Abstract
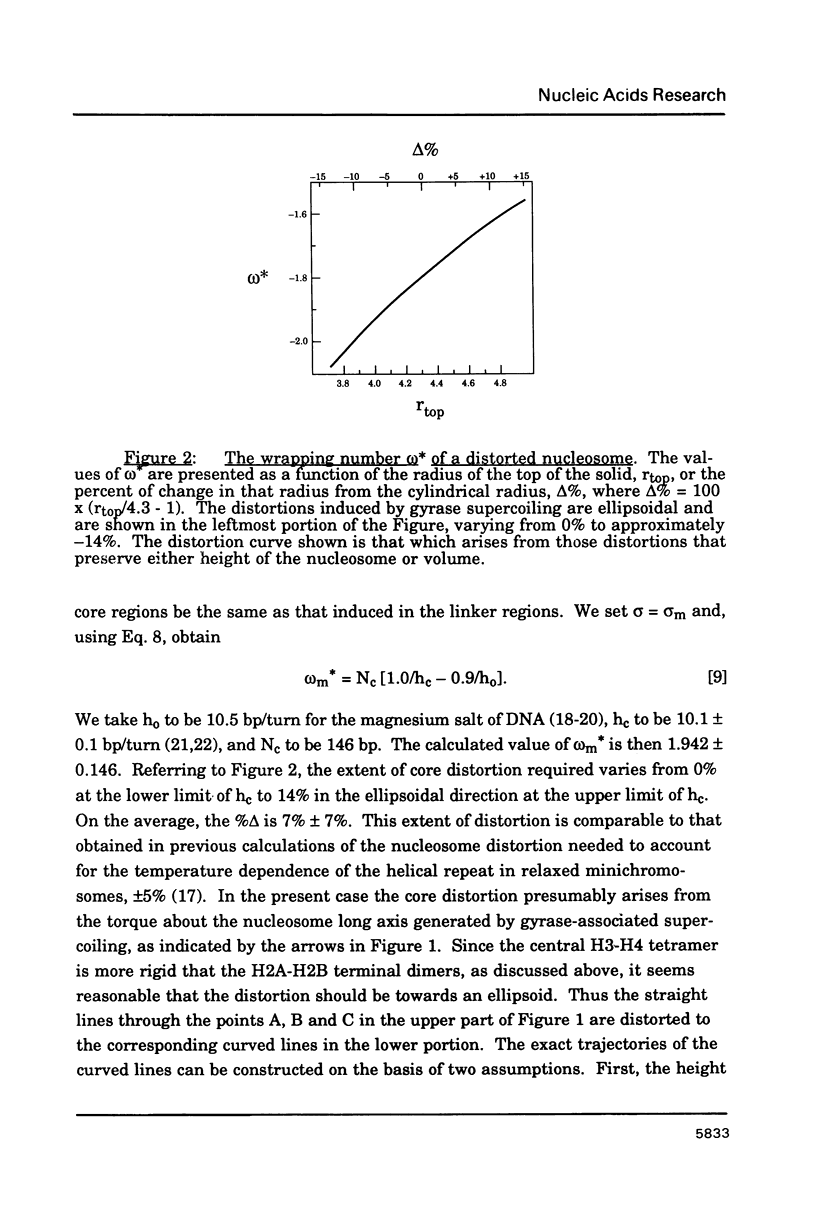
The contribution from each nucleosome to the linking number of minichrosome DNA depends on two factors. These are the wrapping number, omega, which is the number of times the DNA wraps about the axis of the nucleosome; and the winding number, phi, which is the number of base pairs on the nucleosome divided by the helical repeat of the DNA. If the nucleosome is distorted with DNA surface contacts being preserved, phi remains unchanged. The wrapping number may still change, however, depending on the extent of the distortion. For example, if the usual cylindrical shape of the nucleosome is deformed into an ellipsoid while preserving the equatorial radius, then the wrapping number will increase. We apply these concepts to minichromosomes torsionally stressed by supercoiling with, for example, DNA gyrase. We analyze the experimental result that the maximum amount of supercoiling obtained by gyrase treatment of minichromosomes is the same as that of naked DNA. In particular, we show that this phenomenon can be explained by a relatively slight distortion of the nucleosome core while maintaining the surface contacts of the DNA on the core.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Bauer W. Supercoiling in closed circular DNA: dependence upon ion type and concentration. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):594–601. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R., Melchior W., Jr, Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Specific sites of interaction between histones and DNA in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4101–4105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum J., Berg P. Simian virus 40 minichromosomes contain torsionally strained DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3048–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G. A., Finch J. T., Lewit-Bentley A. Neutron diffraction studies on crystals of nucleosome cores using contrast variation. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):771–784. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Cozzarelli N. R. Use of site-specific recombination as a probe of DNA structure and metabolism in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilloni G., Di Martino E., Caserta M., di Mauro E. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I reaction is topology dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7071–7085. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Calladine C. R. Sequence-specific positioning of core histones on an 860 base-pair DNA. Experiment and theory. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):143–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Brown R. S., Richmond T., Rushton B., Lutter L. C., Klug A. X-ray diffraction study of a new crystal form of the nucleosome core showing higher resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G. Effect of Z-DNA on nucleosome placement. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Effects of DNA supercoiling on the topological properties of nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2620–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovatter K. R., Martinson H. G. Ribonucleotide-induced helical alteration in DNA prevents nucleosome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1162–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Nucleosomes will not form on double-stranded RNa or over poly(dA).poly(dT) tracts in recombinant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6869–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert S. F., Thomas J. O. Lysine-containing DNA-binding regions on the surface of the histone octamer in the nucleosome core particle. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):191–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Echinomycin and distamycin induce rotation of nucleosome core DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6785–6801. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Histone-like proteins and bacterial chromosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12793–12796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Structure and properties of the bacterial nucleoid. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Stahl H., Koller T., Knippers R. Structure of replicating simian virus 40 minichromosomes. The replication fork, core histone segregation and terminal structures. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):189–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Staphylococcal nuclease makes a single non-random cut in the simian virus 40 viral minichromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Klug A. The bending of DNA in nucleosomes and its wider implications. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):537–561. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Bauer W. R. Applications of the twist difference to DNA structural analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Cozzarelli N. R., Bauer W. R. Helical repeat and linking number of surface-wrapped DNA. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):323–327. doi: 10.1126/science.3388041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
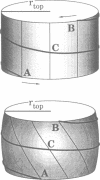
- White J. H., Gallo R., Bauer W. R. Effect of nucleosome distortion on the linking deficiency in relaxed minichromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]