Abstract
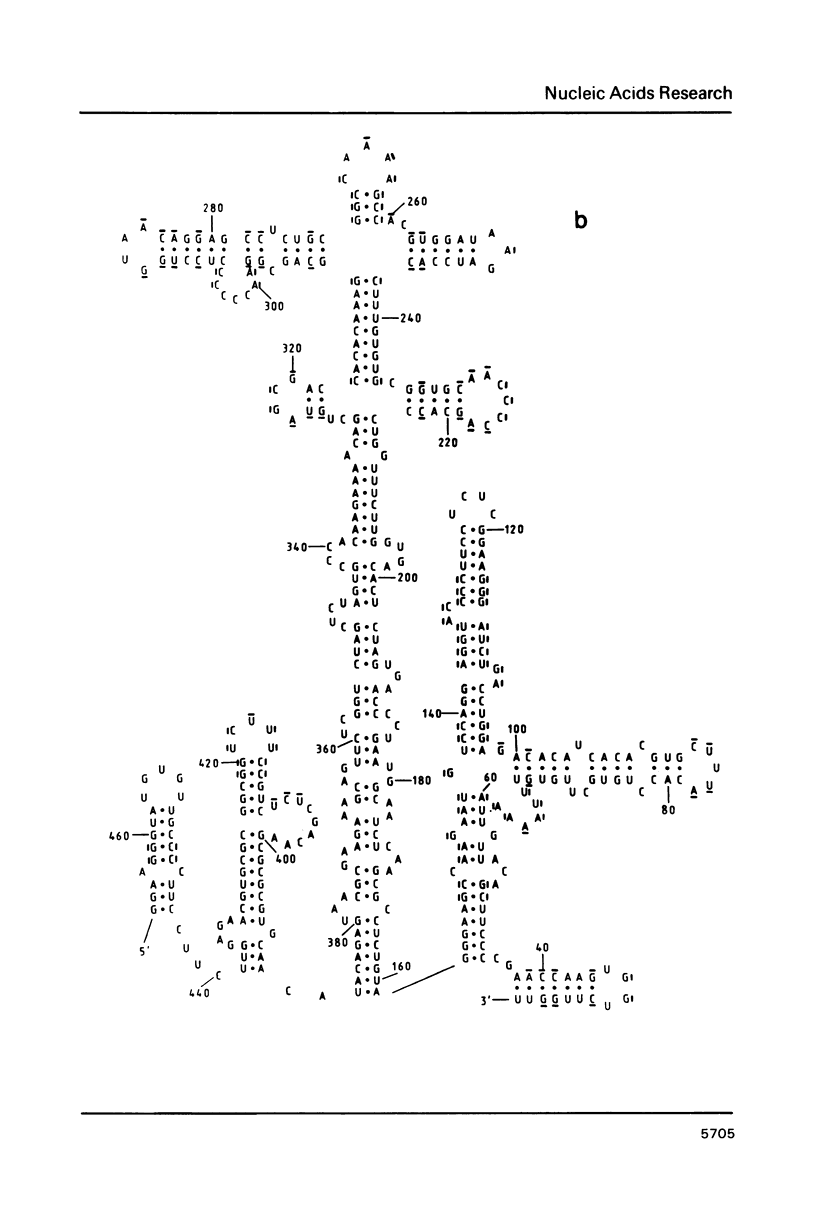
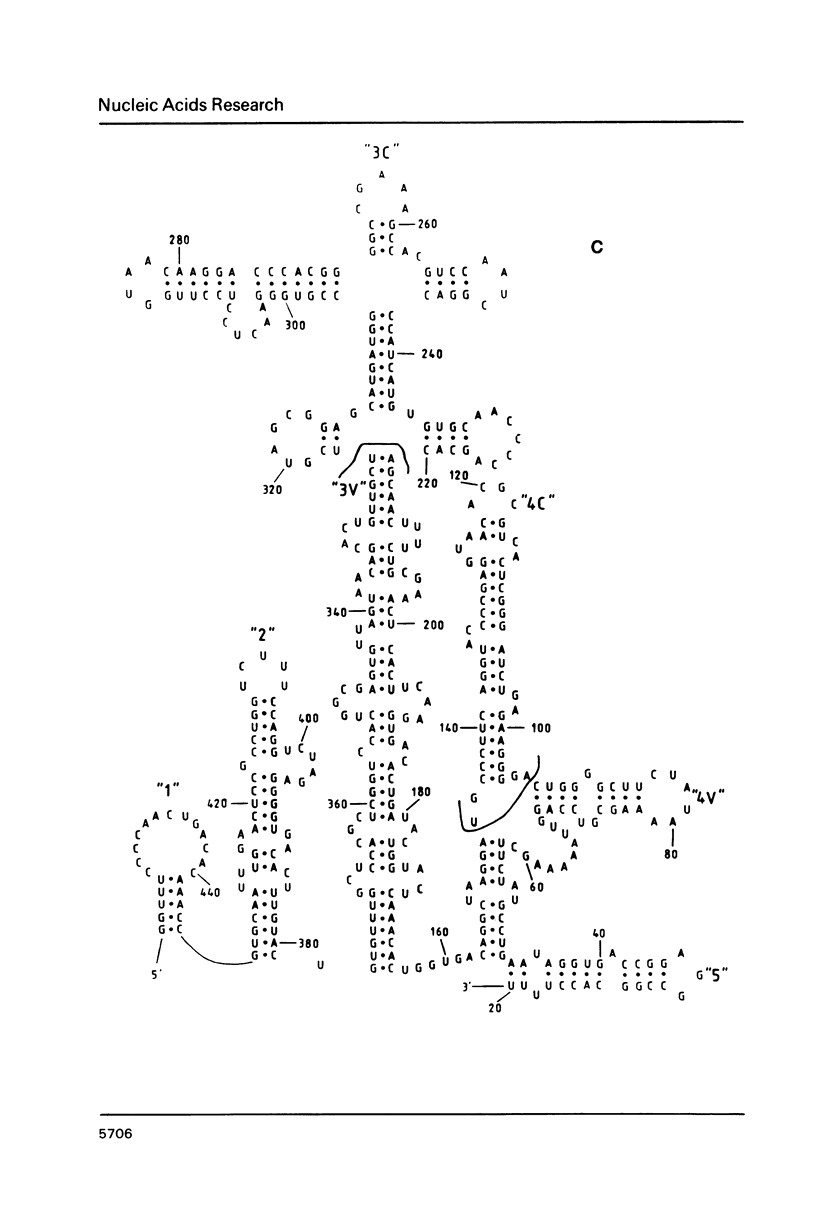
An analysis of published nucleotide sequences of the 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) of 7 cardioviruses and 3 aphthoviruses has allowed us to derive a consensus secondary structure model that differs from that previously proposed for the 5'-UTR of entero- and rhinoviruses, though all these viruses belong to the same family, Picornaviridae. The theoretical model derived here was experimentally supported by investigating the accessibility of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA to modifications with dimethyl sulfate and its susceptibility to S1 and cobra venom nucleases. The possible involvement of the 5"-UTR secondary structure domains in the translational control is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond J. W. The attenuation of poliovirus neurovirulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:153–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Ehrenfeld E. An internal 5'-noncoding region required for translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3068–3072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3068-3072.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinov V. M., Pilipenko E. V., Romanova L. I., Siniakov A. N., Maslova S. V. Sravnenie vtorichnoi struktury 5'-kontsevogo netransliruemogo segmenta RNK neirovirulentnogo i attenuirovannogo shtammov virusa poliomielita. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1988;298(4):1004–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Brown A. L., Currey K. M., Newton S. E., Rowlands D. J., Carroll A. R. Potential secondary and tertiary structure in the genomic RNA of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7067–7079. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. H., Naviaux R. K., vanden Brink K. M., Jordan G. W. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of diabetogenic and nondiabetogenic encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forss S., Strebel K., Beck E., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6587–6601. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Martin E. M. Simple method for the isolation of encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):559–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.559-561.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Kräusslich H. G., Toyoda H., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus polypeptide precursors: expression in vitro and processing by exogenous 3C and 2A proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Stein S., Fu J. L., Stillman L., Klaman L., Roos R. P. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90642-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Cap-independent translation of poliovirus mRNA is conferred by sequence elements within the 5' noncoding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Translational efficiency of poliovirus mRNA: mapping inhibitory cis-acting elements within the 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2219–2227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2219-2227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Borkowski J., Calenoff M., Oh C. K., Ostrowski B., Lipton H. L. Insights into Theiler's virus neurovirulence based on a genomic comparison of the neurovirulent GDVII and less virulent BeAn strains. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90652-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Calenoff M., Rozhon E., Lipton H. L. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequence of the picornavirus Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus indicates that it is closely related to cardioviruses. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1507–1516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1507-1516.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Romanova L. I., Sinyakov A. N., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Conserved structural domains in the 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes: an analysis of the segment controlling translation and neurovirulence. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Welsh J. D., Maizel J. V., Jr Comparative sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of the enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Grubman M. J., Weddell G. N., Moore D. M., Welsh J. D., Fischer T., Dowbenko D. J., Yansura D. G., Small B., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence coding for polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus type A12. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):651–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.651-660.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Park I. W., Evans C. L., Jaynes J. M., Palmenberg A. C. Effects of cDNA hybridization on translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2033–2037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2033-2037.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Pestova T. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Point mutations modify the response of poliovirus RNA to a translation initiation factor: a comparison of neurovirulent and attenuated strains. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


