Abstract
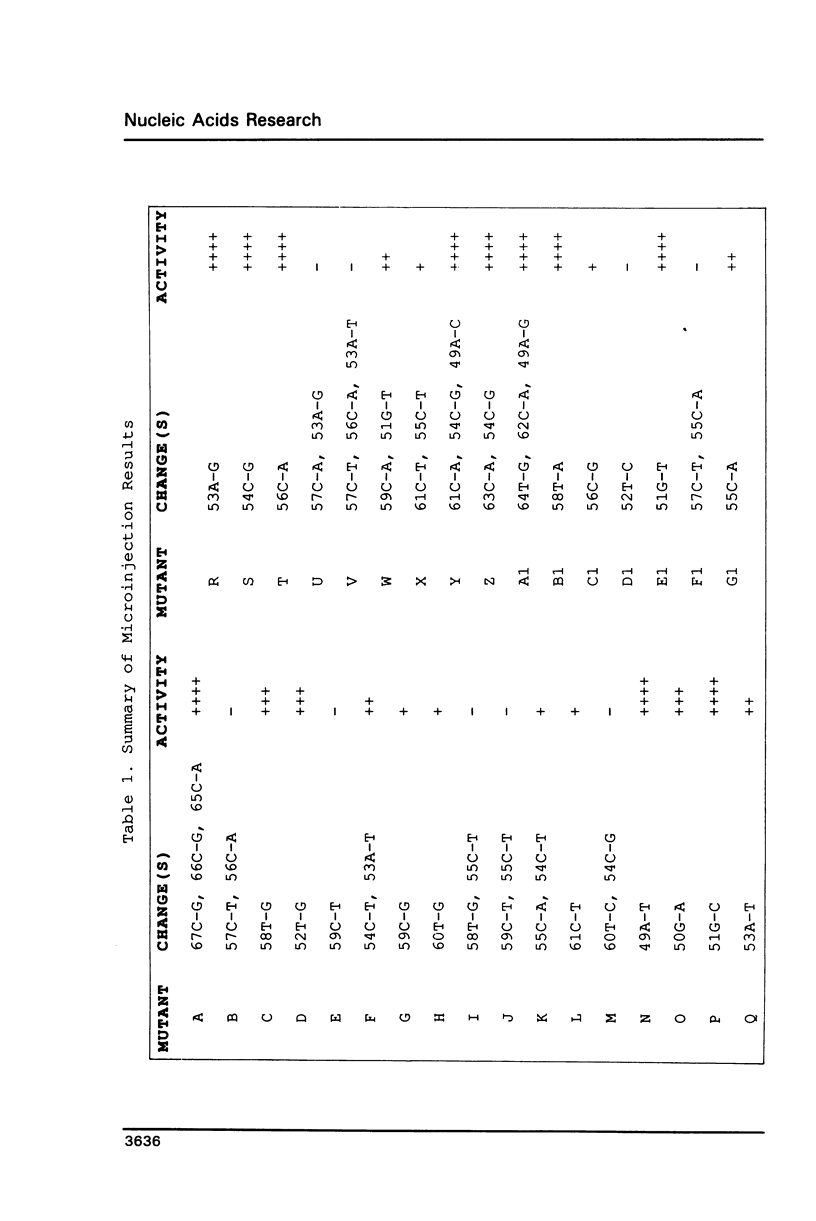
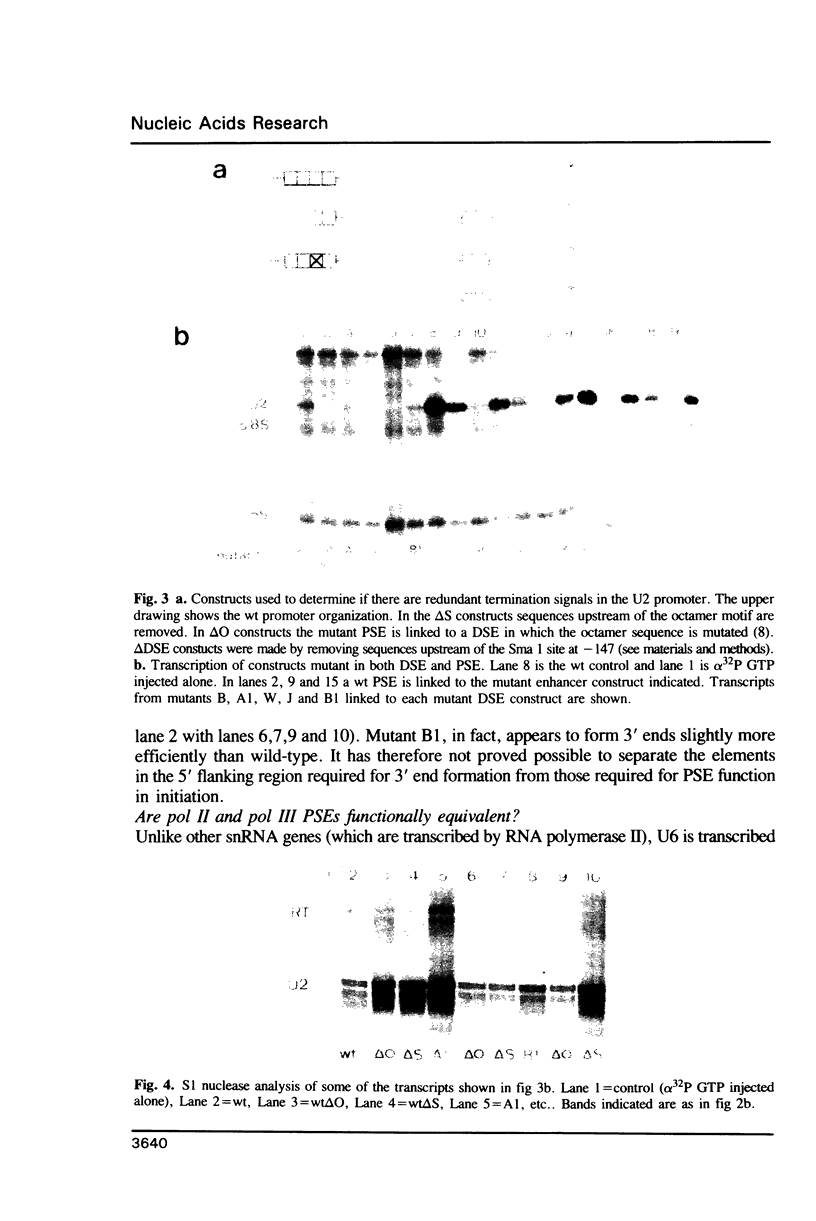
The proximal sequence element (PSE) of a Xenopus U2 snRNA gene has been analysed by extensive local mutagenesis. The PSE is compact, lying between -61 and -50 bp upstream of the transcription start site and is involved in signalling both transcription initiation and 3' end formation. No PSE mutants were found in which these two activities were differentially affected. Analysis of U2 gene promoters mutant in both the PSE and DSE failed to reveal any evidence for multiple signals involved in 3' end formation, leading to the conclusion that the PSE is the only promoter element required for this function. The U2 and U6 PSEs, which direct either pol II or both pol II and pol III transcription respectively, are shown to be functionally interchangeable. Apparent differences in human and Xenopus U2 gene PSE structure are discussed.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ach R. A., Weiner A. M. The highly conserved U small nuclear RNA 3'-end formation signal is quite tolerant to mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2070–2079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Chung J. S., Giglio L., Weiner A. M. Distinct factors with Sp1 and NF-A specificities bind to adjacent functional elements of the human U2 snRNA gene enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):808–817. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dathan N., Frank R., Philipson L., Mattaj I. W. Formation of the 3' end on U snRNAs requires at least three sequence elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson S. I., Murphy J. T., Knuth M. W., Steinberg T. H., Dahlberg J. H., Burgess R. R. Binding of transcription factors to the promoter of the human U1 RNA gene studied by footprinting. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17603–17610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA is directed by a conserved sequence located downstream of the coding region. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1827–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Lucito R. Elements required for transcription initiation of the human U2 snRNA gene coincide with elements required for snRNA 3' end formation. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3125–3134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmaier M., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. Functional characterization of X. laevis U5 snRNA genes. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3071–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Appel B. Xenopus tropicalis U6 snRNA genes transcribed by Pol III contain the upstream promoter elements used by Pol II dependent U snRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2463–2478. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangin M., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Human U2 small nuclear RNA genes contain an upstream enhancer. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):987–995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Skuzeski J. T., Lund E., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Functional elements of the human U1 RNA promoter. Identification of five separate regions required for efficient transcription and template competition. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1795–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Bohmann D., Mattaj I. W. Only two of the four sites of interaction with nuclear factors within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter are necessary for efficient transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6437–6453. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. Positionally exact initiation is required for the formation of a stable RNA polymerase II transcription complex in vivo. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3785–3792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Sequences required for 3' end formation of human U2 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]