Abstract
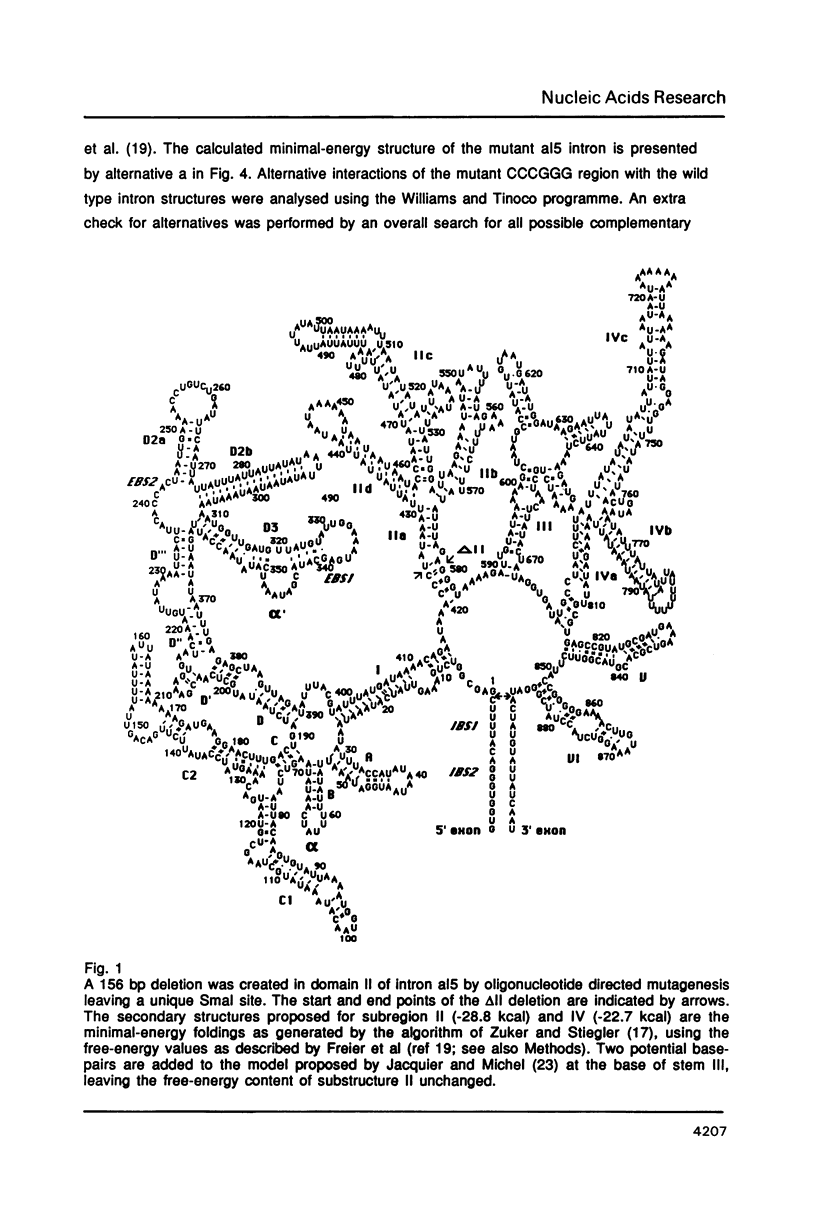
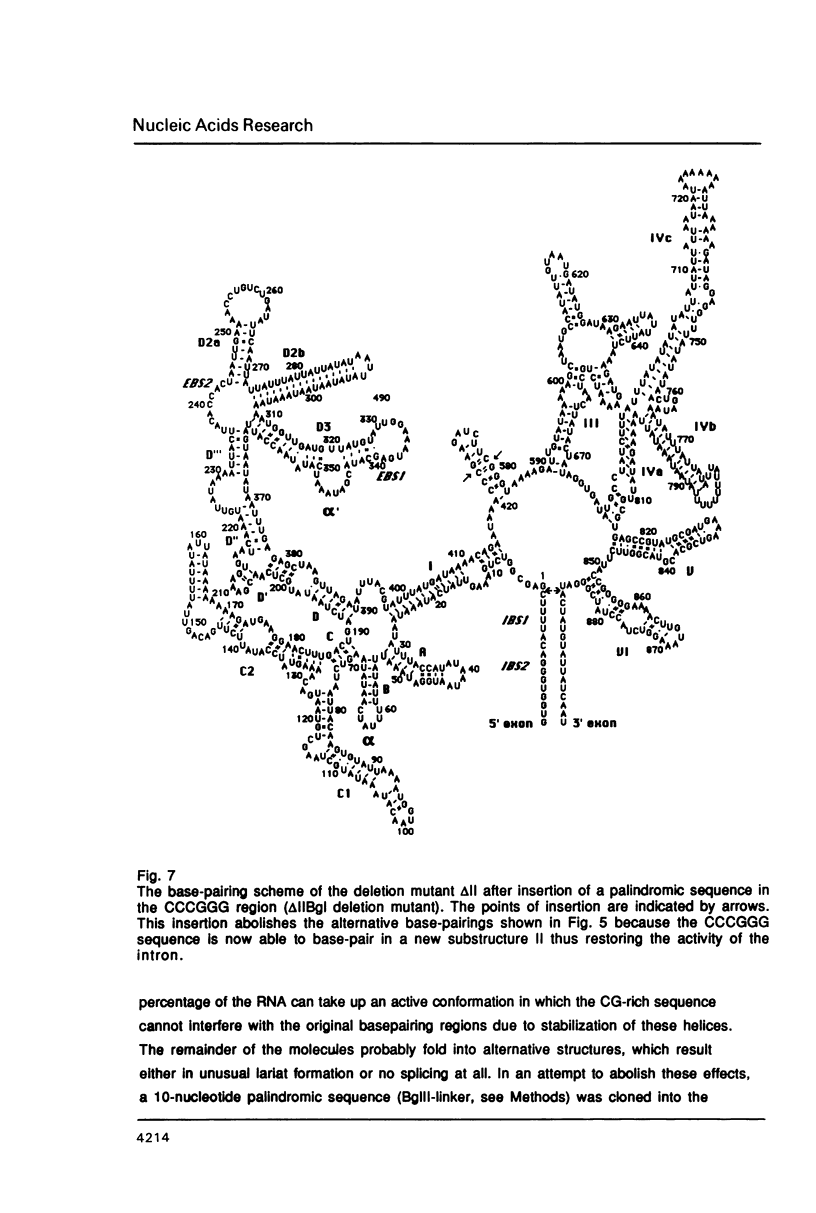
An oligonucleotide-directed deletion of 156 nucleotides has been introduced into the yeast mitochondrial group II intron al5 (887 nt). The deletion comprises almost all of domain II, which is one of the six phylogenetically conserved structural elements of group II introns. This mutant displays reduced self-splicing activity, but results of chemical probing with dimethylsulphate suggest that sequences at the site of the deletion interfere with the normal folding of the intron. This is supported by computer analyses, which predict a number of alternative structures involving conserved intron sequences. Splicing activity could be restored by insertion of a 10-nucleotide palindromic sequence into the unique Smal site of the deletion mutant, resulting in the formation of a small stable stem-loop element at the position of domain II. These results provide a direct correlation between folding of the RNA and its activity. We conclude that at least a large part of domain II of the group II intron al5 is not required for self-splicing activity. This deletion mutant with a length of 731 nucleotides represents the smallest self-splicing group II intron so far known.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C. M13 vectors with T7 polymerase promoters: transcription limited by oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2830–2830. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Multiple exon-binding sites in class II self-splicing introns. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. F., Ahne F., Bonen L. The mitochondrial genome of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The cytochrome b gene has an intron closely related to the first two introns in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cox1 gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E. T., Domenico J. M., Cummings D. J. An additional class II intron with homology to reverse transcriptase in rapidly senescing Podospora anserina. Curr Genet. 1986;10(12):915–922. doi: 10.1007/BF00398289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schmidt C., May K., Schweyen R. J. Determination of functional domains in intron bI1 of yeast mitochondrial RNA by studies of mitochondrial mutations and a nuclear suppressor. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2047–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schmidt C., Schweyen R. J. Identification of splicing signals in introns of yeast mitochondrial split genes: mutational alterations in intron bI1 and secondary structures in related introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6797–6808. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Tanouchi M., Todd C. W., Wallace R. B. Simultaneous deletion of the intervening sequences from the human interferon-gamma gene by oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1987;57(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Van der Horst G., Osinga K. A., Arnberg A. C. Splicing of large ribosomal precursor RNA and processing of intron RNA in yeast mitochondria. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Van der Horst G., Winter A. J., Smit J., Van der Veen R., Kwakman J. H., Grivell L. A., Arnberg A. C. Reactions mediated by yeast mitochondrial group I and II introns. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:213–221. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. L., Jr, Tinoco I., Jr A dynamic programming algorithm for finding alternative RNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):299–315. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., Grivell L. A. Self-splicing of a group II intron in yeast mitochondria: dependence on 5' exon sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1079–1084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04861.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]