXA5, ATF4, ATP1B1, BCL2, BRCA2, BSG, C13ORF15, CAPN6, CASP8, CBX6, CD14, COL18A1, COL6A2, CREB1, CTGF, CX3CL1, CXADR, CXCL10, CXCL13, CYR61, DBP, DCN, DNMT1, DNMT3B, DST, DUSP1, ECT2, | 169 |
| arrest in cell division process of cells | 2.58E-05 | AKAP9, AKAP12, APBB2, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CD274, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDC2L6, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, CEBPD, | 165 |
| survival of cell lines | 1.36E-05 | ACVR2B, ADK, AK5, AKAP8L, ALOX12, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, ATF2, ATP7A, AURKAIP1, BCL2, BDNF, BHLHE40, BMP4, BRCA2, BTC, C7ORF16, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CASP2, CASP9, CCND1, CCRK, CD44, CD81, CD82, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK8, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CHKA, CREB1, CXCL12, CX | 162 |
| differentiation of cell lines | 1.57E-04 | ALG5, AREG, ATF2, B4GALNT1, BCL2, BDH2, BDNF, BHLHE40, BLNK, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CBR2, CBY1, CCND1, CD9, CD14, CD81, CD164, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CDON, CEBPD, CHKA, CHRD, CREBBP, CREG1, CRK, CTGF, CTSB, CUL4A, CXCL12, DAB2, DCN, DDIT3, | 161 |
| movement of cell lines | 3.21E-05 | ACP1, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ARRB2, BCAR1, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CBFB, CCL5, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CD151, CDH5, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLIC4, CNR1, COL18A1, CRK, CRKL, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, CYR61, DCBLD2, DDX3X, DICER1, DNAJA3 | 160 |
| development of blood vessel | 8.83E-10 | ACP1, ACVR1, ADA, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADORA2B, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANGPTL4, APH1A (includes EG:226548), ARHGAP24, ATP7A, B4GALT1, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C1GALT1, CASP8, CCL13, CCND1, CD151, CDH5, CHD7, COL18A1, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL4A2, COL5A1, CRKL, CSPG4, CTGF, | 159 |
| migration of cell lines | 1.73E-05 | ACP1, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, AKT3, ALCAM, ALOX12, ARRB2, BCAR1, BTC, C3, C5ORF13, CBFB, CCL5, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CD151, CDH5, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLIC4, CNR1, COL18A1, CRK, CRKL, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, CYR61, DCBLD2, DDX3X, DICER1, DNAJA3 | 158 |
| digestive organ tumor | 4.50E-03 | ACY1, ADAM12, ADORA2B, AIM2, AKAP1, AKT3, ANTXR1, ANXA1, BAT1, BCL2, BTRC, C14ORF143, CASP8, CD14, CD59, CD274, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CHRNA1, CHRNB1, COBLL1, COL1A1, COL6A3, COPS5, CREB1, CREBBP, CTSB, CTSD, CUGBP1, | 151 |
| adhesion of eukaryotic cells | 1.77E-03 | ACP1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ADRB2, ALOX12, ANGPT2, ANXA1, ANXA5, AOC3, B4GALT1, BMP4, BSG, C3, CASP8, CCL5, CCL13, CCL25, CCNC, CCND1, CD9, CD34, CD44, CD47, CD59, CD81, CD82, CD151, CDK5R1, CERCAM, COL18A1, COL7A1, CORO1A, CTGF, CX3CL1, CXCL2, C | 150 |
| developmental process of mammalia | 3.03E-03 | ACVR1, ADAMTS1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP1, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCND1, CDH5, CDK6, CDKN1B, COL4A2, COMMD1 (includes EG:150684), CREB1, CXCL12, CXXC1, | 145 |
| transformation | 3.54E-03 | ACP1, ADM, AFF4, AKT3, ANGPTL2, ANP32A, ARAF, ARHGEF3, ATF3, BCAR1, BCKDHA, BCL2, BCL10, BIN1, CBFB, CCDC6, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLTC, COL1A1, CREBBP, CRK, CYP2D6, CYTH1, DMTF1, DNAJA3, | 145 |
| developmental process of rodents | 2.79E-03 | ACVR1, ADAMTS1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP1, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCND1, CDH5, CDK6, CDKN1B, COL4A2, COMMD1 (includes EG:150684), CREB1, CXCL12, CXXC1, | 144 |
| benign tumor | 5.55E-03 | ADAM12, ADARB1, AIG1, AK2, AKAP8L, ANXA1, ANXA5, ARFGEF2, ARIH2, ARL4D, ATF2, ATP1A1, ATRN, ATRNL1, BCL2, BCL10, BTRC, CAPN6, CCND1, CDC7, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLEC16A, CNR1, COL18A1, COL6A3, COX6A2, CRABP2, CTGF, CTSB, CYP1B1, CYR61, DNMT1, DNMT3B, DO | 144 |
| developmental process of mice | 3.25E-03 | ACVR1, ADAMTS1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP1, ATP1B1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CBFB, CCND1, CDH5, CDK6, CDKN1B, COL4A2, COMMD1 (includes EG:150684), CREB1, CXCL12, CXXC1, | 143 |
| transformation of cells | 2.33E-03 | ACP1, ADM, AFF4, AKT3, ANGPTL2, ANP32A, ARAF, ARHGEF3, ATF3, BCAR1, BCKDHA, BCL2, BCL10, BIN1, CBFB, CCDC6, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLTC, COL1A1, CREBBP, CRK, CYTH1, DMTF1, DNAJA3, DNMT1, | 141 |
| infection of tumor cell lines | 2.75E-03 | ACADSB, AFG3L1, ANAPC2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, BICD2, C6ORF1, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCT2, CHST1, CLNS1A, CSPP1, CTDP1, CTSZ (includes EG:1522), DDX3X, DLST, DNAJA2, DTX4, DYSF, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, ETHE1, EXOSC5, FAM76B, FBXO21, FGD6, FHL3 | 141 |
| interphase of eukaryotic cells | 8.35E-05 | AKAP12, ARAF, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, C13ORF15, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CREG1 | 139 |
| cell stage of cell lines | 3.70E-04 | AKAP9, AKAP12, ARAF, ATF2, AXIN2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BRCA2, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCK, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, | 139 |
| cell division process of tumor cell lines | 7.03E-04 | AKAP9, APBB2, ATF2, AXIN2, BCAR1, BCL2, BHLHE40, BMP4, BRCA2, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CARD10, CASP2, CCK, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CEBPD, CHKA, C | 136 |
| infection of cervical cancer cell lines | 2.91E-03 | ACADSB, AFG3L1, ANAPC2, AP2M1, ARGLU1, ARHGEF19, ARPC1A, ATG12, ATG16L2, BICD2, C6ORF1, CAMK1D, CAPN6, CCT2, CHST1, CLNS1A, CSPP1, CTDP1, CTSZ (includes EG:1522), DDX3X, DLST, DNAJA2, DTX4, DYSF, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, ETHE1, EXOSC5, FAM76B, FBXO21, FGD6, FHL3 | 136 |
| invasion of cells | 1.48E-04 | ADAM9, ADAM17, ADM, AKT3, ANXA1, AREG, ARF6, ATF3, ATP6V0C, BATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BMP4, BSG, BTC, CCND1, CD9, CD14, CD44, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CHRD, COL18A1, CRK, CSPG4, CTSB, CTSD, CXCL10, CXCL12, DKK3, DLC1, DNMT3B, EGF, EGFR, ENG, ENPP2, ENTPD5, EPHA2, E | 135 |
| angiogenesis | 2.12E-09 | ACP1, ACVR1, ADA, ADAM17, ADAMTS1, ADORA2B, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANGPTL4, APH1A (includes EG:226548), ARHGAP24, ATP7A, B4GALT1, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, C1GALT1, CASP8, CCL13, CCND1, CD151, CDH5, COL18A1, COL4A2, CSPG4, CTGF, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, DDAH1, | 132 |
| invasion of eukaryotic cells | 5.03E-04 | ADAM9, ADAM17, ADM, AKT3, ANXA1, AREG, ARF6, ATF3, BATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BMP4, BSG, BTC, CCND1, CD9, CD14, CD44, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CHRD, COL18A1, CRK, CSPG4, CTSB, CTSD, CXCL10, CXCL12, DKK3, DLC1, DNMT3B, EGF, EGFR, | 127 |
| arrest in cell division process of eukaryotic cells | 2.05E-04 | AKAP9, AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, CLIP1, COL1A1, COPS5, CREB1, CUL1, | 125 |
| survival of tumor cell lines | 1.78E-04 | ACVR2B, ADK, AK5, AKAP8L, ALOX12, ANTXR1, ANTXR2, ATF2, AURKAIP1, BCL2, BDNF, BHLHE40, BRCA2, C7ORF16, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CASP2, CCND1, CCRK, CD44, CD81, CD82, CDK2, CDK6, CDK8, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CHKA, CREB1, CXCL12, CXCR7, DGKA, DUSP1, DUSP5, DUSP14, | 124 |
| colony formation of cells | 5.29E-04 | AKAP12, ANKRD1, ANXA1, ANXA7, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, BNIP3L, CBFB, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD9, CD44, CD82, CDA, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLTC, CNOT7, CRTC1, CTSD, CXCL12, CYR61, DCK, DCN, DDIT3, DLC1, | 124 |
| cell death of neurons | 2.05E-03 | ADA, ADCYAP1R1, ALOX12, ATF3, ATP2C1, B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BID, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP6, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CAST, CCL5, CD200, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CREB1, CREBBP, CTSB, CTSD, CX3CL1, CXCL12, DLX1, DLX2, E2F1, E | 124 |
| cell division process of normal cells 3.95E-04 ADORA2B, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BLNK, BMP4, BRCA2, C13ORF15, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG2, CD44, CD274, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK5, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, COL1A1, CREB1, CXCL10, CYP26B1, DCN, DNM1L, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, | 120 | ||
| ************* | |||
| shape change of eukaryotic cells | 1.01E-07 | ACP1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, ANTXR1, ANXA5, ARHGDIG, ARRB2, ATRN, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BDNF, CAPG, CAST, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCNE1, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD151, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1B, COL18A1, CORO1A, CRK, CRKL, CSPG4, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, DCN, DICER1, DPYSL2, | 119 |
| colony formation of eukaryotic cells | 1.34E-04 | AKAP12, ANKRD1, ANXA1, ANXA7, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, BNIP3L, CBFB, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD9, CD44, CD82, CDA, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLTC, CNOT7, CRTC1, CTSD, CYR61, DCK, DCN, DDIT3, DLC1, DYNC1H1, | 118 |
| interphase of cell lines | 1.65E-04 | AKAP12, ARAF, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CREG1, CUL4A, CXCL12, CYR61, DCN, DD | 117 |
| developmental process of embryonic tissue | 5.85E-04 ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ANGPT2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AREG, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CASP9, CD44, CRKL, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), CX3CL1, CXCL12, DAB2, DPPA4, ECE1, ECE2, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, EGR2, EN1, ENAH, ENPP2, ETS2, EYA1, F2RL1, | 113 | |
| arrest in cell stage of cells | 8.95E-04 | AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDC2L6, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, CLIP1, COPS5, CUL4A, CYP26B1, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, | 113 |
| colon cancer | 1.78E-03 | ABCA5, ADAMTS1, AHCY, AKT3, ANTXR1, AOC3, ATP2A2, AXIN2, C14ORF143, C15ORF23, C15ORF48, C17ORF81, CALD1, CAMK2N1, CCT4, CD274, CDKN3, CDKN1A, CEP55, CNNM2, COG8, COL3A1, COL6A2, CPEB4, CTSB, DGKA, DHDDS, DLGAP5, DNAJB9, DUSP5, EBP, EFNB1, EGFR, EIF4A2, EN | 112 |
| cell death of fibroblast cell lines | 5.44E-06 ABCC4, ACTB, ATF2, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BNIP3L, BRCA2, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLIC4, COPS5, COX5A, CTSB, CTSD, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), CYR61, | 111 | |
| movement of tumor cell lines | 2.65E-05 | ADAM15, ADAM17, AKT3, ALOX12, ARRB2, BCAR1, C5ORF13, CCL5, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CRK, CRKL, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, DCBLD2, DNAJA3, DPYSL2, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ENPP2, ESR1, ETV5, FGFR1, GAB1, GAS6, GDNF, GFER, GIPC1, GJA1, GOL | 110 |
| cell movement of cell lines | 9.01E-05 | ACP1, ADM, ARRB2, BSG, C3, CAPN1, CASP8, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL25, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD81, CD82, CD151, CDH13, CDKN1B, CNR1, CREB3, CRKL, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL10, CXCL12, CXCL13, DGKA, DKK3, DLC1, EGF, EGFR, ENPP2, ESR1, FIGF, FLNA, FOSL2, GAB1, GAS6, G | 110 |
| invasion of cell lines | 6.82E-04 | ADAM9, ADAM17, ADM, AKT3, ANXA1, AREG, ARF6, ATF3, BATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BMP4, BSG, BTC, CD9, CD44, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CHRD, COL18A1, CRK, CSPG4, CTSB, CTSD, CXCL12, DKK3, DLC1, DNMT3B, EGF, EGFR, ENPP2, ENTPD5, EPHA2, | 110 |
| migration of tumor cell lines | 2.19E-05 | ADAM15, ADAM17, AKT3, ALOX12, ARRB2, BCAR1, C5ORF13, CCL5, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CRK, CRKL, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, DCBLD2, DNAJA3, DPYSL2, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ENPP2, ESR1, FGFR1, GAB1, GAS6, GDNF, GFER, GIPC1, GJA1, GOLGA2, H | 109 |
| growth of plasma membrane projections | 2.92E-04 | ADAM17, ADRB2, ANP32A, ARHGAP17, ARTN, BAIAP2, BCAR1, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CD9, CD47, CDK2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CNPY2, CNR1, CNTN2, CREB1, CRK, CXCL12, DNAJA3, DOK4, DPYSL2, E2F1, EFNB1, EFNB2, EGF, EGFR, EIF4EBP1, ELMO2, EPHA2, EPN1, FEZ1, FGFR1, GAB1, GA | 108 |
| growth of neurites | 2.51E-04 | ADAM17, ADRB2, ANP32A, ARHGAP17, ARTN, BAIAP2, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CD9, CD47, CDK2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CNPY2, CNR1, CNTN2, CREB1, CRK, CXCL12, DNAJA3, DOK4, DPYSL2, E2F1, EFNB1, EFNB2, EGF, EGFR, EIF4EBP1, ELMO2, | 107 |
| degradation of protein | 1.62E-04 | ACY1, ADAM17, ADAMTS2, ADAMTS4, ADAMTS7, ALOX12, AMFR, ANAPC2, ANAPC4, ARIH2, AURKAIP1, BACE1, BLMH, BMP1, BTRC, CAPN1, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP6, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CAST, CDC23 (includes EG:8697), CTSB, CTSD, CTSZ (includes EG:1522), DHCR24, DLD, DNAJC1, DP | 105 |
| protein kinase cascade | 9.45E-04 | ADAM9, ADORA2B, ADRB2, AIDA, APOL3 (includes EG:80833), ARAF, ATP2C1, ATP6AP2, AZI2, BCL10, C7ORF16, CRKL, DOK1, DOK4, DUSP4, DUSP22, ECOP, ECT2, EDA2R, EEF1D, EGF, EGFR, F2R, FGF13, FGFR1, FLNA, GJA1, GPS2, HIPK2, HMGA2, | 105 |
| cell cycle progression of eukaryotic cells | 1.93E-03 | AKAP9, APBB2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BLNK, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK2N1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, COL1A1, CREB1, CRK, CUL1, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DMTF1, DUSP1, E2F1, E2 | 104 |
| formation of tissue | 2.19E-06 | ACVR1, ADAM12, ADAM15, ANGPT2, ANTXR2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), ARHGAP22, ARHGAP24, ATF3, ATF4, BDNF, BMP4, CASP8, CBFB, CD44, CD276, CFL1, CHRD, CHST3, COL18A1, COL4A2, CTGF, CTNNBIP1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, DAG1, | 103 |
| cell stage of tumor cell lines | 7.24E-04 | AKAP9, ATF2, AXIN2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BRCA2, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCK, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CREG1, CYLD, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DLGAP5, DUS | 103 |
| arrest in cell division process of cell lines | 1.25E-03 | AKAP9, AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, CLIP1, COPS5, CUL1, CUL4A, CYR61, DCN, D | 103 |
| development of skeleton | 1.71E-05 | ACP2, ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADAMTS4, ADRB2, AEBP1, ANKH, ATF2, AXIN2, BCL2, BMP4, CBFB, CD276, CHD7, CHRD, CHST11, COL12A1, COL1A1, COL5A2, CTGF, DLK1, E2F1, EBP, EGFR, EGR2, EIF2AK3, EN1, ENPP1, ERCC2, ESR1, ETS2, EXT2, EYA1, FBN1, | 102 |
| uterine cancer | 4.42E-03 | ADAM12, ADARB1, AGPAT2, AIG1, AK2, AKAP8L, ARFGEF2, ARIH2, ARL4D, ATRN, ATRNL1, BCL10, BTRC, CAPN6, CDC7, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CLEC16A, COL6A3, CRABP2, CTSB, CYP1B1, CYR61, DOK1, DST, EGFR, EIF4EBP1, | 101 |
| outgrowth of neurites | 2.80E-05 | ADAM17, ADRB2, ANP32A, ARHGAP17, BAIAP2, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CD9, CD47, CDK2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CNPY2, CNR1, CREB1, CRK, CXCL12, DNAJA3, DOK4, DPYSL2, E2F1, EFNB1, EFNB2, EGF, EGFR, ELMO2, EPHA2, EPN1, FEZ1, | 100 |
| arrest in cell stage of eukaryotic cells | 2.89E-04 | AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, CLIP1, COPS5, CUL4A, CYP26B1, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DLGAP5, | 100 |
| formation of filaments | 1.21E-05 | AKAP1, ARF6, ARHGEF2, ARHGEF3, BACE1, BCAR1, CALD1, CAPN1, CDC42EP2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CFL1, COL18A1, COL5A1, CRK, CTGF, DAB2, DLC1, DLGAP5, DPYSL2, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, F2R, FHL1, FMN1, GAP43, GAS7, GNAO1, GNAQ, GNB1, GNG12, GPI, GSN, HGF, HSPA5, HTT, IDE, IN | 99 |
| differentiation of tumor cell lines | 6.54E-04 | ALG5, ATF2, B4GALNT1, BCL2, BDH2, BDNF, BMP4, BTC, CCND1, CD14, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, CREBBP, CREG1, CRK, CTGF, CUL4A, DAB2, DDIT3, DLK1, DMTF1, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ELAVL2, ERBB2IP | 99 |
| development of embryonic tissue | 2.41E-03 | ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR2B, ANGPT2, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AREG, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CD44, CRKL, CX3CL1, CXCL12, DAB2, ECE1, ECE2, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, EGR2, EN1, ENAH, ENPP2, ETS2, EYA1, FGF10, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOSL2, FOXC2, FOXF1, FTO, | 99 |
| developmental process of muscle | 4.52E-06 | ACVR2B, ADAM12, ADRB2, AEBP1, BDNF, BMP4, CDK5, CDKN1A, CDON, CHKB, COL6A3, CRYAB, CXCL10, DUSP1, E2F1, EGR3, ETV1, F2RL1, FEM1C, FGFR1, FHL3, FLNB, FOSL2, FOXC2, FOXF1, FOXO1, FXR1, GAA, GAB1, GATA4, GATA6, GEFT, | 97 |
| adhesion of cell lines | 9.72E-05 | ACP1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ANGPT2, ANXA1, ANXA5, B4GALT1, BSG, C3, CASP8, CCL13, CCNC, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD59, CD81, CD82, CD151, CTGF, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, CYR61, CYTH1, CYTIP, DAB2, DCN, DKK3, E2F1, | 96 |
| invasion of tumor cell lines | 6.00E-04 | ADAM9, ADAM17, ADM, AKT3, ANXA1, AREG, ARF6, ATF3, BATF3, BCAR1, BCL2, BMP4, BSG, BTC, CD9, CD44, CD82, CD151, CDKN1B, CHRD, COL18A1, CRK, CSPG4, CTSB, CTSD, CXCL12, DKK3, DLC1, DNMT3B, EGF, EGFR, ENPP2, ENTPD5, EPHA2, | 96 |
| disease of kidney cell lines | 1.20E-03 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CCL5, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CSNK1E, CTDP1, CTSB, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, GATAD2A, GINS4, HBEGF, HMG | 96 |
| developmental process of tumor | 5.94E-06 | ADAM17, ANGPTL4, ARRB2, B4GALNT1, BCL2, CCND1, CD44, CD59, CD274, CDH5, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CNR1, COL18A1, CRABP2, CREB1, CREBBP, CRYAB, CTSB, DNMT1, DNMT3B, E2F1, E2F3, EGFR, EGR1, EPHA2, ESR1, ETS2, F2R, FGFR1, FGFR2, GADD45A, GDNF, GJA1, HGF, HRAS, | 94 |
| developmental process of fibroblast cell lines | 3.42E-04 | ACP1, AKAP12, ANP32A, AREG, BCAR1, BMP4, CAST, CBFB, CBR2, CBY1, CCND1, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL1A1, CRK, CUL1, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DDIT3, DDX3X, DLK1, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EBF1, EEF1D, EGF, EGFR, | 94 |
| disease of embryonic cell lines | 6.37E-04 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CD44, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CTDP1, DAG1, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EGFR, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, GATAD2A, GINS4, HMGCS1, HNRP | 94 |
| cell death of breast cancer cell lines | 1.83E-06 | ABCC4, ADM, AIM2, ATF2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP6, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CCND1, CD44, CD47, CDKN1A, CRABP2, CTGF, CYB5A, CYLD, CYR61, DAB2, DDIT4, DUSP1, DUSP4, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, | 93 |
| colony formation of cell lines | 7.22E-05 | AKAP12, ANKRD1, ANXA1, ANXA7, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, CBFB, CCL13, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD44, CD82, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLTC, CNOT7, CRTC1, CTSD, CYR61, DCK, DLC1, DYNC1H1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGLN2, EGR1, ETV6, FBLN1, FOXO3, GADD45A, GJA | 93 |
| disease of epithelial cell lines | 9.94E-04 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CTDP1, CXCL2, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, | 93 |
| infection of kidney cell lines | 1.40E-03 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CCL5, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CTDP1, CTSB, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, GATAD2A, GINS4, HMGCS1, HNRPDL, ID | 93 |
| differentiation of connective tissue cells | 1.41E-04 | ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADRB2, AREG, ATF4, AXIN2, BCL2, BMP4, CAPNS1, CASP8, CAST, CBY1, CCL9, CCND1, CD200, CD276, CDK6, CHRD, CREB1, DDIT3, DICER1, DLK1, EBF1, EGFR, ENPP1, FGF10, FGFR1, FIGF, FOSL2, GAS7, GDF5, GDNF, GPX1, IL11, | 92 |
| arrest in interphase of eukaryotic cells | 4.11E-04 | AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CD44, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CUL4A, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3 | 92 |
| infectious disorder of embryonic cell lines | 1.22E-03 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CTDP1, DAG1, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, GATAD2A, GINS4, HMGCS1, HNRPDL, IDH1, IR | 92 |
| infectious disorder of epithelial cell lines | 1.67E-03 | AEBP2, AMDHD2, ANAPC2, AP1G2, ATMIN, ATP6V0C, B4GALNT4, BMP1, CAD, CCDC51, CD164, CDC42EP3, CHST1, CLOCK, CLTA, COL5A1, CRYAB, CTDP1, DAZAP2 (includes EG:9802), DCP2, EIF2B5, ENC1, ERCC1, ETS2, EXOSC10, FXR1, GATAD2A, GINS4, HMGCS1, HNRPDL, IDH1, IRF3, KH | 91 |
| cell death of connective tissue cells | 5.92E-04 | ADAM12, ADM, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, CABLES2, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CCL9, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLIC4, CREB1, CTSD, CYP1B1, DCN, DDIT3, DHCR24, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ESR1, FLNA, FOXO1, GAB1, GABBR1, GLO1 | 88 |
| formation of plasma membrane projections | 6.92E-05 | AKAP12, ARF6, ARHGAP24, BAIAP2, BDNF, CAPNS1, CAST, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CDC42EP1, CDC42EP2, CDKN1B, CRK, CRKL, CTGF, CXCL12, CYR61, DAG1, DPYSL2, EFNB1, EGF, ENAH, EXOC7, FGD3, FGD4, GAB1, GAP43, GDNF, HGF, HRAS, | 87 |
| arrest in cell stage of cell lines | 4.41E-04 | AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, CLIP1, COPS5, CUL4A, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DLGAP5, DUSP1, E2F1, E | 87 |
| formation of cells | 3.57E-03 | ADAM12, ARHGAP22, BDNF, CASP8, CCL5, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD81, CDKN1A, COL18A1, CREBBP, CXCL12, DLK1, EFNB1, EGF, EGR1, ENAH, ENPP2, EPC1, ERCC1, FGF13, FGFR1, FST, FZD1, GDNF, GGT1, GNAO1, GNAQ, HAS2, HGF, HOPX, HRAS, | 86 |
| arrest in cell cycle progression | 2.53E-03 | AKAP9, APBB2, ATF3, BCL2, BMP4, BTRC, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD274, CDC25A, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, COL1A1, COMMD5, CREB1, CREBBP, CUL1, CUL4A, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGFR, EIF4G2, ERN1, FANCA, FANCC, FOXO3, GADD45A, GAS7 | 85 |
| interphase of tumor cell lines | 3.90E-04 | ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CREG1, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, FOXO3, GAD | 84 |
| apoptosis of neurons | 2.21E-03 | ADA, ADCYAP1R1, ATF3, ATP2C1, B4GALNT1, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BID, CASP2, CASP6, CASP9, CCL5, CD200, CDK2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CDKN2D, CREB1, CREBBP, CTSB, CXCL12, DLX1, DLX2, E2F1, EN1, ETV6, F2R, FBXW7, FOXO3, GDF5, | 84 |
| tumorigenesis of cells | 2.21E-03 | ADAM17, ARHGDIG, ARMC10, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, C3, CASP2, CASP9, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CD44, CD82, CD151, CD274, CDKN1A, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, COL18A1, CSNK1E, CTSB, CXADR, CXCL2, CYLD, CYR61, DLC1, DOK1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, EMP2, | 84 |
| formation of eukaryotic cells | 2.48E-03 | ADAM12, ARHGAP22, BDNF, CASP8, CCL5, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD81, CDKN1A, COL18A1, CREBBP, CXCL12, DLK1, EGF, EGR1, ENAH, ENPP2, EPC1, ERCC1, FGF13, FGFR1, FST, FZD1, GDNF, GGT1, GNAO1, GNAQ, HGF, HOPX, HRAS, ID1, IFNGR1, | 84 |
| apoptosis of fibroblast cell lines | 1.00E-04 | ATF2, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, BNIP3L, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLIC4, COPS5, COX5A, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), CYR61, DDIT3, DDX3X, DUSP4, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, | 83 |
| adenocarcinoma | 2.42E-03 | ACY1, AGPAT2, ALDOC, ANXA1, BRCA2, BTRC, CAMK2N1, CBLN1, CCND1, CD14, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, DICER1, DLK1, DYNLRB1, E2F1, EDNRA, EGFR, ENG, ESR1, FGFR1, FOXA3, GJA1, GLG1, GPI, | 83 |
| development of muscle | 9.43E-05 | ADAM12, AEBP1, BDNF, BMP4, CDK5, CDON, CHKB, COL6A3, CRYAB, CXCL10, DUSP1, EGR3, ETV1, F2RL1, FGFR1, FHL3, FLNB, FOSL2, FOXC2, FOXF1, FOXO1, FXR1, GAA, GAB1, GATA4, GATA6, GEFT, GJA1, GJC1, HBEGF, HGF, HLX, HMGA2, | 82 |
| arrest in interphase of cell lines | 4.09E-04 | AKAP12, ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, CEBPD, CHKA, COPS5, CUL4A, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EP400 | 82 |
| cell death of epithelial cell lines | 8.30E-07 | AAK1, ATF3, BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CD44, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CLIC4, CRYAB, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DAB2, DAP3, DDIT3, DLST, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, EGFR, EMP1, EMP2, EMP3, ESR1, FOXO3, HIPK2, HK1, HRAS, | 81 |
| apoptosis of breast cancer cell lines | 9.39E-06 | ADM, AIM2, ATF2, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP6, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CRABP2, CTGF, CYB5A, CYLD, CYR61, DDIT4, DUSP1, DUSP4, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, ESR1, ETS2, FBLN1, | 81 |
| cell stage of normal cells | 1.08E-03 | ADORA2B, AREG, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BMP4, BRCA2, C13ORF15, CCK, CCNB1IP1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, CYP26B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, EGR1, ERCC1, FANCA, | 80 |
| developmental process of connective tissue | 2.75E-03 | ACVR1, ADAMTS1, ADRB2, ATP7A, BCL2, BCL2L11, BMP4, CD9, CD44, CD81, CHST11, DLX2, E2F1, EGF, EGR1, EGR2, EN1, ENPP1, EXT2, FGF10, FGFR2, FOXC2, GGT1, GHR, GJA1, GPC3, GSN, HIP1, HIP1R, HOXA2, HOXA11, HOXD3, HOXD8, HOXD10, | 79 |
| transport of protein | 1.47E-05 | ADRB2, AP1G2, AP1GBP1, AP2M1, AP3B2, AP3S2, AP4B1, APPBP2, ARF2, ARF6, CASP9, CCHCR1, CDK5, CFL1, COL1A1, CTSA, DNAJA2, DRD1, EIF5A, ERGIC1, ERGIC3, GDI2, GOSR1, GOSR2, HLA-DMA, HSPA9, HTT, IGF2R, IPO9, KDELR2, KIF1B, | 76 |
| development of heart | 6.19E-05 | ACADM, ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADM, BCOR, BDNF, BMP4, CASP7, CASP8, CCND1, CHD7, COL3A1, COL5A1, CRK, CRKL, CXADR, DLC1, ECE1, ECE2, EDNRA, ENG, FBN1, FOXC2, GAA, GATA4, GJA1, GJC1, GNAQ, HAS2, HOPX, ID1, ID2, ID3, INSR, JMJD6, | 76 |
| adhesion of tumor cell lines | 1.60E-05 | ACP1, ADAM9, ADAM12, ADAM15, ADAM17, ANXA1, B4GALT1, BSG, CASP8, CCL13, CD9, CD44, CD47, CD59, CD81, CD82, CD151, CX3CL1, CXCL2, CXCL10, CXCL12, CYR61, CYTH1, CYTIP, DAB2, DCN, DKK3, E2F1, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, EMILIN1, | 75 |
| arrest in cell division process of tumor cell lines | 1.51E-03 | ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CEBPD, CHKA, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DLGAP5, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, FOXO3, GADD45A, | 75 |
| gonadal tumor | 1.94E-03 | ADA, AGPAT2, BCL2, BCL10, BTRC, C13ORF15, C4A, CD274, COL18A1, CP, CTNNAL1, DAB2, DHTKD1, DNMT1, DTNA, DYNLRB1, E2F3, EGFR, EPHB6, F2R, FAM171A1, FGFR2, FGFR1OP (includes EG:11116), FLRT2, FOXN2, FZD3, GATA4, GATA6, GSTM1, GSTM5, HDAC11, HIST2H2AA3, HMGA2 | 75 |
| modification of DNA | 2.19E-03 | ATF2, ATF7IP, BRCA2, CCNO, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN2D, COPS5, CREBBP, CSNK1E, DNMT1, DNMT3B, E2F1, EGF, ERCC1, ERCC2, ERCC4, FANCA, FANCC, FEN1, FTH1, GADD45A, GATAD2A, GTF2H4, GTF3A, HGF, HMGN1, HSPA1B, IGF2, IGF2R, MBD4, MCM4, MCM6, MGMT, MLH1, MNAT1, MPG, MR | 75 |
| cell cycle progression of cell lines | 3.93E-03 | AKAP9, APBB2, BCAR1, BCL2, BMP4, BTRC, CAMK2N1, CARD10, CASP2, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CRK, CUL1, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DMTF1, DUSP1, E2F1, E2F2, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ESR1, EZH2, FANCA, FGFR1, FOX | 75 |
| cell death of kidney cell lines | 7.49E-04 | AAK1, BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, BRCA2, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CCBL1, CD44, DAP3, DDIT3, DLST, DUSP4, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, EGFR, EMP1, EMP2, EMP3, GNB2, HGF, HIPK2, HK1, HRAS, HSPA5, HTT, IER3, IRF1, IRS1, ITPR1, MAP2K6, MCL1, | 74 |
| formation of actin filaments | 5.78E-06 | AKAP1, ARF6, ARHGEF2, ARHGEF3, BCAR1, CALD1, CAPN1, CDC42EP2, CDKN1A, CFL1, COL18A1, CRK, CTGF, DAB2, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, F2R, FMN1, GAP43, GAS7, GNAO1, GNAQ, GNB1, GNG12, GPI, GSN, HGF, INPP5B, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, LAT2, | 73 |
| cell movement of tumor cell lines | 2.33E-03 | ARRB2, BSG, C3, CAPN1, CASP8, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CCL25, CD9, CD44, CD81, CD82, CD151, CDH13, CDKN1B, CREB3, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL12, DKK3, DLC1, EGF, EGFR, ESR1, FIGF, FLNA, GAS6, GNB1, GNB2, GPI, HGF, IGF2BP1, ING4, IRS1, | 73 |
| proliferation of epithelial cells | 2.88E-03 | ANGPTL6, B4GALT1, BTRC, CCND1, CCNG2, CD9, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL8A1, CRYAB, E2F1, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, ESR1, FGF10, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXF1, FOXF2, FST, HGF, HMGN1, HRAS, ID1, ID2, IGFBP4, INSR, ITGA3, | 72 |
| apoptosis of connective tissue cells | 1.69E-03 | ADAM12, ADM, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, CABLES2, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CCL9, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLIC4, CREB1, CTSD, DCN, DDIT3, DHCR24, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, ESR1, FOXO1, GAB1, GABBR1, GLO1, HRAS, INSR, MAPK1, MBD4, | 71 |
| ovarian tumor | 2.79E-03 | AGPAT2, BCL2, BCL10, BTRC, C13ORF15, C4A, CD274, COL18A1, CP, CTNNAL1, DAB2, DHTKD1, DNMT1, DTNA, DYNLRB1, E2F3, EGFR, EPHB6, F2R, FAM171A1, FGFR1OP (includes EG:11116), FLRT2, FOXN2, FZD3, GATA4, GATA6, GSTM1, GSTM5, | 71 |
| colony formation of tumor cell lines | 2.50E-05 | ANKRD1, ANXA1, ANXA7, ATF3, BACH2 (includes EG:60468), BCL2, BCL2L11, CCL13, CCNG2, CD44, CD82, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CNOT7, CTSD, CYR61, DLC1, DYNC1H1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGLN2, EGR1, FBLN1, FOXO3, GADD45A, GJA1, HAS2, HGF, | 70 |
| developmental disorder of animal | 3.03E-05 | ARSA, CCND1, CHRD, CLCN7, CSNK1E, DLK1, DOK1, E2F1, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, EGR3, ERCC2, ESR1, FGFR1, FMR1, FOSL2, GDNF, GGT1, GNAQ, HIP1, HIP1R, HIPK2, HOXA5, HRAS, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), HTT, IGF2BP1, INSIG2, INSL3, INSR, ITGA7, | 70 |
| G1 phase of cell lines | 1.63E-03 | AKAP12, BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, COPS5, CREG1, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, E2F1, E2F3, EGF, EGFR, EP400, EPB41L1, GHR, GJA1, GPI, GPS2, | 70 |
| apoptosis of epithelial cell lines | 1.35E-07 | ATF3, BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CD44, CEBPD, CLIC4, CRYAB, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DAB2, DAP3, DDIT3, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, EGFR, ESR1, FOXO3, HIPK2, HRAS, HSPA5, HSPB8, HTT, IER3, INSR, IRF1, IRS1, ITGA5, | 69 |
| cell spreading | 4.83E-05 | ACP1, ANTXR1, ATRN, BCAR1, BCL10, CAST, CCL5, CD44, CD47, CORO1A, CRK, CRKL, CSPG4, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB1, EGF, EPHA2, FBN1, FHL3, GAP43, HGF, HRAS, IGBP1, ING4, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB5, ITGB1BP1, LAMA5, LPAR1, LPP, | 69 |
| growth of fibroblast cell lines | 9.03E-04 | ACP1, AKAP12, ANP32A, AREG, BCAR1, BMP4, CAST, CBFB, CCND1, CDH13, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL1A1, CRK, CUL1, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EEF1D, EGF, EGFR, ERRFI1, ETV6, F2R, GADD45GIP1, GAK, | 69 |
| shape change of cell lines | 2.53E-04 | ACP1, ANGPTL2, ANTXR1, ANXA5, ARHGDIG, BCAR1, BCL2, BCL10, CAST, CCNE1, CD151, CDKN1B, CRK, CYR61, DICER1, DPYSL2, EDNRA, EFNA5, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, FGD4, FHL3, GAP43, GNAQ, GNG12, ING4, INSR, ITGA5, ITGA6, LPAR1, | 68 |
| cell death of fibroblasts | 1.50E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, CABLES2, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CCND1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLIC4, CTSD, CYP1B1, DDIT3, DHCR24, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, FLNA, FOXO1, GAB1, GPX4, HMOX1, HRAS, IGF2, IGF2R, | 68 |
| shape change of normal cells | 1.46E-05 | ANGPT2, ARRB2, ATRN, BCL2, BDNF, CAPG, CAST, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13, CD9, CD44, CD47, CDK5, CDK5R1, COL18A1, CORO1A, CRK, CRKL, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, DCN, EFNB1, EGF, EPHB4, F2R, FBN1, FGFR1, GAP43, GDNF, GSN, HGF, | 67 |
| developmental process of muscle cells | 8.97E-04 | ACADM, ACVR1, AKR1B1, BIN1, BMP4, CBY1, CD9, CD81, CDKN1A, CDON, CEBPD, CXADR, DNAJB6, DUSP1, E2F1, EGFR, EPC1, EPHB4, EZH2, FGF10, FGFR1, FOSL2, FOXO1, GATA4, GNAQ, HGF, HMOX1, HOPX, ID2, ID3, IGF2, ITGA6, ITGA7, KLF4, | 66 |
| inhibition of apoptosis | 8.97E-04 | ADAM17, ADM, ALOX12, ANXA1, ANXA5, BCL2, BDNF, BFAR, BNIP1, BNIP2, CD59, CDKN1A, CDKN2D, CFL1, CIAPIN1, CRYAB, DHCR24, DNAJB9, DUSP1, FOXC2, FOXO1, GDNF, GLO1, GNAQ, GPX1, GSTP1, HBXIP, HGF, HMOX1, HSPA5, HSPA9, | 66 |
| cell death of embryonic cell lines | 3.88E-05 AAK1, BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CD44, COPS5, DAP3, DLST, DPPA4, E2F1, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, EMP1, EMP2, EMP3, HIPK2, HK1, HRAS, HSPA5, HTT, IER3, IRF1, IRS1, MAP2K6, MCL1, PAK2, PEA15, PKN2, PMP22, PPARD, | 65 | |
| developmental disorder of rodents | 1.00E-04 | ARSA, CCND1, CHRD, CLCN7, DLK1, DOK1, E2F1, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, EGR3, ERCC2, FGFR1, FMR1, FOSL2, GDNF, GGT1, GNAQ, HIP1, HIP1R, HIPK2, HOXA5, HRAS, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), HTT, IGF2BP1, INSIG2, INSL3, ITGA7, ITGA11, LIF, MAP2K6, | 65 |
| arrest in cell stage of tumor cell lines | 3.35E-04 | ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DLGAP5, DUSP1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, FOXO3, GADD45A, GOLGA2, GPS2, GSPT1 | 65 |
| migration of endothelial cells | 1.52E-05 | ACP1, ADAM15, ADM, ANGPT2, ANGPTL4, ARHGAP24, ARRB2, CD9, CD81, CD151, CDH5, CDH13, COL18A1, COL4A2, CXCL12, CYR61, DCN, EFNB2, EGFL7, ENG, EPHB4, FGF13, FGFR1, FIGF, FOXC2, GAB1, GIPC1, HGF, ID1, IGF2, IGF2R, ITGA3, | 64 |
| arrest in growth of cells | 2.31E-05 | AKAP12, AKT3, ALCAM, BCL2L11, BMP4, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDH13, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, DAB2, DDIT3, DMTF1, E2F1, EGF, EGR1, ELAC2, ENG, EZH2, FOXO3, GADD45A, GADD45GIP1, HIPK2, HMOX1, HRAS, ID3, IL6ST, IRF1, ITGB4, KLF4, KRT10, L | 64 |
| cell death of muscle cells | 7.60E-04 | ADAM12, ADM, ADRB2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BMP4, BNIP3L, C14ORF153, CACNB2, CAMK2D, CAPN1, CASP8, CASP9, CDC42EP3, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COQ6, CXCL12, DAG1, E2F1, EEF1D, GATA4, GATA6, GNAQ, GNPTG, GPX1, HGF, HK1, HLA-B, HLADMA, HSPB6, HSPB8, ID2, IL6ST, IRF1, LIF, MAP | 63 |
| replication of DNA | 4.54E-03 | AKAP8L, AREG, BCL2, BRCA2, BTC, C4ORF16, CCNE1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, DNAJC2, DUT (includes EG:1854), E2F1, E2F2, EGF, ERCC1, FEN1, GTPBP4, HBEGF, HELB, HMGA2, HMGN1, HRAS, ID1, ID3, INSR, KIAA0101, KRT7, | 63 |
| growth of rodents | 5.78E-03 | ADAMTS1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), AQP1, BDNF, CDKN1B, COL4A2, DLK1, DRD1, E2F1, E2F3, EGF, EGFR, EIF2AK3, EXT2, EZH2, FGFR2, FOSL2, GHR, GNB5, GPC3, GRB10, HIP1, HIP1R, HMOX1, HOXA5, HSPA5, IGF2, IGF2BP1, IGF2R, IRS1, ITPR3, LIF, | 63 |
| developmental process of embryonic cells | 1.32E-04 | ACVR1, ADA, ATP1B1, BAIAP2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, CDC7, CDKN1B, DAB2, DNMT1, EDNRA, EGF, EIF4G2, ENG, EPHB4, ERF, EZH2, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXC2, GAS7, GATA4, GATA6, HBEGF, HGF, HHEX, HMGN1, HOPX, HTT, ID1, ID3, IGF2, IL6ST, | 62 |
| arrest in interphase of tumor cell lines | 1.58E-04 | ATF2, BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMK2N1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDH13, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, FOXO3, GADD45A, GPS2, GSPT1, HAS2, HGF, HRA | 62 |
| apoptosis of kidney cell lines | 2.25E-04 | BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CD44, DAP3, DDIT3, DUSP4, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, EGFR, GNB2, HGF, HIPK2, HRAS, HSPA5, HTT, IER3, IRF1, IRS1, ITPR1, MAP2K6, MCL1, PAK1, PAK2, PEA15, PKN2, PPARD, PPP1R15A (includes EG:23645), | 62 |
| developmental disorder of mice | 3.18E-04 | ARSA, CCND1, CHRD, CLCN7, DLK1, DOK1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR3, ERCC2, FGFR1, FMR1, FOSL2, GGT1, GNAQ, HIP1, HIP1R, HIPK2, HOXA5, HRAS, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), HTT, IGF2BP1, INSIG2, INSL3, ITGA7, ITGA11, LIF, MAP2K6, MAP3K4, | 62 |
| growth of mice | 5.62E-03 | ADAMTS1, ADH5 (includes EG:128), AQP1, BDNF, CDKN1B, COL4A2, DLK1, DRD1, E2F1, E2F3, EGF, EGFR, EIF2AK3, EXT2, EZH2, FGFR2, FOSL2, GHR, GNB5, GPC3, GRB10, HIP1, HIP1R, HOXA5, HSPA5, IGF2, IGF2BP1, IGF2R, IRS1, ITPR3, LIF, LMNA, | 62 |
| disease of tumor | 3.02E-06 | ADAM17, ANP32A, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, ATP2A2, BCL2, BRCA2, BTRC, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CRYAB, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, EPHA2, ESR1, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HMGA2, HRAS, ID2, IFNGR1, IGF2, ITGB5, MAP2K6, | 61 |
| cell spreading of eukaryotic cells | 3.67E-05 | ACP1, ANTXR1, ATRN, BCAR1, BCL10, CAST, CD44, CD47, CORO1A, CRK, CRKL, CSPG4, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB1, EGF, EPHA2, FBN1, FHL3, GAP43, HGF, HRAS, IGBP1, ING4, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB5, ITGB1BP1, LAMA5, LPAR1, LPP, MPRIP, | 61 |
| endocrine gland tumor | 4.83E-03 | ADAMTS1, ANGPT2, ATP1A1, BCL2, CCND1, CD59, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, COPS5, CTSD, CYR61, E2F3, EFNB2, EGFR, ENG, EPHB4, FGFR1, HBEGF, HDAC11, HLA-G, IFITM1, IL15, ITGA3, ITGA5, | 61 |
| S phase of eukaryotic cells | 1.01E-03 | ARAF, BCL2, BCL2L11, BHLHE40, BID, C13ORF15, CAMK2N1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, CXCL12, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, EGFR, FOXO3, GAB1, GADD45A, | 60 |
| cell division process of fibroblast cell lines | 2.00E-03 | ADM, AKAP12, ARAF, AREG, AXIN2, BID, BMP4, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, COPS5, CRK, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, EGFR, EP400, GADD45A, GATA6, GPI, HRAS, ID1, ID2, ID3, IGF2, INSR, | 59 |
| tumorigenesis of tumor | 4.77E-06 | ADAM17, ANP32A, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, ATP2A2, BCL2, BRCA2, BTRC, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, EPHA2, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HMGA2, HRAS, IFNGR1, IGF2, ITGB5, MAP2K6, MMP2, MMP3, | 58 |
| development of tumor | 7.15E-05 | ADAM17, ANGPTL4, BCL2, CCND1, CDH5, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, COL18A1, CTSB, E2F1, E2F3, EGFR, EGR1, EPHA2, ESR1, FGFR2, GDNF, HGF, HRAS, ID1, IER3, IL18, INSR, IRF1, ITGB5, LATS1, LCK, MGAT3, MGMT, MLH1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP14, MYD88, | 58 |
| growth of tumor | 1.89E-04 | ANGPTL4, ARRB2, B4GALNT1, BCL2, CD44, CD59, CD274, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CNR1, COL18A1, CRABP2, CREB1, CREBBP, CTSB, DNMT1, DNMT3B, EGFR, EPHA2, F2R, FGFR1, FGFR2, GADD45A, GJA1, HGF, HRAS, HSPA4, IGF2, IL18, IRF1, ITGA5, ITGB5, | 58 |
| proliferation of muscle cells | 2.53E-03 ABCC4, ADM, AGTRAP, AKR1B1, BMP4, CDH13, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, COMT, CTNNBIP1, CXADR, E2F3, EGF, EGFR, ESR1, FGFR2, GATA4, GATA6, GNAQ, GPX1, HBEGF, HGF, HMGA2, ID2, IL15, ITGA5, ITGA6, KLF4, LIF, LRP1, MMP14, MNAT1, | 58 | |
| cell viability of cell lines | 5.43E-03 | ANTXR1, ANTXR2, BCL2, BNIP2, CDKN1A, CLNS1A, DAB2, DDIT3, DPP3, E2F1, EGF, ESR1, FTH1, GPC1, GPX1, GSTP1, HGF, HIP1, HMOX1, HRAS, HSPA5, IFNZ, IGFBP7, LCK, LMNA, MCL1, MT1E, MT1F, NFKBIA, P4HB, PLAU, PLAUR, PRNP, PTEN, PTPN6, | 57 |
| survival of cervical cancer cell lines | 1.71E-03 | ACVR2B, ADK, AK5, AKAP8L, AURKAIP1, BCL2, BRCA2, CAMK2D, CAMK2N1, CCRK, CDK6, CDK8, CHKA, DGKA, DUSP5, DUSP14, DUSP22, DYRK3, EIF2AK4, INPP5B, KHK, LCK, MAP3K4, MINPP1, MPG, MTMR7, NEK3, PFKFB2, PFKM, PLK2, PPAP2A, PPM1B, | 56 |
| formation of actin stress fibers | 2.05E-04 | AKAP1, ARHGEF2, ARHGEF3, BCAR1, CALD1, CAPN1, CDKN1A, COL18A1, CRK, CTGF, DAB2, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, F2R, GNAO1, GNAQ, GNB1, GNG12, GPI, HGF, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, LIMK1, LPAR1, LPAR4, MAPK11, MPRIP, NET1, NF1, PALLD, | 55 |
| apoptosis of muscle cells | 6.10E-04 | ADM, ADRB2, BCL2, BCL2L11, BMP4, BNIP3L, CAMK2D, CAPN1, CASP8, CASP9, CDC42EP3, CDKN1A, COQ6, CXCL12, DAG1, E2F1, EEF1D, GATA4, GATA6, GNAQ, GNPTG, GPX1, HGF, HLA-B, HLA-DMA, HSPB6, ID2, IL6ST, IRF1, LIF, MAP2K6, MCL1, | 55 |
| apoptosis of embryonic cell lines | 6.22E-06 | BCL2, BCL10, BID, BNIP3L, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CD44, COPS5, DAP3, E2F1, E2F6, ECOP, EGF, HIPK2, HRAS, HSPA5, HTT, IER3, IRF1, IRS1, MAP2K6, MCL1, PAK2, PEA15, PKN2, PPARD, PPP1R15A (includes EG:23645), PPP3R1, PRMT2, PTGIS, | 54 |
| interphase of normal cells | 1.24E-04 | ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, C13ORF15, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG2, CD44, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CEBPD, CHKA, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, ERCC1, FANCC, GAB1, GADD45A, GATA6, GPC1, GRB10, HMGN1, ID2, ID3, IGFBP7, | 54 |
| apoptosis of fibroblasts | 3.69E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BCL2L11, BID, CABLES2, CAPNS1, CASP2, CASP8, CASP9, CCND1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLIC4, CTSD, DDIT3, DHCR24, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, FOXO1, GAB1, HRAS, INSR, MBD4, MCL1, MT1E, MT1F, NEK1, NOTCH1, NUPR1, OPA1, PITPNA, POLB, PRMT2 | 54 |
| metastasis | 4.86E-03 | ACTB, ADAM17, AKAP12, ARHGDIG, ARRB2, ATF2, ATF3, CD44, CD151, CD274, COL18A1, CXCL2, CYP1B1, EGF, EGFR, ENPP2, EPHA2, F2R, FIGF, FUS, HGF, HMGCR, HTATIP2, IFNAR2, IGF2BP1, ITGB4, LAMA5, LCK, LETMD1, MAPK1, MMP2, | 54 |
| arrest in growth of eukaryotic cells | 3.59E-04 | AKAP12, AKT3, BMP4, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, DAB2, DMTF1, E2F1, EGF, EGR1, ELAC2, ENG, EZH2, FOXO3, GADD45GIP1, HMOX1, HRAS, ID3, IL6ST, IRF1, ITGB4, KLF4, KRT10, LIF, LMNA, MAP2K6, MAPK1, | 53 |
| G1 phase of tumor cell lines | 6.17E-04 | BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDK2, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, CREG1, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, GJA1, GPS2, GSPT1, | 53 |
| development of connective tissue | 6.09E-03 | ACVR1, ADAMTS1, ADRB2, ATP7A, BCL2, BMP4, CD9, CD81, CHST11, DLX2, E2F1, EGR2, EN1, ENPP1, FGF10, FGFR2, FOXC2, GJA1, GPC3, HIP1, HIP1R, HOXA2, HOXA11, HOXD3, HOXD8, HOXD10, HOXD13, MAPK3, MMP2, MMP13, MMP14, MSX1, NDST1, PDGFC, PDGFRA, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTGE | 53 |
| tumorigenesis of cell lines | 3.93E-04 | ADAM17, ARMC10, ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, CAST, CCND1, CD44, CD82, CD151, CD274, CDKN1A, COL18A1, CSNK1E, CTSB, CXADR, CXCL2, CYR61, DLC1, EGFR, EGR1, ENPP2, ERF, F2R, GPI, HAS2, HGF, HRAS, HTATIP2, IL18, IRF1, LAMA5, LPP, MAD1L1, | 52 |
| quantity of cell lines | 1.34E-03 | BCL2, BHLHE40, CBFB, CCND1, CCNE1, CD63, CDC25A, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL18A1, CUL4A, E2F1, EDNRA, EGF, EGFR, ERRFI1, ESR1, FGF13, HMOX1, HRAS, IFNZ, IGFBP6, IGFBP7, IL11, INPPL1, JUNB, KLF4, LIF, | 52 |
| arrest in G1 phase of cell lines | 4.26E-03 | AKAP12, BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, COPS5, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EP400, EPB41L1, GHR, GPS2, GSPT1, HRAS, ID3, ITGA5, JAK3, KLF4, LMNA, MA | 51 |
| neurological process of neurites | 8.16E-04 | ALCAM, ANK3, APBB2, ARTN, BACE1, BDNF, CDK5, CDK5R1, CXCL12, DPYSL2, EFNA5, EFNB1, EGR2, ENAH, ETV1, FEZ1, FOXD1, GALNS, GAP43, GDNF, GRIA1, HGF, HOXA1, HOXA2, HRAS, KLF7, LAMC1, MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8IP3, NCAM1, | 50 |
| differentiation of embryonic cells | 6.33E-05 | ACVR1, ADA, BAIAP2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, CDKN1B, DAB2, DNMT1, EGF, EIF4G2, EPHB4, ERF, EZH2, FGFR1, FGFR2, GAS7, GATA4, GATA6, HBEGF, HGF, HHEX, HMGN1, HOPX, HTT, ID3, IGF2, IL6ST, JUNB, LIF, MAPK1, MAPK8IP3, METRN, MMP2, | 49 |
| neurological process of axons | 1.27E-03 | ALCAM, ANK3, APBB2, ARTN, BACE1, BDNF, CDK5, CDK5R1, CXCL12, DPYSL2, EFNA5, EFNB1, EGR2, ENAH, ETV1, FEZ1, FOXD1, GALNS, GAP43, GDNF, GRIA1, HGF, HOXA1, HOXA2, HRAS, KLF7, LAMC1, MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8IP3, NCAM1, | 49 |
| pancreatic tumor | 2.86E-03 | AKAP1, CD59, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1A, COPS5, CREBBP, CTSB, CTSD, CYR61, EGFR, GATA4, GATA6, HBEGF, HLA-G, HOXA5, IFITM1, IL15, ITGA3, ITGAE, ITGB4, KLF4, KRT7, KRT10, MAPK13, MLL3, MSLN, PALLD, | 49 |
| proliferation of breast cancer cell lines | 3.86E-03 | AIM2, BCAR1, BRCA2, BTC, CCND1, CCNE1, CDKN1A, CHKA, CYR61, DCN, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, ESR1, ETS2, FOXO1, GPER, GPX1, HAS2, HOXA1, HSPB8, ID1, ID2, IER3, IGF2, ITGA5, LATS1, MAGED1, MAPK6, MAPK11, MAPK12, MED1, MMP14, | 49 |
| ossification | 8.21E-04 | ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADRB2, ANKH, ATF2, AXIN2, BCL2, BMP4, CBFB, CD276, COL1A1, CTGF, E2F1, EGFR, EGR2, EIF2AK3, EN1, ENPP1, ERCC2, ESR1, EXT2, FETUB, FGFR2, FOSL2, FOXC2, GJA1, GLA, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), MEF2C, MMP13, | 48 |
| cell death of prostate cancercell lines | 4.92E-03 | ALOX12, BCL2, BCL2L11, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CDK5, CDK5R1, COX5A, CREB1, DDIT3, DKK3, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ETS2, FOXO1, FOXO3, FST, GADD45A, GLIPR1, HBEGF, HGF, HOXC6, HSPB8, ID1, IGFBP4, IGFBP7, ITGB5, NFKB2, PLAU, | 48 |
| organization of filaments | 3.43E-04 | ADAMTS2, AGFG1 (includes EG:3267), AKAP2, ARHGEF2, ATP7A, BCAR1, BCL2, CDK2AP2, CDKN1B, CFL1, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, CORO1A, DNAJB6, ENAH, EPB41, EVL, FES, FLNA, FNBP1, FOXC2, GHR, GOLGA2, HAS2, ITGB4, LOX, | 47 |
| morphogenesis of tissue | 2.52E-03 | ACVR2B, AREG, CHST11, CX3CL1, DAG1, DLX2, EGFR, FGF10, FGFR2, FOXC2, FTO, GAA, GAB1, GATA4, GDNF, GREM1, GRSF1, HOXA2, HOXB4, HOXD13, IL11, INSR, IPP, IRX3, IRX5, LAMA5, LIF, LY6E, MEOX2, NDST1, NOTCH1, PTPN11, ROR2, RXRA, | 47 |
| cardiovascular process of organism | 2.46E-04 | ADORA2B, ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BTC, CCND1, CD14, CDH5, COL18A1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB1, EFNB2, ELK3, EPHB4, ESR1, FIGF, HGF, HRAS, IGF2R, IL15, IL18, KLF5, LAMC1, MED1, MMP2, MMP14, NR2F2, NRP1, NRP2, PGF, PRL2C2, PTEN, | 46 |
| S phase of cell lines | 5.58E-04 | ARAF, BCL2, BHLHE40, BID, CAMK2N1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CCNG2, CDC7, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, CXCL12, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, EGFR, FOXO3, GADD45A, GATA6, HGF, HMOX1, ID1, IRS1, MCM10, MPG, MTCH2, MXD4, MXI1, MYBL2, | 46 |
| neuroepithelial tumor | 4.43E-03 | AKAP12, AKT3, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CLK2, CLK4, E2F1, EDNRA, EGFR, ENC1, EPHA3, ESR1, FNTB, GRIA1, GRIA3, HBEGF, HIPK2, HRAS, HSPA5, ID2, IGF2, ITGB5, LPAR1, MGMT, MLH1, MLL3, MMP14, NES, | 46 |
| cell division process of connective tissue cells | 1.72E-04 | ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BRCA2, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, FANCA, FANCC, FIGF, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HBEGF, HMGN1, HRAS, ID2, ID3, IGF2, IGFBP7, IL11, INSR, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, | 45 |
| arrest in growth of cell lines | 4.08E-04 | AKAP12, AKT3, BMP4, CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, DAB2, DMTF1, E2F1, EGF, ELAC2, ENG, EZH2, GADD45GIP1, HMOX1, HRAS, IL6ST, IRF1, ITGB4, KLF4, KRT10, LIF, LMNA, MAP2K6, MAPK1, MAPK3, NOTCH1, PTEN, RASSF5, | 45 |
| formation of cellular protrusions | 7.22E-05 | ARF6, ARHGAP24, BAIAP2, BDNF, CAPNS1, CAST, CD44, CD82, CDKN1B, CRK, CRKL, CTGF, CYR61, DAG1, EGF, FGD4, GAB1, GDNF, HGF, HRAS, HSP90AA1, IQGAP1, ITGA3, ITGA6, ITGB4, LASP1, LPAR1, MPRIP, NISCH, NRP1, PFN1, PKP1, PLAU, | 44 |
| neuroendocrine tumor | 2.41E-03 | BCL2, CCND1, CD59, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1A, CDKN2C, COPS5, CTSD, CYR61, E2F3, EGFR, HBEGF, HLA-G, IFITM1, IL15, ITGA3, ITGAE, ITGB4, KRT7, KRT10, MLL3, MSLN, NCAM1, PALLD, PDGFRA, PLAT, PLAU, POLE3, | 44 |
| apoptosis of prostate cancer cell lines | 6.23E-03 | ALOX12, BCL2, BCL2L11, CASP7, CASP8, CASP9, CDK5, CDK5R1, COX5A, CREB1, DKK3, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ETS2, FOXO1, FOXO3, FST, GADD45A, GLIPR1, HBEGF, HGF, HOXC6, HSPB8, ID1, IGFBP4, IGFBP7, ITGB5, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, | 44 |
| cell division process of fibroblasts | 1.54E-05 | ATF2, ATF3, BCL2, BRCA2, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, FANCA, FANCC, FIGF, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HBEGF, HMGN1, HRAS, ID2, ID3, IGF2, IL11, INSR, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, | 43 |
| arrest in cell division process of normal cells | 1.57E-03 | ATF2, CCND1, CD44, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CHKA, COL1A1, CREB1, CYP26B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, ERCC1, FANCA, FANCC, FOXO3, GADD45A, GPC1, HRAS, ID2, IGFBP7, JAK3, LY6C1, MAP2K6, MBD4, MLH1, MNAT1, MYBL2, NFKBIA, | 43 |
| tumorigenesis of organ | 2.23E-03 | AKAP12, AREG, BCL2, BRCA2, CCNE1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CUL1, CYP1B1, DNMT1, E2F1, EPHA2, ESR1, GADD45A, GSTP1, HBEGF, HGF, HRAS, KLF9, KRT10, LCK, MMP3, NDRG1, NOTCH1, PPARD, PTEN, PTTG1, RBL1, SIGIRR, SKP2, SPP1, TCIRG1, TGFBR2, TIMP1, TSC2, TXN | 43 |
| guidance of axons | 1.18E-03 | ALCAM, ANK3, APBB2, ARTN, BDNF, CDK5, CDK5R1, CXCL12, DPYSL2, EFNA5, EFNB1, EGR2, ENAH, ETV1, FEZ1, FOXD1, GALNS, GAP43, HGF, HOXA1, HOXA2, HRAS, KLF7, MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8IP3, NRP1, NRP2, PDIA3, PLXNA2, PTPRF, | 42 |
| catabolism of protein | 2.92E-03 | ACY1, AMFR, ANAPC2, ANAPC4, ARIH2, BTRC, CAST, CDC23 (includes EG:8697), DHCR24, EGLN2, FBXO2, FBXO6, FLNA, GJA1, ITCH, KIAA0368, PJA1, PSENEN, PSMB3, PSMC2, RELA, RNF6, RNF40, SELS, SGSM3, SIAH1, SIAH2, SKP2, SQSTM1, | 42 |
| angiogenesis of organism | 5.70E-07 | ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BTC, CCND1, CDH5, COL18A1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB2, ELK3, EPHB4, FIGF, HGF, HRAS, IGF2R, IL15, IL18, KLF5, LAMC1, MED1, MMP2, MMP14, NR2F2, NRP1, NRP2, PGF, PRL2C2, PTEN, PTGS2, RELA, SERPINF1, SMOC2, | 41 |
| branching morphogenesis | 3.45E-06 | AREG, B4GALT1, BCL2, BMP4, CD44, CRK, CX3CL1, DICER1, DLX2, EFNA5, EFNB2, EGF, EPHB4, ESR1, EYA1, FGF10, FGFR1, GAB1, GDNF, GPC3, GREM1, GZF1, HGF, HOXA11, HOXD13, IL11, ITGA5, ITGA6, LAMA5, MFGE8, MMP14, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, | 41 |
| attachment of cells | 1.25E-05 | ACP1, ADAM15, BCAR1, BTC, CD44, CDH13, CXCL12, DAB2, DCN, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ENG, F11R, HRAS, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), IGF2, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB5, LOX, LRP1, LRPAP1, MMP2, PLAU, PLAUR, PLD1, PTEN, PTGER2, PTK2B, | 41 |
| morphogenesis of animal | 1.30E-03 | BMP4, CDON, CHD7, CHST11, CRABP2, CYP26B1, DICER1, ECE1, EN1, FGF10, FGFR1, FMN1, GATA4, GATAD2A, GDF5, GNAQ, GREM1, HOXA9, HOXA11, HOXD10, HOXD13, KIAA1715, LMBR1, LRP4, LRP5, MED1, MSX1, NOTCH1, PBX2, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTCH1, PTHLH, RARG, SLC31A1, SMAD2, SM | 41 |
| serous ovarian carcinoma | 2.70E-03 | AGPAT2, BCL10, C13ORF15, C4A, CP, CTNNAL1, DAB2, DHTKD1, DTNA, E2F3, EPHB6, F2R, FAM171A1, FGFR1OP (includes EG:11116), FLRT2, FOXN2, FZD3, GATA6, GSTM5, HIST2H2AA3, IGFBP4, LRIG1, MFAP5, NOTCH4, PAPSS2, PDGFRA, PPAP2A, RECK, RNF144B, RRAS, SEMA3C, SLIT2, | 41 |
| organization of cytoskeleton | 6.15E-03 | ATP2C1, BCAR1, CCL13, CD44, CD47, CD82, CFL1, CRKL, CXCL12, DLC1, EFNA5, EFNB1, ENG, EPHA2, F2RL1, FLNA, GAS6, GDNF, HGF, LCK, MARCKS (includes EG:4082), MSN, MYH9, NF1, PAK1, PLAU, PLAUR, PLS3, PLXNB2, PTK2B, PTPN1, | 41 |
| disease of primary tumor | 7.76E-04 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, BTRC, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HMGA2, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, NF1, PRDM2, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, RRM2, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, | 40 |
| morphology of tissue | 1.72E-03 | BDNF, CCND1, CDKN1B, COL18A1, EBF1, FMR1, FOXC2, FOXO1, GJA1, GSN, HGF, HTT, ID2, IL6ST, INSR, KIF3A, KRT10, LDLR, LFNG, LIF, LTBP4, MMP2, NCAM1, OTX1, PDGFRA, PLEC1, PLOD3, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTEN, RARG, RXRA, SERPINH1, SLC31A1, | 40 |
| development of limb | 4.93E-03 | CHD7, CHST11, CRABP2, CYP26B1, DICER1, E2F1, ECE1, EN1, FGF10, FGFR1, FMN1, GDF5, GJA1, GNAQ, GREM1, HGF, HOXA9, HOXA11, HOXD10, HOXD13, KIAA1715, LMBR1, LRP4, LRP5, MED1, MSX1, NOTCH1, PBX2, PGF, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTCH1, | 40 |
| neuroendocrine carcinoma | 1.69E-04 | BCL2, CD59, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1A, CDKN2C, COPS5, CTSD, CYR61, EGFR, HBEGF, HLA-G, IFITM1, IL15, ITGA3, ITGAE, ITGB4, KRT7, KRT10, MLL3, MSLN, NCAM1, PALLD, PDGFRA, PLAT, PLAU, POLE3, PSMB5, PTEN, PTGES, RELA, RRM2, SPP1, TIMP1, TY | 39 |
| formation of filopodia | 3.50E-04 | AKAP12, ARHGAP24, BAIAP2, CAPNS1, CCL13, CD47, CTGF, CYR61, DAG1, ENAH, FGD3, FGD4, GAP43, HGF, HRAS, ITGA3, ITGA6, ITGB4, LAMA5, MARCKS (includes EG:4082), MTSS1, MYD88, MYO10, NEO1, NF1, PAK1, PKP1, PPP1R9A, PTK2B, PVR, | 39 |
| migration of endothelial cell lines | 4.40E-04 | ALCAM, ALOX12, BTC, CBFB, CD151, CDH5, CDKN1B, COL18A1, CTSB, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CYR61, DICER1, EGF, EGFR, FGF13, FIGF, FOXO1, FOXO3, HGF, HHEX, HOXA9, ID1, ID3, IL18, MEOX2, NCL, NRP1, PLAU, PTEN, PTGS2, PTK2B, PTN, SDC2, | 39 |
| tumorigenesis of primary tumor | 1.28E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, BTRC, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HMGA2, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, NF1, PRDM2, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, RRM2, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, STX2, TGFBR2, THBS1, THBS2, WNT10B, XRC | 39 |
| morphogenesis of embryo | 2.27E-03 | BMP4, CDON, CHD7, CHST11, CRABP2, CYP26B1, DICER1, ECE1, EN1, FGF10, FGFR1, FMN1, GATA4, GATAD2A, GDF5, GNAQ, GREM1, HOXA9, HOXA11, HOXD10, HOXD13, KIAA1715, LMBR1, LRP4, LRP5, MED1, MSX1, NOTCH1, PBX2, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTCH1, RARG, SMAD2, SMARCA4, TBX3, TBX | 39 |
| arrest in G1 phase of tumor cell lines | 3.00E-03 | BCL2, BHLHE40, BTRC, CAMK1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CYR61, DCN, DDIT3, DUSP1, EGF, EGFR, EPB41L1, GPS2, GSPT1, ID3, ITGA5, KLF4, MLH1, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, | 38 |
| developmental disorder of muscle cells | 3.00E-03 | ADRB2, ANGPT2, CAMK2D, CDKN1B, DUSP1, EDNRA, EGF, FOXF1, FOXF2, FOXO3, GATA4, GATA6, GNAQ, GPX1, HBEGF, HSPB8, IER3, IGF2, IL11, IL18, LIF, MAP2K5, MAP2K6, MAPK1, MSX1, NFKBIA, PLAU, PPP3CA, PPP3R1, PTEN, PTGES, PTGS2, | 38 |
| disease of malignant tumor | 1.01E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, BTRC, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, NF1, PRDM2, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, RRM2, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, STX2, TGFBR2, THBS1, | 37 |
| development of kidney | 2.27E-03 | ACVR2B, ADAMTS1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), AQP11, AREG, BCL2, BCL2L11, BDNF, BMP4, C1GALT1, CX3CL1, EYA1, FBN1, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXC2, FOXD1, GDNF, GFRA1, GPC3, GREM1, HOXA11, IL11, INSR, JMJD6, KIF3A, LRP4, MMP14, NF1, OSR1, | 37 |
| developmental process of endothelial cell lines | 2.08E-04 | ALCAM, ALOX12, ATF3, BTC, CCL13, CD151, CDH5, CDKN1B, CLIC4, COL18A1, COL1A1, CXCL12, CYR61, DGKA, ECT2, EGF, EGFR, FES, FOXO1, FOXO3, HGF, ID1, ID3, MMP2, NAB2, NRP1, PTEN, PTN, SLIT2, SMOC2, TFAP2A, THBS1, THBS2, TIMP2, | 36 |
| developmental process of adipocytes | 4.41E-04 | ADRB2, CAST, CBY1, CCND1, CREB1, DDIT3, DLK1, EBF1, ENPP1, FGF10, GPX1, IL11, INSR, IRS1, LIF, MED1, METTL8, MMP3, NOTCH1, PARP2, PPARD, PRG4 (includes EG:10216), RARRES2, RGS2, RUNX1T1, SCAND1, SMAD2, SOCS1, SOD2, TBL1X, | 36 |
| ubiquitination of protein | 8.82E-04 | AMFR, ATG3, BCL10, CAND1, CAPN1, CARD10, CAST, CUL1, FBXO2, FBXW7, G2E3, GSPT1, ITCH, MGRN1, MUL1, PCNP, PPARD, PPIL2, RNF144B, SIAH1, SIAH2, SMURF1, STUB1, TPP2, TRAF6, UBA1, UBB, UBE2D3, UBE2E1, UBE2L3, UBE2N, | 36 |
| tumorigenesis of malignant tumor | 1.67E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, BTRC, CD44, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, CTSB, CYP1B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, EGR1, FOXP3, HGF, HIP1, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, NF1, PRDM2, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, RRM2, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, STX2, TGFBR2, THBS1, | 36 |
| cell spreading of cell lines | 3.01E-03 | ACP1, ANTXR1, BCAR1, BCL10, CAST, CYR61, EGF, EPHA2, FHL3, GAP43, ING4, ITGA5, LPAR1, MPRIP, PAK1, PALLD, PFN1, PLAU, PPFIA1, PTK2B, PTPN12, PTPN14, PVR, RTN4, SIRPA, SNAI2, SPHK1, SPP1, TESK1, TGFBI, THBS1, TIAM1, TSPAN7, | 36 |
| migration of fibroblast cell lines | 2.05E-05 | ACP1, BCAR1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CLIC4, CRKL, CXCL10, DDX3X, EGF, EGFR, FIGF, GNG12, HAS2, HBEGF, IL18, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGB1BP1, LRPAP1, MEOX2, MMP14, MYLK, PALLD, PDGFD, PDGFRA, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN11, PTPN12, PVR, | 35 |
| developmental process of kidney cell lines | 4.75E-04 | ABCC5, CDKN1A, CHKA, CRK, DLGAP5, DLST, EGF, ESR1, F2RL1, FOXC2, GAB1, GAK, GDNF, HAS2, HBEGF, HGF, HRAS, ITGA5, LMNA, LOX, MT1E, MT1F, NFYB, NINL, PKP3, PMP22, PTP4A3, PTPN14, SLC30A1, STEAP2, TPM2, TPP2, TSC2, UNC5B, | 35 |
| differentiation of adipocytes | 7.64E-04 | ADRB2, CAST, CBY1, CCND1, CREB1, DDIT3, DLK1, EBF1, ENPP1, FGF10, GPX1, INSR, IRS1, LIF, MED1, METTL8, MMP3, NOTCH1, PARP2, PPARD, PRG4 (includes EG:10216), RARRES2, RGS2, RUNX1T1, SCAND1, SMAD2, SOCS1, SOD2, TBL1X, | 35 |
| migration of connective tissue cells | 1.20E-03 | BCAR1, CAPNS1, CCND1, CD44, CDKN1B, COL1A1, CYR61, EGF, F2R, FLNB, GRLF1, HBEGF, HGF, IGBP1, ITGA5, ITGB1BP1, LPP, LRP1, LRPAP1, MAPK1, MRC2, PALLD, PLAUR, PLEC1, PRKAR1A, PTN, PTPN2, RAMP2, SDC4, SPP1, STAT3, TGFBR2, | 35 |
| interphase of fibroblast cell lines | 1.48E-03 | AKAP12, ARAF, BID, BMP4, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, COPS5, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, EP400, GADD45A, GATA6, GPI, HRAS, IRS1, LATS1, LMNA, MAP2K6, PPAP2C, PTPN11, PTTG1, PVR, | 35 |
| development of lung | 2.73E-03 | ACVR2B, ADA, ADAMTS2, BMP4, DICER1, FGF10, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXF1, GPC3, GREM1, HOXA5, IGF2, JMJD6, LAMA5, LOX, MMP2, MMP14, NOTCH1, PDGFRA, PDPN, PPP1CA, PPP3R1, PTGES, RBP1, RQCD1, SMAD2, SP1, TBX4, TBX5, TGFB2, | 35 |
| cell division process of breast cancer cell lines | 4.78E-03 | BHLHE40, CAMK1, CAMKK1, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DCN, EGF, EGFR, ESR1, EZH2, FOXO3, HAS2, HBEGF, HRAS, LATS1, MLH1, PTEN, PTHLH, RRAD, RXRA, SIAH1, SKP2, SMARCA4, | 35 |
| pancreatic carcinoma | 5.54E-05 | CD59, CDC2L6, CDK2, CDK5, CDK6, CDK8, CDK10, CDKN1A, COPS5, CTSD, CYR61, HBEGF, HLA-G, IFITM1, IL15, ITGA3, ITGAE, ITGB4, KRT7, KRT10, MLL3, MSLN, PALLD, PDGFRA, PLAT, PLAU, POLE3, PTEN, PTGES, RELA, RRM2, SPP1, TIMP1, TYMS | 34 |
| attachment of eukaryotic cells | 3.08E-04 | ACP1, ADAM15, BCAR1, BTC, CD44, CDH13, CXCL12, DCN, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ENG, HRAS, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), IGF2, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB5, LOX, LRP1, LRPAP1, MMP2, PLAU, PLAUR, PLD1, PTGER2, PTK2B, TGFBI, THBS2, | 34 |
| formation of lamellipodia | 8.27E-04 | ARHGAP24, BAIAP2, BDNF, CD44, CD82, CDKN1B, CRK, CRKL, CTGF, CYR61, EGF, FGD4, GAB1, GDNF, HGF, HRAS, HSP90AA1, ITGA6, ITGB4, LASP1, LPAR1, MPRIP, NISCH, NRP1, PLAU, PVR, PVRL1, PVRL3, SDC4, SEMA3A, SPHK1, SWAP70, TPM1, | 34 |
| disease of liver | 1.04E-03 | ATF4, BCL2, CCND1, CCNE1, CD14, CDKN1B, DNMT3B, E2F1, ENG, FGFR1, FGFR2, GADD45A, HGF, IRS1, LHX2, MED1, MMP13, MT1E, MT1F, MYD88, NDRG1, NFE2L1, PDGFC, PLAU, SCG5, SKP2, SOCS1, SPP1, STAT1, TGFBR2, TIMP1, TSC2, VEGFA, | 34 |
| quantity of tumor cell lines | 1.62E-03 | BCL2, BHLHE40, CCND1, CDC25A, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CUL4A, E2F1, EGF, ESR1, FGF13, HMOX1, IFNZ, IGFBP6, IGFBP7, INPPL1, JUNB, KLF4, LIF, MCTS1, MYBL2, PEG3, PTGS2, PTHLH, RBBP4, SKP2, TIMP3, TPP2, TSC2, | 34 |
| morphogenesis of limb | 3.63E-03 | CHD7, CHST11, CRABP2, CYP26B1, DICER1, ECE1, EN1, FGF10, FGFR1, FMN1, GDF5, GNAQ, GREM1, HOXA9, HOXA11, HOXD10, HOXD13, KIAA1715, LMBR1, LRP4, LRP5, MED1, MSX1, NOTCH1, PBX2, PRRX1, PRRX2, PTCH1, RARG, SMARCA4, TBX3, TBX4, | 34 |
| migration of fibroblasts | 5.51E-04 | BCAR1, CAPNS1, CCND1, CDKN1B, COL1A1, CYR61, EGF, F2R, FLNB, GRLF1, HBEGF, HGF, IGBP1, ITGA5, ITGB1BP1, LPP, LRP1, LRPAP1, MAPK1, MRC2, PALLD, PLAUR, PLEC1, PRKAR1A, PTPN2, RAMP2, SDC4, SPP1, STAT3, TGFBR2, THBS1, | 33 |
| arrest in cell stage of normal cells | 8.96E-04 | ATF2, CCND1, CD44, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CHKA, CYP26B1, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, EGF, ERCC1, FANCC, FOXO3, GADD45A, GPC1, IGFBP7, JAK3, MAP2K6, MBD4, MLH1, MNAT1, MYBL2, PTEN, PTTG1, RELA, RPS6KA2, SP1, TFDP1, XPC | 33 |
| developmental process of colon cancer cell lines | 1.42E-03 | AHSA1, AREG, BCL2, BCL2L11, CAMK2N1, CCND1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL18A1, CTSD, DUSP5, EGF, EGFR, EGR2, ENC1, FDXR, FES, GADD45A, GREM1, IGF2, IGF2R, ITGA5, KLF4, NDRG1, PDLIM4, PTEN, PTPN1, SDC2, STAT3, SUFU, TAX1BP3, | 33 |
| formation of extracellular matrix | 7.60E-04 | ADAMTSL4, ADM, APBB2, ATP7A, B4GALT1, CCDC80, COL18A1, COL4A6, CYR61, DCN, EMILIN1, ERCC2, FBLN1, FOXF1, FOXF2, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), KAZALD1, NF1, NFKB2, NID1, OLFML2B, PDGFRA, PTX3, RECK, ROR2, SMARCA4, SMOC1, | 32 |
| activation of NFkB binding site | 9.69E-04 | ATF3, BCL2, BTRC, CD14, CREBBP, EGF, F2RL1, HGF, IER3, IL18, LY96, MAP3K14, MAVS, MYD88, NFKB2, NFKBIA, NFKBIB, NFKBID, NFKBIE, PRKRA, PRMT2, RALA, RELA, SMAD1, TLR6, TNFAIP3, TNFRSF25, TNFRSF1A, TRADD, TRAF6, VCAM1, | 32 |
| dephosphorylation of amino acids | 1.92E-03 | BCL2, CDC25C, CTDP1, DUSP1, DUSP3, DUSP4, DUSP5, DUSP22, EYA1, MTMR7, PDP2, PPAP2A, PPM1B, PPM1F, PPP1CA, PPP1CB, PPP2CB, PPP3CA, PPP3R1, PTEN, PTPN1, PTPN2, PTPN6, PTPN11, PTPN12, PTPN14, PTPN18, PTPN22, PTPRE, PTPRF, | 32 |
| developmental process of embryonic stem cells | 1.92E-03 | BAIAP2, BCL2L11, BMP4, CDC7, DNMT1, EIF4G2, ENG, EPHB4, EZH2, GATA4, GATA6, HHEX, HTT, ID1, ID3, IL6ST, LIF, MAPK1, MAPK8IP3, NMT1, NR4A2, PTEN, PTPN11, PTTG1, RBL1, SOX2, SRF, STAT3, TERF1, TLN1, VEGFA, WWTR1 | 32 |
| experimentally-induced diabetes | 1.92E-03 | ALOX12, ANXA1, ANXA5, AQP1, C3, CCNG1, CD200, CEBPD, CNGB1, CP, DDAH1, DUSP1, EXOC7, FGFR1, HLA-C, HMGCL, ID1, IFITM3, IRF1, KLF4, MT1F, PDLIM4, PPAP2B, PPT2, PSMC2, PTPN1, RSAD2, SCARB1, SCN1B, SPP1, TIMP1, VEGFA | 32 |
| carcinoma in situ | 3.59E-03 | ABCC4, ANO6, ASS1, BHLHE40, C3, COL7A1, CX3CL1, ENTPD5, FCGR3A, FGFR2, FLNA, GPC1, GPRC5A, HMGA2, HRAS, IER3, IRF1, ITGB4, KRT7, LY6E, MFGE8, MIPEP, MXRA8, MYL9 (includes EG:10398), PTEN, RBL1, SGK269, SMARCD3, SMS, | 32 |
| arrest in developmental process of tumor cell lines | 4.37E-03 | CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, DAB2, E2F1, EZH2, GADD45GIP1, HMOX1, IL6ST, IRF1, KLF4, KRT10, LIF, MAP2K6, MAPK1, MAPK3, NOTCH1, PTEN, RASSF5, RBL1, RUNX1T1, SKP2, SMARCA4, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT1, STAT3, TGFBR2, | 32 |
| cell stage of connective tissue cells | 1.57E-04 | ATF2, ATF3, BRCA2, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, FIGF, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, ID2, ID3, IGFBP7, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PLK2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 31 |
| cell spreading of normal cells | 2.60E-03 | ATRN, CAST, CD44, CD47, CORO1A, CRK, CRKL, CXCL12, EFNB1, EGF, FBN1, HGF, HRAS, IGBP1, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB5, ITGB1BP1, LAMA5, LPP, PALLD, PTK2B, SDC4, SEMA3A, SRF, STAT3, THBS1, THBS2, TIAM1, TLN1 | 31 |
| proliferation of carcinoma cell lines | 4.80E-03 | AKT3, ANXA1, BID, CASP2, CDK5, CDK5R1, CDKN1A, CXCL12, CYR61, DLC1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, ERCC1, FANCC, GAS6, HGF, HK1, IGF2, IL18, ITPR1, NDUFAF2, NEK2, PLAU, PTGS2, RAP1GAP (includes EG:5909), RELA, SKP2, SLC25A6, TSPO | 31 |
| arrest in growth of tumor cell lines | 5.82E-03 | CBX7, CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, DAB2, E2F1, EZH2, GADD45GIP1, HMOX1, IL6ST, IRF1, KLF4, KRT10, LIF, MAP2K6, MAPK1, MAPK3, NOTCH1, PTEN, RASSF5, RBL1, SKP2, SMARCA4, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT1, STAT3, TGFBR2, UBE2D3 | 31 |
| cell stage of fibroblasts | 4.34E-05 | ATF2, ATF3, BRCA2, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, FIGF, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, ID2, ID3, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PLK2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 30 |
| targeting of protein | 1.63E-04 | AP3M1, CCHCR1, EIF5A, ERBB2IP (includes EG:55914), GIPC1, GPHN, HPS4, HSPA9, LTBP2, MYO6, NUPL2, OPTN, PEX6, PEX7, PEX19, PICK1, PPP1R3C, PTPN11, RAB27A, STXBP4, SYNJ2BP, TIMM9, TIMM44, TOMM22, TRNT1, TSPO, XPO5, XPO6, | 30 |
| proliferation of endothelial cell lines | 3.95E-04 | ATP6V0A2, CBFB, CDH13, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COL18A1, DAB2, DGKA, DICER1, EGF, EGFR, ENG, F2R, FGF13, FIGF, FOXO1, HGF, HHEX, NCL, NRP1, NRP2, PTEN, PTN, PTPN1, PTX3, SEMA3A, SEMA3F, SKP2, TNFRSF25, VEGFA | 30 |
| proliferation of dermal cells | 1.44E-03 | ANGPTL6, CCNG2, CDH13, CDK2, CDKN1A, EGF, EPHA2, FGF10, FST, HGF, IGFBP4, INSR, JUNB, KLK8, KRT10, LRIG1, PPARD, PTCH1, PTEN, PTGER2, PTGS2, PTHLH, PTPRK, RBL1, RXRA, SGK3, SLC7A11, SNAI2, TOM1L1, VDR | 30 |
| ductal carcinoma | 3.52E-03 | AGPAT2, ANXA1, CCND1, CDKN1A, COX4I1, CP110, CSPP1, DDHD2, DDX19B, EPHA2, EYA1, FAM96B, GSPT1, HSPB8, IER3, ING4, MKI67, MT1E, MT1F, PPFIA1, PXDN, RBM4B, SAT2, SERPINF1, STAU2, TNXB, TPD52, TRIM16, WWTR1, ZNF703 | 30 |
| growth of colon cancer cell lines | 5.27E-03 | AHSA1, AREG, BCL2, BCL2L11, CAMK2N1, CCND1, CDKN1A, COL18A1, CTSD, DUSP5, EGF, EGFR, EGR2, ENC1, FDXR, FES, GADD45A, IGF2, IGF2R, ITGA5, KLF4, PDLIM4, PTEN, PTPN1, SDC2, STAT3, SUFU, TAX1BP3, TGFBR2, TIAM1 | 30 |
| interphase of connective tissue cells | 2.03E-05 | ATF2, ATF3, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, ID2, ID3, IGFBP7, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PLK2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 29 |
| angiogenesis of animal | 4.18E-04 | ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BTC, CCND1, CDH5, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB2, ELK3, HGF, HRAS, KLF5, MED1, MMP2, MMP14, NR2F2, NRP1, NRP2, PGF, PTEN, RELA, SERPINF1, SMOC2, SPHK1, THBS1, TNFRSF1A, VEGFA, VEGFC, WARS | 29 |
| ruffling | 5.53E-04 | ARF6, ARHGAP17, BAIAP2, CAPG, CCL13, CRK, CXCL12, EFNB1, EGF, GSN, HGF, HMOX1, HRAS, INPPL1, INSR, IRS1, MTSS1, MYO1C, PAK1, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, PTK2B, SPHK1, SPP1, SWAP70, TIAM1, TSC2, WASF1 | 29 |
| proliferation of epidermal cells | 1.22E-03 | ANGPTL6, CCNG2, CDH13, CDK2, CDKN1A, EGF, EPHA2, FGF10, FST, HGF, INSR, JUNB, KLK8, KRT10, LRIG1, PPARD, PTCH1, PTEN, PTGER2, PTGS2, PTHLH, PTPRK, RBL1, RXRA, SGK3, SLC7A11, SNAI2, TOM1L1, VDR | 29 |
| assembly of extracellular matrix | 3.85E-03 | ADAMTSL4, APBB2, ATP7A, B4GALT1, CCDC80, COL18A1, COL4A6, CYR61, DCN, EMILIN1, ERCC2, FBLN1, FOXF1, FOXF2, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), KAZALD1, NF1, NFKB2, NID1, OLFML2B, PDGFRA, RECK, SMARCA4, SMOC1, SMOC2, TGFB2, TGFBI, | 29 |
| developmental process of epithelial cell lines | 5.79E-03 | ABCC5, AREG, BTC, CCND1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CHKA, CXCL2, DAB2, DLGAP5, DLST, EGF, ENG, ESR1, ETV6, HGF, ID2, NINL, NOTCH1, PTHLH, PTP4A3, RBBP9, RXRA, SPP1, TFE3, TGFB2, TGFBR3, TPP2, UNC5B | 29 |
| interphase of fibroblasts | 1.30E-05 | ATF2, ATF3, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, GAB1, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, ID2, ID3, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PLK2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 28 |
| Dupuytren contracture | 1.31E-03 | ADAMTS1, ADAMTS2, ADAMTS4, ADAMTS6, COL12A1, COL16A1, COL17A1, COL18A1, COL1A1, COL22A1, COL3A1, COL4A2, COL4A5, COL4A6, COL5A1, COL5A2, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL7A1, COL8A1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP13, MMP14, MMP16, TIMP1, TIMP2, | 28 |
| delay in initiation of cell division process of eukaryotic cells | 1.31E-03 | BCL2, CASP2, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CREG1, DLGAP5, ECT2, ELAC2, GADD45A, GRB10, IGFBP7, IL15, INSR, JUNB, KLF4, KLF9, LIMK1, MPG, PTEN, PTTG1, RAD21, RASSF5, SOD2, STAT1, TFDP1 | 28 |
| neoplasia of cells | 3.38E-03 | ARHGDIG, ATF2, ATF3, CD44, CD151, CD274, COL18A1, CXCL2, EGF, ENPP2, F2R, FIGF, HGF, HRAS, HTATIP2, IGF2BP1, ITGB4, LAMA5, MAD1L1, MAPK1, NFKBIA, NFKBIB, PPARD, SOCS1, TGFBR2, TIMP1, TXNIP, WISP1 | 28 |
| migration of smooth muscle cells | 4.21E-03 | ADM, CCL5, CD47, CDKN1B, DUSP1, EGF, EGFL7, FGFR1, HBEGF, HGF, IGFBP4, IL18, ITGB5, LDLR, MAPK1, MAPK3, MEOX2, NEO1, PLAT, PLAU, PLAUR, PTGS2, PTPRF, RAMP2, SDC4, SPP1, THBS1, TIMP1 | 28 |
| invasion of normal cells | 5.19E-03 | CCND1, CD151, CXCL10, EGF, ENG, ETV6, EZH2, FST, GAB1, HGF, HRAS, IL18, ITGA5, ITGA6, ITGB4, LRP1, LRPAP1, MMP14, NF1, SPP1, STAT3, THBS2, TIMP1, TIMP2, | 28 |
| morphogenesis of eukaryotic cells | 6.19E-05 | BDNF, CCND1, CD82, COL18A1, CRK, CXCL2, EFNB2, EGF, EPHB4, GAB1, GDNF, HGF, ITGA6, MMP2, NFKB2, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, PTEN, PTK2B, PVRL2, RELA, SLC1A3, SPR, STC1, TFAP2A, TIMP2, VCAM1 | 27 |
| growth of kidney cell lines | 4.62E-04 | ABCC5, CDKN1A, CHKA, DLGAP5, DLST, EGF, ESR1, F2RL1, GAK, HAS2, HRAS, ITGA5, LMNA, LOX, MT1E, MT1F, NINL, PKP3, PMP22, PTP4A3, SLC30A1, STEAP2, | 27 |
| angiogenesis of mammalia | 8.23E-04 | ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BTC, CCND1, CDH5, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB2, ELK3, HGF, HRAS, KLF5, MED1, MMP2, MMP14, NR2F2, PGF, PTEN, RELA, SERPINF1, SMOC2, SPHK1, THBS1, TNFRSF1A, VEGFA, VEGFC, WARS | 27 |
| growth of epithelial cell lines | 2.32E-03 | ABCC5, AREG, BTC, CCND1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CHKA, CXCL2, DAB2, DLGAP5, DLST, EGF, ENG, ESR1, ETV6, HGF, NINL, NOTCH1, PTHLH, PTP4A3, RBBP9, RXRA, TFE3, TGFB2, TGFBR3, TPP2, UNC5B | 27 |
| angiogenesis of mice | 6.53E-04 | ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BTC, CCND1, CDH5, CXCL12, CYR61, EFNB2, ELK3, HGF, HRAS, KLF5, MED1, MMP2, MMP14, NR2F2, PGF, PTEN, RELA, SMOC2, SPHK1, THBS1, TNFRSF1A, VEGFA, VEGFC, WARS | 26 |
| cardiovascular process of tumor | 6.53E-04 | ADAM17, ANGPTL4, B4GALNT1, BCL2, CDH5, COL18A1, CRYAB, CTSB, EPHA2, FGFR2, HGF, HRAS, IL18, ITGB5, MMP2, MMP3, MMP14, NRP1, PGF, PLAU, THBS1, | 26 |
| closure of tissue | 8.72E-04 | BCL10, BMP4, CFL1, CREBBP, DLC1, ENAH, FTO, FZD3, FZD6, GRLF1, HIPK2, IRX3, IRX5, ITGA3, ITGA6, PDGFRA, PFN1, PLXNB2, PTGS1, PTGS2, PTK7, RGMA, TRAF6, | 26 |
| differentiation of embryonic stem cells | 1.15E-03 | BAIAP2, BCL2L11, BMP4, DNMT1, EIF4G2, EPHB4, EZH2, GATA4, GATA6, HHEX, HTT, ID3, IL6ST, LIF, MAPK1, MAPK8IP3, NMT1, NR4A2, PTPN11, RBL1, SOX2, SRF, STAT3, | 26 |
| arrest in interphase of normal cells | 4.02E-03 | ATF2, CCND1, CD44, CDC25C, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CHKA, DCN, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, ERCC1, FANCC, GADD45A, GPC1, IGFBP7, JAK3, MAP2K6, MBD4, MNAT1, | 26 |
| dwarfism | 3.92E-05 | CHST3, COL1A1, E2F1, EBP, EGFR, FGFR1, FGFR2, FLNA, GGT1, GHR, HIP1, HIP1R, HOXA5, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), ITGA11, LBR, LIF, MAP2K6, MMP13, PAPSS2, PEX7, PTHLH, ROR2, SMPD3, VEGFA | 25 |
| proliferation of keratinocytes | 1.84E-04 | CCNG2, CDH13, CDKN1A, EGF, EPHA2, FGF10, FST, HGF, INSR, JUNB, KLK8, KRT10, LRIG1, PPARD, PTCH1, PTEN, PTGER2, PTGS2, PTHLH, PTPRK, RXRA, SGK3, SNAI2, | 25 |
| closure of embryonic tissue | 1.23E-03 | BCL10, BMP4, CFL1, CREBBP, DLC1, ENAH, FTO, FZD3, FZD6, GRLF1, HIPK2, IRX3, IRX5, ITGA3, ITGA6, PFN1, PLXNB2, PTGS1, PTGS2, PTK7, RGMA, TRAF6, TSC2, | 25 |
| cell division process of bone cancer cell lines | 2.71E-03 | BHLHE40, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNG1, CDC25A, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, CDKN2C, DUSP1, E2F1, EGF, GJA1, GPS2, IGF2, LATS1, MAP2K6, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, PKMYT1, RBL1, RPL23, TOPBP1, TP53BP1 | 25 |
| morphogenesis of skeleton | 3.46E-03 | ACVR2B, CHST11, EYA1, FMN1, FOXC2, HOXA2, HOXA5, HOXA7, HOXB4, HOXB5, HOXB6, HOXD3, HOXD4, HOXD8, HOXD10, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), OSR2, PRKRA, PRRX1, PRRX2, RECQL4, RYK, TBX4, TFAP2A, WNT9A | 25 |
| developmental process of breast cell lines | 1.30E-03 | AREG, BCL2L11, C8ORF4, CCND1, CDK2, CHKA, DAB2, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, ETS2, GAS6, HAS2, HRAS, HSPB8, IER3, IGF2, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, RELB, SPP1, STAT3, | 24 |
| retraction of plasma membrane projections | 2.25E-03 | BCAR1, BDNF, CRK, F2R, GNAQ, GPI, GSN, HGF, HRAS, IL6ST, ITGA3, LIF, LPAR4, MSN, MYH9, OTX1, RDX, RICS, RRAD, RRAS, RYK, SEMA3A, SEMA3D, TIAM1 | 24 |
| adenomyosis | 3.75E-03 | AIG1, CBX6, CD14, DST, ESR1, GPI, GPX1, HBA2, IL15, IQGAP1, LGMN, MFAP3L, MTHFD2, NFIC, NME7, PDS5B, PEG3, PMEPA1, PRDX5, RHOU, STX7, TBL1X, THBS1, | 24 |
| metastasis of cells | 4.76E-03 | ARHGDIG, ATF2, ATF3, CD44, CD151, CD274, COL18A1, CXCL2, EGF, ENPP2, F2R, FIGF, HGF, HTATIP2, IGF2BP1, ITGB4, LAMA5, MAPK1, NFKBIA, NFKBIB, SOCS1, | 24 |
| development of extraembryonic tissue | 5.99E-03 | ACVR1B, ADAMTS1, APH1A (includes EG:226548), BMP4, CCNF, COL18A1, ENPP2, ETV6, FGF13, FOXO1, GATA6, HGF, MMP2, NRP1, NRP2, PTEN, PTPN11, PTX3, SFRS5, SMAD2, TFDP1, THBS1, TIMP3, VEGFA | 24 |
| differentiation of tissue | 5.99E-03 | BMP4, CDKN1A, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DAB2, DPPA4, EGFR, ETS2, EXT2, FEM1C, FOSL2, HRAS, KLF5, LIF, MEOX2, MSX1, NDRG1, PDK4, PEG3, PRKG2, RARG, SGPL1, | 24 |
| nuclear export | 5.99E-03 | AGFG1 (includes EG:3267), ANP32A, BAT1, CAMK1, CCHCR1, DDX19B, EIF5A, HHEX, HSPA9, KHDRBS1, LSG1, MALT1, NUDT4, NUP50, NUP98, NUP107, NUPL2, PTPN11, RANGRF, SMG6, XPO5, XPO6, XPO7, XPOT | 24 |
| re-entry into cell division process of cells | 5.99E-03 | BCL2, BRCA2, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, E2F1, E2F2, EGF, EGFR, FOXO3, GAS6, HMG20B, ID1, ID2, ID3, RBL1, SKP2, | 24 |
| pancreatic adenocarcinoma | 4.43E-06 | CD59, CDKN1A, COPS5, CTSD, CYR61, HBEGF, HLA-G, IFITM1, ITGA3, ITGAE, ITGB4, KRT7, KRT10, MLL3, MSLN, PLAT, PLAU, PTEN, PTGES, RELA, RRM2, SPP1, TIMP1 | 23 |
| angiogenesis of tumor | 1.83E-04 | ADAM17, ANGPTL4, BCL2, CDH5, COL18A1, CTSB, EPHA2, FGFR2, HGF, HRAS, IL18, ITGB5, MMP2, MMP3, MMP14, NRP1, PGF, THBS1, THBS2, TIMP1, VASH1, VEGFA, | 23 |
| neurological disorder of tissue | 1.83E-03 | B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, C3, CCL5, CREB1, CXCL10, DAG1, EIF2AK3, HTT, IL18, ITGB4, LPAR1, MYD88, NDRG1, PITPNA, PLAT, PMP22, SNCA, SPG7, SPHK1, SPP1, | 23 |
| infiltrating duct breast carcinoma | 2.41E-03 | AGPAT2, CCND1, COX4I1, CP110, CSPP1, DDHD2, DDX19B, EPHA2, EYA1, FAM96B, GSPT1, ING4, MT1E, MT1F, PPFIA1, RBM4B, SAT2, SERPINF1, STAU2, TNXB, TPD52, | 23 |
| cell death of gonadal cell lines | 5.17E-03 | ANTXR1, ANTXR2, BTC, CASP8, CCL5, CDKN1A, DDIT3, DUSP1, EGF, GHR, HRAS, ITGA5, MAP3K11, MCL1, MGMT, PAK2, PDIA3, PLD1, PLSCR1, POLB, SGMS1, SGMS2, | 23 |
| growth of breast cell lines | 3.07E-05 | AREG, BCL2L11, C8ORF4, CCND1, CDK2, EGF, EGFR, EPHA2, ETS2, GAS6, HAS2, HRAS, HSPB8, IER3, IGF2, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, RELB, SPP1, STAT3, TGFBR3, TIMP2 | 22 |
| morphogenesis of embryonic tissue | 1.06E-03 | ACVR2B, AREG, CX3CL1, EGFR, FGF10, FTO, GATA4, GDNF, GREM1, HOXD13, IL11, INSR, IRX3, IRX5, MEOX2, NOTCH1, ROR2, SMAD2, TBX3, TCF7, TGFB2, TIMP2 | 22 |
| disease of carcinoma | 2.57E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, CDKN1B, E2F1, EGR1, HGF, HIP1, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, STX2, TGFBR2, VEGFA, | 22 |
| re-entry into cell division process of eukaryotic cells | 2.57E-03 | BCL2, BRCA2, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CCNF, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2D, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, FOXO3, GAS6, HMG20B, ID1, ID2, ID3, RBL1, SKP2 | 22 |
| cardiomyopathy of mice | 5.61E-03 | ACSL1, ANGPT2, BNIP3L, CACNB2, CASP8, CAST, CREB1, DICER1, DYSF, GNAQ, INSR, LMNA, LTBP4, MAP2K5, PPP1CA, PTPN11, RCE1, RXRA, SGCB, SOD2, TNNT2, | 22 |
| formation of epithelial tissue | 5.61E-03 | ADAM15, ANTXR2, ARHGAP22, ARHGAP24, ATF3, BDNF, CBFB, CD44, COL18A1, COL4A2, CX3CL1, CXCL12, FGF13, MMP14, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, PTK2B, PTN, SDC2, | 22 |
| migration of brain cancer cell lines | 1.72E-04 | BCAR1, C5ORF13, CRK, CXCL12, EGF, EGR1, ENPP2, GAS6, HGF, LPAR1, MAPK8IP3, MMP14, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, PTN, PVR, SEMA3F, SIRPA, VEGFA, VEGFC | 21 |
| sprouting of eukaryotic cells | 2.59E-04 | ANGPT2, ANGPTL2, BCL2, BDNF, CDK5R1, COL18A1, CYR61, DCN, DICER1, EPHB4, GAP43, GDNF, NAB2, NDST1, REM1, RNASEN, RTN4, SPP1, THBS1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 21 |
| S phase of fibroblast cell lines | 3.82E-04 | ARAF, BID, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDKN1B, COPS5, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, GADD45A, GATA6, IRS1, PPAP2C, PTPN11, RBL1, SKP2 | 21 |
| arrest in cell division process of connective tissue cells | 7.84E-04 | ATF2, CCND1, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, FANCA, FANCC, GADD45A, HRAS, IGFBP7, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PARP2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, | 21 |
| cell stage of bone cancer cell lines | 7.84E-04 | BHLHE40, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, DUSP1, E2F1, GJA1, GPS2, LATS1, MAP2K6, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, PKMYT1, RBL1, RPL23, TOPBP1, TP53BP1 | 21 |
| development of endothelial cells | 7.84E-04 | COL18A1, CXCL2, EFNB2, ENG, EPHB4, FGF13, GPX1, HGF, MEOX2, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, PTK2B, RELA, SEMA3A, STC1, THBS1, TIMP2, VASH1, VCAM1, VEGFA, | 21 |
| formation of endothelial tube | 1.51E-03 | ADAM15, ARHGAP22, ARHGAP24, ATF3, BDNF, CBFB, CD44, COL18A1, COL4A2, CX3CL1, CXCL12, FGF13, MMP14, PLAU, PLAUR, PTEN, PTK2B, PTN, SDC2, TGFBR2, | 21 |
| skeletal and muscular process of tissue | 1.51E-03 | ACVR1, ADRB2, BCL2, BMP4, CD9, CD81, E2F1, EGFR, EGR2, ENPP1, FGFR2, FOSL2, GAA, GJA1, MMP13, MMP14, PTK2B, RBL1, RSAD2, SMURF1, STAT1 | 21 |
| neurological disorder of nervous tissue | 2.74E-03 | B4GALNT1, BACE1, BCL2, C3, CCL5, CREB1, CXCL10, DAG1, EIF2AK3, HTT, IL18, ITGB4, LPAR1, MYD88, NDRG1, PITPNA, PLAT, PMP22, SPG7, SPP1, TLR2 | 21 |
| mineralization of bone | 3.62E-03 | ACVR1, ACVR2B, ADRB2, ANKH, BMP4, CD276, EIF2AK3, EN1, ENPP1, ERCC2, ESR1, FETUB, FGFR2, GLA, MMP13, PHEX, PTHLH, PTN, SOX9, TNFRSF11B, VDR | 21 |
| development of hair follicle | 4.72E-03 | ACVR1B, ATP7A, BCL2, CCND1, E2F1, EGF, EGFR, FOXQ1, FST, GFRA1, HGF, LRP4, NOTCH1, NSDHL, PTGS2, PTHLH, RELA, SGK3, SOX9, TGFB2, TRAF6 | 21 |
| tumorigenesis of carcinoma | 4.72E-03 | ARRB2, ATF2, BRCA2, CDKN1B, E2F1, EGR1, HGF, HIP1, HRAS, ITGB5, MMP3, MMP14, PTEN, PTGS2, PTPN1, SOCS1, SOCS3, STAT3, STX2, TGFBR2, WNT10B | 21 |
| angiogenesis of cells | 6.43E-05 | CCL13, CD151, COL18A1, CTSB, DGKA, ECT2, FGF13, FIGF, LAMA5, MEOX2, PLAUR, SEMA3A, SMOC2, TGFB2, THBS1, THBS2, TIMP2, VASH1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 20 |
| migration of colon cancer cell lines | 1.63E-04 | BCAR1, CD44, CD82, CRK, CRKL, CXCL10, EFNB1, EGFR, HGF, IGF2, IGFBP4, ING4, ITGA6, ITGB4, KLF4, PPFIA1, PTPN11, PTPN12, ST6GAL1, VEGFA | 20 |
| arrest in cell division process of fibroblasts | 3.75E-04 | ATF2, CCND1, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, FANCA, FANCC, GADD45A, HRAS, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, PARP2, RELA, SKP2, TFDP1, XRCC6 | 20 |
| disease of mammary gland | 3.75E-04 | BRCA2, BTRC, CCND1, CDC25A, CDK2, CDKN1B, EGFR, ESR1, HGF, HRAS, MFGE8, MMP3, MMP14, NOTCH1, PAK1, PTEN, PTGER2, PTGS2, PTPRE, TIMP1 | 20 |
| cardiovascular process of cornea | 1.57E-03 | ADAMTS1, ANGPTL4, CCL13, CDH5, COL18A1, CSPG4, CYR61, EGF, EPHA2, FGF13, FIGF, HGF, IGF2, IL18, PRL2C2, SERPINF1, THBS1, VCAM1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 20 |
| initiation of cell division process of cells | 1.57E-03 | BLNK, CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, CXCL12, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GAB1, GATA6, IRS1, NOTCH1, PDGFRA, PTPN2, SKP2 | 20 |
| cell cycle progression of connective tissue cells | 2.15E-03 | BCL2, CCND1, CCNF, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, FANCA, FANCC, GADD45A, HRAS, ID2, IGF2, INSR, JUNB, PARP2, RBL1, SKP2, TFDP1, XRCC6 | 20 |
| development of metanephros | 2.90E-03 | APH1A (includes EG:226548), AREG, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CX3CL1, EYA1, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXC2, GDNF, GPC3, GREM1, HOXA11, IL11, INSR, NF1, OSR1, SLIT2, TIMP2 | 20 |
| closure of neural tube | 5.07E-03 | BCL10, CFL1, CREBBP, DLC1, ENAH, FTO, FZD3, FZD6, GRLF1, IRX3, IRX5, ITGA3, ITGA6, PFN1, PLXNB2, PTK7, RGMA, TRAF6, TSC2, VANGL2 | 20 |
| S phase of fibroblasts | 1.50E-04 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDC7, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, GAB1, GRB10, ID2, ID3, IRS1, JUNB, PLK2, SKP2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 19 |
| tubulation of endothelial cell lines | 1.50E-04 | ALCAM, ALOX12, BTC, CDH5, CLIC4, COL1A1, CXCL12, CYR61, EGF, FES, FOXO1, FOXO3, HGF, ID1, ID3, NAB2, PTN, SLIT2, VEGFA | 19 |
| interphase of bone cancer cell lines | 2.37E-04 | BHLHE40, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, DUSP1, E2F1, GJA1, GPS2, MAP2K6, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, RBL1, RPL23, TOPBP1, | 19 |
| initiation of cell stage of cells | 1.15E-03 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, CXCL12, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GAB1, GATA6, IRS1, NOTCH1, PDGFRA, PTPN2, SKP2 | 19 |
| proliferation of chondrocytes | 1.62E-03 | CCND1, CDKN1A, CTGF, DICER1, FOSL2, GABBR1, GDF5, GGT1, GHR, IL18, IRS1, NFKB2, PPBP, PRKG2, PTHLH, RBL1, RELA, STAT1, STC1 | 19 |
| formation of membrane ruffles | 2.24E-03 | ARHGAP24, ARHGEF2, BCAR1, CCND1, COL18A1, EGF, FLNA, GAS6, ITGA6, ITGB4, LTBP2, PAK1, PIP5K1B, PLEKHA1, RICS, RND1, SNTA1, USP6NL, VAV3 | 19 |
| cell spreading of tumor cell lines | 4.11E-03 | BCL10, EGF, GAP43, ING4, ITGA5, MPRIP, PAK1, PFN1, PLAU, PPFIA1, PTPN14, PVR, SIRPA, SNAI2, SPHK1, TESK1, THBS1, TIAM1, VCAM1 | 19 |
| cell movement of endothelial cells | 5.44E-03 | ANGPT2, CD81, CD151, CSPG4, CXCL12, DGKA, FGFR1, HGF, IGF2R, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, PDGFRA, PRL2C2, SEMA3A, SEMA3F, THBS1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 19 |
| invasion of melanoma cell lines | 4.67E-05 | BCAR1, BMP4, CD151, CHRD, CSPG4, CTSB, CXCL12, ENPP2, HGF, LAMA5, MMP2, MMP14, MMP16, PTEN, RHOC, SDCBP, SPP1, STAT3 | 18 |
| disease of epidermis | 3.44E-04 | BCL2, CCND1, COL17A1, E2F1, KRT10, NFKBIA, NOTCH1, PPARD, PTEN, PTGS2, RARG, RBL1, RELB, TGFBR2, TNFRSF1A, VEGFA, XPA, XPC | 18 |
| cell cycle progression of fibroblasts | 1.15E-03 | BCL2, CCND1, CCNF, CDC25C, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, FANCA, FANCC, GADD45A, HRAS, ID2, IGF2, INSR, JUNB, PARP2, RBL1, SKP2, XRCC6 | 18 |
| cell death of organ | 1.15E-03 | AKT3, CD14, FBN1, GSTZ1 (includes EG:2954), MAP2K5, MED1, MT1E, MT1F, NFE2L1, PTPN1, RXRA, SCG5, SIGIRR, SOCS1, SOD2, STAT1, STAT3, TRAF1 | 18 |
| skeletal and muscular process of bone | 3.21E-03 | ACVR1, ADRB2, BCL2, BMP4, CD9, CD81, E2F1, EGR2, ENPP1, FGFR2, GJA1, MMP13, MMP14, PTK2B, RBL1, RSAD2, SMURF1, STAT1 | 18 |
| attachment of cell lines | 4.35E-03 | ADAM15, BTC, CD44, CDH13, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, IGF2, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, LOX, LRP1, PLAU, PLAUR, PLD1, PTGER2 | 18 |
| cell death of sensory neurons | 7.68E-04 | BCL2, BDNF, CASP9, CDK5, CDKN2D, CREB1, DLX1, DLX2, GJB2, HIPK2, HTT, KLF7, LRP1, LRPAP1, NFKBIA, PRNP, RELA | 17 |
| re-entry into cell division process of cell lines | 1.67E-03 | BRCA2, CAST, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDC25C, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, EGFR, FOXO3, GAS6, HMG20B, ID1, ID2, ID3, SKP2 | 17 |
| sprouting of normal cells | 1.67E-03 | ANGPT2, BCL2, BDNF, CDK5R1, COL18A1, CYR61, DCN, EPHB4, GAP43, GDNF, NAB2, NDST1, REM1, RTN4, SPP1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 17 |
| morphogenesis of normal cells | 2.39E-03 | BDNF, COL18A1, CXCL2, EFNB2, EPHB4, GAB1, HGF, NFKB2, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, PTK2B, PVRL2, RELA, SLC1A3, SPR, STC1, VCAM1 | 17 |
| ossification of tissue | 6.19E-03 | ACVR1, ADRB2, BCL2, BMP4, E2F1, EGFR, EGR2, ENPP1, FGFR2, FOSL2, GJA1, MMP13, MMP14, PTK2B, RBL1, RSAD2, SMURF1 | 17 |
| attachment of tumor cell lines | 4.63E-04 | ADAM15, CD44, CDH13, EFNB1, EGF, EGFR, EGR1, IGF2, ITGA3, ITGA5, ITGA6, LRP1, PLAU, PLAUR, PLD1, PTGER2 | 16 |
| hyperproliferation of epidermis | 7.30E-04 | BCL2, CCND1, E2F1, NFKBIA, NOTCH1, PPARD, PTEN, PTGS2, RARG, RBL1, RELB, TFAP2A, TGFBR2, TNFRSF1A, XPA, XPC | 16 |
| development of metanephric bud | 1.12E-03 | AREG, BCL2, BDNF, BMP4, CX3CL1, EYA1, FGFR1, FGFR2, FOXC2, GDNF, GPC3, GREM1, HOXA11, IL11, SLIT2, TIMP2 | 16 |
| moiety attachment of essential amino acids | 1.67E-03 | ACVR1B, BCL2, CDK5, DUSP1, HK1, MAPK1, MYLK, PLOD3, PRMT3, PRMT7, SBK1, SGK1, SGK3, SUV39H1, TNKS, TTK | 16 |
| initiation of cell division process of eukaryotic cells | 2.42E-03 | BLNK, CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GAB1, GATA6, IRS1, SKP2 | 16 |
| G2 phase of normal cells | 4.80E-03 | ATF2, CCNG2, CDC25C, ERCC1, FANCC, GADD45A, GPC1, GRB10, HMGN1, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, RELA, XPC | 16 |
| initiation of S phase of eukaryotic cells | 7.35E-05 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GAB1, GATA6, IRS1, SKP2 | 15 |
| cell movement of smooth muscle cells | 1.07E-03 | CCND1, ENPP2, HGF, IL6ST, LDLR, LOX, MMP2, PLAU, PLAUR, PTPN1, PTPN11, STAT3, THBS1, TRIB1, WISP2 | 15 |
| hyperplasia of epidermis | 1.07E-03 | BCL2, CCND1, E2F1, NFKBIA, NOTCH1, PPARD, PTEN, PTGS2, RARG, RBL1, RELB, TGFBR2, TNFRSF1A, XPA, XPC | 15 |
| shape change of endothelial cells | 1.07E-03 | ANGPT2, BCL2, COL18A1, CRK, CYR61, DCN, EFNB1, EPHB4, NAB2, NDST1, PTK2B, REM1, SPP1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 15 |
| development of endothelial cell lines | 1.63E-03 | ATF3, CCL13, CD151, CDKN1B, COL18A1, CYR61, DGKA, ECT2, HGF, MMP2, PTEN, SMOC2, TFAP2A, TIMP2, VEGFA | 15 |
| branching of normal cells | 2.43E-03 | BDNF, BMP4, COL18A1, EGF, FGF10, GAS6, GDNF, HGF, HOXA11, NFKBIA, SMAD1, STX2, TIMP1, TIMP2, VEGFA | 15 |
| dilated cardiomyopathy of mice | 3.52E-03 | ACSL1, CASP8, CAST, CREB1, DICER1, GNAQ, INSR, LMNA, MAP2K5, PPP1CA, PTPN11, RCE1, RXRA, TNNT2, ZMPSTE24 | 15 |
| entry into cell division process | 1.03E-04 | CCND1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, ID3, JUNB, PLK2, RBL1, SKP2, | 14 |
| dwarfism of mice | 9.86E-04 | E2F1, EGFR, FGFR1, GGT1, HIP1, HIP1R, HOXA5, ITGA11, LIF, MAP2K6, PTHLH, ROR2, SMPD3, VEGFA | 14 |
| entry into cell stage of fibroblast cell lines | 9.86E-04 | ARAF, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, PPAP2C, PTPN11, SKP2 | 14 |
| morphology of connective tissue | 9.86E-04 | CCND1, FMR1, FOXC2, GSN, KIF3A, LTBP4, MMP2, PDGFRA, PRRX1, PRRX2, SMAD1, SOX9, TGFBR2, THBS1 | 14 |
| entry into cell division process of fibroblast cell lines | 1.56E-03 | ARAF, CCND1, CCNE1, CDC25A, CDK2, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, PPAP2C, PTPN11, SKP2 | 14 |
| arrest in interphase of connective tissue cells | 2.39E-03 | ATF2, CCND1, CDC25C, CDKN1A, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, GADD45A, IGFBP7, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, RELA, TFDP1 | 14 |
| G1 phase of bone cancer cell lines | 3.54E-03 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDK6, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, DUSP1, GJA1, GPS2, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, RBL1, RPL23, TOPBP1 | 14 |
| arrest in interphase of bone cancer cell lines | 5.11E-03 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDK5RAP3 (includes EG:80279), CDKN1A, DUSP1, GPS2, MAP2K6, MNAT1, MTBP, MYBL2, RBL1, RPL23, TOPBP1, TP53BP1 | 14 |
| developmental process of | 5.11E-03 | ADA, CDKN1B, EGF, ENG, ERF, FGFR2, HBEGF, HOPX, JUNB, RXRA, SOX2, SP1, SRF, | 14 |
| emigration of leukocytes | 5.11E-03 | ANXA1, CCL13, CD44, CD99L2, CXCL2, CXCL12, CYTIP, F11R, LAMA5, RELA, SIRPA, SPP1, TNFRSF1A, VCAM1 | 14 |
| binding of tumor cells | 2.79E-04 | CD14, CD44, CD47, CXCL12, DAG1, GFRA1, ITGA3, ITGA5, PDIA3, PLAUR, SEMA3B, | 13 |
| differentiation of embryonic tissue | 8.76E-04 | BMP4, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), DAB2, DPPA4, ETS2, FOSL2, HRAS, LIF, MEOX2, NDRG1, RARG, SGPL1, SPHK1 | 13 |
| morphogenesis of cell lines | 1.44E-03 | CCND1, CD82, COL18A1, CRK, EGF, GAB1, GDNF, HGF, ITGA6, MMP2, PTEN, TFAP2A, | 13 |
| vascularization of cornea | 1.44E-03 | ADAMTS1, CCL13, COL18A1, CYR61, EGF, HGF, IGF2, IL18, PRL2C2, SERPINF1, THBS1, VEGFA, VEGFC | 13 |
| developmental process of | 2.29E-03 | BDNF, CDK5, CDON, EGR2, ITGA6, LAMC1, MAP2K6, NAB1, NAB2, NF1, NFKBIA, | 13 |
| migration of cervical cancer cell lines | 3.49E-03 | CD151, CXCL2, CXCL12, DCBLD2, EGF, ESR1, GFER, HGF, MYO10, PLD1, SLC9A3R1, TFAP2A, WDR44 | 13 |
| arrest in interphase of fibroblasts | 5.17E-03 | ATF2, CCND1, CDC25C, CDKN1A, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, GADD45A, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, RELA, TFDP1 | 13 |
| entry into S phase of | 2.00E-04 | CCND1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, ID3, JUNB, PLK2, TFDP1, TFE3 | 12 |
| cell division process of liver | 3.97E-04 | BCL2, CCND1, CCNE1, E2F2, EGF, EGR1, ERCC1, HGF, INSR, PTPRF, SKP2, VEGFA | 12 |
| cell death of liver | 7.33E-04 | CD14, GSTZ1 (includes EG:2954), MED1, MT1E, MT1F, NFE2L1, PTPN1, RXRA, SCG5, SIGIRR, SOCS1, SOD2 | 12 |
| follicular thyroid carcinoma | 7.33E-04 | ADAMTS1, ANGPT2, EFNB2, EGFR, ENG, EPHB4, FGFR1, ITGA5, MMP2, PTTG1, SPP1, | 12 |
| endochondral ossification | 1.28E-03 | ATF2, COL1A1, CTGF, E2F1, HSPG2 (includes EG:3339), MEF2C, MMP14, NAB1, NAB2, PEX7, PTHLH, SMURF1 | 12 |
| organization of collagen fibrils | 1.28E-03 | ADAMTS2, ATP7A, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, FOXC2, LOX, NF1, SERPINH1, | 12 |
| entry into S phase of fibroblast | 2.12E-03 | ARAF, CCND1, CDC25A, DDX3X, DMTF1, E2F1, E2F3, E2F6, EGF, PPAP2C, PTPN11, | 12 |
| formation of tumor cell lines | 2.12E-03 | CDKN1A, COL18A1, EGR1, FZD1, GNAO1, GNAQ, HRAS, KIF23, LIMK1, RGS12, | 12 |
| necrosis of organ | 2.12E-03 | CD14, GSTZ1 (includes EG:2954), MED1, MT1E, MT1F, NFE2L1, RXRA, SCG5, SIGIRR, SOCS1, SOD2, TRAF1 | 12 |
| invasion of pancreatic cancer | 3.36E-03 | ADM, CTSD, EGF, EPHA2, GDNF, HGF, NRP1, PLAT, PLAU, SEL1L, TIMP1, TIMP2 | 12 |
| sprouting of endothelial cells | 3.36E-03 | ANGPT2, BCL2, COL18A1, CYR61, DCN, EPHB4, NAB2, NDST1, REM1, SPP1, VEGFA, | 12 |
| phosphorylation of L-threonine | 5.13E-03 | ACVR1B, BCL2, CDK5, DUSP1, HK1, MAPK1, MYLK, SBK1, SGK1, SGK3, TNKS, TTK | 12 |
| shape change of epithelial | 1.63E-05 | CRK, CRKL, EGF, FBN1, FGFR1, GSN, HGF, ITGA3, LAMA5, STAT3, TIAM1 | 11 |
| migration of microvascular | 2.75E-04 | ADM, COL18A1, EFNB2, FOXC2, GAB1, RECK, TGFBR2, TIMP1, TIMP2, VAV3, VEGFA | 11 |
| G2 phase of connective tissue | 5.61E-04 | ATF2, CDC25C, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, IRS1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, | 11 |
| apoptosis of sensory neurons | 5.61E-04 | CASP9, CDKN2D, CREB1, DLX1, DLX2, HIPK2, KLF7, LRP1, LRPAP1, PRNP, RELA | 11 |
| binding of cancer cells | 5.61E-04 | CD44, CXCL12, DAG1, GFRA1, ITGA3, ITGA5, PDIA3, PLAUR, SEMA3B, THBS1, VCAM1 | 11 |
| necrosis of liver | 5.61E-04 | CD14, GSTZ1 (includes EG:2954), MED1, MT1E, MT1F, NFE2L1, RXRA, SCG5, SIGIRR, | 11 |
| proliferation of neuronal | 1.06E-03 | BDNF, CDON, CFL1, CNR1, E2F1, E2F3, EGF, GDNF, NCAM1, VEGFA, WNT7B | 11 |
| morphogenesis of endothelial | 1.87E-03 | COL18A1, CXCL2, EFNB2, EPHB4, HGF, NOTCH1, NOTCH4, PTK2B, RELA, STC1, | 11 |
| morphology of bone | 3.11E-03 | CCND1, FMR1, FOXC2, KIF3A, MMP2, PDGFRA, PRRX1, PRRX2, SMAD1, TGFBR2, | 11 |
| trafficking of leukocytes | 3.11E-03 | ANXA1, AOC3, CCL5, CCL13, CD44, CXCL10, CXCL13, ENPP2, NEDD9, NT5E, | 11 |
| Ehlers-Danlos syndrome | 5.64E-05 | ADAMTS2, ADAMTS4, ATP7A, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, TNXB, ZMPSTE24, | 10 |
| chemotaxis of neurons | 1.57E-04 | BDNF, CXCL12, EFNB1, GDNF, GFRA1, NRP2, RGS3, SEMA3A, SEMA3F, SLIT2 | 10 |
| G2 phase of fibroblasts | 7.90E-04 | ATF2, CDC25C, GADD45A, GRB10, HMGN1, JUNB, MAP2K6, MBD4, MYBL2, RELA | 10 |
| initiation of S phase of cell | 7.90E-04 | CDK6, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GATA6, IRS1 | 10 |
| cell division process of | 1.53E-03 | BCL2, CCND1, CCNE1, E2F2, EGF, ERCC1, HGF, INSR, PTPRF, SKP2 | 10 |
| expression of E2F binding site | 2.73E-03 | CCND1, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, RBL1, REEP5, SP1, TFDP1, TFDP2 | 10 |
| gastrulation of mice | 2.73E-03 | ACVR1, DAB2, EXT2, HTT, LAMA5, NUP98, SCXB, SMAD2, SRF, TJP2 | 10 |
| hyperactive behavior of mice | 2.73E-03 | BDNF, CLOCK, DKK3, FGFR1, FMR1, FXR2, GABBR1, HTT, LRP1, TGFBR2 | 10 |
| size of thymus gland | 4.59E-03 | B4GALNT1, CCND1, CDKN1B, HOXA9, JAK3, MAD1L1, MGMT, MLH1, SOCS1, VCAM1 | 10 |
| attachment of connective | 1.91E-04 | BCAR1, HRAS, LRP1, LRPAP1, MMP2, PTK2B, TGFBI, THBS2, TIMP2 | 9 |
| chemotaxis of axons | 1.91E-04 | ARTN, BDNF, NRP1, NRP2, PICK1, SEMA3A, SEMA3B, SEMA3F, SLIT2 | 9 |
| neurological disorder of nerves | 2.20E-03 | B4GALNT1, BACE1, DAG1, ITGB4, MYD88, NDRG1, PMP22, SPG7, TLR2 | 9 |
| transcription of E2F binding | 2.20E-03 | E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, RBL1, REEP5, SP1, TFDP1, TFDP2 | 9 |
| cell spreading of epithelial | 2.16E-04 | CRK, CRKL, FBN1, HGF, ITGA3, LAMA5, STAT3, TIAM1 | 8 |
| attachment of fibroblasts | 6.33E-04 | BCAR1, HRAS, LRP1, LRPAP1, MMP2, TGFBI, THBS2, TIMP2 | 8 |
| growth of fibrosarcoma cell | 6.33E-04 | CDKN1A, EGR1, HGF, IL18, PLAU, RELA, SDC2, STAT1 | 8 |
| maturation of blood vessel | 6.33E-04 | ANGPT2, CDH5, ENPP2, ETV6, FOXO3, MMP2, RECK, VEGFA | 8 |
| chemotaxis of brain cells | 1.52E-03 | BDNF, CXCL12, EFNB1, NRP2, RGS3, SEMA3A, SEMA3F, SLIT2 | 8 |
| survival of gonadal cell lines | 1.52E-03 | ANTXR1, ANTXR2, ATP7A, BCL2, ITGA5, MGMT, RAD51C, XRCC1 | 8 |
| apoptosis of heart cell lines | 5.88E-03 | ANKRD1, BCL2, BNIP2, DDIT3, HGF, IL18, SPHK1, TXNIP | 8 |
| branching morphogenesis of | 5.88E-03 | CRK, EFNB2, EGF, EPHB4, GAB1, GDNF, HGF, NOTCH1 | 8 |
| cell viability of neuroblastoma | 5.88E-03 | BCL2, DPP3, GPC1, HMOX1, P4HB, PRNP, SNCA, SQSTM1 | 8 |
| proliferation of skin cancer cell | 5.88E-03 | CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CRK, EGF, HGF, PTCH1, PTGER2, THBS1 | 8 |
| cell division process of kidney | 7.62E-04 | CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CXCL10, EGF, ITGB4, MAPK1, PTGS2 | 7 |
| developmental process of | 7.62E-04 | BMP4, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), ETS2, F2RL1, MAPK1, NDRG1, PBRM1 | 7 |
| activation of E2F binding site | 2.04E-03 | CDCA4, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, RBL1, TFDP1 | 7 |
| developmental disorder of | 2.04E-03 | BTRC, CDKN1B, E2F1, EGFR, ESR1, FGF10, PAK1 | 7 |
| diabetic retinopathy | 2.04E-03 | AKR1B1, HGF, PTGS1, PTGS2, SERPINF1, VCAM1, VEGFA | 7 |
| initiation of S phase of | 2.04E-03 | COPS5, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, GATA6, IRS1 | 7 |
| neurological disorder of sciatic | 2.04E-03 | DAG1, ITGB4, MYD88, NDRG1, PMP22, SPG7, TLR2 | 7 |
| quantity of caveolae | 2.04E-03 | DAB2, EGF, EGFR, HRAS, PIP5K1B, SYNJ2, VEGFA | 7 |
| G2/M phase transition of | 4.49E-03 | ATF2, CDC25C, GADD45A, IRS1, JUNB, MBD4, RELA | 7 |
| binding of vesicles | 4.49E-03 | ACTR1A, DCTN4, DCTN6, GGA2, MYO5A, RBP1, SNCA | 7 |
| development of lymphoid | 4.49E-03 | CXCL13, ID2, MAP3K14, NFKB2, RELA, RELB, TNFRSF1A | 7 |
| scattering of tumor cell lines | 4.49E-03 | CRK, EGF, EGFR, ETV5, GDNF, HGF, MMP14 | 7 |
| transactivation of E2F binding | 1.45E-04 | CDCA4, E2F1, E2F2, E2F3, E2F6, TFDP1 | 6 |
| apoptosis of germ cell tumor | 8.13E-04 | BCL2, CCNG1, CDKN1B, CXCL12, GATA4, MEF2C | 6 |
| cell division process of | 8.13E-04 | CDKN1B, CXCL10, EGF, ITGB4, MAPK1, PTGS2 | 6 |
| degradation of Gelatin | 8.13E-04 | ADAM12, ADAM15, CSPG4, MMP14, MMP16, TIMP3 | 6 |
| biosynthesis of chondroitin | 2.62E-03 | B4GALNT1, CHST3, CHST7, CHST11, CHST12, CSGALNACT1 | 6 |
| cell movement of skin cancer | 2.62E-03 | CD151, EGF, FIGF, HGF, ITGA6, ITGB4 | 6 |
| chemorepulsion of neurites | 2.62E-03 | NRP1, NRP2, SEMA3A, SEMA3B, SEMA3F, SLIT2 | 6 |
| degeneration of myofiber | 2.62E-03 | CD9, CD81, CUGBP1, DTNA, PLAU, STRA13 | 6 |
| initiation of S phase of | 2.62E-03 | CCND1, CCNE1, CDK2, GAB1, IRS1, SKP2 | 6 |
| neurological process of brain | 2.62E-03 | BDNF, DLG4, MYO5A, RBL1, THBS1, THBS2 | 6 |
| organic aciduria | 2.62E-03 | BCKDHA, BCKDHB, DBT, DLD, MLYCD, SOD2 | 6 |
| shape change of dermal cells | 2.62E-03 | EGF, FBN1, GSN, ITGA3, STAT3, TIAM1 | 6 |
| termination of cell cycle | 2.62E-03 | CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, E2F1, ID2, TFDP1 | 6 |
| termination of cell division | 2.62E-03 | CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, E2F1, ID2, TFDP1 | 6 |
| G0 phase of fibroblast cell | 6.33E-03 | BMP4, CCNE1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, COPS5, PVR | 6 |
| G2/M phase transition of | 6.33E-03 | ATF2, CDC25C, GADD45A, JUNB, MBD4, RELA | 6 |
| adhesion of lung cancer cell | 6.33E-03 | ADAM9, B4GALT1, CXCL12, SEMA3F, THBS1, VCAM1 | 6 |
| chemoattraction of neurons | 6.31E-04 | CXCL12, EFNB1, GDNF, GFRA1, RGS3 | 5 |
| chemotaxis of skin cancer cell | 6.31E-04 | CD151, EGF, FIGF, ITGA6, ITGB4 | 5 |
| cell cycle progression of | 3.06E-03 | CCND1, CCNE1, E2F2, EGF, SKP2 | 5 |
| demyelination of nerves | 3.06E-03 | B4GALNT1, DAG1, ITGB4, NDRG1, PMP22 | 5 |
| quantity of clathrin-coated pits | 3.06E-03 | DAB2, EGF, EGFR, PIP5K1B, SYNJ2 | 5 |
| renal lesion | 3.06E-03 | EGFR, MT1E, MT1F, PLAT, TSC2 | 5 |
| tubulo-interstitial fibrosis of | 3.06E-03 | C3, CD59A, MMP2, PTHLH, SKP2 | 5 |
| assembly of sarcomere | 2.76E-03 | CAMK2D, GATA4, HBEGF, LIF | 4 |
| demyelination of sciatic nerve | 2.76E-03 | DAG1, ITGB4, NDRG1, PMP22 | 4 |
| developmental process of | 2.76E-03 | E2F1, GAB1, SRF, STC1 | 4 |
| differentiation of glial | 2.76E-03 | BMP4, EGFR, EIF2B5, NOTCH1 | 4 |
| differentiation of primitive | 2.76E-03 | HRAS, RARG, SGPL1, SPHK1 | 4 |
| differentiation of trophoblast | 2.76E-03 | BMP4, CUL7 (includes EG:9820), ETS2, NDRG1 | 4 |
| formation of endodermal cells | 2.76E-03 | FZD1, GNAO1, GNAQ, SMAD2 | 4 |
| hypoplasia of exocrine gland | 2.76E-03 | BTRC, CDKN1B, ESR1, FGF10 | 4 |
| loss of mesencephalic neurons | 2.76E-03 | BDNF, CASP8, CASP9, GDNF | 4 |
| maple syrup urine disease, | 2.76E-03 | BCKDHA, BCKDHB, DBT, DLD | 4 |
| transformation of embryonic | 2.76E-03 | FGFR1, FGFR2, HAS2, HRAS | 4 |
| © 2000-2009 Ingenuity | |||
| Systems, Inc. All rights | |||
P-values are from IPA Tool. The criteria applied for the search of major biological function categories were maximum number of genes and the P-value of significa
Table S4.
Gene sets Identified by GSEA
| Specific genes enriched in Klf4-null MEFs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | PROBE | RUNNING ES | CORE ENRICHMENT |
| BILE_ACID_BIOSYNTHESIS | |||
| row_17 | AKR1D1 | -0.492 | Yes |
| row_18 | SOAT2 | -0.471 | Yes |
| row_19 | ALDH2 | -0.405 | Yes |
| row_20 | ADH7 | 0.001 | Yes |
| ZUCCHI_EPITHELIAL_DN | |||
| row_18 | STRN4 | -0.597 | Yes |
| row_19 | PPM1G | -0.591 | Yes |
| row_20 | PDLIM1 | -0.550 | Yes |
| row_21 | ANXA1 | -0.480 | Yes |
| row_22 | PICALM | -0.363 | Yes |
| row_23 | CXCL1 | -0.195 | Yes |
| row_24 | AREG | 0.001 | Yes |
| CROONQUIST_IL6_RAS_U | |||
| row_17 | CCL4 | -0.468 | Yes |
| row_18 | CCL5 | 0.001 | Yes |
| HSA04640_HEMATOPOIETIC_CELL_LINEAGE | |||
| row_57 | ITGA6 | -0.469 | Yes |
| row_58 | CSF1 | -0.461 | Yes |
| row_59 | CD9 | -0.459 | Yes |
| row_60 | CD44 | -0.392 | Yes |
| row_61 | CD34 | -0.310 | Yes |
| row_62 | ITGA5 | -0.222 | Yes |
| row_63 | CD14 | -0.123 | Yes |
| row_64 | ITGA3 | 0.005 | Yes |
| BCRPATHWAY | |||
| row_25 | VAV1 | -0.508 | Yes |
| row_26 | BTK | -0.507 | Yes |
| row_27 | RAC1 | -0.484 | Yes |
| row_28 | MAPK3 | -0.476 | Yes |
| row_29 | CALM2 | -0.433 | Yes |
| row_30 | JUN | -0.387 | Yes |
| row_31 | PPP3CA | -0.335 | Yes |
| row_32 | BLNK | 0.001 | Yes |
| LEE_MYC_E2F1_DN | |||
| row_44 | ABCD3 | -0.489 | Yes |
| row_45 | IGF1 | -0.479 | Yes |
| row_46 | G0S2 | -0.481 | Yes |
| row_47 | CYP7B1 | -0.460 | Yes |
| row_48 | MCM10 | -0.440 | Yes |
| *** | |||
| row_49 | PXMP2 | -0.421 | Yes |
| row_50 | ELOVL5 | -0.396 | Yes |
| row_51 | RGS16 | -0.326 | Yes |
| row_52 | EGFR | -0.206 | Yes |
| row_53 | NETO2 | 0.001 | Yes |
| HSA04012_ERBB_SIGNALING_PATHWAY | |||
| row_67 | EREG | -0.415 | Yes |
| row_68 | ERBB2 | -0.408 | Yes |
| row_69 | CAMK2B | -0.410 | Yes |
| row_70 | AKT2 | -0.402 | Yes |
| row_71 | MAP2K4 | -0.386 | Yes |
| row_72 | MAPK3 | -0.373 | Yes |
| row_73 | PAK3 | -0.357 | Yes |
| row_74 | EIF4EBP1 | -0.344 | Yes |
| row_75 | JUN | -0.328 | Yes |
| row_76 | SRC | -0.310 | Yes |
| row_77 | ARAF | -0.304 | Yes |
| row_78 | PAK1 | -0.269 | Yes |
| row_79 | HBEGF | -0.209 | Yes |
| row_80 | EGFR | -0.137 | Yes |
| row_81 | AREG | 0.000 | Yes |
| ZHAN_PCS_MULTIPLE_MYELOMA_SPKD | |||
| row_16 | IFIT3 | -0.671 | Yes |
| row_17 | CTGF | -0.614 | Yes |
| row_18 | LGALS3BP | -0.484 | Yes |
| row_19 | TSPAN7 | -0.257 | Yes |
| row_20 | AREG | 0.000 | Yes |
| HSA04140_REGULATION_OF_AUTOPHAGY | |||
| row_18 | PRKAA1 | -0.532 | Yes |
| row_19 | ULK2 | -0.509 | Yes |
| row_20 | GABARAPL1 | -0.463 | Yes |
| row_21 | PIK3R4 | -0.389 | Yes |
| row_22 | ATG3 | 0.005 | Yes |
| HSA04940_TYPE_I_DIABETES_MELLITUS | |||
| row_15 | CPE | -0.377 | Yes |
| row_16 | FAS | -0.360 | Yes |
| row_17 | HSPD1 | -0.336 | Yes |
| row_18 | ICA1 | 0.007 | Yes |
| POMEROY_DESMOPLASIC_VS_CLASSIC_MD_DN | |||
| row_31 | NUCB1 | -0.430 | Yes |
| row_32 | SFRS2IP | -0.404 | Yes |
| row_33 | PSMB5 | -0.347 | Yes |
| row_34 | CRABP2 | 0.000 | Yes |
| LEE_MYC_TGFA_DN | |||
| row_45 | G0S2 | -0.535 | Yes |
| row_46 | CYP7B1 | -0.516 | Yes |
| row_47 | MCM10 | -0.500 | Yes |
| row_48 | PXMP2 | -0.484 | Yes |
| row_49 | ELOVL5 | -0.464 | Yes |
| row_50 | RGS16 | -0.404 | Yes |
| row_51 | EGFR | -0.298 | Yes |
| row_52 | PTP4A3 | -0.184 | Yes |
| row_53 | NETO2 | 0.001 | Yes |
| HSA00760_NICOTINATE_AND_NICOTINAMIDE_METABOLISM | |||
| row_17 | NT5C2 | -0.620 | Yes |
| row_18 | NNMT | -0.478 | Yes |
| row_19 | ENPP1 | -0.242 | Yes |
| row_20 | NT5E | 0.007 | Yes |
| CELL_MOTILITY | |||
| row_36 | FLNA | -0.457 | Yes |
| row_37 | BCL9L | -0.451 | Yes |
| row_38 | ACTN4 | -0.429 | Yes |
| row_39 | MSN | -0.411 | Yes |
| row_40 | F2R | -0.383 | Yes |
| row_41 | THBS1 | -0.353 | Yes |
| row_42 | F11R | -0.330 | Yes |
| row_43 | ANXA1 | -0.293 | Yes |
| row_44 | CTGF | -0.250 | Yes |
| row_45 | CXCL10 | -0.194 | Yes |
| row_46 | ENPP2 | -0.109 | Yes |
| row_47 | CCL5 | 0.002 | Yes |
| TYROSINE_METABOLISM | |||
| row_24 | ALDH3B1 | -0.410 | Yes |
| row_25 | FAH | -0.308 | Yes |
| row_26 | ADH7 | 0.001 | Yes |
| INFLAMMATORY_RESPONSE_PATHWAY | |||
| row_10 | THBS1 | -0.678 | Yes |
| row_11 | LAMC1 | -0.564 | Yes |
| row_12 | LCK | -0.436 | Yes |
| row_13 | LAMA5 | -0.264 | Yes |
| row_14 | COL3A1 | 0.011 | Yes |
| HSA04060_CYTOKINE_CYTOKINE_RECEPTOR_INTERACTION | |||
| row_176 | ACVR1B | -0.461 | Yes |
| row_177 | CCL27 | -0.457 | Yes |
| row_178 | TSLP | -0.454 | Yes |
| row_179 | TNFSF4 | -0.452 | Yes |
| row_180 | CSF1 | -0.450 | Yes |
| row_181 | TNFSF11 | -0.446 | Yes |
| row_182 | LTBR | -0.441 | Yes |
| row_183 | IL23A | -0.438 | Yes |
| row_184 | CXCR6 | -0.433 | Yes |
| row_185 | IL17RA | -0.435 | Yes |
| row_186 | TGFB2 | -0.434 | Yes |
| row_187 | EDA2R | -0.429 | Yes |
| row_188 | IL18RAP | -0.426 | Yes |
| row_189 | TGFB1 | -0.420 | Yes |
| row_190 | TNFRSF10B | -0.413 | Yes |
| row_191 | ACVR1 | -0.410 | Yes |
| row_192 | IL12RB1 | -0.413 | Yes |
| row_193 | LIF | -0.401 | Yes |
| row_194 | TNFRSF9 | -0.392 | Yes |
| row_195 | IFNGR1 | -0.377 | Yes |
| row_196 | HGF | -0.362 | Yes |
| row_197 | CCL7 | -0.346 | Yes |
| row_198 | VEGFA | -0.329 | Yes |
| row_199 | CX3CL1 | -0.312 | Yes |
| row_200 | VEGFC | -0.288 | Yes |
| row_201 | EGFR | -0.262 | Yes |
| row_202 | CXCL10 | -0.234 | Yes |
| row_203 | TGFBR2 | -0.203 | Yes |
| row_204 | CXCL12 | -0.168 | Yes |
| row_205 | IL6ST | -0.130 | Yes |
| row_206 | CCL2 | -0.091 | Yes |
| row_207 | CXCL1 | -0.047 | Yes |
| row_208 | CCL5 | 0.001 | Yes |
| UVC_LOW_C2_DN | |||
| row_12 | MYO10 | -0.534 | Yes |
| row_13 | SLIT2 | -0.362 | Yes |
| row_14 | CXCL12 | 0.004 | Yes |
| CELL_SURFACE_RECEPTOR_LINKED_SIGNAL_TRANSDUCTION | |||
| row_98 | ARHGEF2 | -0.460 | Yes |
| row_99 | ISGF3G | -0.451 | Yes |
| row_100 | IL18RAP | -0.454 | Yes |
| row_101 | TNFRSF10B | -0.445 | Yes |
| row_102 | FLNA | -0.437 | Yes |
| row_103 | ECGF1 | -0.428 | Yes |
| row_104 | IL12RB1 | -0.416 | Yes |
| row_105 | LIF | -0.397 | Yes |
| row_106 | RAMP2 | -0.380 | Yes |
| row_107 | HGF | -0.355 | Yes |
| row_108 | STC2 | -0.330 | Yes |
| row_109 | STC1 | -0.303 | Yes |
| row_110 | ANXA1 | -0.274 | Yes |
| row_111 | CD14 | -0.241 | Yes |
| row_112 | LY6E | -0.200 | Yes |
| row_113 | CXCL10 | -0.157 | Yes |
| row_114 | ADRB2 | -0.113 | Yes |
| row_115 | IL6ST | -0.057 | Yes |
| row_116 | CCL2 | 0.003 | Yes |
| HSA04620_TOLL_LIKE_RECEPTOR_SIGNALING_PATHWAY | |||
| row_73 | RAC1 | -0.500 | Yes |
| row_74 | CCL4 | -0.495 | Yes |
| row_75 | NFKB1 | -0.497 | Yes |
| row_76 | TLR8 | -0.489 | Yes |
| row_77 | CHUK | -0.491 | Yes |
| row_78 | AKT2 | -0.487 | Yes |
| row_79 | MAP2K4 | -0.476 | Yes |
| row_80 | MAP2K3 | -0.466 | Yes |
| row_81 | MAPK3 | -0.455 | Yes |
| row_82 | IRAK1 | -0.448 | Yes |
| row_83 | TRAF3 | -0.435 | Yes |
| row_84 | JUN | -0.426 | Yes |
| row_85 | RELA | -0.416 | Yes |
| row_86 | CASP8 | -0.405 | Yes |
| row_87 | TLR2 | -0.396 | Yes |
| row_88 | SPP1 | -0.375 | Yes |
| row_89 | NFKBIA | -0.358 | Yes |
| row_90 | NFKB2 | -0.324 | Yes |
| row_91 | CD14 | -0.277 | Yes |
| row_92 | MAPK12 | -0.223 | Yes |
| row_93 | CXCL10 | -0.166 | Yes |
| row_94 | MAPK13 | -0.094 | Yes |
| row_95 | CCL5 | 0.001 | Yes |
| HSA04340_HEDGEHOG_SIGNALING_PATHWAY | |||
| row_41 | CSNK1G1 | -0.586 | Yes |
| row_42 | STK36 | -0.586 | Yes |
| row_43 | RAB23 | -0.586 | Yes |
| row_44 | GLI3 | -0.580 | Yes |
| row_45 | SUFU | -0.567 | Yes |
| row_46 | PTCH1 | -0.552 | Yes |
| row_47 | WNT3A | -0.532 | Yes |
| row_48 | BTRC | -0.530 | Yes |
| row_49 | WNT10A | -0.496 | Yes |
| row_50 | WNT10B | -0.426 | Yes |
| row_51 | WNT9A | -0.321 | Yes |
| row_52 | BMP4 | -0.164 | Yes |
| row_53 | WNT7B | 0.002 | Yes |
| GO_ROS | |||
| row_22 | LTC4S | -0.524 | Yes |
| row_23 | STK25 | -0.488 | Yes |
| row_24 | PDLIM1 | -0.416 | Yes |
| row_25 | DUSP1 | -0.279 | Yes |
| row_26 | CCL5 | 0.001 | Yes |
| LEE_E2F1_DN | |||
| row_43 | MCM10 | -0.485 | Yes |
| row_44 | PXMP2 | -0.473 | Yes |
| row_45 | ELOVL5 | -0.457 | Yes |
| row_46 | ITPR1 | -0.424 | Yes |
| row_47 | GSTO1 | -0.386 | Yes |
| row_48 | EGFR | -0.305 | Yes |
| row_49 | PPCS | -0.166 | Yes |
| row_50 | NETO2 | 0.001 | Yes |
| Specific genes enriched in wild type MEFs | |||
| PROSTAGLANDIN_AND_LEUKOTRIENE_METABOLISM | |||
| row_0 | PTGIS | 0.276 | Yes |
| row_1 | CBR3 | 0.497 | Yes |
| row_2 | PTGS1 | 0.628 | Yes |
| INTRINSICPATHWAY | |||
| row_0 | PROS1 | 0.255 | Yes |
| row_1 | COL4A6 | 0.502 | Yes |
| row_2 | COL4A5 | 0.659 | Yes |
| HSA04612_ANTIGEN_PROCESSING_AND_PRESENTATION | |||
| row_0 | TAP2 | 0.277 | Yes |
| row_1 | LGMN | 0.401 | Yes |
| row_2 | PSME1 | 0.432 | Yes |
| row_3 | TAP1 | 0.448 | Yes |
| row_4 | CIITA | 0.480 | Yes |
| row_5 | HSP90AA1 | 0.514 | Yes |
| LAL_KO_3MO_UP | |||
| row_0 | PLA2G7 | 0.221 | Yes |
| row_1 | GPNMB | 0.426 | Yes |
| row_2 | TREM2 | 0.487 | Yes |
| row_3 | FKBP5 | 0.478 | Yes |
| row_4 | SLC40A1 | 0.507 | Yes |
| GH_AUTOCRINE_UP | |||
| row_0 | ID3 | 0.053 | Yes |
| row_1 | SCAMP5 | 0.104 | Yes |
| row_2 | ALCAM | 0.154 | Yes |
| row_3 | IGFBP7 | 0.193 | Yes |
| row_4 | COL4A6 | 0.232 | Yes |
| row_5 | TLE2 | 0.267 | Yes |
| row_6 | BLVRB | 0.295 | Yes |
| row_7 | GRIA1 | 0.324 | Yes |
| row_8 | SFXN5 | 0.344 | Yes |
| row_9 | ID1 | 0.368 | Yes |
| row_10 | PPA2 | 0.386 | Yes |
| row_11 | VTI1A | 0.391 | Yes |
| row_12 | UQCR | 0.394 | Yes |
| row_13 | ADK | 0.408 | Yes |
| row_14 | MOBKL2B | 0.420 | Yes |
| row_15 | SPATA7 | 0.429 | Yes |
| row_16 | MRPL28 | 0.431 | Yes |
| row_17 | SH3KBP1 | 0.439 | Yes |
| row_18 | CFL2 | 0.442 | Yes |
| row_19 | BSG | 0.444 | Yes |
| row_20 | MOGAT2 | 0.451 | Yes |
| row_21 | SSR4 | 0.459 | Yes |
| row_22 | SAR1B | 0.465 | Yes |
| row_23 | PIR | 0.467 | Yes |
| row_24 | AXL | 0.469 | Yes |
| row_25 | GMPR | 0.475 | Yes |
| row_26 | PSMB2 | 0.481 | Yes |
| row_27 | SLC43A1 | 0.485 | Yes |
| row_28 | GPR12 | 0.482 | Yes |
| row_29 | G3BP | 0.488 | Yes |
| HSA02010_ABC_TRANSPORTERS_GENERAL | |||
| row_0 | TAP2 | 0.192 | Yes |
| row_1 | ABCD4 | 0.294 | Yes |
| row_2 | ABCA3 | 0.353 | Yes |
| row_3 | ABCC10 | 0.418 | Yes |
| row_4 | ABCC5 | 0.465 | Yes |
| row_5 | ABCC3 | 0.503 | Yes |
| row_6 | ABCA7 | 0.534 | Yes |
| row_7 | TAP1 | 0.540 | Yes |
| IL2RBPATHWAY | |||
| row_0 | JAK3 | 0.217 | Yes |
| row_1 | SOCS3 | 0.274 | Yes |
| row_2 | MAPK1 | 0.353 | Yes |
| row_3 | SOCS1 | 0.429 | Yes |
| row_4 | IRS1 | 0.499 | Yes |
| row_5 | CRKL | 0.545 | Yes |
| SMITH_HCV_INDUCED_HCC_UP | |||
| row_0 | GSTA4 | 0.309 | Yes |
| row_1 | SDHC | 0.378 | Yes |
| row_2 | PMVK | 0.386 | Yes |
| row_3 | PDCD5 | 0.416 | Yes |
| row_4 | PIR | 0.450 | Yes |
| row_5 | IMPA2 | 0.469 | Yes |
| row_6 | COPS5 | 0.485 | Yes |
| row_7 | ANXA7 | 0.510 | Yes |
| row_8 | NOLA2 | 0.523 | Yes |
| HOX_GENES | |||
| row_0 | HOXD4 | 0.092 | Yes |
| row_1 | HOXB5 | 0.176 | Yes |
| row_2 | HOXA5 | 0.251 | Yes |
| row_3 | HOXA2 | 0.319 | Yes |
| row_4 | MEIS1 | 0.376 | Yes |
| row_5 | PRRX1 | 0.414 | Yes |
| row_6 | HOXA7 | 0.461 | Yes |
| row_7 | HOXD3 | 0.500 | Yes |
| NI2_LUNG_DN | |||
| row_0 | TRAP1 | 0.257 | Yes |
| row_1 | CEBPD | 0.470 | Yes |
| row_2 | ABCC3 | 0.584 | Yes |
| row_3 | LGTN | 0.639 | Yes |
| row_4 | HSP90AA1 | 0.702 | Yes |
| MAGRANGEAS_MULTIPLE_MYELOMA_IGL_VS_IGK_DN | |||
| row_0 | GSTM5 | 0.178 | Yes |
| row_1 | TJP2 | 0.328 | Yes |
| row_2 | SMARCA1 | 0.407 | Yes |
| row_3 | CSNK2A2 | 0.466 | Yes |
| row_4 | UBE4A | 0.503 | Yes |
| HSA04630_JAK_STAT_SIGNALING_PATHWAY | |||
| row_0 | JAK3 | 0.054 | Yes |
| row_1 | SOCS2 | 0.111 | Yes |
| row_2 | IL11 | 0.166 | Yes |
| row_3 | OSMR | 0.214 | Yes |
| row_4 | STAT3 | 0.253 | Yes |
| row_5 | IFNGR2 | 0.270 | Yes |
| row_6 | SOCS3 | 0.281 | Yes |
| row_7 | CCND2 | 0.300 | Yes |
| row_8 | SOCS1 | 0.319 | Yes |
| row_9 | CTF1 | 0.338 | Yes |
| row_10 | SOCS5 | 0.358 | Yes |
| row_11 | GHR | 0.369 | Yes |
| row_12 | PIK3R2 | 0.382 | Yes |
| row_13 | CISH | 0.392 | Yes |
| row_14 | SPRY4 | 0.406 | Yes |
| row_15 | IL15 | 0.398 | Yes |
| row_16 | SPRY3 | 0.408 | Yes |
| row_17 | STAT1 | 0.418 | Yes |
| row_18 | CCND1 | 0.426 | Yes |
| row_19 | PIAS4 | 0.429 | Yes |
| row_20 | AKT3 | 0.435 | Yes |
| row_21 | CREBBP | 0.441 | Yes |
| row_22 | PIK3R5 | 0.437 | Yes |
| row_23 | GRB2 | 0.442 | Yes |
| row_24 | LEPR | 0.449 | Yes |
| row_25 | IFNAR2 | 0.440 | Yes |
| row_26 | PIAS3 | 0.438 | Yes |
| row_27 | JAK2 | 0.443 | Yes |
| row_28 | EPO | 0.448 | Yes |
| row_29 | CBLB | 0.447 | Yes |
| row_30 | TYK2 | 0.451 | Yes |
| GLUTATHIONE_METABOLISM | |||
| row_0 | GSTA4 | 0.165 | Yes |
| row_1 | GSTM2 | 0.297 | Yes |
| row_2 | IDH1 | 0.384 | Yes |
| row_3 | GSTM5 | 0.469 | Yes |
| row_4 | GSTM1 | 0.555 | Yes |
| row_5 | GSTZ1 | 0.625 | Yes |
| row_6 | GSTO2 | 0.699 | Yes |
| HSA03022_BASAL_TRANSCRIPTION_FACTORS | |||
| row_0 | GTF2H4 | 0.132 | Yes |
| row_1 | GTF2F2 | 0.182 | Yes |
| row_2 | TAF13 | 0.264 | Yes |
| row_3 | TBPL2 | 0.333 | Yes |
| row_4 | GTF2E1 | 0.375 | Yes |
| row_5 | TAF7L | 0.420 | Yes |
| row_6 | TAF9B | 0.466 | Yes |
| row_7 | GTF2I | 0.511 | Yes |
| row_8 | GTF2H3 | 0.528 | Yes |
| row_9 | TAF6L | 0.562 | Yes |
| row_10 | GTF2A1 | 0.583 | Yes |
| SPPAPATHWAY | |||
| row_0 | PTGS1 | 0.273 | Yes |
| row_1 | GNB1 | 0.391 | Yes |
| row_2 | MAPK1 | 0.500 | Yes |
| TNFALPHA_TGZ_ADIP_DN | |||
| row_0 | IDH1 | 0.218 | Yes |
| row_1 | ALAD | 0.362 | Yes |
| row_2 | RGS2 | 0.495 | Yes |
| row_3 | IDH3G | 0.591 | Yes |
| row_4 | CDKN2C | 0.662 | Yes |
| ADIP_HUMAN_UP | |||
| row_0 | ADORA2B | 0.136 | Yes |
| row_1 | ALDH6A1 | 0.247 | Yes |
| row_2 | LPL | 0.345 | Yes |
| row_3 | RXRA | 0.383 | Yes |
| row_4 | ACSL1 | 0.381 | Yes |
| row_5 | CRYAB | 0.410 | Yes |
| row_6 | PFKFB3 | 0.437 | Yes |
| row_7 | LYPLA1 | 0.465 | Yes |
| row_8 | RXRB | 0.469 | Yes |
| row_9 | KCNH2 | 0.483 | Yes |
| row_10 | LBP | 0.476 | Yes |
| row_11 | CTSG | 0.464 | Yes |
| row_12 | GPD1 | 0.475 | Yes |
| row_13 | DGAT1 | 0.482 | Yes |
| row_14 | PLCD1 | 0.490 | Yes |
| row_15 | ATP8A2 | 0.496 | Yes |
| row_16 | ABCE1 | 0.499 | Yes |
| row_17 | FABP5 | 0.493 | Yes |
| row_18 | SMARCB1 | 0.499 | Yes |
| ERKPATHWAY | |||
| row_0 | STAT3 | 0.180 | Yes |
| row_1 | PDGFRA | 0.290 | Yes |
| row_2 | GNB1 | 0.401 | Yes |
| BRCA1_SW480_DN | |||
| row_0 | GRB10 | 0.390 | Yes |
| row_1 | COL16A1 | 0.462 | Yes |
| row_2 | RXRB | 0.475 | Yes |
| row_3 | BAX | 0.486 | Yes |
| row_4 | SEMA3B | 0.515 | Yes |
| row_5 | GRB2 | 0.537 | Yes |
| row_6 | PIN1 | 0.555 | Yes |
| NF90_DN | |||
| row_0 | SLC1A3 | 0.276 | Yes |
| row_1 | CXCR7 | 0.355 | Yes |
| row_2 | IRX5 | 0.449 | Yes |
| row_3 | ASNS | 0.485 | Yes |
| row_4 | RAD52 | 0.514 | Yes |
| row_5 | CUGBP2 | 0.545 | Yes |
| row_6 | AXL | 0.567 | Yes |
| row_7 | CREBBP | 0.589 | Yes |
| row_8 | NMT1 | 0.606 | Yes |
| row_9 | GAL | 0.606 | Yes |
| row_10 | POLD2 | 0.612 | Yes |
| HSA04742_TASTE_TRANSDUCTION | |||
| row_0 | TAS1R2 | 0.322 | Yes |
| row_1 | GNB1 | 0.410 | Yes |
| row_2 | PRKX | 0.461 | Yes |
| row_3 | TAS1R3 | 0.452 | Yes |
| row_4 | PRKACA | 0.485 | Yes |
| ET743PT650_COLONCA_DN | |||
| row_0 | ALCAM | 0.180 | Yes |
| row_1 | TIAM1 | 0.255 | Yes |
| row_2 | ID1 | 0.339 | Yes |
| row_3 | COMMD1 | 0.394 | Yes |
| row_4 | ATBF1 | 0.438 | Yes |
| HSA00590_ARACHIDONIC_ACID_METABOLISM | |||
| row_0 | PTGIS | 0.192 | Yes |
| row_1 | CBR3 | 0.345 | Yes |
| row_2 | PTGS1 | 0.434 | Yes |
| STAEGE_EFTS_UP | |||
| row_0 | CYP26B1 | 0.191 | Yes |
| row_1 | CCK | 0.337 | Yes |
| row_2 | KCNAB3 | 0.410 | Yes |
| row_3 | EGR2 | 0.436 | Yes |
| row_4 | TMEM29 | 0.462 | Yes |
| row_5 | CCND1 | 0.484 | Yes |
| row_6 | ZDHHC21 | 0.492 | Yes |
| row_7 | CLEC11A | 0.499 | Yes |
The criteria for the GSEA analysis was P < 0.05 and false discovery rate (FDR) <25%.
References
- 1.Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20009–20017. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.33.20009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31384–31390. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.49.31384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McConnell BB, Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Yang VW. The diverse functions of Kruppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology. Bioessays. 2007;29:549–557. doi: 10.1002/bies.20581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Chanchevalap S, Dalton WB, Hisamuddin IM, Yang VW. Kruppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res. 2005;15:92–96. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dang DT, Bachman KE, Mahatan CS, Dang LH, Giardiello FM, Yang VW. Decreased expression of the gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor gene in intestinal adenomas of multiple intestinal neoplasia mice and in colonic adenomas of familial adenomatous polyposis patients. FEBS Lett. 2000;476:203–207. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01727-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J. Sp1 and kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2001;188:143–160. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kaczynski J, Cook T, Urrutia R. Sp1- and Kruppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol. 2003;4:206. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-2-206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Feinberg MW, Cao Z, Wara AK, Lebedeva MA, Senbanerjee S, Jain MK. Kruppel-like factor 4 is a mediator of proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:38247–38258. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509378200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ghaleb AM, Aggarwal G, Bialkowska AB, Nandan MO, Yang VW. Notch inhibits expression of the Kruppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal epithelium. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:1920–1927. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ghaleb AM, McConnell BB, Nandan MO, Katz JP, Kaestner KH, Yang VW. Haploinsufficiency of Kruppel-like factor 4 promotes adenomatous polyposis coli dependent intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7147–7154. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ghaleb AM, Yang VW. The Pathobiology of Kruppel-like Factors in Colorectal Cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2008;4:59–64. doi: 10.1007/s11888-008-0011-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hamik A, Lin Z, Kumar A, Balcells M, Sinha S, Katz J, Feinberg MW, Gerzsten RE, Edelman ER, Jain MK. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates endothelial inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:13769–13779. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700078200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kanai M, Wei D, Li Q, Jia Z, Ajani J, Le X, Yao J, Xie K. Loss of Kruppel-like factor 4 expression contributes to Sp1 overexpression and human gastric cancer development and progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6395–6402. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xu J, Lu B, Xu F, Gu H, Fang Y, Huang Q, Lai M. Dynamic down-regulation of Kruppel-like factor 4 in colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134:891–898. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0353-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nandan MO, Yang VW. The role of Kruppel-like factors in the reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24:1343–1355. doi: 10.14670/hh-24.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Villarreal G Jr., Zhang Y, Larman HB, Gracia-Sancho J Koo A., Garcia-Cardena G. Defining the regulation of KLF4 expression and its downstream transcriptional targets in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391:984–989. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S. Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2007;448:313–317. doi: 10.1038/nature05934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wernig M, Meissner A, Foreman R, Brambrink T, Ku M, Hochedlinger K, Bernstein BE, Jaenisch R. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature. 2007;448:318–324. doi: 10.1038/nature05944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maherali N, Sridharan R, Xie W, Utikal J, Eminli S, Arnold K, Stadtfeld M, Yachechko R, Tchieu J, Jaenisch R, Plath K, Hochedlinger K. Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:55–70. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li Y, McClintick J, Zhong L, Edenberg HJ, Yoder MC, Chan RJ. Murine embryonic stem cell differentiation is promoted bySOCS-3 and inhibited by the zinc finger transcription factor Klf4. Blood. 2005;105:635–637. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999;22:356–360. doi: 10.1038/11926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, Lee CS, Labosky PA, Yang VW, Kaestner KH. The zinc -finger transcription factor Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon. Development. 2002;129:2619–2628. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.11.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Swamynathan SK, Katz JP, Kaestner KH, Ashery-Padan R, Crawford MA, Piatigorsky J. Conditional deletion of the mouse Klf4 gene results in corneal epithelial fragility, stromal edema, and loss of conjunctival goblet cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:182–194. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00846-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, Actman L, McNally SR, Silberg DG, Furth EE, Kaestner KH. Loss of Klf4 in mice causes altered proliferation and differentiation and precancerous changes in the adult stomach. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:935–945. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hagos EG, Ghaleb AM, Dalton WB, Bialkowska AB, Yang VW. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts null for the Kruppel-like factor 4 gene are genetically unstable. Oncogene. 2009;28:1197–1205. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen X, Whitney EM, Gao SY, Yang VW. Transcriptional profiling of Kruppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation. J Mol Biol. 2003;326:665–677. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01449-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Whitney EM, Ghaleb AM, Chen X, Yang VW. Transcriptional profiling of the cell cycle checkpoint gene kruppel-like factor 4 reveals a global inhibitory function in macromolecular biosynthesis. Gene Expr. 2006;13:85–96. doi: 10.3727/000000006783991908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Todaro GJ, Green H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:5116–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091062498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dennis G Jr., Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W Lane HC., Lempicki RA. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Niwa H, Burdon T, Chambers I, Smith A. Self-renewal of pluripotent embryonic stem cells is mediated via activation of STAT3. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2048–2060. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.13.2048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Matsuda T, Nakamura T, Nakao K, Arai T, Katsuki M, Heike T, Yokota T. STAT3 activation is sufficient to maintain an undifferentiated state of mouse embryonic stem cells. EMBO J. 1999;18:4261–4269. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.15.4261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen X, Johns DC, Geiman DE, Marban E, Dang DT, Hamlin G, Sun R, Yang VW. Kruppel-like factor 4 (gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor) inhibits cell proliferation by blocking G1/S progression of the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:30423–30428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101194200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang W, Geiman DE, Shields JM, Dang DT, Mahatan CS, Kaestner KH, Biggs JR, Kraft AS, Yang VW. The gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (Kruppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21WAF1/Cip1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18391–18398. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C000062200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yoon HS, Chen X, Yang VW. Kruppel-like factor 4 mediates p53-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2101–2105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211027200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yoon HS, Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Hisamuddin IM, Dalton WB, Yang VW. Kruppel-like factor 4 prevents centrosome amplification following gamma-irradiation-induced DNA damage. Onco-gene. 2005;24:4017–4025. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yoon HS, Yang VW. Requirement of Kruppel-like factor 4 in preventing entry into mitosis following DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5035–5041. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307631200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lochter A, Sternlicht MD, Werb Z, Bissell MJ. The significance of matrix metalloproteinases during early stages of tumor progression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;857:180–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Morrison CJ, Overall CM. TIMP independence of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 activation by membrane type 2 (MT2)-MMP is determined by contributions of both the MT2-MMP catalytic and hemopexin C domains. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:26528–26539. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603331200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:161–174. doi: 10.1038/nrc745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Witty JP, Wright JH, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases are expressed during ductal and alveolar mammary morphogenesis, and misregulation of stromelysin-1 in transgenic mice induces unscheduled alveolar development. Mol Biol Cell. 1995;6:1287–1303. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.10.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stallings-Mann M, Radisky D. Matrix metallo-proteinase-induced malignancy in mammary epithelial cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185:104–110. doi: 10.1159/000101310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Przybylo JA, Radisky DC. Matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition: tumor progression at Snail's pace. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:1082–1088. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Morris JR. SUMO in the mammalian response to DNA damage. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010;38:92–97. doi: 10.1042/BST0380092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morris JR, Boutell C, Keppler M, Densham R, Weekes D, Alamshah A, Butler L, Galanty Y, Pangon L, Kiuchi T, Ng T, Solomon E. The SUMO modification pathway is involved in the BRCA1 response to genotoxic stress. Nature. 2009;462:886–890. doi: 10.1038/nature08593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Galanty Y, Belotserkovskaya R, Coates J, Polo S, Miller KM, Jackson SP. Mammalian SUMO E3-ligases PIAS1 and PIAS4 promote responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Nature. 2009;462:935–939. doi: 10.1038/nature08657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wei Z, Yang Y, Zhang P, Andrianakos R, Hasegawa K, Lyu J, Chen X, Bai G, Liu C, Pera M, Lu W. Klf4 interacts directly with Oct4 and Sox2 to promote reprogramming. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2969–2978. doi: 10.1002/stem.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jiang J, Chan YS, Loh YH, Cai J, Tong GQ, Lim CA, Robson P, Zhong S, Ng HH. A core Klf circuitry regulates self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:353–360. doi: 10.1038/ncb1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rowland BD, Bernards R, Peeper DS. The KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:1074–1082. doi: 10.1038/ncb1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Utikal J, Polo JM, Stadtfeld M, Maherali N, Kulalert W, Walsh RM, Khalil A, Rheinwald JG, Hochedlinger K. Immortalization eliminates a roadblock during cellular reprogramming into iPS cells. Nature. 2009;460:1145–1148. doi: 10.1038/nature08285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Marion RM, Strati K, Li H, Murga M, Blanco R, Ortega S, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Serrano M, Blasco MA. A p53-mediated DNA damage response limits reprogramming to ensure iPS cell genomic integrity. Nature. 2009;460:1149–1153. doi: 10.1038/nature08287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li H, Collado M, Villasante A, Strati K, Ortega S, Canamero M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. The Ink4/Arf locus is a barrier for iPS cell reprogramming. Nature. 2009;460:1136–1139. doi: 10.1038/nature08290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kawamura T, Suzuki J, Wang YV, Menendez S, Morera LB, Raya A, Wahl GM, Belmonte JC. Linking the p53 tumour suppressor pathway to somatic cell reprogramming. Nature. 2009;460:1140–1144. doi: 10.1038/nature08311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hong H, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Kanagawa O, Nakagawa M, Okita K, Yamanaka S. Suppression of induced pluripotent stem cell generation by the p53-p21 pathway. Nature. 2009;460:1132–1135. doi: 10.1038/nature08235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Niwa H, Ogawa K, Shimosato D, Adachi K. A parallel circuit of LIF signalling pathways maintains pluripotency of mouse ES cells. Nature. 2009;460:118–122. doi: 10.1038/nature08113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]