Abstract
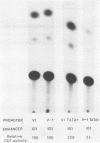
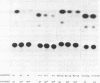
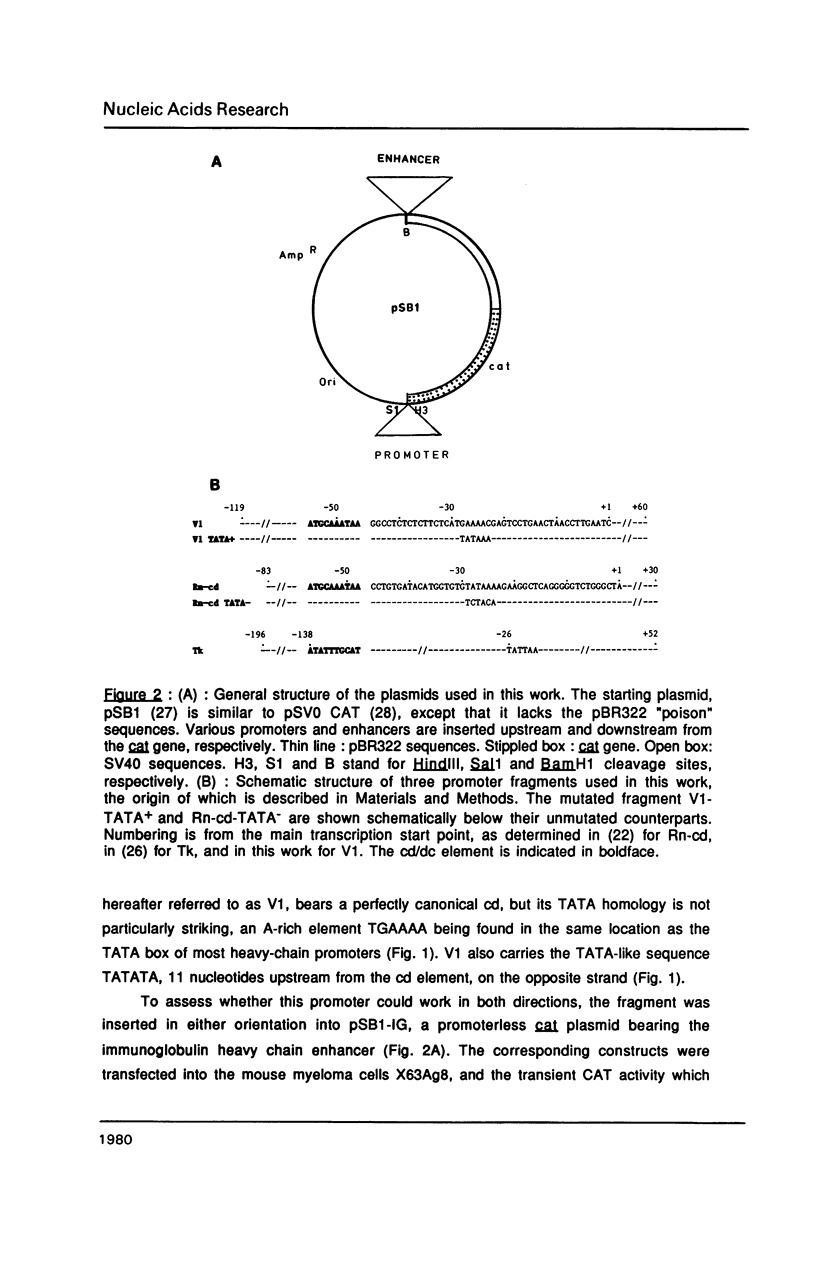
We show that the promoter from the mouse VH441 heavy-chain immunoglobulin gene, when present on plasmids transiently introduced into myeloma cells, promotes transcription bidirectionally, due to the presence on both strands of TATA-like sequences bracketing the highly conserved decanucleotide element. The two divergent promoters compete for the transcriptional machinery, their relative strength ultimately reflecting the likeness of the two TATA boxes to the consensus sequence. Moreover, their relative activity is also strongly influenced by certain point mutations within the distally located heavy-chain enhancer. The bearing of these results on current concepts of promoter function is discussed.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Bothwell A. Mutational analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9626–9630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C., Berenson J., Goverman J., Boyer P. D., Crews S., Siu G., Calame K. An immunoglobulin promoter region is unaltered by DNA rearrangement and somatic mutation during B-cell development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7731–7749. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Leys E. J., McEwan R. N., Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Analysis of the mouse dhfr promoter region: existence of a divergently transcribed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1847–1858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyen N., Leblond-Francillard M., Holm I., Dreyfus M., Rougeon F. Analysis of promoter and enhancer cell type specificities and the regulation of immunoglobulin gene expression. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Doyen N., Rougeon F. The conserved decanucleotide from the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter induces a very high transcriptional activity in B-cells when introduced into an heterologous promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Hanahan D. Bidirectional activity of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):192–198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., French B. A., Schwartz R. J. The chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene promoter region exhibits partial dyad symmetry and a capacity to drive bidirectional transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4587–4597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. UASs and enhancers: common mechanism of transcriptional activation in yeast and mammals. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):303–305. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Nikaido T., Miyata T., Moriwaki K., Honjo T. The nucleotide sequences of rearranged and germline immunoglobulin VH genes of a mouse myeloma MC101 and evolution of VH genes in mouse. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):277–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Nishimura Y., Watanabe T. The antibody molecule to common acute lymphocytic leukemia (cALL) antigen used the identical or closely related VH gene segment as that of MOPC-21 immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):642–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Proximal and distal domains that control in vitro transcription of the adenovirus IVa2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. E., Stanway C., Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene depends on an upstream activation sequence but does not require TATA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4335–4343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Jones S. D., Bond B., Yamamoto K. R. The immunoglobulin octanucleotide: independent activity and selective interaction with enhancers. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.3029871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Foster J., Stauber C., Stafford J. Cell-type specific regulation of a kappa immunoglobulin gene by promoter and enhancer elements. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:49–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner G., Schirm S., Müller-Baden B., Weber F., Schaffner W. Redundancy of information in enhancers as a principle of mammalian transcription control. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. The MES-1 murine enhancer element is closely associated with the heterogeneous 5' ends of two divergent transcription units. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4558–4569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]