Abstract
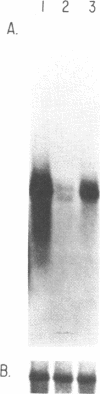
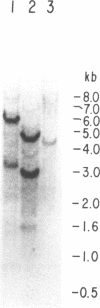
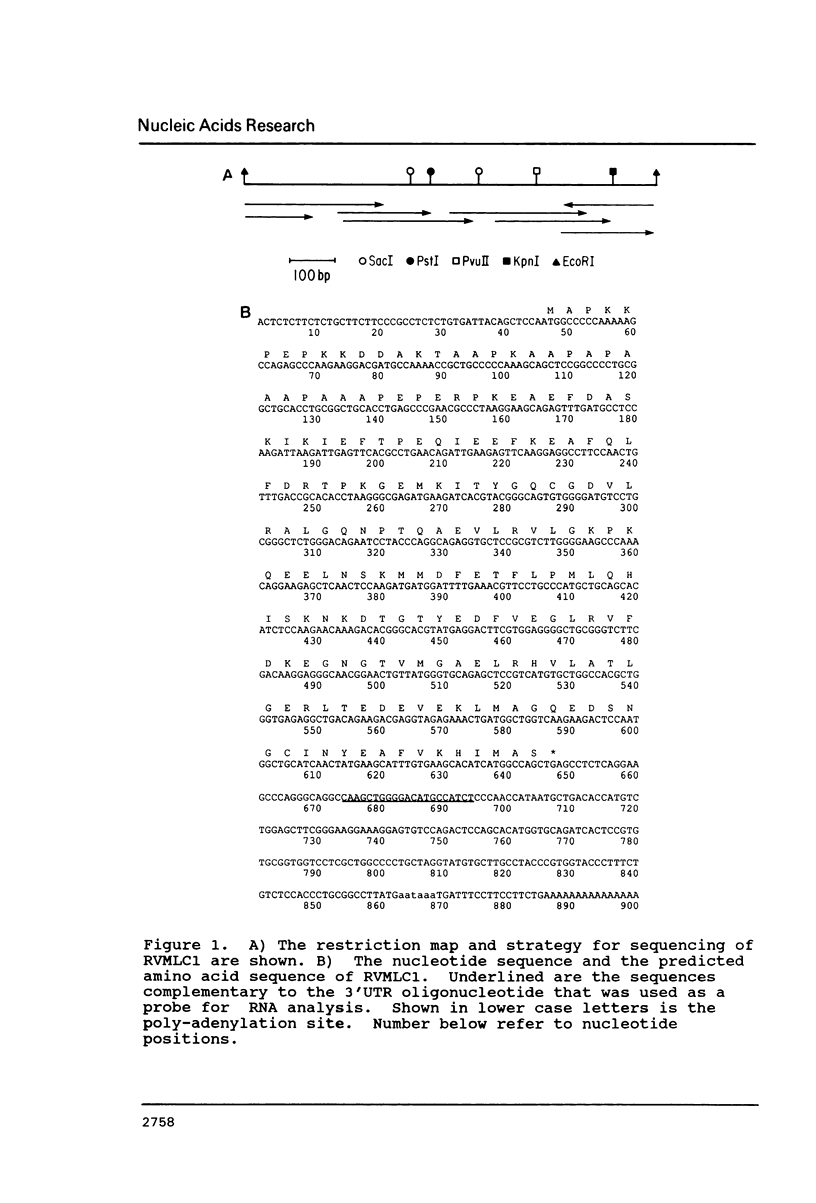
Cardiac myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoform distribution has been shown to undergo changes during development, in response to hormonal stimuli, and during pathologic states like hypertension. We initiated a study of myosin light chain 1 (MLC1) expression in cardiac tissue to determine whether MLC1 undergoes changes similar to those seen for MHC. We isolated a full length cDNA for the predominant MLC1 sequence in rat hearts. This gene is expressed in ventricular tissue at much higher levels than in atrial tissue. Based on its expression pattern and sequence homology, this cDNA encodes the rat ventricular MLC1 and has been named RVMLC1. RVMLC1 is expressed at very low levels in cardiac tissue during early development and is expressed abundantly after birth and in adult hearts. The expression of RVMLC1 was found not to change in the hearts of rats with renovascular hypertension.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Cohen A., Robert B., Fiszman M. Y., Bonhomme F., Guénet J. L., Leader D. P., Buckingham M. E. The myosin alkali light chains of mouse ventricular and slow skeletal muscle are indistinguishable and are encoded by the same gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8578–8584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Robert B., Cohen A., Garner I., Sassoon D., Weydert A., Buckingham M. E. Structure and sequence of the myosin alkali light chain gene expressed in adult cardiac atria and fetal striated muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12669–12676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Robert B., Fiszman M. Y., Leader D. P., Buckingham M. E. The same myosin alkali light chain gene is expressed in adult cardiac atria and in fetal skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):461–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00712583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P., Léger J., Dechesne C. A., Dureau G., Anoal M., Léger J. J. Local changes in myosin types in diseased human atrial myocardium: a quantitative immunofluorescence study. Circulation. 1985 Aug;72(2):272–279. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citi S., Kendrick-Jones J. Regulation of non-muscle myosin structure and function. Bioessays. 1987 Oct;7(4):155–159. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Jakes R., Kendrick-Jones J., Leszyk J., Barouch W., Theibert J. L., Spiegel J., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Amino acid sequence of myosin essential light chain from the scallop Aquipecten irradians. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7651–7656. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechesne C. A., Léger J., Bouvagnet P., Mairhofer H., Léger J. J. Local diversity of myosin expression in mammalian atrial muscles. Variations depending on age and thyroid state in the rat and the rabbit. Circ Res. 1985 Nov;57(5):767–775. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Cloning and characterization of cDNA sequences corresponding to myosin light chains 1, 2, and 3, troponin-C, troponin-T, alpha-tropomyosin, and alpha-actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11078–11086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller D. L., Gianola K. M., Leinwand L. A. A highly conserved mouse gene with a propensity to form pseudogenes in mammals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2797–2803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E., Shi Q. W., Floroff M., Mickle D. A., Wu T. W., Olley P. M., Jackowski G. Molecular cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of a human ventricular myosin light chain 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2353–2353. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., McGrath P. A., Hale P. T. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of rat cardiac myosin: effects of hypophysectomy and thyroxine replacement. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Nov;10(11):1053–1076. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp K. E., Gulick J., Robbins J. Structural and transcriptional analysis of a chicken myosin heavy chain gene subset. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16536–16545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. C., Cribbs L., Delaney P., Chien K. R., Siddiqui M. A. Heart myosin light chain 2 gene. Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNA and expression in normal and hypertensive rat. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2866–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C., Saidapet C., Delaney P., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Expression of ventricular-type myosin light chain messenger RNA in spontaneously hypertensive rat atria. Circ Res. 1988 Jun;62(6):1093–1097. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinwand L. A., Saez L., McNally E., Nadal-Ginard B. Isolation and characterization of human myosin heavy chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3716–3720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Identification and characterization of mRNAs regulated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3156–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompré A. M., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Expression of the cardiac ventricular alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6437–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Chambers A. P., Nadal-Ginard B. Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maita T., Umegane T., Kato Y., Matsuda G. Amino-acid sequence of the L-1 light chain of chicken cardiac-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D., Low E., Litten R., 3rd, Brayden J., Alpert N. Calcium-activated muscle from hypertrophied rabbit hearts. Mechanical and correlated biochemical changes. Circ Res. 1979 Feb;44(2):279–287. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercadier J. J., Lompré A. M., Wisnewsky C., Samuel J. L., Bercovici J., Swynghedauw B., Schwartz K. Myosin isoenzyme changes in several models of rat cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 1981 Aug;49(2):525–532. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.2.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto Y., Sekine T., Grammer J., Yount R. G. The essential light chains constitute part of the active site of smooth muscle myosin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):78–80. doi: 10.1038/324078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Strehler E. E., Garfinkel L. I., Gubits R. M., Ruiz-Opazo N., Nadal-Ginard B. Fast skeletal muscle myosin light chains 1 and 3 are produced from a single gene by a combined process of differential RNA transcription and splicing. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13595–13604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Daubas P., Akimenko M. A., Cohen A., Garner I., Guenet J. L., Buckingham M. A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez L. J., Gianola K. M., McNally E. M., Feghali R., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Leinwand L. A. Human cardiac myosin heavy chain genes and their linkage in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5443–5459. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer J., Malhotra A., Hirsch C., Capasso J., Schaible T. F. Physiologic cardiac hypertrophy corrects contractile protein abnormalities associated with pathologic hypertrophy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1300–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI110729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Lompre A. M., Bouveret P., Wisnewsky C., Whalen R. G. Comparisons of rat cardiac myosins at fetal stages in young animals and in hypothyroid adults. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14412–14418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel U., Bober E., Winter B., Lenz S., Lohse P., Arnold H. H. The complete nucleotide sequences of cDNA clones coding for human myosin light chains 1 and 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4989–4989. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Kushmerick M. J., Mabuchi K., Sréter F. A., Gergely J. Myosin alkali light chain and heavy chain variations correlate with altered shortening velocity of isolated skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9034–9039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M. Myosin from fetal hearts contains the skeletal muscle embryonic light chain. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):731–733. doi: 10.1038/286731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]