Abstract
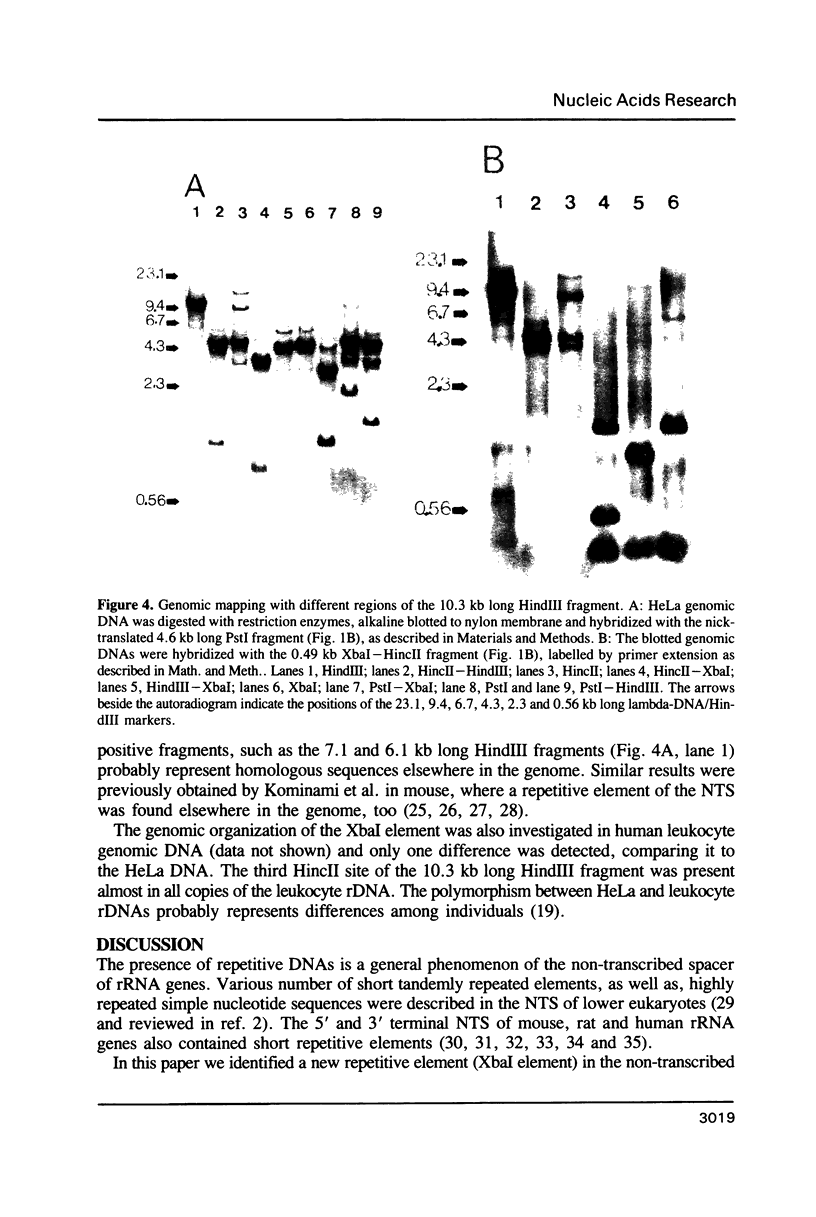
A new repetitive DNA region was identified in the non-transcribed spacer of human rDNA, namely a long (4.6 kb) sequence motif (Xbal element) was present in two copies. The repeating unit composed of two parts. One of them consisted of unique nucleotide sequences, interrupted by some simple sequences. The other, about 3.1 kb long one assembled only from highly repeated simple sequences. The unique sequence region contained two, inverted copies of the human AluI type repetitive DNA family. The authors suggest that the XbaI elements may flank the tandem arrays of human rRNA genes as terminal repeats and they might function both as the origin of rDNA replication and/or site of homologous recombination.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Kuehn M. The genetic behaviour of a cloned mouse ribosomal DNA segment mimics mouse ribosomal gene evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):743–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Analysis of the regions flanking the human insulin gene and sequence of an Alu family member. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4091–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. ATP stimulates the binding of simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen to the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Krystal M., Arnheim N. Structure and evolution of human and African ape rDNA pseudogenes. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):29–37. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. Eukaryotic DNA replication: yeast bares its ARSs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jun;13(6):212–217. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikaraishi D. M., Buchanan L., Danna K. J., Harrington C. A. Genomic organization of rat rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6437–6452. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Borowiec J. A., Ishimi Y., Deb S., Tegtmeyer P., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen requires three core replication origin domains for DNA unwinding and replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8267–8271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Hidvégi E. J. Cloning and characterization of a Novikoff hepatoma ribosomal DNA-fragment containing the initiation site of transcription. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1984;19(3-4):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Tora L., Kelemen G., Hidvégi E. J. Supercoil induced S1 hypersensitive sites in the rat and human ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3263–3277. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Stang H. D., Browne J. K., Martin M. O., Huot M., Lipeles J., Salser W. Human ribosomal RNA gene spacer sequences are found interspersed elsewhere in the genome. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Amplified ribosomal spacer sequence: structure and evolutionary origin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90639-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M., Moriwaki K. A mouse type 2 Alu sequence (M2) is mobile in the genome. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):87–89. doi: 10.1038/301087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Sudo K., Yoshikura H., Suzuki H., Moriwaki K., Hilgers J., Muramatsu M. A polymorphic repetitive-sequence PR1 family. Evidence for meiotic instability. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Urano Y., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M., Moriwaki K., Yoshikura H. Novel repetitive sequence families showing size and frequency polymorphism in the genomes of mice. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):209–228. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Arnheim N. Length heterogeneity in a region of the human ribosomal gene spacer is not accompanied by extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Simeone A., D'Esposito M., Scotto L., Fidanza V., de Falco A., Boncinelli E. Molecular analysis of the heterogeneity region of the human ribosomal spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Mitchelson K., de Winter R. The promotion of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:207–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczka D. L., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of rat ribosomal DNA. The highly repetitive sequences that flank the ribosomal RNA transcription unit are homologous and contain RNA polymerase III transcription initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):141–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J., Elder J. T., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1151–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrany G., Tanaka N., Kishimoto T., Ishikawa Y., Kato H., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Structural determinant of the species-specific transcription of the mouse rRNA gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):349–353. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Dover G. A. Transcription of the tandem array of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster does not terminate at any fixed point. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1267–1273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Tautz C., Webb D., Dover G. A. Evolutionary divergence of promoters and spacers in the rDNA family of four Drosophila species. Implications for molecular coevolution in multigene families. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):525–542. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of rat ribosomal DNA II. identification of the highly repetitive DNA in the 3' non-transcribed spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavachev L. P., Georgiev O. I., Braga E. A., Avdonina T. A., Bogomolova A. E., Zhurkin V. B., Nosikov V. V., Hadjiolov A. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the spacer regions flanking the rat rRNA transcription unit and identification of repetitive elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2799–2810. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]