Abstract
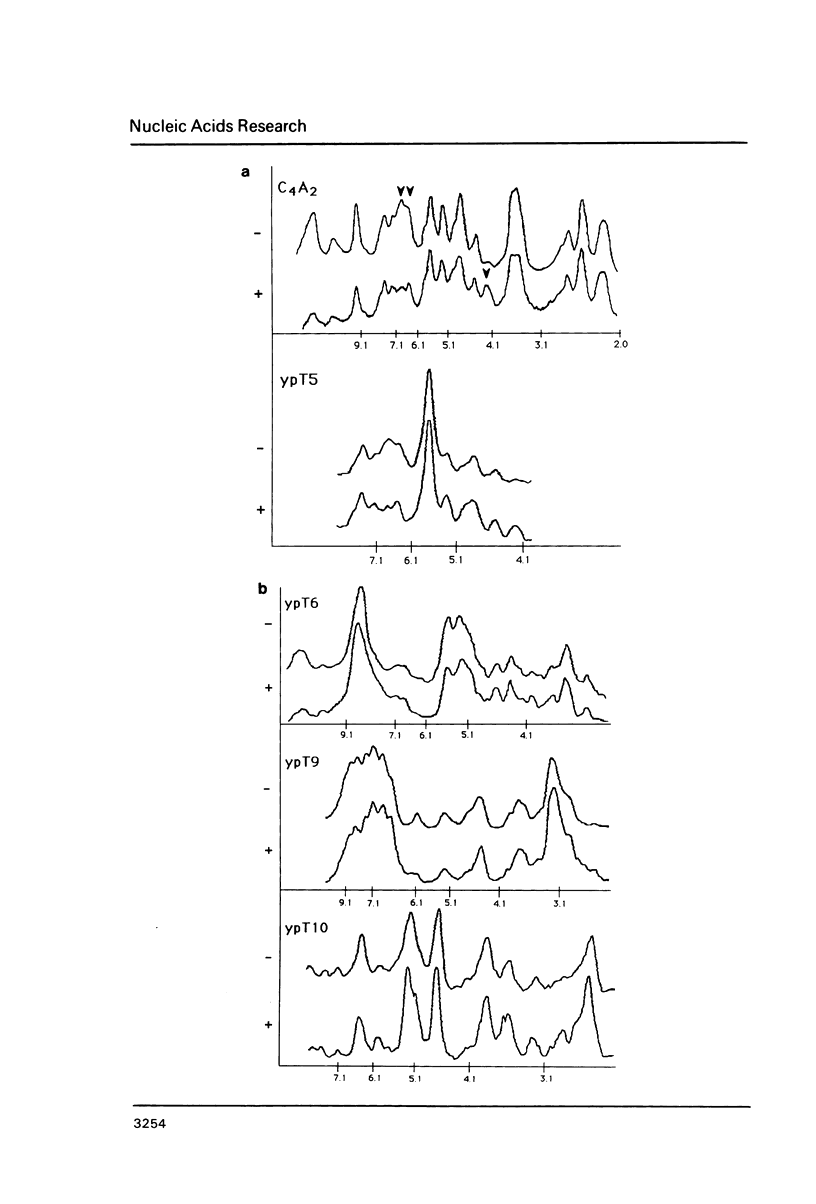
We explored the ability of S. cerevisiae to utilize heterologous DNA sequences as telomeres by cloning germline (micronuclear) DNA from Tetrahymena thermophila on a linear yeast plasmid that selects for telomere function. The only Tetrahymena sequences that functioned in this assay were (C4A2)n repeats. Moreover, these repeats did not have to be derived from Tetrahymena telomeres, although we show that micronuclear telomeres (like macronuclear telomeres) of Tetrahymena terminate in (C4A2)n repeats. Chromosome-internal restriction fragments carrying (C4A2)n repeats also stabilized linear plasmids and were elongated by yeast telomeric repeats. In one case, the C4A2 repeat tract was approximately 1.5 kb from the end of the genomic Tetrahymena DNA fragment that was cloned, but this 1.5 kb of DNA was missing from the linear plasmid. Thus, yeast can utilize internally located tracts of telomere-like sequences, after the distal DNA is removed. The data provide an example of broken chromo-some healing, and underscore the importance of the telomeric repeat structure for recognition of functional telomeric DNA in vivo.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres: do the ends justify the means? Cell. 1984 May;37(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Tsao S. G., Diamond C. H., Ohashi P. S., Tsao N. N., Pearlman R. E. Reorganization of unique and repetitive sequences during nuclear development in Tetrahymena thermophila. Can J Biochem. 1982 Sep;60(9):847–853. doi: 10.1139/o82-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button L. L., Astell C. R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome III left telomere has a type X, but not a type Y', ARS region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1352–1356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. M., Blackburn E. H. The internally located telomeric sequences in the germ-line chromosomes of Tetrahymena are at the ends of transposon-like elements. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover R. K., Brunk C. F. Macronuclear DNA molecules of Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):900–905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D., Herrick G. Telomeric properties of C4A4-homologous sequences in micronuclear DNA of Oxytricha fallax. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., Futcher B., Morgan R., McFadden G. Cloning of the vaccinia virus telomere in a yeast plasmid vector. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B., Szauter P., Pardue M. L., Szostak J. W. Transfer of yeast telomeres to linear plasmids by recombination. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J., Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. Identification of the telomeric sequence of the acellular slime molds Didymium iridis and Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9143–9152. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futcher A. B., Cox B. S. Maintenance of the 2 microns circle plasmid in populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):612–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.612-622.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Thorburn P. C. Healing of broken linear dicentric chromosomes in yeast. Genetics. 1984 Feb;106(2):207–226. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Blackburn E. H. Reproducible and variable genomic rearrangements occur in the developing somatic nucleus of the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2039–2050. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. Dynamics of telomere length variation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Claus T. E., Szostak J. W. Characterization of two telomeric DNA processing reactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4642–4650. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Chromosome length controls mitotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Dani G. M., Spear B. B., Zakian V. A. Elaboration of telomeres in yeast: recognition and modification of termini from Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Blackburn E. H. Generation of telomere-length heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler E. A., Ryan T., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally regulated telomere addition in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5569–5585. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. Cloning yeast telomeres on linear plasmid vectors. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. M., Szostak J. W., Petes T. D. Is there left-handed DNA at the ends of yeast chromosomes? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):84–86. doi: 10.1038/302084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C. Elimination of specific DNA sequences from the somatic nucleus of the ciliate Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):783–789. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Yao C. H. Repeated hexanucleotide C-C-C-C-A-A is present near free ends of macronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7436–7439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Blanton H. M., Wetzel L., Dani G. M. Size threshold for Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes: generation of telocentric chromosomes from an unstable minichromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):925–932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]