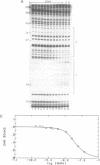
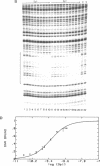
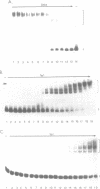
Abstract
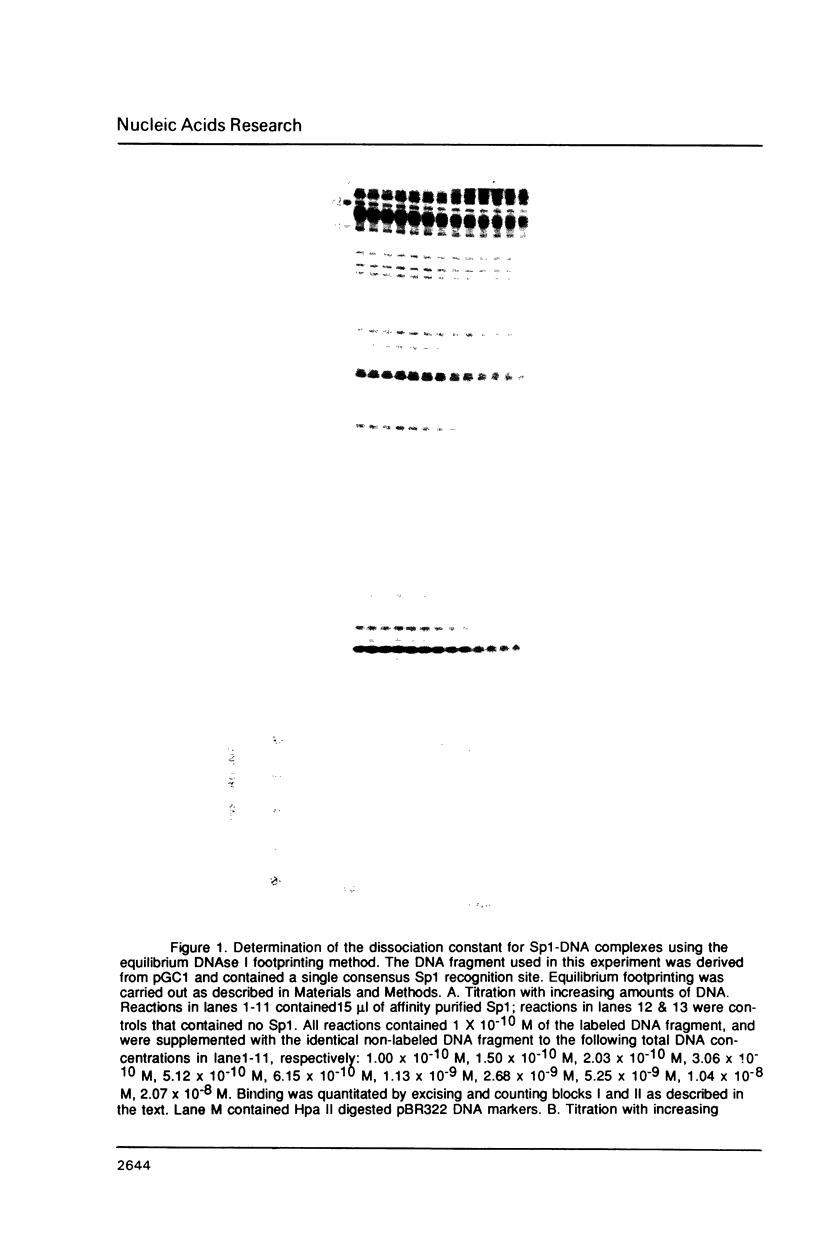
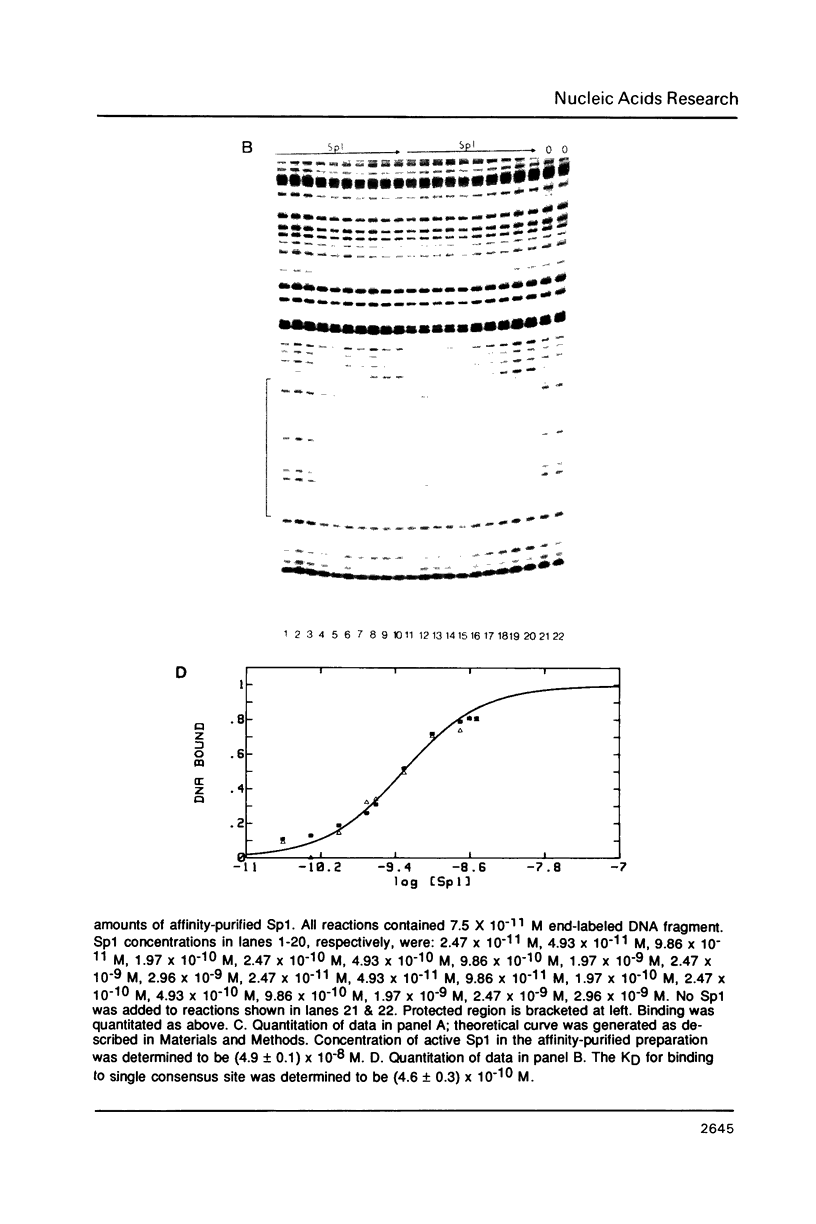
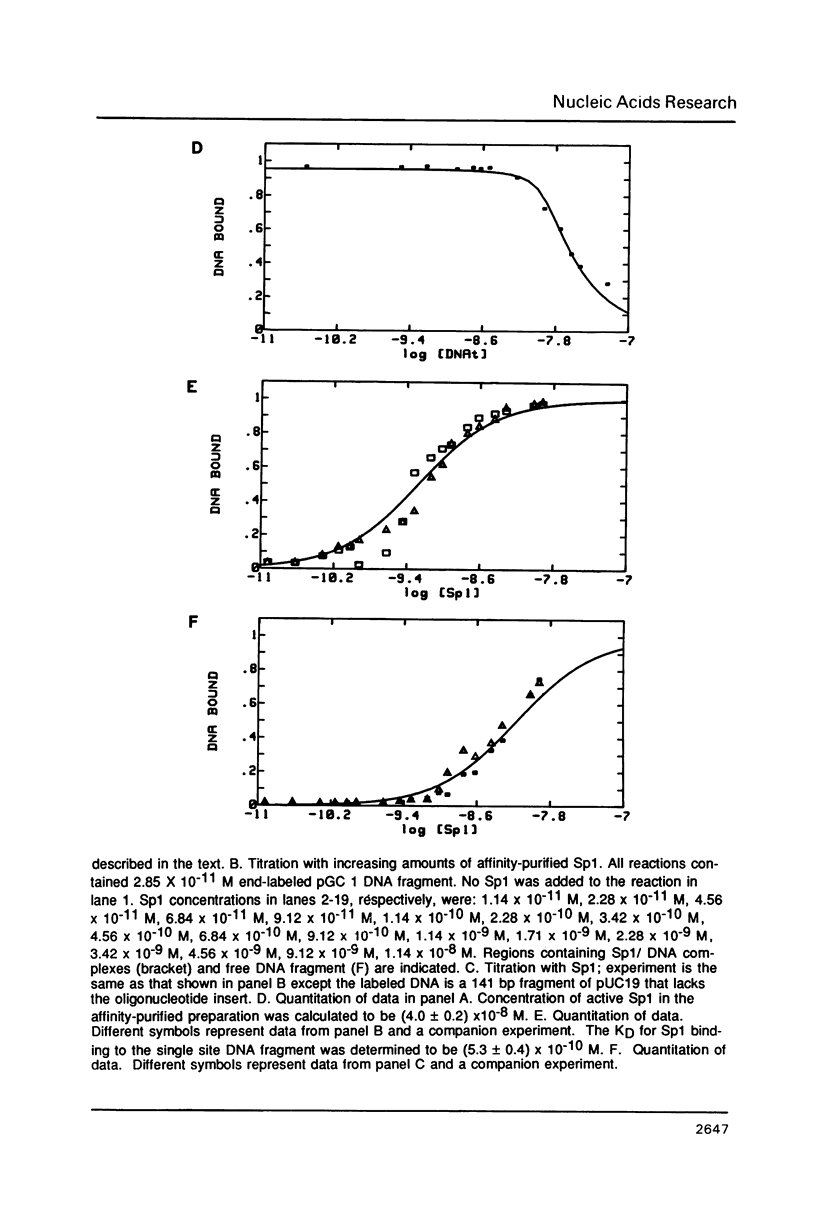
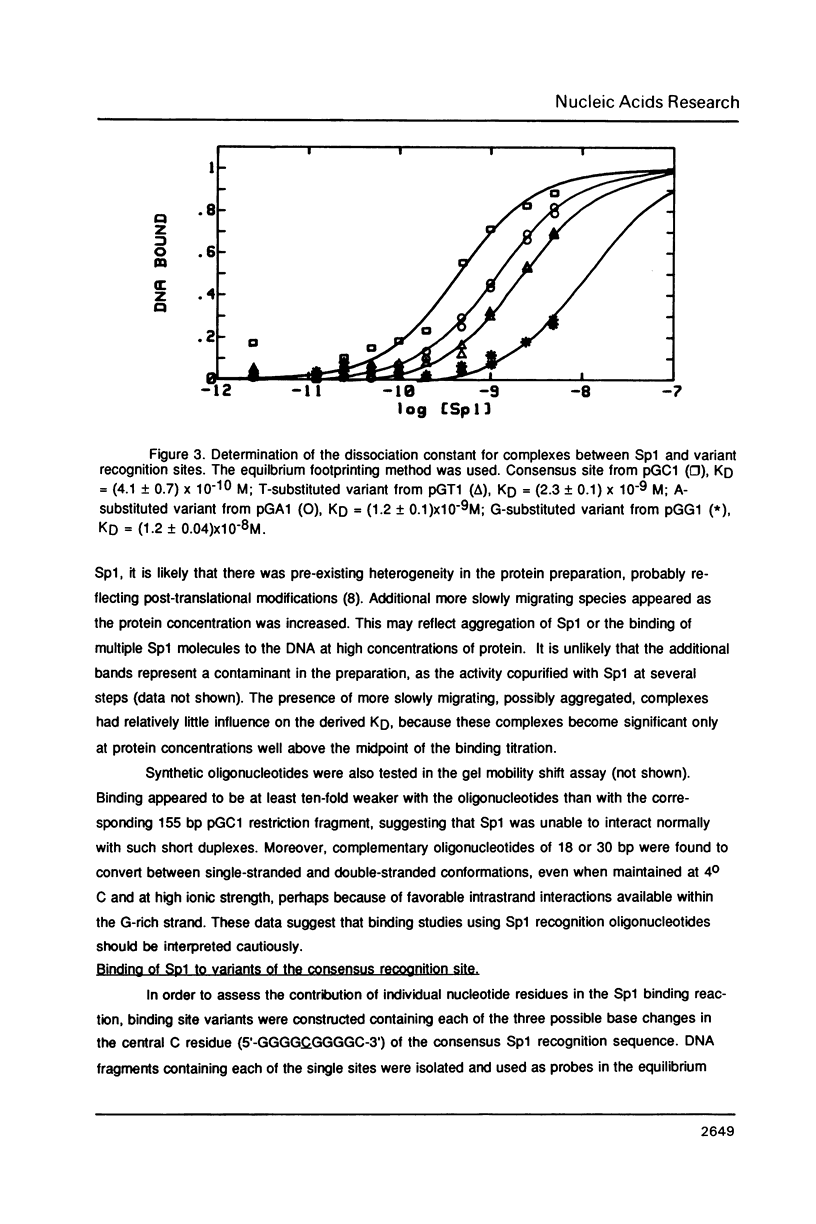
The equilibrium constant was determined for the binding of the transcription factor Sp1 to a single consensus GC box DNA recognition site, (5'-GGGGCGGGGC-3'). For these experiments, single copies of the recognition site were synthesized and cloned in a standard plasmid background. Binding was measured either by a footprinting assay modified so that the binding reaction was at equilibrium, or by a gel mobility shift assay. The concentration of active Sp1 in the reactions and the dissociation constant were determined by computer-assisted fitting to theoretical curves. Values for the dissociation constant obtained in different experiments ranged from 4.1 X 10(-10) M to 5.3 X 10(-10) M. Several variants of the consensus recognition site were also tested. An A-substituted variant (5'-GGGGAGGGGC-3') and a T-substituted variant (5'-GGGGTGGGGC-3') were bound 3-fold and 6-fold more weakly than the consensus site, respectively. A G-substituted variant (5'-GGGGGGGGGC-3') was bound at least 30-fold more weakly than the consensus site. These findings help distinguish between alternative models for Sp1-DNA recognition. They are consistent with the presence of specific hydrogen-bond contacts between Sp1 and the central C-G base pair, but provide no particular evidence to support a model where local DNA structure is the dominant factor in the interaction.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenowitz M., Senear D. F., Shea M. A., Ackers G. K. "Footprint" titrations yield valid thermodynamic isotherms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8462–8466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenowitz M., Senear D. F., Shea M. A., Ackers G. K. Quantitative DNase footprint titration: a method for studying protein-DNA interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:132–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., DeChiara T., Efstratiadis A. A promoter of the rat insulin-like growth factor II gene consists of minimal control elements. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):61–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington M. A., Jones P. A., Imagawa M., Karin M. Cytosine methylation does not affect binding of transcription factor Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2066–2070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höller M., Westin G., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Sp1 transcription factor binds DNA and activates transcription even when the binding site is CpG methylated. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1127–1135. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Riggs A. D. The general affinity of lac repressor for E. coli DNA: implications for gene regulation in procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA binding by proteins. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1182–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.2842864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]